Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrogen Analyzer
Uploaded by
Bikas SahaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydrogen Analyzer
Uploaded by
Bikas SahaCopyright:
Available Formats
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
TRAINING MODULE
HYDROGEN ANALYSER
MAKE: MAIHAK
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 1 of 1
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
TOPICS COVERED IN THIS MODULE:
1. INTRODUCTION
2. PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
3. SAMPLING SYSTEM
4. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
5. CALIBRATION
6. MAINTENANCE
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 2 of 2
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
INTRODUCTION:
The hydrogen analyser installed in our complex is detecting hydrogen based on thermal conductivity
principle . There are total 10 hydrogen analysers installed all over the RPL complex.
The following is the complete breakup of analysers spread over the complex:
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 3 of 3
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION:
Thermal conductivity principle:
Within the TCD cell are four resistive filaments , suspended in individual cavities in a metal block and
connected electrically as legs of wheatstone bridge
Two filaments work as sample side and remaining two as reference side.
When sample and reference gases flow through the cell, this gas takes away some heat from the filaments (
heat absorption of gas is depending on its thermal conductivity), which changes the temperature of
filaments.
Change in temperature of filaments also changes the resistance of the filaments.
This change in resistance causes change in current through the iflaments, which can be calibrated to detect
the conductivity and the type of gas.
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 4 of 4
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
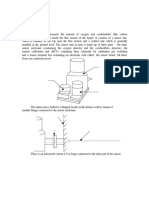
SAMPLING SYSTEM:
ANALYSER
6
5
4
8
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 5 of 5
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
The detailed description of all the parts mentioned in the above figure is as below:
1. Sampling point: The point where from sample is being taken for analysis. In the analyser used
in our complex, the sample is taken from the stack and is usually at a height of 5-6m. The
sample is being pumped into the analyser with the help of vacuum pump
2. Pressure reducing device: Brings down the sample gas pressure down to the allowable
pressure
3. Gas lines: the gas lines must be made from stainless steel tubes.
4. Dust filter: an external dust filter is used to avoid the contamination in the sample
5. Analyser bypass: increases the sample gas flow to the analyser in order to have a quick
response time.
6. Flowmeter: to set the correct sample gas flow through the analyser.
7. Flame arrestor: To prevent flames from entering the gas analyser.
8. Test gas feed: Used to verify the operation of the analyser with the help of standard zero and
span calibration test gases.
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 6 of 6
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION:
The main CPU board processes the electronic signal , manipulates it according to the parameters
chosen by the user, stores and remembers all variables/options, calculates calibration
parameters, determines hydrogen concentrations and output those concentrations to the front
LCD and analog terminals. It also controls temp. of optical bench to approx. 55 deg.C and offers
the user a variety of status and troubleshooting of outputs.
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 7 of 7
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
Calibration / validation:
The analyser has three different types of calibration procedures:
1. Automatic calibration,
2. Manual calibration with automatic feed of the test gases,
3. Manual calibration with manual feed of the test gases.
Note: When the control input “Service/Cal.” is disabled the menu functions for
calibration cannot be accessed.
The applied method for calibration is the manual calibration (3) with manual feed of the
test gases.
Preparation before calibration:
The following items need to be programmed before a manual calibration can be
performed:
?? Nominal calibration gas values
?? Span delay time
?? Calibration measuring time
Setting the nominal calibration gas values:
The nominal values of the calibration gases can be set as reference value during the
calibration. During the actual manual calibration the values may be changed e.g. when
another calibration bottle is applied.
?? Call-up menu 63, : main menu ? calibr. parameter,
?? Select zero gas or a test gas (A,B,C). The current settings are displayed.
Note: For the test gases, which are not applicable, make sure that “—“ is entered,
a zero value will result in a wrong (multi-point) calibration !
?? Select gas pump – off and select the desired measuring component and enter the
reference value as indicated on the gas cylinder analysis certificate,
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 8 of 8
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
Setting the span delay time :
This is in fact the response time of the analyser system including the sample
conditioning system.
?? Call-up menu 6361 , : main menu ? settings ? calibr. parameter ?
autom. calibration ? span delay time,
?? Set the span delay time in sec. Standard setting is 30 sec.
