Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk Factors:: Pathophysiology of Alzheimer'S Disease
Uploaded by
Jordz Placi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesOriginal Title
ALZHEIMERS-DISEASE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesRisk Factors:: Pathophysiology of Alzheimer'S Disease
Uploaded by
Jordz PlaciCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
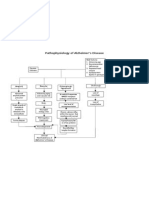
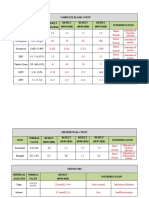
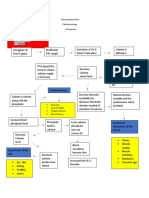
RISK FACTORS:
Advance age
Neurotransmitters
deficiencies
Repeated head
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE trauma
Apolipoprtein
CAUSES: epsilon 4 genotype
UNKOWN
AMYLOID VASCULAR Glutamatergic Cholinergic
HYPOTHESIS HYPOTHESIS Hypothesis Hypothesis
Advancing in aging N-methyl-D aspartate
Abnormal amyloid (NMDA) receptors undergo
and vascular risk
protein precursor sustained low level activation
factors of the brain.
cleavage
neurotransmission
Brain
hypoperfusion
Single strands of Loss of neurologic
insoluble b-amyloid Low level of neurons
is release in the Neurolgialenergy neurotransmission
crisis
Forms plaques
Chronic Calcium reflux
within the neuron that infers
Mild cognitive with normal signal
Increase anxiety Loss of
impairment transduction.
Difficulty organizing thoughts and acytylcholine
thinking logically (Ach)
Shortened attention span Hyperphosporylati
Problems coping with new Neuro- on of tau proteins
situation degeneration
Wandering/getting lost
Taking longer to complete daily
Poor judgement Neurofibribillary
task
Memory loss tangles formation
Repeating questions things
Loosing/misplacing
Loss of spontancity
MILD ALZHIMERS DISEASE
- REFERENCE: slideshare m-_sumbe,
- Niah.nih.gov
- Module NCM105week 13
You might also like
- NeurologyDocument33 pagesNeurologyjhqmpzg7sjNo ratings yet
- Neurology MnemonicsDocument11 pagesNeurology MnemonicsOstaz100% (1)
- Retinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentDocument3 pagesRetinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentJordz Placi100% (1)
- Neurology Board ReviewDocument16 pagesNeurology Board ReviewNabeel Kouka, MD, DO, MBA, MPH67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsTiger Knee100% (1)
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Document461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer DiseaseDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Alzheimer DiseaseTrixia Almendral100% (1)
- Childhood Epilepsy Etiology, Epidemiology & ManagementDocument6 pagesChildhood Epilepsy Etiology, Epidemiology & ManagementJosh RoshalNo ratings yet
- Seizure and EpilepsyDocument18 pagesSeizure and EpilepsyJamal JosephNo ratings yet
- Psychopathology of Schizophrenia (Theoretical)Document1 pagePsychopathology of Schizophrenia (Theoretical)Robert Joseph Sison100% (5)
- Pathology of Peripheral Nerve and Skeletal Muscle - DADocument46 pagesPathology of Peripheral Nerve and Skeletal Muscle - DASinta Dewi AdityaniNo ratings yet
- The Nurse's Guide to Communicable DiseasesDocument461 pagesThe Nurse's Guide to Communicable DiseasesJordz Placi100% (1)
- NCP Dengue Fever Hyperthermia and Acute PainDocument4 pagesNCP Dengue Fever Hyperthermia and Acute PainJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Craniotomy Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCraniotomy Nursing Care PlanJordz Placi100% (2)
- Convulsions in ChildrenDocument12 pagesConvulsions in ChildrenShesly Philomina0% (1)
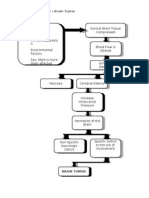
- Pathophysiology - Brain TumorDocument1 pagePathophysiology - Brain Tumornories_150% (2)
- 10 - Disorders of Consciousness and Language I (Coma and Confusional States) LectureDocument119 pages10 - Disorders of Consciousness and Language I (Coma and Confusional States) LectureRanjit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke: The Normal Blood Supply To The Brain Is DisruptedDocument5 pagesIschemic Stroke: The Normal Blood Supply To The Brain Is DisruptedMelchora Lea Castro SorianoNo ratings yet
- NP1 - ToprankDocument16 pagesNP1 - ToprankAllaiza Cristille100% (1)
