Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020
Uploaded by
Shyam Sundar JanaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020
Uploaded by
Shyam Sundar JanaCopyright:
Available Formats
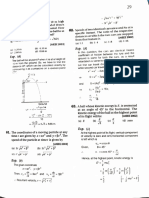
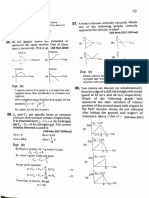
z u e g a i nd e c r e a s e the heat is supplied
starts boiling again. at constant pressure, the
es and water only. When we heat the gas of the gas
volume of the gas apart from temperature
does some external
rises. When the gas expands, it
steamline So in this case, the
iclne water work for increasing the volume.
heat is supplied.
of the gas.
ICe steam
(a) to raise the temperature
for expansion.
b) to do the mechanical work
to increasee
As a result more amount of heat is required
the temperature of the gas through the same
temperature amount
tan be asily seen from the graph that as pressure when the pressure is kept constant. Hence Cp is always
Increases
the melting point of ice decreases. greater than the value of C.
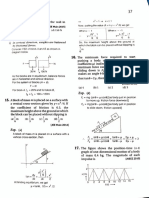
&():In an
irreversible process, there always 43. (a)
loss of energy. This is because energy
CUS Some
the dissipative force is not44. (a): Second law of thermodynamics can be
working
sentin against explained with the help of example ofrefrigerator, as
mrovered back. Some ireversible processes occur in we know that in refrigerator, the working
substance
nature such as
friction where extra work is needed to
extracts heat from colder body and rejects a largge
in water
cancel the effect of friction. Salt dissolves amount of heat to a hotter body with the help of an
salt and
but a salt does not separate by itselfinto pure external agency i.e., the electric supply of the
pure water.
refrigerator. No refrigerator can ever work without
36. (a): In a perfectly reversible system, there is no extemal supply of electric energy to it.
l0ss of energy. Losses can be minimised, friction can
(c): An isolated system may have any process
ereduced, the resistance in L-C oscillating system45. isothermal, adiabatic. cyclic etc.
such as
Can also be negligible. But one cannot completely
46. (c): Assertion is true but reason is false. is
climinate energy losses, which will makes a perfectly
TEversible system, an ideal one. In an adiabatic process, no exchange of heat
permissible i.e., dQ 0. =
37. (a): Adiabatic expansion produces cooling. dl= - dw
As, do= dU + dW=0
8. b): In an isolated system the entropy increases 47.
(a): In adiabatic process, no heat transfer takes
accordance with the second law of place between gas and surrounding i.e. AQ=0
ermodynamics.
From definition of specific heat,C==mAT =0
(a): Efficiency n=1-=1-2 Again, for isothermal process, AT= 0
b ) : Assertion is true. Due to cooling of milk, C =
disorder lecreases. Hence entropy decreases. Reason mAT
You might also like
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- 3tane3tan30 : Do Kftot or (Pil MG Sine+Document1 page3tane3tan30 : Do Kftot or (Pil MG Sine+Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- X X Orx : Given Angles Andt2 Flights FlightsDocument1 pageX X Orx : Given Angles Andt2 Flights FlightsShyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Charged 2 12) Potential: Conducting Spherical Having Along (PassingDocument1 pageCharged 2 12) Potential: Conducting Spherical Having Along (PassingShyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Oblen:4: O.05 Cal/T ' C, Ye?? Bgot 20CDocument1 pageOblen:4: O.05 Cal/T ' C, Ye?? Bgot 20CShyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Froposal Report: Coci Cnariot Te ABCDocument1 pageFroposal Report: Coci Cnariot Te ABCShyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Purpos e This Report Is To.: ExaminelDocument1 pagePurpos e This Report Is To.: ExaminelShyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 11 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 11 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 Oct 2020Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 6545 Us35000Document4 pages6545 Us35000Rafael BarrosNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7 ASD Basic Load CombosDocument1 pageASCE 7 ASD Basic Load CombosAamirShabbirNo ratings yet
