Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Database Basic
Uploaded by
Madhu Bisht0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document discusses the key aspects of a database management system (DBMS). It outlines the reasons for using a DBMS, including data independence, integrity, security and concurrent access. It also covers the purpose of a DBMS in addressing issues like redundancy, inconsistency and isolation. Additionally, it examines the different data models, architecture, components, advantages and disadvantages of a DBMS.
Original Description:
Original Title
database basic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the key aspects of a database management system (DBMS). It outlines the reasons for using a DBMS, including data independence, integrity, security and concurrent access. It also covers the purpose of a DBMS in addressing issues like redundancy, inconsistency and isolation. Additionally, it examines the different data models, architecture, components, advantages and disadvantages of a DBMS.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesDatabase Basic
Uploaded by
Madhu BishtThe document discusses the key aspects of a database management system (DBMS). It outlines the reasons for using a DBMS, including data independence, integrity, security and concurrent access. It also covers the purpose of a DBMS in addressing issues like redundancy, inconsistency and isolation. Additionally, it examines the different data models, architecture, components, advantages and disadvantages of a DBMS.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
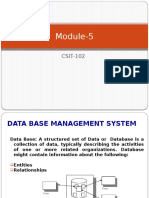
Why Use a DBMS?
Data independence and efficient access
Data integrity and security
Uniform data administration
Concurrent access, recovery from crashes
Purpose of DBMS
Data redundancy and inconsistency
Difficulty in new program to carry out each new task
Data isolation
Integrity problems
Security problems
Data models
There are three types of model.
Hierarchical Model
Network Model
Relational Model
Architecture
External Level
Conceptual Level
Internal Level
Components of DBMS
Hardware
Software
Data
People
Procedure
Advantage of DBMS
Controlling Redundancy
Sharing of Data
Data Consistency
Integration of Data
Integration Constraints
Data Security
Report Writers
Disadvantage of DBMS
Cost of Hardware and Software
Cost of Data Conversion
Cost of Staff Training
Appointing Technical Staff
Database Damage
Content of the Seminar and pdf report for Database Management System (DBMS)
What is Database Management System?
Brief History
Why Use a DBMS?
Purpose of DBMS
Data models
Architecture of DBMS
levels or layers of DBMS architecture
Components of DBMS
Advantage of DBMS
Disadvantage of DBMS
DBMS Languages
References
You might also like
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To DB AND DB EnvironmentDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To DB AND DB EnvironmentAmmr AmnNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To DBMSDocument20 pagesUnit-I Introduction To DBMSanandnilewarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management System: Poonam MehtaDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Database Management System: Poonam Mehtacyka blyatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document31 pagesLecture 3W Game CreationNo ratings yet
- CSC271 Database Systems: Lecture # 4Document31 pagesCSC271 Database Systems: Lecture # 4Ivy JaniceNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Tinsae D. (MSC.) : Cs-224 - Fundamentals of Database SystemDocument28 pagesInstructor: Tinsae D. (MSC.) : Cs-224 - Fundamentals of Database SystemmNo ratings yet
- Data Redundancy and InconsistencyDocument4 pagesData Redundancy and InconsistencybalainsaiNo ratings yet
- What Is Database Management System?Document6 pagesWhat Is Database Management System?Anil ShresthaNo ratings yet
- ICT502 - Introduction To Database and Database EnvironmentDocument27 pagesICT502 - Introduction To Database and Database EnvironmentN -No ratings yet
- Module-5: CSIT-102Document20 pagesModule-5: CSIT-102Abdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Dbms Unit 1 PptsDocument37 pagesDbms Unit 1 Pptsteam 8No ratings yet
- The Three-Schema Architecture: Characteristics of The Database ApproachDocument2 pagesThe Three-Schema Architecture: Characteristics of The Database ApproachOliberNo ratings yet
- Limitations of File-Based SystemDocument2 pagesLimitations of File-Based SystemArslNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Fundamental Database Concepts PDFDocument48 pagesLecture 01 Fundamental Database Concepts PDFSharmainne PaleNo ratings yet
- Data Base Management SystemDocument35 pagesData Base Management SystemramNo ratings yet
- DBMS Ninja NotesDocument134 pagesDBMS Ninja NotesYASH VARDHANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DBMSDocument29 pagesIntroduction To DBMSMeera SuryaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Basic DB ConceptsDocument24 pages1 - Basic DB Conceptsبلبيي لرلاررلاNo ratings yet
- Database Systems and Data Models: Course:DDBDocument23 pagesDatabase Systems and Data Models: Course:DDBsyed hamzaNo ratings yet
- RDBMS An IntroductionDocument84 pagesRDBMS An Introductionkonda Sasi Snehith reddyNo ratings yet
- Iare DBMS Lecture Notes PDFDocument161 pagesIare DBMS Lecture Notes PDFAyushGuptaNo ratings yet
- Data ModelsDocument14 pagesData ModelsMUGEN FORFUNNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Database ManagementDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Database ManagementMohammad Yaseen PashaNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument25 pagesDatabase Management Systemsabhinavgupta2010No ratings yet
