Professional Documents
Culture Documents
An Ethernet Hub
Uploaded by
shinsmart92Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
An Ethernet Hub
Uploaded by
shinsmart92Copyright:
Available Formats
An Ethernet hub, active hub, network hub, repeater hub or electrical signal, and broadcasts these packets out
s these packets out to all other the central node as one of these special
hub is a device for connecting multiple twisted pair or fibre optic devices on the network. devices, some confusion is possible, since
Ethernet devices together and making them act as a single network this practice may lead to the misconception
segment. Hubs work at the physical layer (layer 1) of the OSI that a physical star network requires the
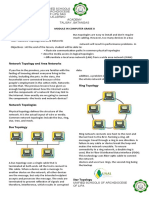
Star
model. The device is a form of multiport repeater. Repeater hubs central node to be one of these special
also participate in collision detection, forwarding a jam signal to Main article: Star network
devices, which is not true because a simple
all ports if it detects a collision. network consisting of three computers
Star network topology connected as in note 2.) above also has the
Hubs also often come with a BNC and/or Attachment Unit topology of the physical star.
Interface (AUI) connector to allow connection to legacy 10BASE2 In local area networks with a star topology, each
or 10BASE5 network segments. The availability of low-priced network host is connected to a central hub. In contrast
network switches has largely rendered hubs obsolete but they are Star networks may also be described as
to the bus topology, the star topology connects each either broadcast multi-access or
still seen in older installations and more specialized applications.
node to the hub with a point-to-point connection. All nonbroadcast multi-access (NBMA),
traffic that traverses the network passes through the depending on whether the technology of
Technical information central hub. The hub acts as a signal booster or the network either automatically
repeater. The star topology is considered the easiest propagates a signal at the hub to all spokes,
A network hub is a fairly unsophisticated broadcast device. Hubs topology to design and implement. An advantage of or only addresses individual spokes with
do not manage any of the traffic that comes through them, and any each communication.
the star topology is the simplicity of adding additional
packet entering any port is regenerated and broadcast out on all
other ports. Since every packet is being sent out through all other nodes. The primary disadvantage of the star topology
Extended star
ports, packet collisions result—which greatly impedes the smooth is that the hub represents a single point of failure.
flow of traffic. A type of network topology in which a network that is
Notes based upon the physical star topology has one or more
The need for hosts to be able to detect collisions limits the number repeaters between the central node (the 'hub' of the
of hubs and the total size of a network built using hubs (a network star) and the peripheral or 'spoke' nodes, the repeaters
A point-to-point link (described above) is
built using switches does not have these limitations). For 10 Mbit/s being used to extend the maximum transmission
sometimes categorized as a special instance
networks built using repeater hubs, the 5-4-3 rule must be distance of the point-to-point links between the
followed: up to 5 segments (4 hubs) are allowed between any two of the physical star topology – therefore,
the simplest type of network that is based central node and the peripheral nodes beyond that
end stations. For 100 Mbit/s networks, the limit is reduced to 3
segments (2 hubs) between any two end stations, and even that is upon the physical star topology would which is supported by the transmitter power of the
only allowed if the hubs are of the a delay variety.[citation needed] Some consist of one node with a single point-to- central node or beyond that which is supported by the
hubs have manufacturer specific stack ports allowing them to be point link to a second node, the choice of standard upon which the physical layer of the physical
combined in a way that allows more hubs than simple chaining which node is the 'hub' and which node is
star network is based.
through Ethernet cables, but even so, a large fast Ethernet network the 'spoke' being arbitrary[1].
is likely to require switches to avoid the chaining limits of hubs.