Setting the calibration measuring time :
This time starts after the span delay time. It is used to measure the calibration gas value
by gathering a number of measured values and computing the average.
?? Call-up menu 6362 , : main menu ? settings ? calibr. parameter ?
autom. calibration ? calibration measuring time,
?? Set the calibration measuring time in sec. Standard setting is 180 sec.
Manual calibration:
?? Call-up main menu 4 - 2 and just follow the instruction steps as displayed.
?? Shut off the sample inlet valve before letting the calibration gas pass through
analyser .
?? Make sure to set the correct flow rate for the cylinder (10-100 l/hr)
?? The pressure in the line should be 0.1-1 bar
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 9 of 9
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
MAINTENANCE:
Maintenance of the Maihak CO2 /O2 stack gas analyser is mainly limited to the daily visual
checks of the sample conditioning system and the proper settings for the sample flow through the
analyser.
The application on a stack-sample, which normally contains a high dust load, high temperatures
and a high amount of water vapour, establishes extensive sample conditioning requirements, this
because of the analyser parts are sensitive to clogging, condensation and oxidation, like both
sample cells of this analyser.
For these reasons the regular inspection of the sampling conditions is essential.
Regular preventive checks:
Daily visual checks: (see also Daily visual check sheet)
??Check the presence of sample flow to the analyser
??Check the conditions of the analyser gas connections,
??Check the function “lamp”, which should be illuminated green, if the indication is red,
observe the display message and take appropriate action,
??Check the service “lamp”, which should not be illuminated. If the lamp is on, observe
the display message and take appropriate action,
Weekly check:
??Check the presence of any fault condition by means of displaying “Status check – 21’
??Check working condition of sampling system components viz. dryer, cooler, filter
??Check presence of steam used for heating sample lines.
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 10 of 10
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
Six-months check:
??Check all gas channels for a possible leakage (see next section)
??Check / replace internal safety filter.
Leak check:
1. Close the inlet- and outlet-valve of the fast loop,
2. Wait till the analyser flow has stopped,
3. Switch the analyser to the zero calibration mode, call up via the main menu
respectively 4 – 2 – 1
4. Select zero gas.
5. Open the zero gas bomb and set the pressure regulator to zero setting (no analyser
flow) and keep the span-gas bottle closed (pressure should be zero),
6. Disconnect the outlet connection of the analyser and connect a water-filled U-tube
(height about 1.5 m) to the analyser outlet,
7. Carefully rise the setting of the bomb regulator to a setting just below 2 psig, so the
water U-tube will indicate about 1400 mm wc,
8. Then close the bomb valve on the zero-gas bomb thoroughly,
9. Wait and observe the pressure indication before the pressure regulator and the water
column indication at the U-tube.
10. If there is a leakage, the pressure will drop with a rate depending on the size of the
leakage.
11. To return to normal operation, follow the steps 1 to10 in reverse order.
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 11 of 11
Training
RELIANCE PETROLEUM LIMITED CES/INS/00 54
JAMNAGAR REFINERY PROJECT
HYDROGEN analyser-MAIHAK make
Note: Maihak specifies a maximum pressure drop (allowable leakage) of 5 mm water
column each 4 minutes.
Locate the leakage by means of “SNOOPY” or water mixed with soap.
