Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Molecule:: Nucleic Acids
Uploaded by
Charles Salcedo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views26 pagesThe document defines nucleic acids as macromolecules that carry genetic information in cells. Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, which contain nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphate groups. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA contains the genetic blueprint in organisms, while RNA assists in protein synthesis. The central dogma explains how DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins.
Original Description:
Original Title
lesson12nucleicacids-191023082856.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines nucleic acids as macromolecules that carry genetic information in cells. Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, which contain nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphate groups. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA contains the genetic blueprint in organisms, while RNA assists in protein synthesis. The central dogma explains how DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views26 pagesOrganic Molecule:: Nucleic Acids
Uploaded by
Charles SalcedoThe document defines nucleic acids as macromolecules that carry genetic information in cells. Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, which contain nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphate groups. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA contains the genetic blueprint in organisms, while RNA assists in protein synthesis. The central dogma explains how DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
C h a p t e r 11
Organic Molecule: Nucleic Acids
Prepared by:
MR. KEVIN FRANCIS E. MAGAOAY
Faculty, SHS Biology Department
Learning Objectives:
Define nucleic acids
Describe the synthesis of nucleic acids
Characterize and enumerate the components of
nucleotide
Differentiate DNA and RNA
Describe central dogma
Learn the process of transcription and translation
Overview:
Definition of nucleic acid
Component of nucleotide
Classifications of nucleic acids
Structure of nucleic acids
Central dogma
Nucleic Acid
The most important macromolecule for the
continuity of life
Nucleic acids carry the genetic blueprint of a
cell and carry instructions for the functioning of
the cell
Provide information to make proteins
Nucleic Acid
The monomer of nucleic acid is nucleotides
and when combined together forms a
polynucleotide which is the major component
of nucleic acid
Nucleotide
Components of nucleotide:
o Nitrogenous bases
o Sugar
o Phosphate group
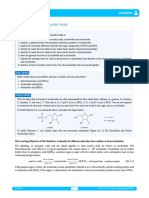
Nitrogenous Bases
Classified into:
Purines: are bases such as Adenine and
Guanine
Pyrimidines: are bases such as Cytosine,
Thymine and Uracil
Nitrogenous Bases
Sugar
The general name for the sugar component of
nucleotide is ribose
The sugar component of RNA is D-ribose and in
DNA is 2-Deoxy-D-ribose
The combination of sugar and nitrogenous base
is known as nucleoside
Sugar
Nucleoside
Base Sugar Nucleoside
Adenine Deoxy-D-ribose Deoxyadenosine
Guanine Deoxy-D-ribose Deoxyguanosine
Thymine Deoxy-D-ribose Deoxythymidine
Cytosine Deoxy-D-ribose Deoxycytidine
Nucleoside
Base Sugar Nucleoside
Adenine D-ribose Adenosine
Guanine D-ribose Guanosine
Uracil D-ribose Uridine
Cytosine D-ribose Cytidine
Phosphate Group
Is the third component of
nucleotide
When phosphate group
bond to -C𝐻2 OH of a
nucleoside, the result is
nucleotide
Two Major Types of Nucleic Acids
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Is the genetic material
found in all living
organisms
Composed of two strands
Ribonucleic Acid
Mostly involved in protein
synthesis
Composed of one strand
Structure of Nucleic Acid
The primary structure is the sequence of
nucleotides itself which has two parts: the
backbone of the molecule and the bases that
are the side chain group
The backbone of DNA consists of sugar and
phosphate group
Structure of Nucleic Acid
The backbone has 2 ends: a 3’
–OH end and a 5’ –OH end
Nitrogenous bases are the
side chain
Structure of Nucleic Acid
The secondary structure of DNA
is the established 3 –
dimensional structure
DNA is composed of 2 strands
entwined around each other in a
double helix
Bidirectional: Leading and
Lagging Strands
Types of RNA
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Carry the genetic information
from DNA in the nucleus
directly to the cytoplasm
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Ensures the proper alignment
of mRNA and ribosomes
Types of RNA
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Carries the correct amino
acid to the site of protein
synthesis
Central Dogma
Central Dogma
Transcription: DNA-RNA
Translation: RNA-codon of amino acid
In complementary base pairing, A, T, G and C
on the template DNA strand specify U, A, C and
G respectively, on the RNA strand being
synthesized
Sample problems
1. What amino acid sequence is produced from the
RNA sequence: ACGAAAGAA?
2. Using the codon chart, what is the sequence of
amino acids that is produced when CCAAGCTCT
is translated? (hint: CCAAGCTCT is a DNA
sequence)
3. How many codons are present in the sequence:
AUGCCGAAACGU?
Sample problems
4. What amino acids are produced from the codon
sequence AUGCCGAAACGU?
5. The sequence of a short DNA segment is
ATGGCAATA. What would be the sequence of the
complementary strand after transcription and
translation?
6. What is the corresponding RNA sequence of the DNA
strand: GCTTTTCAAAAA?