If the repeaters in a network that is based upon the
After the special case of the point-to-point physical extended star topology are replaced with hubs
Most hubs detect typical problems, such as excessive collisions link, as in note 1.) above, the next simplest
and jabbering on individual ports, and partition the port, or switches, then a hybrid network topology is created
type of network that is based upon the
disconnecting it from the shared medium. Thus, hub-based physical star topology would consist of one that is referred to as a physical hierarchical star
Ethernet is generally more robust than coaxial cable-based central node – the 'hub' – with two topology, although some texts make no distinction
Ethernet (e.g. 10BASE2), where a misbehaving device can separate point-to-point links to two between the two topologies.
adversely affect the entire collision domain. Even if not partitioned peripheral nodes – the 'spokes'.
automatically, a hub simplifies troubleshooting because they
remove the need to troubleshoot faults on a long cable with Distributed Star
multiple taps; status lights on the hub can indicate the possible Although most networks that are based
problem source or, as a last resort, devices can be disconnected upon the physical star topology are A type of network topology that is composed of
from a hub one at a time much more easily than from a coaxial commonly implemented using a special individual networks that are based upon the physical
cable. device such as a hub or switch as the star topology connected together in a linear fashion –
central node (i.e., the 'hub' of the star), it is i.e., 'daisy-chained' – with no central or top level
Hubs are classified as Layer 1 (physical layer) devices in the OSI also possible to implement a network that is connection point (e.g., two or more 'stacked' hubs,
model. At the physical layer, hubs support little in the way of based upon the physical star topology using
along with their associated star connected nodes or
sophisticated networking. Hubs do not read any of the data passing a computer or even a simple common
through them and are not aware of their source or destination. A connection point as the 'hub' or central 'spokes').
hub simply receives incoming Ethernet frames, regenerates the node – however, since many illustrations of
the physical star network topology depict
You might also like
- CEH Document 007 ShibsDocument411 pagesCEH Document 007 ShibsAB Learning studioNo ratings yet
- MCBSC Workshop: - Sebastian Sanchez, Techincal Project Manager - Ran Amx Claro Ar, Uy, Py - 18-09-2017Document89 pagesMCBSC Workshop: - Sebastian Sanchez, Techincal Project Manager - Ran Amx Claro Ar, Uy, Py - 18-09-2017Matias AyllonNo ratings yet
- Catalyst 3650 Series Switches Best Practices GuideDocument14 pagesCatalyst 3650 Series Switches Best Practices GuideEDWIN GREGORIO MARIN VARGASNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) System SimulationDocument21 pagesOrthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) System SimulationNakibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision NetworkingDocument7 pagesQuick Revision Networkingzahir khanNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: LAN Topologies Physical Bus Topology Advantages of Bus TopologyDocument8 pagesNetwork Topologies: LAN Topologies Physical Bus Topology Advantages of Bus TopologyMary Ann SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6-NETWORK TOPOLOGY-Real-World NetworksDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 6-NETWORK TOPOLOGY-Real-World NetworksCamille S. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Cir 209 (Lecture 7) Network - Topologies - FinalDocument11 pagesCir 209 (Lecture 7) Network - Topologies - Finaldancanongori9No ratings yet
- Comparison Between Network Topologies PDFDocument2 pagesComparison Between Network Topologies PDFNikhil Gobhil100% (1)
- Week 03 Network Concepts and Network Media PDFDocument63 pagesWeek 03 Network Concepts and Network Media PDFikonNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument20 pagesNetwork TopologiesMd IshteyaqueNo ratings yet