Be careful when introducing the water into the analyser ! Switch off the analyser first
and avoid contact with the electronics
CHECKED BY : CES INSTRUMENTATION REV 00
APS ISSUE 00
TRAINING MANUAL DATE 9/07/2000
APPROVED BY:
HSG AUTHOR: NRB
F:\Inst \system\analyser\learning\trg module\16.doc Page 12 of 12
You might also like
- Tutorial MagIC Net 2.XDocument99 pagesTutorial MagIC Net 2.XJuan Diego Aznar Fernández100% (1)
- 052KP 01 New 24" Gas Transmission Pipeline To Alkhalij Power Generation Station Control /ESD and Operating Philosophy 052KP 01 PHL IN 001, Rev.01Document26 pages052KP 01 New 24" Gas Transmission Pipeline To Alkhalij Power Generation Station Control /ESD and Operating Philosophy 052KP 01 PHL IN 001, Rev.01Jabel Oil Services Technical DPTNo ratings yet
- Hook Ups PDFDocument8 pagesHook Ups PDFAnonymous d7Jde8No ratings yet
- P&ID For Inst Scope ReferenceDocument1 pageP&ID For Inst Scope Referenceprabudass pNo ratings yet
- Thermax - NTPC PresentationDocument57 pagesThermax - NTPC PresentationPiyush MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Refinery Lube Oil System P&I DiagramDocument2 pagesPakistan Refinery Lube Oil System P&I Diagrammuieed siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Work Instruction FOR: Charpy Impact TestDocument4 pagesWork Instruction FOR: Charpy Impact TestmahendraNo ratings yet
- 2021 Subsector OutlooksDocument24 pages2021 Subsector OutlooksHungNo ratings yet
- 42-HRSG IO ListDocument18 pages42-HRSG IO ListessameldinNo ratings yet
- BOP - DCS IO List Rev 2.4 (27.01.2014)Document566 pagesBOP - DCS IO List Rev 2.4 (27.01.2014)vinospaceshuttleNo ratings yet
- Compressors OperationDocument35 pagesCompressors OperationSalim Chohan100% (1)
- NTPC Limited: (A Government of India Enterprise)Document7 pagesNTPC Limited: (A Government of India Enterprise)Yogesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- F&G Cause and Effect Matrix for Salalah Methanol ProjectDocument6 pagesF&G Cause and Effect Matrix for Salalah Methanol ProjectpavanNo ratings yet
- Control System Configuration PDFDocument2 pagesControl System Configuration PDFjuliunNo ratings yet
- Design Basis - Package - B224-999-80-43 EDB-1002Document12 pagesDesign Basis - Package - B224-999-80-43 EDB-1002Esakki muthu100% (1)
- Write Up On LPBP SystemDocument9 pagesWrite Up On LPBP SystemKhushboo PandeyNo ratings yet
- Control Loop 13Document15 pagesControl Loop 13nmulyonoNo ratings yet
- 418000E4422 R0 Write Up On Electro Hydraulic ControllerDocument10 pages418000E4422 R0 Write Up On Electro Hydraulic ControllerkoinsuriNo ratings yet
- Adani Power PG 17 Control Design Criteria BTGDocument17 pagesAdani Power PG 17 Control Design Criteria BTGManikanda PrabhuNo ratings yet
- HPBP Writeup Dadri-IIDocument17 pagesHPBP Writeup Dadri-IIrajan_me083No ratings yet
- DS For Chlorine Analyzer-Rev-0Document26 pagesDS For Chlorine Analyzer-Rev-0anbesivam87_49857255No ratings yet
- TPP Motorised ValveDocument1 pageTPP Motorised ValvenogeshwarNo ratings yet
- DHT Question Answer BankDocument41 pagesDHT Question Answer BankBikas Saha100% (3)
- Signal Flow Diagram: Electronics Division, Bangalore - 26Document65 pagesSignal Flow Diagram: Electronics Division, Bangalore - 26Deepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Controls & Instrumentation FOR 660 MW Supercritical Unit at TirodaDocument23 pagesControls & Instrumentation FOR 660 MW Supercritical Unit at TirodaAakash kumar ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- HAazopDocument35 pagesHAazopSaravanan ElangovanNo ratings yet
- SMP PH AnalyserDocument4 pagesSMP PH AnalyserSreekanthMylavarapuNo ratings yet
- 1081 Camid Vs Op DigestDocument2 pages1081 Camid Vs Op DigestLennart Reyes67% (3)
- HindalcoDocument28 pagesHindalcoSiddhant Satpathy100% (1)
