Professional Documents
Culture Documents
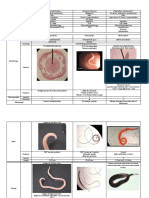
F. Buski F. Hepatica F. Gigantica C. Sinensis H. Heterophyes M. Yokagawai
Uploaded by
Joan Delos ReyesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F. Buski F. Hepatica F. Gigantica C. Sinensis H. Heterophyes M. Yokagawai
Uploaded by
Joan Delos ReyesCopyright:
Available Formats
TREMATODES
F. Buski F. Hepatica F. Gigantica C. Sinensis H. Heterophyes M. Yokagawai
Other names/ Large intestinal fluke. Sheep liver fluke large liver flukes Chinese liver fluke Heterophid fluke Heterophid fluke
Common name
Adult morphology and No shoulder; 5 cm by 1.5 Presence of shoulder; 3 cm Presence of shoulder; Each end of the 1.0 by 0.5 mm; grayish approximately 1.5 by
size cm by 1 cm 75 mm by 15 mm adult worm is narrower pyriform organism, scaly 0.5 mm; pyriform
than the midportion of appearance. with tapering at the
the body ; 2 by 0.5 cm anterior end and
rounding
at the posterior end
Eggs 128-140 μm by 78-85 μm 128-150 μm by 60-90 μm 128-150 μm by 60-90 Presence of distinct Presence of shoulders Presence of shoulders
μm shoulders and but discrete, lack of but discrete, lack of
presence of small knob terminal knob; 30 by 15 terminal knob; 30 by 15
opposite operculum;30 μm. μm.
by 15 μm
Integument Smooth and unarmed Smooth and unarmed Smooth and unarmed Smooth and unarmed Smooth and unarmed Smooth and unarmed
Thick shell Thin shell
Ovary branched tubular small and dendritic Single; rounded Small located at the Small located at the
anterior end of the anterior end of the
testes testes
Testes Tandem dendritic two branched tubules, dendritic and cover Two testes towards the large and diagonal to large and diagonal to
located in the middle and two-thirds of the posterior end each other each other
posterior regions of the posterior portion
body
Infective stage to man Metacercariae Metacercariae Metacercariae encysted metacercariae Metacercariae Metacercariae
Diagnostic stage Feces Feces Feces stool Feces Feces
specimens or duodenal
aspirates
1st intermediate host Snail Snail Snail Snail Snail Snail
2nd intermediate host Watery plants Watery plants Watery plants Fresh water fish or Fresh water fish Fresh water fish
shrimp
Definitive host Human; cattle or sheep Human; sheep Human; ruminants Human; Dogs or cats Human; Dogs or cats; Human; Dogs or cats;
Fish eating mammals Fish eating mammals
and birds and birds
Larval forms cercariae cercariae cercariae cercariae cercariae cercariae
Lab methods Recovery of the adult Recovery of the adult Recovery of the adult Enterotest Enterotest; Careful Enterotest; Careful
Fasciolopsis worm; Fasciolopsis worm; Fasciolopsis worm; microscopic examination microscopic examination
Enterotest, ELISA, and Enterotest, ELISA, and gel Enterotest, ELISA, and
gel diffusion diffusion gel diffusion
Mode of transmission Ingestion of infected Ingestion of infected Ingestion of infected ingestion of Ingestion of infected Ingestion of infected
watery plant watery plant watery plant undercooked fish undercooked fish undercooked fish
contaminated by C.
sinensis
Habitat Small intestine Bile ducts Bile ducts Bile ducts Small intestine Small intestine
Preventive measures Exercising proper human Exercising proper human Exercising proper practicing proper avoidance of consuming avoidance of consuming
fecal disposal and fecal disposal and human fecal disposal sanitation procedures; undercooked undercooked
sanitation sanitation and sanitation avoiding the ingestion of fish; practicing proper fish; practicing proper
Practices Practices Practices raw, undercooked, or fecal fecal
freshly pickled disposal disposal
freshwater
fish and shrimp
Disease caused and Fasciolopsiasis. Fasciolopsiasis. Sheep liver Fascioliasis. Clonorchiasis. Heterophyiasis. Metagonimiasis.
