Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) Nucleus
Uploaded by
Ryan ForteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) Nucleus
Uploaded by
Ryan ForteCopyright:
Available Formats
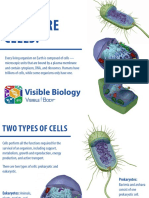
CELL The Cell Cycle
Cell
Basic Unit of Life The cell cycle is a series of events
Serves as it’s basic functioning unit that cells go through as they grow
and divided.
Two Major Categories:
Phases of Cell Cycle
EUKARYOTES
PROKARYOTES M phase – the division of the
cell nucleus or mitosis takes
Prokaryote – Greek PRO(Before) KARYON place.
( Nucleus) means “Before the nucleus”. Cytokinesis – the division of
the cytoplasm takes place
Eukaryotes – those cells that starts out with during this phase.
a nucleus. Greek, EU (true), KARYON
(Nucleus). G1 phase – a period of
activity in which cells do
Difference between PRO & EU most of their growing cells
increase in size and synthesis
PROKARYOTIC new proteins and organelles.
- Prokaryotic Cells include bacteria
- Prokaryotic Cells have a cell S phase – which follows the
membrane and cytoplasm but G1 is when the
without nucleus. chromosomes are replicated
- Most Prokaryotic Cells are and the synthesis of DNA
surrounded by stiff cell wall occurs.
- Prokaryotic Cells are usually very
small G2 phase – the shortest of
- Ribosomes of Prokaryotic Cells the three phases of
contain more different proteins than interface.
those found in eukaryotes.
- MITOSIS
EUKARYOTES Comes from greek word “mitos”
- Plants, animals, protists and fungi meaning “thread” describing the
are made up of eukaryotic cells. threadlike chromosomes that
- Eukaryotic cells are larger appear in the cell just before it
- Eukaryotic cells contains a variety of divides into two. Mitosis occurs in
membranous organelles somantic or body cells.
- Eukaryotic cells have true nucleus-
an organelle consisting of a double Prophase – the chromatin
layer of membrane that encloses the condenses into
genetic material. chromosomes.
CELL DIVISION – cells reproduce by dividing Metaphase – the
into two called. Each dividing cell is called chromosomes line up at the
mother or parent cell and it’s descendants center of the cell or at its
are called daughter cells. Parents cell equator.
transmit DNA to daughter cells. Cell division
is often referred to as cellular reproduction. Anaphase – the sister
chromatids separate into
individual chromosomes and
move apart.
Telophase – the MICROBIAL ECOLOGY – Study of
chromosomes gather at relationship between microbes and the
opposite ends of the cell and environment.
lose their distinct shapes.
PLANKTON – algae bacteria serve as food
for many microscopic organisms in the
MEIOSIS ocean.
- Type of cell division that occurs only BIOTECHNOLOGY – use of microorganisms
on reproductive cells or gametes. In in industry.
humans and all other mammals,
meiosis in reproductive cells results ANTIBIOTIC – is a substance produced by
in sperms and eggs. microorganism that are effective in killing or
- inhibiting the growth of other
Difference between mitosis and meiosis microorganisms.
Meiosis results in the production of Infectious diseases – results when a
daughter cells that have half the pathogen colonizes the body and
number of chromosomes of the subsequently causes disease.
parent cell.
Microbial intoxification – person ingests a
Daughter cells that are produced by toxin (poisonous substance)
meiosis are not all alike
VIRUSES
The number cells produced by
meiosis is different. In mitosis one They possess either DNA or RNA, unlike
parent cell produces two daughter living cells, which possess both.
cells while in meiosis one parent’s
cell divides twice to produce four They are unable to replicate or multiply on
daughter cells. their own.
MICRO-ORGANISM Unlike cells, they do not divide by binatu
- Are said to be ubiquitous, meaning fission
they are virtually everywhere.
Microbiology – study of microorganisms
Pathogens – Disease – causing
microorganism.
Nonpathogenic- do not cause disease
Indigenous microflora – microbes that can
prevent or reduce the growth of pathogens.
Opportunistic pathogens or opportunists –
organisms that colonize our bodies.
Decomposer or Saprophytes – an organism
that lives on dead and or decaying organic
matter.
BIOREMEDIATION – capable of
decomposing industrial wastes.