- Steam and Water Sampling System: Larsen & Toubro Limited Epc Power Training ManualDocument13 pagesSteam and Water Sampling System: Larsen & Toubro Limited Epc Power Training ManualABVSAINo ratings yet
- KMPCL 6í-600MW DCS FSSS Writeup R1.1Document74 pagesKMPCL 6í-600MW DCS FSSS Writeup R1.1MAGUNAMNo ratings yet
- IPS-MBD21907-In-506 - Datasheet of Pressure Transmitter - ADocument7 pagesIPS-MBD21907-In-506 - Datasheet of Pressure Transmitter - ANikhil KarkeraNo ratings yet
- Gek 106852aDocument10 pagesGek 106852awednetoxNo ratings yet
- Atrs Logic Diagrams - Turbine Operation LogicDocument76 pagesAtrs Logic Diagrams - Turbine Operation LogicKhushboo PandeyNo ratings yet
- 19 Boiler ESP System Commissioning Procedure-Töàtéëtö TÖñs Ÿt +T+ƑF Âf Ò Ä Û+Document31 pages19 Boiler ESP System Commissioning Procedure-Töàtéëtö TÖñs Ÿt +T+ƑF Âf Ò Ä Û+kvsagarNo ratings yet
- SMP SilicaDocument25 pagesSMP SilicaSreekanthMylavarapuNo ratings yet
- T07073-LBH-SY-M001 Rev.A PDFDocument43 pagesT07073-LBH-SY-M001 Rev.A PDFRanjanaWajeNo ratings yet
- SMP For Silica Hach 5500scDocument7 pagesSMP For Silica Hach 5500scPrince MaheshNo ratings yet
- PP10CC 0009 6mal Yr Abc 001Document30 pagesPP10CC 0009 6mal Yr Abc 001anbesivam87No ratings yet
- Cep ChangeoverDocument1 pageCep ChangeoverSUBHASISH MUKHERJEENo ratings yet
- Captive Power Plant - Encon Measures: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine FutureDocument20 pagesCaptive Power Plant - Encon Measures: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine Futuremujeebtalib100% (1)
- 2093-FE-7903 Rev. CDocument34 pages2093-FE-7903 Rev. CAyush ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument43 pagesThermalSahuManish100% (1)
- Uong Bi 300 MW Extension Power Plant: OwnerDocument32 pagesUong Bi 300 MW Extension Power Plant: OwnerAmEnPro100% (1)
- Dcs Feb 20Document271 pagesDcs Feb 20skypeNo ratings yet
- B 125674001 PaDocument18 pagesB 125674001 Pazizu1234No ratings yet
- Standard Operation Procedure: H2 Storage Tank Draining, Hydrotest & Filling 4X600 MW TPP Val, Jharsuguda, OdishaDocument4 pagesStandard Operation Procedure: H2 Storage Tank Draining, Hydrotest & Filling 4X600 MW TPP Val, Jharsuguda, Odishaabhrrajjit SANo ratings yet
- RideDocument8 pagesRidewahyuNo ratings yet
- SGC Hpsu (LP Bypass) Logic DiagramDocument21 pagesSGC Hpsu (LP Bypass) Logic DiagramKhushboo PandeyNo ratings yet
- 9112 575 Opr 704 00046 - 01Document16 pages9112 575 Opr 704 00046 - 01Anonymous qT80dF24dNo ratings yet
- BOMAFA Corporate Profile EnglishDocument6 pagesBOMAFA Corporate Profile Englishshan07011984No ratings yet
- Recommended Schemes & Writeup of Auto ControlsDocument25 pagesRecommended Schemes & Writeup of Auto ControlsShirshendu RoyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Boiler ExplosionDocument18 pagesCase Study - Boiler ExplosionSatish ChavanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Kinetic Energy As A Selection Criteria For Control ValvesDocument9 pagesFluid Kinetic Energy As A Selection Criteria For Control ValvesVijay KabboorNo ratings yet
- 9112 575 Opr 704 00048 - 01Document12 pages9112 575 Opr 704 00048 - 01Anonymous qT80dF24dNo ratings yet
- Technical Documents of The BoilerDocument20 pagesTechnical Documents of The BoilerMatias Mancilla0% (1)
- 4 Fire & Gas Detection System: Type of Detector LocationDocument3 pages4 Fire & Gas Detection System: Type of Detector LocationBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Ioties Document No:-Mccpl-Pctl-Acc-Doc-M-0001 - Rev. P3Document23 pagesIoties Document No:-Mccpl-Pctl-Acc-Doc-M-0001 - Rev. P3pramodtryNo ratings yet
- PZ D CS Pi SP 015 02Document60 pagesPZ D CS Pi SP 015 02epbamdadNo ratings yet
- Detergent FlushingDocument36 pagesDetergent FlushingSam100% (1)
- BHELDocument4 pagesBHELNageswara Reddy GajjalaNo ratings yet