- Fdar TorioDocument3 pagesFdar TorioJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Handbook of the Neuroscience of AgingFrom EverandHandbook of the Neuroscience of AgingPatrick R. HofNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease: Risk Factors, Causes, HypothesesDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease: Risk Factors, Causes, HypothesesMichael RolandNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsCleobebs AgustinNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Coma Levels and CausesDocument6 pagesMental Status Coma Levels and CausesMicah LatosaNo ratings yet
- Week 14 Course Task - Sagun AltheaDocument5 pagesWeek 14 Course Task - Sagun AltheaHermin TorresNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINDocument4 pagesDegenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINHermin TorresNo ratings yet
- Osms - It/alzheimers-Disease: Pathology & CausesDocument1 pageOsms - It/alzheimers-Disease: Pathology & Causesdysa ayu shalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Brain and PsychiatryDocument107 pagesBrain and PsychiatryQubricNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On Schizoaffective Disorder: EchopraxiaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology On Schizoaffective Disorder: EchopraxiaAgeededin Hart100% (1)
- Psychopathology of Schizophrenia (Client)Document1 pagePsychopathology of Schizophrenia (Client)Robert Joseph Sison67% (3)
- Neurological disorders and treatments summarizedDocument8 pagesNeurological disorders and treatments summarizedKunal KatyayanNo ratings yet
- Ataxia PresentationDocument11 pagesAtaxia PresentationS RiarNo ratings yet
- Degenerative and Demyelinating Disorders - Dr. WongDocument7 pagesDegenerative and Demyelinating Disorders - Dr. WongMonique BorresNo ratings yet
- Myoclonus PDFDocument49 pagesMyoclonus PDFAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Dams - DVT (New)Document48 pagesDams - DVT (New)Msd KishorNo ratings yet
- Dementia Recentupdates 130920080812 Phpapp01Document58 pagesDementia Recentupdates 130920080812 Phpapp01SantanuNo ratings yet
- Pathway Tumor OtakDocument3 pagesPathway Tumor OtakASIH DEVINo ratings yet
- Intensive Management of Status EpilepticusDocument41 pagesIntensive Management of Status EpilepticussnyNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument3 pagesIndexمحمد صديق المنشاوىNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases That Can Affect Our Nervous SystemDocument1 pageCommon Diseases That Can Affect Our Nervous SystemJhe-An PilapilNo ratings yet
- Terminology of PsychiatryDocument6 pagesTerminology of PsychiatryHassan.shehri100% (1)
- COURSE TASK 6 - Degenerative Table SummaryDocument2 pagesCOURSE TASK 6 - Degenerative Table SummaryJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- DR Dwi Putro Widodo - Epilepsy Seizures and SyndromesDocument37 pagesDR Dwi Putro Widodo - Epilepsy Seizures and SyndromesMuhammad HerryNo ratings yet
- Basis Neurobiologi DepresiDocument24 pagesBasis Neurobiologi DepresiAhmad Shafwan NatsirNo ratings yet
- UMNLand AHCDocument27 pagesUMNLand AHCdrmamodoNo ratings yet
- Clase Cefalea 2016Document60 pagesClase Cefalea 2016Juliana AndradeNo ratings yet
- Alzheimers DiseaseDocument11 pagesAlzheimers DiseaseCHRISTIAN RAY ALPAS PASILIAONo ratings yet
- NEURODocument17 pagesNEUROALIZA BAKILNo ratings yet
- Amnesia DemensiaDocument2 pagesAmnesia DemensiaAlexander TegarNo ratings yet
- Smart Art For Developmental AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesSmart Art For Developmental Abnormalitiesk.s.persauddNo ratings yet
- Neurology and Special Senses ' Neurology and Special Senses ' Section IiiDocument20 pagesNeurology and Special Senses ' Neurology and Special Senses ' Section IiiLuis Jose VelazquezNo ratings yet
- SEIZURE DISORDERS IN CHILDRENDocument47 pagesSEIZURE DISORDERS IN CHILDRENSven OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- DemenciaDocument1 pageDemenciamariasalvador0503No ratings yet