Sample problems
7. What is the codon sequence of the DNA
sequence; GCTTTTCAAAAA?
8. Using the codon chart, what is the sequence of
amino acids that is produced when the DNA
sequence AGCCAATGC is translated?
You might also like
- Preclinical Biochemistry and Medical Genetics Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Biochemistry and Medical Genetics Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1No ratings yet
- Psych - 1000 - Practice Exam (October) Sec 004Document14 pagesPsych - 1000 - Practice Exam (October) Sec 004karanvir_gill3383No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acid ProjectPramod Etarvi100% (7)
- Nucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidDocument60 pagesNucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidWillar Deanson Navarro100% (1)
- Stopping World Hungry EssayDocument6 pagesStopping World Hungry Essayapi-318032750100% (1)
- AP Biology Lab-02Document27 pagesAP Biology Lab-02ldlewis0% (2)
- The Pathophysiology of CancerDocument1 pageThe Pathophysiology of Cancermisskitcat100% (11)
- Genetics SyllabusDocument6 pagesGenetics SyllabusKumael JafriNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecule:: Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesOrganic Molecule:: Nucleic Acidsako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document107 pagesLesson 3Christian CuevasNo ratings yet
- Nucleicacids2eee2 120426222747 Phpapp01Document26 pagesNucleicacids2eee2 120426222747 Phpapp01Nash DeniegaNo ratings yet
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocument3 pagesLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNo ratings yet
- Linkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNADocument3 pagesLinkages Form The Sugar-Phosphate Backbone of Both DNA and RNAed modoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDDocument30 pagesBiochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDZayan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesStructure of Nucleic AcidsHanz Glitzer MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument137 pagesNucleic AcidCJ Batindaan RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument67 pagesNucleic AcidHeddy MyoiNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Nucleic AcidDocument28 pages1.5 Nucleic AcidLak Judin IINo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument88 pagesNucleic AcidJoyce Jimenez100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidsDocument9 pagesNucleic AcidsRex Blanco NuñezNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis RevisedDocument60 pagesNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Revisedemanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesNucleic AcidsДмитрий МатвеевNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument33 pagesChapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsSofeaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles: Organisms Are Made of CellsDocument10 pagesBasic Principles: Organisms Are Made of CellsEllu SeethaNo ratings yet
- Dna 1Document31 pagesDna 1Dr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Jane Valine BalinoNo ratings yet
- In-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesIn-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisGbenga AjaniNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument47 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistryjohn2001royNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument41 pagesBiochemIram KhanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 5Document10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 5Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- The Nucleic AcidsDocument94 pagesThe Nucleic Acidsmeklit birhanuNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides Chemistry and MetabolismDocument65 pagesNucleotides Chemistry and MetabolismSmiling AngelNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Dna and Rna: Jon Paul M. Reyes, RMT, MBA, MSMLS Program Chair College of Medical TechnologyDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of Dna and Rna: Jon Paul M. Reyes, RMT, MBA, MSMLS Program Chair College of Medical TechnologyRich Darlene Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter Summary 10Document18 pagesBiochemistry Chapter Summary 10Kyle BroflovskiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and NucleotidesDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids and NucleotidesWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Aid NoteDocument5 pagesNucleic Aid NoteKaye BaguhinNo ratings yet
- PHD l3 GenesDocument35 pagesPHD l3 GenesDereen NajatNo ratings yet
- BIO 111 Lecture 8-Nucleic AcidsDocument47 pagesBIO 111 Lecture 8-Nucleic AcidsChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Notes C22 121Document20 pagesNotes C22 121Gopi NathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MBDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - MBMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- 5.nucleic AcidDocument24 pages5.nucleic AcidAzizi ZainodinNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Structure and FunctionDocument45 pagesNucleic Acids: Structure and FunctionJahanzeb SafdarNo ratings yet
- 28.01 - Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pages28.01 - Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsMarch SamNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure NotesDocument8 pagesDNA Structure NotesSabina BabaievaNo ratings yet
- Paper - IV Molecular BiologyDocument236 pagesPaper - IV Molecular BiologyNaruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Dnarna PPTDocument32 pagesDnarna PPTgianexp123No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 5Document9 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 5Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- Aji Sutrisno Food Science and Technology Universitas Brawijaya (Ub)Document81 pagesAji Sutrisno Food Science and Technology Universitas Brawijaya (Ub)Gandhes Cintya DewiNo ratings yet