- Guided Wave Radar in Steam Boiler Service: Measuring Water Level Accurately Despite ChallengesDocument14 pagesGuided Wave Radar in Steam Boiler Service: Measuring Water Level Accurately Despite ChallengesRoger SeaverNo ratings yet
- Price List MSRP For WEB PDFDocument3 pagesPrice List MSRP For WEB PDFnavneetNo ratings yet
- Work Instruction FOR: Spectro AnalysisDocument3 pagesWork Instruction FOR: Spectro AnalysismahendraNo ratings yet
- NGP Instrument & Utility Air TestDocument5 pagesNGP Instrument & Utility Air Testwqs_19No ratings yet
- fuelsLAB 18MEL58Document95 pagesfuelsLAB 18MEL58Vinayak Govind Chary RudravelliNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Question - ANSDocument7 pagesHeat Exchanger Question - ANSBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- SAFETY PAPER CHEMICALSDocument11 pagesSAFETY PAPER CHEMICALSBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Q & Paper For GelsDocument5 pagesQ & Paper For GelsBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Safety QuestionsDocument6 pagesSafety QuestionsBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- HT Operation Validation Questions General AnsDocument6 pagesHT Operation Validation Questions General AnsBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Gas Cylinder Safety - ANSDocument1 pageGas Cylinder Safety - ANSBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Compressor FAQsDocument1 pageReciprocating Compressor FAQsBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Contractor'S Safety Performance Evaluation: S.No Check Points Answer 1Document3 pagesContractor'S Safety Performance Evaluation: S.No Check Points Answer 1Bikas SahaNo ratings yet
- H2S Related Activity DHT - VGOHTDocument3 pagesH2S Related Activity DHT - VGOHTBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Compressor FAQsDocument1 pageReciprocating Compressor FAQsBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Flare Question - ANSDocument2 pagesFlare Question - ANSBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Fire Services Day - 05Document1 pageFire Services Day - 05bikas_sahaNo ratings yet
- Fire Quiz QuestionsDocument29 pagesFire Quiz QuestionsAshish PattanaikNo ratings yet
- DHT, VGOHT - Catloading Diagram - Oct2005Document3 pagesDHT, VGOHT - Catloading Diagram - Oct2005Bikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Contractor'S Safety Performance Evaluation: S.No Check Points Answer 1Document3 pagesContractor'S Safety Performance Evaluation: S.No Check Points Answer 1Bikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Computer Installations Q & ADocument1 pageComputer Installations Q & ABikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Flame Ionisation DetectorDocument4 pagesFlame Ionisation DetectorBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Process Control Presentation QuestionnaireDocument1 pageAdvanced Process Control Presentation QuestionnaireBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Compressor Seals For H2 Recycle Service.Document6 pagesCompressor Seals For H2 Recycle Service.Bikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Compressors: Presentation By: U K UpadhyayDocument36 pagesCompressors: Presentation By: U K UpadhyayBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 1 Quizform: 350Kg/Cm2 52Kg/Cm2 250Kg/Cm2 30Kg/Cm2Document1 pagePage 1 of 1 Quizform: 350Kg/Cm2 52Kg/Cm2 250Kg/Cm2 30Kg/Cm2bikas_sahaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Gas Chromatography TechniqueDocument12 pagesIntroduction to Gas Chromatography TechniqueBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Dry Gas Seal System StandarDocument8 pagesDry Gas Seal System StandarRonny AjaNo ratings yet