- Dr. Moch. Bahrudin, SP.S: Bagian Neurologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah MalangDocument34 pagesDr. Moch. Bahrudin, SP.S: Bagian Neurologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah MalangputrimeilissaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderPae EdejerNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Guide to Types, Causes, Diagnosis and PrognosisDocument14 pagesCerebral Palsy Guide to Types, Causes, Diagnosis and PrognosisAfifah NaurahNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Psychopathophysiology: Psychosocial Stressor and Interpersonal EventsDocument2 pagesPsychopathophysiology: Psychosocial Stressor and Interpersonal EventsMiyuki Bartolaba MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy-Students 2016Document85 pagesEpilepsy-Students 2016Alberto MayorgaNo ratings yet
- APP Neurodev2Document103 pagesAPP Neurodev2gabrielaNo ratings yet
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome Pathogenesis and DiagnosisDocument2 pagesGuillain-Barré Syndrome Pathogenesis and Diagnosispurnama baktiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument152 pagesCerebral PalsyPrateek Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- Diagrams & Illustrations of Dementia Signs & SymptomsDocument1 pageDiagrams & Illustrations of Dementia Signs & Symptomsdysa ayu shalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Use of Electroconvulsive Therapy To Patient With Schizophrenia and Other Mental IllnessDocument1 pageUse of Electroconvulsive Therapy To Patient With Schizophrenia and Other Mental IllnessJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media DialogueDocument1 pageOtitis Media DialogueJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Ear Pain ReliefDocument3 pagesNursing Care for Ear Pain ReliefJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nursing Student Stress & ResilienceDocument1 pageNursing Student Stress & ResilienceJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nursing Student Stress & ResilienceDocument1 pageNursing Student Stress & ResilienceJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media DialogueDocument1 pageOtitis Media DialogueJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nursing Student Stress & ResilienceDocument1 pageNursing Student Stress & ResilienceJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- RECOMMENDATIONS Dengue FeverDocument1 pageRECOMMENDATIONS Dengue FeverJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- WEEK 14 Ear Ana Dxtic TestsDocument35 pagesWEEK 14 Ear Ana Dxtic TestsJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Recomm Schisto MajanDocument3 pagesRecomm Schisto MajanJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nursing Student Stress & ResilienceDocument1 pageNursing Student Stress & ResilienceJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Nures ApaDocument1 pageNures ApaJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Gi NelecDocument52 pagesGi NelecJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- LABS Part 2Document3 pagesLABS Part 2Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- LABS Part 2 Jagna SchistosomiasisDocument3 pagesLABS Part 2 Jagna SchistosomiasisJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Muskulo Geria-1Document40 pagesMuskulo Geria-1Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Muskulo Geria-1Document40 pagesMuskulo Geria-1Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Gi NelecDocument52 pagesGi NelecJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Monitoring blood glucose levels and kidney functionDocument9 pagesMonitoring blood glucose levels and kidney functionJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety Protocols: Dr. Michael Bautista Dr. Ethyl Salvador-CayetanoDocument35 pagesHealth and Safety Protocols: Dr. Michael Bautista Dr. Ethyl Salvador-CayetanoJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - Aids2Document31 pagesChapter 21 - Aids2Sanjeevan Aravindan (JEEV)No ratings yet
- (884 KB) Eyeball Anatomy Sagittal View - EBM Consult HandoutDocument3 pages(884 KB) Eyeball Anatomy Sagittal View - EBM Consult HandoutJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Ncenl07 Activity 1Document1 pageNcenl07 Activity 1Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region V - BicolDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region V - BicolKevin Viernes GaraisNo ratings yet
