Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circle Theorems PDF
Uploaded by
Joseph MusabukaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circle Theorems PDF
Uploaded by
Joseph MusabukaCopyright:
Available Formats
Circle Theorems
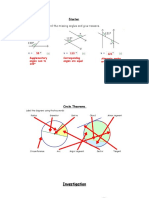
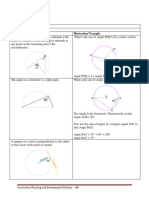
x = 62 ÷ 2 = 31º
1) Angle at the centre
The angle at the centre is twice the angle at
the circumference (standing on the same chord).
x = y = 21º
2) Angles in the same segment
Angles at the circumference standing on
the same chord and in the same segment
are equal.
x = 90º y = 180 – 60 – 90 = 30º
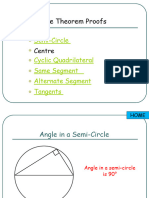
3) Angle in a semicircle
Angles at the circumference standing on
a diameter are equal to 90º.
x = 180 – 100 = 80º
4) Cyclic quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral whose 4 vertices lie on the
circumference of a circle is called a
cyclic quadrilateral.
Opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral
add up to 180º (supplementary angles). A + C = 180º y = 180 – 85 = 95º
B + D = 180º
y = 360 – 90 – 90 – 30 = 150º
x = 90º
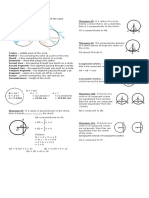
5) Tangents to a circle
A tangent to a circle is always perpendicular
to a radius at the point of contact (90º angle).
Two tangents drawn from the same point are
equal in length. TA = TB
6) Alternate segment
The angle between a tangent and a chord is
equal to any angle made by that chord in the
alternate segment.
x = 25º
y = 72º
©MathsWatch Ltd www.mathswatch.com info@mathswatch.com
You might also like
- Civic Education Questions Grade 10-12Document59 pagesCivic Education Questions Grade 10-12Joseph Musabuka92% (53)
- Civic Education Questions Grade 10-12Document59 pagesCivic Education Questions Grade 10-12Joseph Musabuka92% (53)
- Circle Theorems PDFDocument1 pageCircle Theorems PDFJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- Key Transversal Notes WorksheetsDocument5 pagesKey Transversal Notes WorksheetsKelsey Scofield0% (1)
- Circle Theorems: Add Up To 180º (Supplementary Angles)Document1 pageCircle Theorems: Add Up To 180º (Supplementary Angles)liberto21No ratings yet
- Circle Theorems Year 10 DrillingDocument10 pagesCircle Theorems Year 10 DrillingPugarnes GopalanNo ratings yet
- 6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFDocument1 page6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFNarenNo ratings yet
- Find The Missing Angles and Give Reasons.: StarterDocument26 pagesFind The Missing Angles and Give Reasons.: StarterAmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic: ST NDDocument8 pagesQuadratic: ST NDtheturfkitchenNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus TrigonometryDocument77 pagesPre Calculus TrigonometryTeacher JasonNo ratings yet
- Angle Math PresentationDocument17 pagesAngle Math Presentationstefani anindyaNo ratings yet
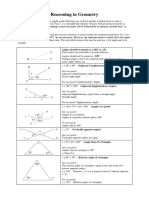
- A Guide To Reasoning in Plane Geometry SolutionsDocument4 pagesA Guide To Reasoning in Plane Geometry SolutionsCamloc LuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Trigonometry: 5.1 Introduction of Trigonometry FunctionDocument21 pagesChapter 5: Trigonometry: 5.1 Introduction of Trigonometry FunctionMWPNo ratings yet
- Kidmath - Introduction To Geometry: Notation: We Name Points by Capital Letters. Two Points A and B DetermineDocument4 pagesKidmath - Introduction To Geometry: Notation: We Name Points by Capital Letters. Two Points A and B DetermineJames WigtonNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems: DR J Frost (Jfrost@tiffin - Kingston.sch - Uk)Document30 pagesCircle Theorems: DR J Frost (Jfrost@tiffin - Kingston.sch - Uk)Jump SkillNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocument11 pagesReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringPaulyne TuganoNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems-32D9FDocument4 pagesCircle Theorems-32D9Fwater bottleNo ratings yet
- Algebra 12 AnglesDocument44 pagesAlgebra 12 AnglesTrixie Agustin100% (1)
- Write Up of All Angle RulesDocument6 pagesWrite Up of All Angle RulesNancy RadwanNo ratings yet
- Geometry FlashCardsDocument26 pagesGeometry FlashCardsjcargs3100% (1)
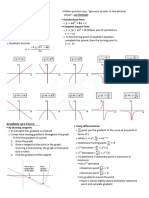
- Chapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Document18 pagesChapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Angel Angel100% (1)
- Must-Know Terms and Expressions - SUB - MATERIALDocument14 pagesMust-Know Terms and Expressions - SUB - MATERIAL박민재No ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutDocument15 pagesTopic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutShine100% (1)
- Worksheets IN TrigonometryDocument11 pagesWorksheets IN TrigonometryJUN JUN HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- 2lessons Circle TheoremsDocument29 pages2lessons Circle TheoremsFATMA HINDI / F MOHAMMED HUSSEIN HINDI -No ratings yet