- Flame Ionisation DetectorDocument4 pagesFlame Ionisation DetectorBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- GC PresentationDocument54 pagesGC PresentationBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Chromatography overviewDocument15 pagesChromatography overviewBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- O2-CO AnalyzerDocument23 pagesO2-CO AnalyzerBikas SahaNo ratings yet
- GC Material 4Document8 pagesGC Material 4Bikas SahaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template CONTENT 5Document2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template CONTENT 5Edward Barber100% (3)
- Caed102: Financial MarketsDocument2 pagesCaed102: Financial MarketsXytusNo ratings yet
- 2003 June Calc Paper 6 (H)Document20 pages2003 June Calc Paper 6 (H)abbasfazilNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Research On Emerging Pedagogies For The Future of Education, Trauma-Informed, Care, and Pandemic Pedagogy Aras BozkurtDocument535 pagesHandbook of Research On Emerging Pedagogies For The Future of Education, Trauma-Informed, Care, and Pandemic Pedagogy Aras BozkurtBrenda MoysénNo ratings yet
- Entry Test Result MPhil 2014 PDFDocument11 pagesEntry Test Result MPhil 2014 PDFHafizAhmadNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1: You Should Spend About 20 Minutes On This TaskDocument1 pageWriting Task 1: You Should Spend About 20 Minutes On This TaskRodrigo MoraesNo ratings yet
- Acquisition of SharesDocument3 pagesAcquisition of SharesChaudhary Mohsin RazaNo ratings yet
- Joysticks For Hoist & Crane Control SystemsDocument5 pagesJoysticks For Hoist & Crane Control SystemsRunnTechNo ratings yet
- How efficient is a wind turbineDocument8 pagesHow efficient is a wind turbinejNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Improvement SchemeDocument110 pagesWater Supply Improvement SchemeLeilani JohnsonNo ratings yet
- CIMA Introduction To NLPDocument4 pagesCIMA Introduction To NLPsambrefoNo ratings yet
- No or Islamic Bank OurStory EnglishDocument45 pagesNo or Islamic Bank OurStory EnglishTalib ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valves 2/2 210: Pilot Operated FL Oating Diaphragm 3/8 To 2Document4 pagesSolenoid Valves 2/2 210: Pilot Operated FL Oating Diaphragm 3/8 To 2AlexanderNo ratings yet
- IWR 0174 Ed12 - Jabra Headsets Amplifiers - OmniPCXplatforms - SoftphonesDocument83 pagesIWR 0174 Ed12 - Jabra Headsets Amplifiers - OmniPCXplatforms - SoftphonesAsnake TegenawNo ratings yet
- Odoo JS Framework Rewrite Brings New Views and TestingDocument68 pagesOdoo JS Framework Rewrite Brings New Views and TestingglobalknowledgeNo ratings yet
- New Product Introduction Process: August 16, 2016Document30 pagesNew Product Introduction Process: August 16, 2016JuliaChenNo ratings yet
- Title Page - Super King Air C90CGTi FusionDocument2 pagesTitle Page - Super King Air C90CGTi Fusionsergio0% (1)
- Index NumbersDocument23 pagesIndex NumbersemmaNo ratings yet
- Report On Indian Education SystemDocument7 pagesReport On Indian Education SystemYashvardhanNo ratings yet
- Andrija Kacic Miosic - Razgovor Ugodni Naroda Slovinskoga (1862)Document472 pagesAndrija Kacic Miosic - Razgovor Ugodni Naroda Slovinskoga (1862)paravelloNo ratings yet
- Standards in Nursing Education ProgrammeDocument13 pagesStandards in Nursing Education ProgrammeSupriya chhetryNo ratings yet
- Order From U.S. Disctrict Judge Jesus G. Bernal To Chino Valley UnifiedDocument9 pagesOrder From U.S. Disctrict Judge Jesus G. Bernal To Chino Valley UnifiedBeau YarbroughNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument8 pagesSafety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingFerry Dela RochaNo ratings yet
- Veritas d1.6.1 FinalDocument28 pagesVeritas d1.6.1 FinalgkoutNo ratings yet
- Storytelling Tips from Salesforce CEO Marc BenioffDocument2 pagesStorytelling Tips from Salesforce CEO Marc BenioffvsrajkumarNo ratings yet