- UNIT 14 - On-Screen DigitizingDocument6 pagesUNIT 14 - On-Screen DigitizingResti KharismaNo ratings yet
- InfoDocument18 pagesInfoKaran Verm'aNo ratings yet
- 0606 Additional Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesDocument9 pages0606 Additional Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 Serieswai yanNo ratings yet
- ECE ExperimentDocument13 pagesECE Experimentasm98090% (1)
- Baulkham Hills 2012 2U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument11 pagesBaulkham Hills 2012 2U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsYe ZhangNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: Overview of Graphics SystemsDocument25 pagesComputer Graphics: Overview of Graphics Systemsshibina balakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Mohamad Fakhari Mehrjardi - 1Document18 pagesMohamad Fakhari Mehrjardi - 1Hilmi SanusiNo ratings yet
- Ball Charge ManagementDocument14 pagesBall Charge ManagementSalud Y SucesosNo ratings yet
- PLX7100A Digital Mobile C-Arm X-Ray Machine: 1. Technical SpecificationDocument3 pagesPLX7100A Digital Mobile C-Arm X-Ray Machine: 1. Technical SpecificationAbdalhakeem AlturkyNo ratings yet
- Evaluating of Rutting in Highways & Providing Its Solution in Terms of Stone Matrix Asphalt.Document7 pagesEvaluating of Rutting in Highways & Providing Its Solution in Terms of Stone Matrix Asphalt.IJRASETPublications100% (1)
- Lecture 2: Stacks and Queues: CSE 373: Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument31 pagesLecture 2: Stacks and Queues: CSE 373: Data Structures and AlgorithmsTawsifNo ratings yet
- Integrals - Integral Calculus - Math - Khan Academy PDFDocument7 pagesIntegrals - Integral Calculus - Math - Khan Academy PDFroberteleeroyNo ratings yet
- Presentation5 EV ArchitectureDocument26 pagesPresentation5 EV ArchitectureJAYKUMAR MUKESHBHAI THAKORNo ratings yet
- BCIT COMP 8505 Final Project Covert Channel Exfiltration by Wesley Kenzie, June 2011Document39 pagesBCIT COMP 8505 Final Project Covert Channel Exfiltration by Wesley Kenzie, June 2011Wesley KenzieNo ratings yet
- MTH 108Document10 pagesMTH 108GetlozzAwabaNo ratings yet
- Reaktor 5 Core Manual EnglishDocument210 pagesReaktor 5 Core Manual EnglishmonistoNo ratings yet
- Bodybuilder Guidelines: Update: 2011-22Document438 pagesBodybuilder Guidelines: Update: 2011-22thkimzone73100% (12)
- Installation, Operation, and Maintenance ManualDocument54 pagesInstallation, Operation, and Maintenance ManualIsmael Berlanga ResNo ratings yet
- Computer Dictionary PDFDocument95 pagesComputer Dictionary PDFMarjenneilNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (The Answers Are Provided After The Last Question.)Document6 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (The Answers Are Provided After The Last Question.)VijendraNo ratings yet
- Newvhdl Syllabus (It&Cse)Document2 pagesNewvhdl Syllabus (It&Cse)Mude Kishore NaikNo ratings yet
- HydrometerDocument13 pagesHydrometerShubhrajit MaitraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading LAA Grade 10Document54 pages2nd Grading LAA Grade 10Urduja Kyle OdiacerNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties of Gem Substances Educational Objective: This Exercise, Unit 7 in The Above Syllabus, Will Introduce Students To Skills andDocument19 pagesOptical Properties of Gem Substances Educational Objective: This Exercise, Unit 7 in The Above Syllabus, Will Introduce Students To Skills andCarl SoriaNo ratings yet
- MA201 Mechanical Vertical Machining Center 133-134Document2 pagesMA201 Mechanical Vertical Machining Center 133-134Ali HashmiNo ratings yet
- ORC - Airbag SystemDocument13 pagesORC - Airbag SystemGarikoitz FranciscoeneNo ratings yet
- Quantities Survey MethodsDocument73 pagesQuantities Survey MethodsparvezNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryDocument23 pagesAssignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryAman AmanNo ratings yet