Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brain Regions - Diencephalon, Brainstem, Limbic System
Uploaded by
Opio IsaacOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain Regions - Diencephalon, Brainstem, Limbic System
Uploaded by
Opio IsaacCopyright:
Available Formats
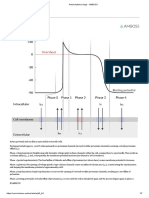
Diencephalon and brainstem - AMBOSS https://next.amboss.com/us/article/-60DnS#Zbce829cc1853a5a86dadca0...
Search… O
Diencephalon and brainstem Last updated: Sep 24, 2020
QBANK SESSION LEARNED
Summary
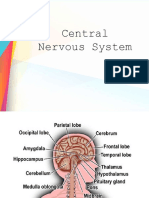
The diencephalon is the caudal part of the forebrain (prosencephalon) located between the
midbrain (mesencephalon) and the cerebrum (telencephalon). It consists of the thalamus,
hypothalamus, epithalamus, and subthalamus. The thalamus is the relay center for sensory
information. The hypothalamus regulates autonomic function and the endocrine system. The
epithalamus, which consists of the pineal gland, habenula, habenular commissure, and stria
medullaris, regulates the sleep-wake cycle. The subthalamus, which contains the
subthalamic nuclei, is part of the indirect basal ganglia circuit and is involved in the inhibition of
unnecessary movements. The brain stem is the caudal part of the brain and consists of the
midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. The brain stem regulates autonomic function
(respiration, circulation, lacrimation, salivation), controls visual and auditory reflexes, and
maintains vigilance. It is also a hub through which run all ascending sensory pathways,
descending motor pathways, and other local pathways of the central nervous system. The
limbic system is a group of brain pathways that consists of the amygdala, hypothalamus,
thalamus, hippocampus, and limbic cortex. These are involved in memory formation,
regulation of appetite and satiety, a�ention, emotional responses, and sexual arousal. The
ventricular system consists of four interconnected ventricles (a pair of lateral ventricles,
third ventricle, and fourth ventricle). It is involved in the production, transport, and drainage of
cerebrospinal fluid, which plays a role in waste removal and cushioning the brain.
NOTES FEEDBACK
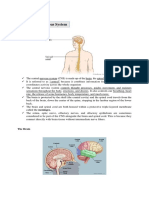
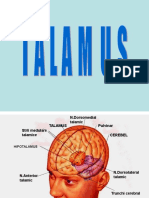
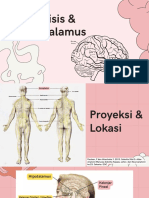
Diencephalon
The diencephalon makes up the caudal part of the forebrain between the telencephalon and
midbrain. It consists of the hypothalamus, thalamus, epithalamus, and the subthalamus.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus functions as the central control center for the autonomic nervous system
and endocrine function. Its nuclei produce releasing hormones for the anterior pituitary and the
1 of 1 16/10/2020, 11:23
You might also like
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Forebrain Structure and Function: Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Cerebral CortexDocument4 pagesForebrain Structure and Function: Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Cerebral CortexAj VesquiraNo ratings yet
- Dia GridDocument7 pagesDia GridMark Ross CanaoayNo ratings yet
- Anatomia e Sistema NerosoDocument8 pagesAnatomia e Sistema NerosoChloe BujuoirNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument10 pagesThe BrainTida TpNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ppt. Lec. 1Document49 pagesNeuro Ppt. Lec. 1Jay successNo ratings yet
- Ms - Angeline M.SC (N) Previous Year Psychiatric Nursing Choithram College of NursingDocument79 pagesMs - Angeline M.SC (N) Previous Year Psychiatric Nursing Choithram College of NursingPankaj TirkeyNo ratings yet
- Brain & Limbic SystemDocument63 pagesBrain & Limbic Systemgopscharan100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology CVADocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CVAmaryrose_jordan100% (6)
- The Cns Portfolio EditionDocument9 pagesThe Cns Portfolio Editionapi-438492450No ratings yet
- "Cognitive Psychology": Sir Faisal Mumtaz Zeeshan Akhtar Bsap 3 005 20 Jan, 2021Document9 pages"Cognitive Psychology": Sir Faisal Mumtaz Zeeshan Akhtar Bsap 3 005 20 Jan, 2021Zeeshan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Brain and FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of The Brain and FunctionsLee Ayn PoncardasNo ratings yet
- Nervous System EditedDocument36 pagesNervous System EditedMellida Kate Winslet T.No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemkitkat22phNo ratings yet
- Otak Dan NN CranialisDocument74 pagesOtak Dan NN CranialisDebri ErwendiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument30 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologySheila Mae PanisNo ratings yet
- PsychologyDocument6 pagesPsychologymahbinaalone7No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Brain: Brain DivisionsDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The Brain: Brain DivisionsUsagi TsukinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainkazelleNo ratings yet
- CNS Guide: Brain and Spinal Cord Control Body FunctionsDocument18 pagesCNS Guide: Brain and Spinal Cord Control Body FunctionsMeg ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy of Nervous SystemJoie MirandaNo ratings yet