You might also like
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cell 2 PDFDocument22 pagesCell 2 PDFMary Juanna T. MacandogNo ratings yet
- LESSONS in BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesLESSONS in BIOCHEMMikhael Jay IglesiasNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Basis of Life: Topic Learning OutcomesDocument18 pagesThe Cellular Basis of Life: Topic Learning OutcomesJiboy MixNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Unit 1Document45 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Unit 1lc camposoNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Cell OrganisationDocument3 pagesGeneral Principles of Cell Organisation22194No ratings yet
- Bio Exam ReviewerDocument10 pagesBio Exam ReviewerMarlon JonasNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDocument37 pagesGenetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- ENMANUEL MC 3 BSN1 Assignment No. 2 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic First TrinalDocument6 pagesENMANUEL MC 3 BSN1 Assignment No. 2 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic First TrinalJason Carbon EnmanuelNo ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes Final-2Document58 pagesMicrobiology Notes Final-2arvindk962706No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Cellular ReproductionDocument3 pagesChapter 5: Cellular ReproductionDarwin Competente LagranNo ratings yet
- Biology ImperialDocument80 pagesBiology ImperialHubert CiskowskiNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Exam - General BiologyDocument12 pages1st Summative Exam - General BiologyAgatha AquinoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument94 pagesCell Divisionazfdin100% (2)
- Cell Exploration: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument11 pagesCell Exploration: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesMay PaviaNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument3 pagesThe CellMary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function ReviewerDocument4 pagesCell Structure and Function ReviewerLeandre Jasmine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Relab Term 3Document57 pagesRelab Term 3Nqobile NjokoNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONDocument48 pagesThe Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Summary Essential Cell Biology by Alberts EnglishDocument52 pagesSummary Essential Cell Biology by Alberts EnglishBeatriz GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Gr.10 Remote Learning Workbook Term 3Document58 pagesGr.10 Remote Learning Workbook Term 3ffalchemyNo ratings yet
- Term 3 Life Science Remote Learning BookletDocument57 pagesTerm 3 Life Science Remote Learning BookletAgrarianNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Cell ComparisonDocument10 pagesVisibleBody Cell ComparisonAnjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Izat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmDocument18 pagesIzat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmSuhailina Mohd IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 General BiologyDocument7 pagesBio 101 General BiologyMohammed kashimNo ratings yet
- Mitosis PPTDocument30 pagesMitosis PPTKyexia Nazarene TarrayoNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 CELL AND NUCLEAR DIVISION My Notes 2020Document20 pagesTOPIC 3 CELL AND NUCLEAR DIVISION My Notes 2020reeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- The Five Kingdoms BiologyDocument13 pagesThe Five Kingdoms BiologyMuhtasim RafidNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Intro To Biochem (Lesson 2)Document6 pagesModule 1 - Intro To Biochem (Lesson 2)janmariefernandez0No ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - The Cell CycleDocument13 pagesLecture 7 - The Cell CycleDequanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - The Cell CycleDocument13 pagesLecture 7 - The Cell CycleDequanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten:: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument12 pagesChapter Ten:: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionShivani Shree SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesLESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Midterm Performance Task 1Document3 pagesMidterm Performance Task 1Mary Grace E. CerioNo ratings yet
- 4 Science 2 RPK - Chap 5 Cell Division (Part 1)Document58 pages4 Science 2 RPK - Chap 5 Cell Division (Part 1)zanayanNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationDocument12 pages1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationMo_Bash1No ratings yet
- Binary FissionDocument4 pagesBinary FissionVINDHYA SHANKERNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Week 1Document3 pagesGen Bio Week 1Lucy AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 1: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument7 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 1: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeCharmaine PamesaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- General Biology 1Document7 pagesGeneral Biology 1Charmaine PamesaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cytology CelllDocument48 pages1 Cytology CelllSamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BiologyFransiel B. AkistoyNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell The Unit of LifeRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-7 - Cell DivisionsDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-7 - Cell DivisionsMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument23 pagesCell DivisionInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Document26 pagesCell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Lamin N CeesayNo ratings yet