- Answers of Chapter 1 Review QuestionsDocument17 pagesAnswers of Chapter 1 Review QuestionswaqasNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter 2 Network TopologyDocument9 pages2 Chapter 2 Network TopologyDivina Labuguen TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Network Topology 1Document10 pagesNetwork Topology 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Assignment No 1 PDFDocument3 pagesData Communication Assignment No 1 PDFaman khanNo ratings yet
- Net 101 Chapter 3Document3 pagesNet 101 Chapter 3Fherry AlarcioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networks1Document14 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networks1HwnmNo ratings yet
- CN Assignment 1Document13 pagesCN Assignment 1SHUBHAM SHAHNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument23 pagesUnit - 3 Introduction To Computer NetworkingAbhinav KhannaNo ratings yet
- DCCChapter 5Document13 pagesDCCChapter 5Getnete degemuNo ratings yet
- CN Lec 2Document33 pagesCN Lec 2Areeb MirzaNo ratings yet
- TopologyDocument6 pagesTopologyHaruhi SuzumiyaNo ratings yet
- p1 Explain How Networks Communicate PDFDocument3 pagesp1 Explain How Networks Communicate PDFfaisal saghirNo ratings yet
- Star TopologyDocument8 pagesStar TopologyAbigail ParungaoNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Concepts of Lan & DLL Protocols: Categores of Computer NetworksDocument15 pagesUNIT-1 Concepts of Lan & DLL Protocols: Categores of Computer NetworksDinesh PalavalasaNo ratings yet
- Network System Administration and SecurityDocument137 pagesNetwork System Administration and SecurityKevin NeshNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument54 pagesNetworkingSubisma ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Networking 1.2Document7 pagesNetworking 1.2Echo greenNo ratings yet
- Fahad Ali Khan Sp09-Bce-044Document6 pagesFahad Ali Khan Sp09-Bce-044Fahad Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Token Bus (IEEE 802)Document9 pagesToken Bus (IEEE 802)anon_185146696No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2Document12 pagesAssignment 1 2Sakshi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: 10.1 10.2 NetworkDocument22 pagesComputer Networks: 10.1 10.2 NetworkNitin MishraNo ratings yet
- Networking WorkDocument5 pagesNetworking Workmani125715No ratings yet
- Network TopologgyDocument16 pagesNetwork Topologgyobafemiadeyemo11No ratings yet
- Network Topology and Area Networks: Module in Computer Grade 8Document5 pagesNetwork Topology and Area Networks: Module in Computer Grade 8Cymon AriolaNo ratings yet
- ICT Fundamentals ReportDocument49 pagesICT Fundamentals ReportJigs OlbesNo ratings yet
- Advantages of A Linear Bus TopologyDocument5 pagesAdvantages of A Linear Bus Topologynirav4042No ratings yet
- CH 05Document15 pagesCH 05Mohd FareeduddinNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Network Topology Ashis Talukder, PHDDocument27 pagesWelcome: Network Topology Ashis Talukder, PHDGolam Mehbub SifatNo ratings yet
- Topologies: Project Report ONDocument13 pagesTopologies: Project Report ONSiddhesh HaldankarNo ratings yet
- Cchapter 1 - Part IIDocument39 pagesCchapter 1 - Part IIBezabh AbebawNo ratings yet
- Distributed Topology Construction of Bluetooth Wireless Personal Area NetworksDocument11 pagesDistributed Topology Construction of Bluetooth Wireless Personal Area NetworksSasikanth MareeduNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: Lecture # 2Document21 pagesNetwork Topologies: Lecture # 2Monika RehmanNo ratings yet
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDocument11 pagesStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- Network IntroDocument48 pagesNetwork IntroJerlon ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Types of TopologiesDocument17 pagesTypes of Topologiesgwapogi0320No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Satyam SinghNo ratings yet
- About Topology: 1. What Is A Topology?Document7 pagesAbout Topology: 1. What Is A Topology?happyharrNo ratings yet
- CN Lab ManualDocument20 pagesCN Lab ManualShanu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Star TopologyDocument7 pagesStar TopologyadelenyamhuriNo ratings yet
- Networking Assignment 1Document9 pagesNetworking Assignment 1M.Bilal JattNo ratings yet
- NCS Unit 2 - Network TopologiesDocument16 pagesNCS Unit 2 - Network Topologiesnanobala15No ratings yet