- Brain & Cranial Nervous SystemDocument74 pagesBrain & Cranial Nervous SystemMAHARANINo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document44 pagesNervous System 1Farina FaraziNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Brainangel16_88No ratings yet
- Thalamus and Limbic System: Key Structures in Emotion and MemoryDocument18 pagesThalamus and Limbic System: Key Structures in Emotion and MemoryОксана КрасильниковаNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the BrainDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the BrainEnna PaulaNo ratings yet
- General Brain Structure N FunctionDocument6 pagesGeneral Brain Structure N Function'Niq Hdyn100% (1)
- Asd NotesDocument9 pagesAsd NotesZosmita Shane GalgaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainJonathan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Brain and Structute(1)Document10 pagesBrain and Structute(1)dhatreyi.g.gubbalaNo ratings yet
- AD 7 The Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesAD 7 The Nervous SystemBernard SalimNo ratings yet
- What Are The Three Major Divisions of The Brain-Forebrain, Midbrain and HindbrainDocument1 pageWhat Are The Three Major Divisions of The Brain-Forebrain, Midbrain and HindbrainMichael S. PetryNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainLhyn BagunuNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument56 pagesNervous Systemfatimamuzammil406No ratings yet
- PSYCH 240 The Brain PaperDocument4 pagesPSYCH 240 The Brain PaperTammy PoeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyremegelbristolNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Concepts of Psychobiology: Kasturba Gandhi Nursing CollegeDocument36 pagesSeminar On Concepts of Psychobiology: Kasturba Gandhi Nursing CollegeNarmadhaNo ratings yet
- ThalamusDocument21 pagesThalamusTem GemechuNo ratings yet
- The Human Encep-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesThe Human Encep-WPS OfficeMd RanaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemJoyce NieveraNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Vertebrate Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesStructure of The Vertebrate Nervous SystemMadhavan MbbsNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemAppyNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesBrain Structures and FunctionsAndrea RamirezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The BrainDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The BrainFlorenza Marie OlleresNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BraineriannajNo ratings yet
- Matter. Gyri and The Grooves Are Called SulciDocument2 pagesMatter. Gyri and The Grooves Are Called SulciFrances BarenoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The Central Nervous SystemKristine AlejandroNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR ON PSYCHOBIOLOGY CONCEPTSDocument21 pagesSEMINAR ON PSYCHOBIOLOGY CONCEPTSdhivyaram100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Nervous SystemnanatdaboyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy of BrainAlex Bañares Eusebio Jr.100% (1)
- CHAPTER 15: NERVOUS SYSTEM, Brain and Cranial Nerve: Embryology of The BrainDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 15: NERVOUS SYSTEM, Brain and Cranial Nerve: Embryology of The BrainDyah Ayu Pratama SariNo ratings yet
- Structure of Brain and Its FunctionDocument12 pagesStructure of Brain and Its FunctionDr.Shahana banuNo ratings yet
- HumanasdhDocument4 pagesHumanasdhPatricia Camille FermoNo ratings yet
- 4-The Nervous SystémDocument6 pages4-The Nervous SystémEma FröhlichováNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of StrokeDocument4 pagesAnatomy of StrokeMarvin Manuel RamosNo ratings yet
- Midterm Psych Module 7Document14 pagesMidterm Psych Module 7Ladybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of the DiencephalonDocument7 pagesStructure and Functions of the DiencephalonLipi UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- NEUROANATOMYDocument24 pagesNEUROANATOMYCamille CarlosNo ratings yet
- Chap-21 Neural Control and CordinationDocument48 pagesChap-21 Neural Control and CordinationMANIK CHHABRANo ratings yet
- Pinch Technology Report PDFDocument76 pagesPinch Technology Report PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- TEE2205 AND TEMB2204 CONTROL SYSTEMS TEST QUESTIONSDocument1 pageTEE2205 AND TEMB2204 CONTROL SYSTEMS TEST QUESTIONSOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Quality in Stone Quarry AreasDocument6 pagesGround Water Quality in Stone Quarry AreasOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- WritingResearchReport PDFDocument22 pagesWritingResearchReport PDFLaravel HomeNo ratings yet
- Unemployment: Causes of UnemploymemtDocument3 pagesUnemployment: Causes of UnemploymemtOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- QuarryDocument100 pagesQuarryOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Diuretics - AMBOSS PDFDocument9 pagesDiuretics - AMBOSS PDFOpio Isaac100% (1)