- Mystical Rose College of Science and Technology: Stage 1: InterphaseDocument4 pagesMystical Rose College of Science and Technology: Stage 1: InterphaseLaarni ToleteNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Illustrated ReportDocument21 pagesCell Biology Illustrated ReportIlze Krauze100% (11)
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument6 pagesMeiosis and MitosisSummer LoveNo ratings yet
- PONCE - Module 3 - BSN-2 - A18Document6 pagesPONCE - Module 3 - BSN-2 - A18Ponce Kristel Mae ONo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument17 pagesMitosisr2591220No ratings yet
- SOCIOLOGYDocument2 pagesSOCIOLOGYRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- Cell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) NucleusDocument2 pagesCell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) NucleusRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- SOCIOLOGYDocument2 pagesSOCIOLOGYRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- Athletics: Track EventsDocument5 pagesAthletics: Track EventsRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- AOB A.D. Engineering ServicesDocument1 pageAOB A.D. Engineering ServicesRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- David Hume (171-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageDavid Hume (171-WPS OfficeAl-aziz Bara PungutanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) NucleusDocument2 pagesCell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) NucleusRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- Part # 2 Myth Is A Folklore Genre Consisting of Narratives That Play A Fundamental Role in ADocument2 pagesPart # 2 Myth Is A Folklore Genre Consisting of Narratives That Play A Fundamental Role in ARyan ForteNo ratings yet
- Origin and Evolution of EarthDocument4 pagesOrigin and Evolution of EarthIndiangeologist80% (5)
- Abstract This Paper Presents A New Theory of The Universe Which Updates The Big Bang TheoryDocument6 pagesAbstract This Paper Presents A New Theory of The Universe Which Updates The Big Bang TheoryRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- Folk and Country Music PlaylistDocument3 pagesFolk and Country Music PlaylistRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- Abstract This Paper Presents A New Theory of The Universe Which Updates The Big Bang TheoryDocument6 pagesAbstract This Paper Presents A New Theory of The Universe Which Updates The Big Bang TheoryRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- Cold N Brew MenuDocument3 pagesCold N Brew MenuRizki FitriaNo ratings yet
- Amies A 114 - 3Document17 pagesAmies A 114 - 3Syed Umar Farooq100% (1)
- Varactor AssignmentDocument9 pagesVaractor Assignmentjawad_h89No ratings yet
- The Finite Element Method Applied To Agricultural Engineering - A Review - Current Agriculture Research JournalDocument19 pagesThe Finite Element Method Applied To Agricultural Engineering - A Review - Current Agriculture Research Journalsubhamgupta7495No ratings yet
- Texas Instruments FootprintsDocument7 pagesTexas Instruments FootprintsSteve SmithNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Technical BrochurDocument7 pagesKomatsu Technical BrochurBenjamin MossoNo ratings yet
- Wilson FR & Power Cable CatalogDocument56 pagesWilson FR & Power Cable CatalogRohim SuhadiNo ratings yet
- Coca ColaDocument50 pagesCoca Colamariyha PalangganaNo ratings yet
- Web+Presentation+12+July+2016 EA+-+Eric+LumeDocument57 pagesWeb+Presentation+12+July+2016 EA+-+Eric+LumetranthabinNo ratings yet
- Advanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsDocument4 pagesAdvanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsAnkit SoniNo ratings yet
- JCHT35K9 EngDocument5 pagesJCHT35K9 EngRodica PuscauNo ratings yet
- The Explanation of The Fundamentals of Islamic BeliefDocument95 pagesThe Explanation of The Fundamentals of Islamic BeliefbooksofthesalafNo ratings yet
- 5 Years High and Low PointsDocument7 pages5 Years High and Low PointsNaresh Kumar VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Beretta 92fs PistolDocument12 pagesBeretta 92fs PistolMustansir Bandukwala67% (3)
- CAT25256 EEPROM Serial 256-Kb SPI: DescriptionDocument22 pagesCAT25256 EEPROM Serial 256-Kb SPI: DescriptionPolinho DonacimentoNo ratings yet
- Scientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test BankDocument44 pagesScientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test Bankpurelychittra3ae3100% (24)
- Collage Lab PDFDocument145 pagesCollage Lab PDFmaa siddhi92% (12)
- Nano ScienceDocument2 pagesNano ScienceNipun SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Progress Report Week#9 UlubeluDocument6 pagesProgress Report Week#9 UlubelutiantaufikNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Selectividad Acti9Document34 pages1.1 - Selectividad Acti9Bladimir MichelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument11 pagesChemistry Notesraifaisal9267% (12)
- ELC609F12 Lec0 IntroductionDocument16 pagesELC609F12 Lec0 IntroductionMohammed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Age ProblemDocument31 pagesAge ProblemKenny CantilaNo ratings yet
- Theology of Work and Practical ImplicationsDocument28 pagesTheology of Work and Practical ImplicationsVinicius CardosoNo ratings yet
- Jib Crane Assembly ManualDocument76 pagesJib Crane Assembly ManualRobert Cumpa100% (1)
- DIY Paper Sculpture: The PrincipleDocument20 pagesDIY Paper Sculpture: The PrincipleEditorial MosheraNo ratings yet
- 1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016Document3 pages1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016api-292307509No ratings yet
- VlsiDocument79 pagesVlsimdhuq1No ratings yet
- Model: P660 Series: Differential Pressure Gauge With Diaphragm ElementDocument6 pagesModel: P660 Series: Differential Pressure Gauge With Diaphragm ElementTÀi VÕNo ratings yet
- Suneet Narayan Singh (Updated CV), NDocument4 pagesSuneet Narayan Singh (Updated CV), Nnishant gajeraNo ratings yet