- Aji Sutrisno Food Science and Technology Universitas Brawijaya (Ub)Document81 pagesAji Sutrisno Food Science and Technology Universitas Brawijaya (Ub)Nirma MardinitaNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument36 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyMafel JumuadNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument30 pagesNucleic AcidMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids RevisionDocument15 pagesNucleic Acids RevisionGilbert ossullivanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic acidsLECTUREDocument116 pagesNucleic acidsLECTUREKesha Marie TalloNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering Class 6Document3 pagesBiochemical Engineering Class 6Vittal PiseNo ratings yet
- LecturerDocument42 pagesLectureratef.salman.grNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ReportDocument15 pagesNucleic Acid Reportmumu memeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document5 pagesChapter 5 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20prat.medbooksNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: The Raw Materials of Cell The Building Blocks of Life The Molecules of CellsDocument61 pagesBiomolecules: The Raw Materials of Cell The Building Blocks of Life The Molecules of CellsKenneth NicolasNo ratings yet
- Bnbi Oral PresentationDocument17 pagesBnbi Oral PresentationAshria Sonali PrakashNo ratings yet
- From My Students Most of AllDocument147 pagesFrom My Students Most of AllRamin HamzaNo ratings yet
- NAT SCI 9 Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNAT SCI 9 Nucleic Acidskjgbitoon00125No ratings yet
- Medical Genetic II Dna RnaDocument49 pagesMedical Genetic II Dna RnaHarry ManuhutuNo ratings yet
- Objectives Means of Verification (MOV) Description of The MOV Presented AnnotationsDocument3 pagesObjectives Means of Verification (MOV) Description of The MOV Presented AnnotationsCharles SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Excercize 1-3Document3 pagesExcercize 1-3Charles SalcedoNo ratings yet
- List of Internet Acronyms: Acronyms A To L Acronyms M To ZDocument8 pagesList of Internet Acronyms: Acronyms A To L Acronyms M To ZCharles SalcedoNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument2 pagesExercisesCharles SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Earth SystemDocument18 pagesEarth SystemCharles SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Business Math Week 9Document9 pagesBusiness Math Week 9Charles Salcedo75% (8)
- Datta 2005Document9 pagesDatta 2005lacisagNo ratings yet
- Performance of The AVENIO Tumor Tissue Analysis Kits Across Illumina Sequencing PlatformsDocument4 pagesPerformance of The AVENIO Tumor Tissue Analysis Kits Across Illumina Sequencing PlatformspappuNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsDocument20 pagesCH 7 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsRokia GhariebNo ratings yet
- Meiosis in Onion Bud Cell...Document3 pagesMeiosis in Onion Bud Cell...abinashp295No ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Gene Interaction and Gene MappingDocument26 pagesLecture 9 Gene Interaction and Gene MappingSaakshi PalNo ratings yet
- 234&othjxat Fo/Kku LHKK (Ks DK Ernku Dsunzksa Ls Lac) Ch-,Y-Vks-Dh V - Ru LWPHDocument27 pages234&othjxat Fo/Kku LHKK (Ks DK Ernku Dsunzksa Ls Lac) Ch-,Y-Vks-Dh V - Ru LWPHrajeev kumarNo ratings yet
- BIOINFODocument15 pagesBIOINFOSunilNo ratings yet
- Potential of rDNA Technology in Revolutionizing FutureDocument23 pagesPotential of rDNA Technology in Revolutionizing FutureNusra FaizNo ratings yet
- Extensions To Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype To PhenotypeDocument27 pagesExtensions To Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype To PhenotypeWaleed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 - Mutagenesis PDFDocument5 pagesUnit 10 - Mutagenesis PDFvuivevuiveNo ratings yet
- GegDocument126 pagesGegRicardo RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Northern Blot PDFDocument8 pagesNorthern Blot PDFerick ortiz lopezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Cell Cycle ContinuationDocument17 pagesLesson 5 Cell Cycle ContinuationKamaki RyuNo ratings yet
- Sex Linked TraitsDocument2 pagesSex Linked TraitsSebastian Enriquez EstradaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2017Document12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2017Ege Arda AkyürekNo ratings yet
- RAPD Markers For Identifying Oil Palm Jacq.) Parental Varieties & and The HybridDocument7 pagesRAPD Markers For Identifying Oil Palm Jacq.) Parental Varieties & and The HybridRamNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Document20 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Jay B. Villamer100% (2)
- Genetics NursingDocument6 pagesGenetics Nursingrakesh rathNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Science Topic B1.1 Classification, Variation and Inheritance Test 13 - 14Document10 pagesEdexcel GCSE Science Topic B1.1 Classification, Variation and Inheritance Test 13 - 14Paul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Quick Rubric - 1Document2 pagesQuick Rubric - 1api-356824125No ratings yet
- PDF 2 Conductas para LiderarDocument2 pagesPDF 2 Conductas para LiderarCatalinaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Resource Announcements-2019-Saad-e00215-19.full - Grupo 5Document3 pagesMicrobiology Resource Announcements-2019-Saad-e00215-19.full - Grupo 5Wilgen Daniel Tapia CurillaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics Assignment InstructionsDocument13 pagesMendelian Genetics Assignment InstructionspavNo ratings yet
- Genetika PopulasiDocument48 pagesGenetika PopulasiRoy SinagaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrial DiseaseDocument46 pagesMitochondrial DiseaseRania ZahoNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasikan Berdasarkan Asalnya Stem CellDocument2 pagesKlasifikasikan Berdasarkan Asalnya Stem CellfathinanisaNo ratings yet