- MathDocument53 pagesMathmarcNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorem Circle Theorem: X 2y X 2yDocument1 pageCircle Theorem Circle Theorem: X 2y X 2yAziah binti Hj. jamaluddinNo ratings yet
- AnGLES N Triang.sDocument11 pagesAnGLES N Triang.sjayNo ratings yet
- Geometry Cheatsheet: DefinitionsDocument3 pagesGeometry Cheatsheet: DefinitionsJane ChangNo ratings yet
- Class05 MathG6 Notes Feb 13-18Document9 pagesClass05 MathG6 Notes Feb 13-18杨小强No ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryFranc VenturaNo ratings yet
- I. Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDocument7 pagesI. Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesF RUAMAR, ADRIENNE MAE M.No ratings yet
- A Sum of 360 Degrees 2Document10 pagesA Sum of 360 Degrees 2lam044980No ratings yet
- Angles and TrianglesDocument52 pagesAngles and TrianglesadithNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Distance From The CenterDocument7 pagesMathematics: Distance From The CenterSchool PurposeNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - Circle TheoremsDocument30 pagesCSEC Mathematics - Circle TheoremsCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry Hand OutDocument7 pagesPlane Trigonometry Hand OutKRISTINE CHAD NAVALES CANTALEJONo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument18 pagesCircle TheoremsSamuel MalileNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument28 pagesGeometryASHWIN .A.S.No ratings yet
- Triangles Dan SegitigaDocument45 pagesTriangles Dan Segitigasefira maulida100% (1)
- Properties TrianglesDocument13 pagesProperties TrianglesCaletha BurtonNo ratings yet
- MATH30-1 Unit 3 - Lecture Notes: Homework Listing Textbook Sections Question Numbers WorksheetsDocument44 pagesMATH30-1 Unit 3 - Lecture Notes: Homework Listing Textbook Sections Question Numbers WorksheetsBecca BobsterNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry Hand OutDocument6 pagesPlane Trigonometry Hand Outmary christy mantalabaNo ratings yet
- NGEC 9 Module 1 (Week 2-3) - Student Copy To UploadDocument93 pagesNGEC 9 Module 1 (Week 2-3) - Student Copy To Uploadvjan LeonorNo ratings yet
- Geometry: WWW - Percenti Leclasses - in Live - Percentil Eclasses - in Download Mobile APP FromDocument73 pagesGeometry: WWW - Percenti Leclasses - in Live - Percentil Eclasses - in Download Mobile APP FromVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Reviewer Chap3 Trigonometry 1Document15 pagesPre Calculus Reviewer Chap3 Trigonometry 1ndjwndnnd sjwjhsbdbdbdNo ratings yet
- Proof Circle Theorems (Brilliant!)Document17 pagesProof Circle Theorems (Brilliant!)j2r92k7hr9No ratings yet
- Circle-Theorem Number 1Document8 pagesCircle-Theorem Number 1carado077No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - TrigonometryDocument18 pagesChapter 4 - TrigonometryDamon LeongNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Lines & AnglesDocument52 pagesGeometry: Lines & AnglesrobertNo ratings yet
- Schoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and FormulasDocument40 pagesSchoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and Formulassudhakaralla1100% (2)
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Geometrykssuhasreddy_3743947No ratings yet
- GeometryDocument4 pagesGeometryGivemore ChipembereNo ratings yet
- Fungsi TrigonometriDocument110 pagesFungsi TrigonometriM IkhsanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Angles and Shapes Remember:: Math Department-Part 4:geometryDocument3 pagesLesson 1: Angles and Shapes Remember:: Math Department-Part 4:geometryNagy ElrahebNo ratings yet
- Geometry Concept Booklet 025d90b26ada3Document10 pagesGeometry Concept Booklet 025d90b26ada3Khushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Tec Milenio - Geometry Trigonometry AnglesDocument4 pagesTec Milenio - Geometry Trigonometry AnglesBryan CamargoNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Percentage Purity and Yield Complete NotesDocument2 pagesPercentage Purity and Yield Complete NotesJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6. Chemical Reactions and Ionic EquationsDocument24 pagesTopic 6. Chemical Reactions and Ionic EquationsJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- NOTES - 4.3 - Atomic - Mass - Isotopes - 2017 - SlideshowDocument16 pagesNOTES - 4.3 - Atomic - Mass - Isotopes - 2017 - SlideshowJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- Bf6501cf5ae7 PDFDocument2 pagesBf6501cf5ae7 PDFJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- BF 6501 CF 5 Ae 7Document2 pagesBF 6501 CF 5 Ae 7Joseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Force NotesDocument7 pagesCentripetal Force NotesJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- Additional Maths Grade 12 Final BookletDocument16 pagesAdditional Maths Grade 12 Final BookletJoseph Musabuka100% (1)