- NefrologiDocument25 pagesNefrologifitriNo ratings yet
- PA y Depresión en Nepal 2017Document8 pagesPA y Depresión en Nepal 2017Alfredo PérezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3. Handling and Mass Production of Biological Control AgentsDocument5 pagesExercise 3. Handling and Mass Production of Biological Control AgentsRoxan AngonNo ratings yet
- Community Question Bank (N.a)Document41 pagesCommunity Question Bank (N.a)Sumaya AfifyNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypoparathyroidism PathophysiologymaricarNo ratings yet
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument6 pagesPityriasis Versicolorh8j5fnyh7dNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Rapport de CasDocument6 pagesCase Report: Rapport de CasWidya KartikaNo ratings yet
- What Is Nano Silver - Nano Silver PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Is Nano Silver - Nano Silver PDFvijuNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet - NITRIC ACID PDFDocument9 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet - NITRIC ACID PDFJunaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2021 Property Benefits SummaryDocument30 pages2021 Property Benefits SummaryTracy BonannoNo ratings yet
- Resume About NoiseDocument5 pagesResume About NoiseElsa MutiaraNo ratings yet
- Does Masturbation Cause Acne in Men?Document3 pagesDoes Masturbation Cause Acne in Men?AndyJenkinsNo ratings yet
- Risk factors of diabetic retinopathy and vision threatening diabetic retinopathy and vision threatening diabetic retinopaty based on diabetic retinopathy screening program in greater bandung, west java.astriDocument14 pagesRisk factors of diabetic retinopathy and vision threatening diabetic retinopathy and vision threatening diabetic retinopaty based on diabetic retinopathy screening program in greater bandung, west java.astriSi PuputNo ratings yet
- Clobazam As First Add On What Is The Evidence and Experience - Final Deck - 14 Feb 2023Document51 pagesClobazam As First Add On What Is The Evidence and Experience - Final Deck - 14 Feb 2023veerraju tvNo ratings yet
- NCP For Older Adults With Sleep DisturbanceDocument17 pagesNCP For Older Adults With Sleep DisturbanceAlienda Puspita PutriNo ratings yet
- Kounis Syndrome A Pediatric PerspectiveDocument10 pagesKounis Syndrome A Pediatric PerspectiveAna Belén Artero CastañoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders: Chromosomal Abnormalities and Down SyndromeDocument27 pagesGenetic Disorders: Chromosomal Abnormalities and Down SyndromeMerwan KemalNo ratings yet
- Activity - Nutrition On The Internet Worksheet 3Document2 pagesActivity - Nutrition On The Internet Worksheet 3Carlo FernandoNo ratings yet
- First Responders: The Heroes Who Answer Emergency CallsDocument11 pagesFirst Responders: The Heroes Who Answer Emergency CallsDIANA MARIE MOTA ABREUNo ratings yet
- Week1 - NAILCARE (Sek)Document2 pagesWeek1 - NAILCARE (Sek)rhyzeneNo ratings yet
- 13 AntibioticsAntiRetroviralsAIDS PDFDocument90 pages13 AntibioticsAntiRetroviralsAIDS PDFjenniferluzonNo ratings yet
- Rabbithematology PDFDocument12 pagesRabbithematology PDFHuda HudaNo ratings yet
- 07 - Towards Elimination DR Gottfried HirnschallDocument24 pages07 - Towards Elimination DR Gottfried HirnschallAjeet LohanaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Form (Sample)Document1 pageVaccination Form (Sample)Godfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.No ratings yet
- Sexual Health Awareness ScaleDocument17 pagesSexual Health Awareness ScaleezazpsychologistNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanHannah ChiuNo ratings yet
- Addressing Barriers, Stigma and Discrimination Surrounding HIV and Viral HepatitisDocument17 pagesAddressing Barriers, Stigma and Discrimination Surrounding HIV and Viral HepatitisAlemayehu KebedeNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Bells PalsyDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Bells Palsyklbndecnd100% (1)