treatment Praziquantel rot. Dichlorophenol Dichlorophenol praziquantel praziquantel praziquantel
or albendazole
TREMATODES
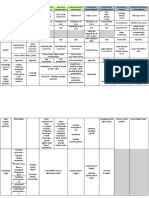
P. Westermani E. Ilocanum O. Felineus S. Japonicum S. Mansoni S. Haematobium
Other names/ Oriental lung fluke cat liver fluke Blood fluke. Manson’s blood fluke Bladder fluke
Garrison's fluke
Common name
Adult morphology 1 cm by 0.7 cm 5 to 15 mm(0.5-1.5 cm) 7 mm to 12 mm by 2 Female: 2 cm Female: 2 cm Female: 2 cm
and size long and 1to 2 mm wide mm to 3 mm Male: 1.5 cm Male: 1.5 cm Male: 1.5 cm
Surrounds female Surrounds female Surrounds female
Eggs Prominent operculum with 19-30 µm long by 10-20 Oblong ; 50-85 μm by Somewhat Somewhat oblong ; 110-
Immature, very small
Shoulders; obvious terminal µm wide 38-60 μm roundish ; 112-182 μm 170 μm by
Shell thickening opposite operculum with germ by 40-75 μm 38-70 μm
Operculum; 78-120 μm
ball/yolk (straw colored)
long; 45-60 μm wide
Integument Prominent operculum with operculated and possess Female: ridged and Female: ridged and Female: ridged and
shoulders; obvious terminal Plaque-like scales
prominent opercular pitted and possesses pitted and possesses pitted and possesses
shell thickening opposite 'shoulders' and and fewer spines than in the fewer spines than in the fewer spines than in the
operculum abopercular knob oral sucker oral sucker oral sucker
Male: Anterior to the Male: Anterior to the Male: Anterior to the
acetabulum, the acetabulum, the acetabulum, the
integumental surfaces integumental surfaces integumental surfaces
are devoid of spines are devoid of spines are devoid of spines
Ovary Lobed; off-centered near Anterior to the testes 2-3 eggs 2-3 eggs 2-3 eggs
Lobed
the center of the worm
Testes Lobed; adjacent from each Two testes lying one 6-9 testicular masses 6-9 testicular masses 6-9 testicular masses
Tandem and deeply
other located at the behind the other in the
posterior end lobed posterior portion of the
body
Infective stage to Metacercariae Metacercariae Metacercariae Cercariae Cercariae Cercariae
man
Diagnostic stage Sputum stool or rectal biopsy stool or rectal biopsy urine
Eggs in stool Eggs in stool
specimens specimens
1st intermediate host Snail Snail Snail Snail Snail Snail
2nd intermediate Crustecean; crabs Snails; tadpoles; fish fish
host
Definitive host Human Human; mammals or Human; fish-eating Human Human Human
duck mammals
Larval forms Cercariae Miracardium Cercariae miracidium miracidium miracidium
Lab methods Serologic tests Serologic tests Enterotest immunodiagnostic immunodiagnostic immunodiagnostic
techniques, techniques, techniques,
including ELISA including ELISA including ELISA
Mode of Ingestion of infected Ingestion of infected ingesting undercooked skin penetration by skin penetration by skin penetration by
transmission undercooked crayfish or undercooked fish fish containing cercariae cercariae cercariae
crabs metacercariae
Habitat Lung tissue Bile and pancreatic ducts veins that veins that veins surrounding the
Duodenum
surround the intestinal surround the intestinal bladder
tract; blood passages of tract; blood passages of
the liver the liver
Preventive measures Avoiding Avoiding human Avoiding human proper human waste proper human waste proper human waste
Human ingestion of ingestion of ingestion of disposal and disposal and disposal and
undercooked crayfish and undercooked fish and undercooked fish and control of the snail control of the snail control of the snail
crabs and exercising proper exercising proper exercising proper population; avoid population; avoid population; avoid
disposal of human disposal of human disposal of human contact with potentially contact with potentially contact with potentially
Waste products Waste products Waste products contaminated water contaminated water contaminated water