- Diuretics - AMBOSSTWO PDFDocument11 pagesDiuretics - AMBOSSTWO PDFOpio Isaac0% (1)
- Atuhairwe JoanDocument1 pageAtuhairwe JoanOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- 2005 Pharm 501 Autonomics PDFDocument30 pages2005 Pharm 501 Autonomics PDFumergulgNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressants - AMBOSS PDFDocument7 pagesImmunosuppressants - AMBOSS PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Cns Drugs PDFDocument84 pagesCns Drugs PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- CMA611S-2016-CMA311S - Notes (2010) - Unit 2 PDFDocument24 pagesCMA611S-2016-CMA311S - Notes (2010) - Unit 2 PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Antiemetics - AMBOSSDocument4 pagesAntiemetics - AMBOSSOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design GuideDocument15 pagesConcrete Mix Design Guidekarthiksamp100% (1)
- Antihistamines - AMBOSS PDFDocument5 pagesAntihistamines - AMBOSS PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs Guide: Classes, Uses & Side EffectsDocument4 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs Guide: Classes, Uses & Side EffectsOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Glucocorticoids - AMBOSS PDFDocument8 pagesGlucocorticoids - AMBOSS PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Drugs - AMBOSSDocument13 pagesAntidiabetic Drugs - AMBOSSOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics - AMBOSS PDFDocument7 pagesAntipsychotics - AMBOSS PDFOpio Isaac100% (1)
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Uses, Types & Side EffectsDocument5 pagesCalcium Channel Blockers: Uses, Types & Side EffectsOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWODocument6 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWOOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic 2 PDFDocument7 pagesAntiarrhythmic 2 PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants - AMBOSSDocument7 pagesAntidepressants - AMBOSSOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument9 pages1 SMaaNo ratings yet
- ThalamusDocument21 pagesThalamusTem GemechuNo ratings yet
- TALAMUS and its connectionsDocument37 pagesTALAMUS and its connectionsDaniela GiorocNo ratings yet
- Paxinos The Rat Brain 60 PDFDocument1 pagePaxinos The Rat Brain 60 PDFjoseuri2011No ratings yet
- HipotalamusDocument33 pagesHipotalamusBlanaru VictorNo ratings yet
- CNS DevelopmentDocument158 pagesCNS DevelopmentMubashir SiyalNo ratings yet
- JEEVADHARA 2016 December Malayalam MatterDocument81 pagesJEEVADHARA 2016 December Malayalam MatterSanuj SuseelanNo ratings yet
- DiensefalonDocument31 pagesDiensefalonIngrid AykeNo ratings yet
- 10 TalamusDocument74 pages10 TalamusAna-Maria AnaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDocument23 pagesExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- 4th Laboratory Activity Gallus DomesticusDocument4 pages4th Laboratory Activity Gallus DomesticusZia Ammarah SaripNo ratings yet
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocument14 pagesEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- El Tálamo: Aspectos Neurofuncionales: Related PapersDocument8 pagesEl Tálamo: Aspectos Neurofuncionales: Related PapersAlvear KatitaNo ratings yet
- The Magical World of Midbrain Activation UnlockedDocument30 pagesThe Magical World of Midbrain Activation UnlockedRaja GopeNo ratings yet
- Development of Embryo ChickDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Embryo ChickSafira Dwi OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo DevelopmentDocument5 pagesChick Embryo DevelopmentPaula Manalo-SuliguinNo ratings yet
- Development of Nervous SystemDocument59 pagesDevelopment of Nervous SystemtuhinNo ratings yet
- Brain Regions - Diencephalon, Brainstem, Limbic SystemDocument1 pageBrain Regions - Diencephalon, Brainstem, Limbic SystemOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- CVA Case StudyDocument20 pagesCVA Case Studybetchai18100% (5)
- 33HR ChickDocument7 pages33HR ChickJasper PanosoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoDocument13 pagesActivity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoFerhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- Diencephalon Thalamus and EpithalamusDocument19 pagesDiencephalon Thalamus and EpithalamusIgme Mocke StraussNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Hypothalamus and HypophysisDocument3 pagesAnatomy of Hypothalamus and HypophysisshindyNo ratings yet
- Guppy Brain Atlas SmallerDocument4 pagesGuppy Brain Atlas Smallerapi-394354061No ratings yet
- The Departmentof Biological SciencefrogembryoDocument11 pagesThe Departmentof Biological SciencefrogembryoFerhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- 33 HR Chick EmbryoDocument12 pages33 HR Chick EmbryoErvin AblazaNo ratings yet
- Frog Germ LayerDocument4 pagesFrog Germ LayerEricka GalangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Hypothalamus & Pituitary GlandDocument13 pagesAnatomy of the Hypothalamus & Pituitary GlandCindy DunduNo ratings yet
- Paxinos The Rat Brain 60Document1 pagePaxinos The Rat Brain 60joseuri2011No ratings yet
- DiencephalonDocument24 pagesDiencephalonHostiuc Alex RaulNo ratings yet