- ?DBMS ? Interview Que & Ans by InterviewbitDocument26 pages?DBMS ? Interview Que & Ans by InterviewbitPrashant Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Week01 - Introduction To DatabasesDocument22 pagesWeek01 - Introduction To DatabasesMuhammad Asghar KhanNo ratings yet
- DBMS Interview Questions: Click HereDocument26 pagesDBMS Interview Questions: Click HerewasifNo ratings yet
- Two-Tier Architecture:: CREC. Dept. of CSEDocument7 pagesTwo-Tier Architecture:: CREC. Dept. of CSEMonica TimberNo ratings yet
- What Is DatabaseDocument19 pagesWhat Is DatabaseNutan SannailaNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument22 pagesDBMSANUREET KAURNo ratings yet
- Mba Sem-1 Presentation On DBMS & RDBMS: Submitted By:-Bhalodia Sanket Jethwa Gautam Mavani HardikDocument34 pagesMba Sem-1 Presentation On DBMS & RDBMS: Submitted By:-Bhalodia Sanket Jethwa Gautam Mavani HardikSanketBhalodiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document31 pagesLecture 01asdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - What's in A DatabaseDocument33 pagesChapter 1 - What's in A Databasenguyenquangphuoc5922No ratings yet
- Database Management System: Dr. Neha Gulati University Business School Panjab UniversityDocument30 pagesDatabase Management System: Dr. Neha Gulati University Business School Panjab UniversityNavneet Nanda100% (1)
- 3.1 The Hierarchy of DataDocument4 pages3.1 The Hierarchy of DataSarah RanduNo ratings yet
- CH 1introductory Concepts of DbmsDocument30 pagesCH 1introductory Concepts of DbmslineshNo ratings yet
- File System and DatabseDocument50 pagesFile System and DatabseHerry SofyanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 - DB OverviewDocument37 pagesLecture 04 - DB OverviewThiwanka TisseraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - ObjectivesDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - ObjectivesFIZA SAIFNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Intro To Information ManagementDocument10 pagesLec 1 Intro To Information ManagementJeffrey Fernandez PapaNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To DatabasesDocument23 pages1 Introduction To DatabasesJoana Key Abat SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Do The MathDocument37 pagesDo The MathKorra JagadeeshwarNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument32 pagesDatabasejehoshua35No ratings yet
- Database Architecture: CSC 401: Database Management SystemDocument28 pagesDatabase Architecture: CSC 401: Database Management SystemMohitul ShafirNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit1 NotesDocument24 pagesDBMS Unit1 Notesteam 8No ratings yet
- Data Base System NotesDocument76 pagesData Base System NotesAli HassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document21 pagesLecture 01Shahroz RasheedNo ratings yet
- PC 318 DBMS: Prepared By: Darwin N. DesamparadoDocument21 pagesPC 318 DBMS: Prepared By: Darwin N. DesamparadoEztiven LaykeNo ratings yet
- DB Lec 1&2Document28 pagesDB Lec 1&2Adnan AsifNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Databases: Chapter 1Document24 pagesIntroduction To Databases: Chapter 1Md Sakawat HossainNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Notes CC RamadeviDocument31 pagesUnit 4 Notes CC RamadeviJaswanth RachaNo ratings yet
- Database Architecture: CSC 401: Database Management SystemDocument28 pagesDatabase Architecture: CSC 401: Database Management SystemDhrubo SarkerNo ratings yet
- Relational Model - Docx25Document3 pagesRelational Model - Docx25M.a. RayhanNo ratings yet
- DBMS (KCS501) SSaxenaDocument51 pagesDBMS (KCS501) SSaxenaKhushi PachauriNo ratings yet
- 02 DbenvironmentDocument30 pages02 Dbenvironmentjames mutekesaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Full NotesDocument99 pagesDBMS Full NotesMD ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- Auditing Database Systems - 1Document46 pagesAuditing Database Systems - 1Arlyn AlonzoNo ratings yet
- 1st Top 52 DBMS Interview Questions (2022) - JavatpointDocument25 pages1st Top 52 DBMS Interview Questions (2022) - Javatpointomkar gaikwadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Chap - 1Document34 pagesIntroduction To Database Chap - 1saleemNo ratings yet
- Data Base/ MY SQL: BY: Amar Singh, PGT Comp. Sci. KV Shalimar BaghDocument33 pagesData Base/ MY SQL: BY: Amar Singh, PGT Comp. Sci. KV Shalimar BaghMadhu BishtNo ratings yet
- SQL / RDBMS: Class XiDocument26 pagesSQL / RDBMS: Class XiMadhu BishtNo ratings yet
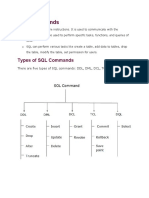
- Database CommandDocument7 pagesDatabase CommandMadhu BishtNo ratings yet
- Date Sheet July Montly TestDocument1 pageDate Sheet July Montly TestMadhu BishtNo ratings yet
- Python - Mysql Database Access: Gadfly MSQL Mysql Postgresql Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Informix Interbase Oracle SybaseDocument10 pagesPython - Mysql Database Access: Gadfly MSQL Mysql Postgresql Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Informix Interbase Oracle SybaseMadhu BishtNo ratings yet
- UDFDocument55 pagesUDFMadhu BishtNo ratings yet
- Physics DLP PDFDocument500 pagesPhysics DLP PDFMadhu BishtNo ratings yet
- GOC Question Bank-20200420174037517680 PDFDocument30 pagesGOC Question Bank-20200420174037517680 PDFMadhu BishtNo ratings yet
- And The Sea, Which Appears To Have Changed Less Washed Their Terribly Transient Feet.'Document2 pagesAnd The Sea, Which Appears To Have Changed Less Washed Their Terribly Transient Feet.'Madhu BishtNo ratings yet
- The Laburnum TopDocument3 pagesThe Laburnum TopMadhu Bisht50% (2)
- The Voice of The RainDocument6 pagesThe Voice of The RainMadhu BishtNo ratings yet