- TopologyDocument1 pageTopologyAlia NadzirahNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument14 pagesNetworkfifen pokaro ousseniNo ratings yet
- ICT ProjectDocument9 pagesICT Projectmuhammadumarlol10yrsNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS of Assignment For Computer Network-IIDocument4 pagesSOLUTIONS of Assignment For Computer Network-IIIshu MiglaniNo ratings yet
- 4335 NetworkingemisDocument4 pages4335 NetworkingemisFavour JamesNo ratings yet
- Network: Chapter 2: Types of NetworkDocument8 pagesNetwork: Chapter 2: Types of NetworksweetashusNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes Sheet: 200-301 CCNADocument17 pagesCornell Notes Sheet: 200-301 CCNAjincamoNo ratings yet
- Interference Mitigation in WSN by Means of Directional Antennas and Duty Cycle ControlDocument12 pagesInterference Mitigation in WSN by Means of Directional Antennas and Duty Cycle ControlJoseph Kumar NagothuNo ratings yet
- Connection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksFrom EverandConnection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksNo ratings yet
- Proposal Wireless PDFDocument7 pagesProposal Wireless PDFDaniel MengeshaNo ratings yet
- Answer-Seizure Ratio: Definition ( - )Document4 pagesAnswer-Seizure Ratio: Definition ( - )Odunlami TomiNo ratings yet
- Galileo Gen2 SchematicDocument28 pagesGalileo Gen2 SchematicGustavo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- White Paper: Altai Wireless Broadband Network DesignDocument15 pagesWhite Paper: Altai Wireless Broadband Network DesignMih NdrainibeNo ratings yet
- 4G TechnologyDocument54 pages4G TechnologyGaurav77% (13)
- Quick and Dirty Subnetting PDFDocument2 pagesQuick and Dirty Subnetting PDFErickReyesNo ratings yet
- Communication - Protocol-TR 42-C1Document13 pagesCommunication - Protocol-TR 42-C1CAMILONo ratings yet
- Wide-Band Orthogonal Frequency Multiplexing (W-OFDM) TechnicalDocument4 pagesWide-Band Orthogonal Frequency Multiplexing (W-OFDM) TechnicalYaumil IranaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of 5G - IoT Communication System 1 - RB - LAB EQUIPMENTDocument32 pagesImplementation of 5G - IoT Communication System 1 - RB - LAB EQUIPMENTMaitrayee PragyaNo ratings yet
- ESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollerDocument10 pagesESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollergessycaNo ratings yet
- E1BERTesterXG2138 PDFDocument3 pagesE1BERTesterXG2138 PDFRicardo Ledessma KortijoNo ratings yet
- 1st Year ComputerDocument1 page1st Year ComputerNaveed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Pix Configuration GuideDocument400 pagesPix Configuration GuideAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Power Control Based Qos Provisioning For Multimedia in W-CdmaDocument27 pagesPower Control Based Qos Provisioning For Multimedia in W-CdmaHaiNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission and RoutingDocument30 pagesData Transmission and RoutingRafee MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Distinguish Between Link and Channel in MultiplexingDocument7 pagesDistinguish Between Link and Channel in MultiplexingZAINALABDEN ALNAWANo ratings yet
- Fortiauthenticator Admin 12Document46 pagesFortiauthenticator Admin 12adnanbwNo ratings yet
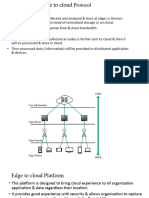
- Edge To Cloud ProtocolDocument21 pagesEdge To Cloud ProtocolMuzammil BalochNo ratings yet
- What Is Outgoing and Incoming Policy in The Router SettingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Outgoing and Incoming Policy in The Router SettingcarlozadaNo ratings yet
- CoboxDocument2 pagesCoboxLeopardLapatratNo ratings yet
- Nis MCQ Answers AllDocument88 pagesNis MCQ Answers AllBhaiNo ratings yet
- TFTP ProtocoloDocument9 pagesTFTP ProtocoloLuisNo ratings yet
- 4ipnet 2017 CatalogueDocument4 pages4ipnet 2017 CatalogueKleng KlengNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security v5Document8 pagesCCNA Security v5Putri Isti ArifahNo ratings yet
- 18TE72 - Wireless Communication Experiential Learning ReportDocument10 pages18TE72 - Wireless Communication Experiential Learning ReportRitika BakshiNo ratings yet
- The ISO - OSI ModelDocument16 pagesThe ISO - OSI Modelprince keshriNo ratings yet
- Tac Xenta911 Xenta511 Manuel UkDocument42 pagesTac Xenta911 Xenta511 Manuel UkSupolNo ratings yet