Disease caused and Paragonimiasis, pulmonary Opisthorchis infection Schistosomiasis, Schistosomiasis, Schistosomiasis,
Echinostomiasis
treatment distomiasis Praziquantel or bilharziasis, swamp bilharziasis, swamp bilharziasis, swamp
Praziquantel albendazole fever, Katayama fever fever, Katayama fever fever, Katayama fever
Praziquantel Praziquantel Praziquantel; Praziquantel
Oxamniquine
You might also like
- 1 Intestinal NematodesDocument2 pages1 Intestinal NematodesKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Guanzon, Assignment of Flagellates and CiliatesDocument2 pagesGuanzon, Assignment of Flagellates and CiliatesIan Paul GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Assignment in CestodesDocument2 pagesAssignment in CestodesDanzel MalicNo ratings yet
- E. Histolytica E. Coli E. Nana Iodemoeba Butschlii (Not Included Nonpathogenic) (Not Included Nonpathogenic)Document2 pagesE. Histolytica E. Coli E. Nana Iodemoeba Butschlii (Not Included Nonpathogenic) (Not Included Nonpathogenic)Joan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Intro To Cestodes TableDocument6 pagesIntro To Cestodes TableChef der Personal und Verwaltung ReichskanzleiNo ratings yet
- Types of intestinal tapeworms and their characteristicsDocument20 pagesTypes of intestinal tapeworms and their characteristicsAbby SiervoNo ratings yet
- 5 Intestinal ProtozoaDocument2 pages5 Intestinal ProtozoaKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Flukes Liver Flukes Lung Flukes Blood Flukes: SinensisDocument3 pagesIntestinal Flukes Liver Flukes Lung Flukes Blood Flukes: SinensisCHO-ON KIMNo ratings yet
- Phylum Platyhelminthes - Cestoda (Tapeworms) Pseudophyllidea (False Tapeworm) Cyclophyllidea (True Tapeworm)Document3 pagesPhylum Platyhelminthes - Cestoda (Tapeworms) Pseudophyllidea (False Tapeworm) Cyclophyllidea (True Tapeworm)Mariel Angelie TuringanNo ratings yet
- 2 MosquitoDocument8 pages2 Mosquito173Swapnaneil BujarbaruahNo ratings yet
- Cestodes TableDocument5 pagesCestodes TableEiveren Mae SutillezaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Summary TableDocument2 pagesKingdom Animalia: Phylum Summary TableRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology: Medina & Albano - Lecture & LaboratoryDocument9 pagesMedical Parasitology: Medina & Albano - Lecture & LaboratoryabigailNo ratings yet
- Class XI, Chp4-Animal Kingdom-1Document5 pagesClass XI, Chp4-Animal Kingdom-1anirudhgupta5050No ratings yet
- Intestinal Nematodes: Ancylostoma, Strongyloides, NecatorDocument4 pagesIntestinal Nematodes: Ancylostoma, Strongyloides, NecatorBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Nematodes (Round Worms) Comparison TableDocument4 pagesNematodes (Round Worms) Comparison TableJoshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Mapeh TapewormsDocument12 pagesMapeh Tapewormsfreid jaredNo ratings yet
- INTESTINAL NEMATODEDocument4 pagesINTESTINAL NEMATODEXyrza PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Survey Table 2020Document10 pagesVertebrate Survey Table 2020Evan JackNo ratings yet
- Nematodes: Ascaris Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura Enterobius VermicularisDocument4 pagesNematodes: Ascaris Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura Enterobius VermicularisMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- Biomphalaria&Aus Tralorbis Onchomelania Bulinus&PhysopsisDocument4 pagesBiomphalaria&Aus Tralorbis Onchomelania Bulinus&PhysopsisOlib OlieNo ratings yet
- Helminths 12Document34 pagesHelminths 12malakaiad212No ratings yet
- Reviewr Parasite Nematodes Whole PDFDocument12 pagesReviewr Parasite Nematodes Whole PDFDavid Ryan MangawilNo ratings yet
- Mosquitoes 131019090213 Phpapp01Document92 pagesMosquitoes 131019090213 Phpapp01Aparna KinginiNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Tretamodes: Lung Flukes and OthersDocument9 pagesParasitology: Tretamodes: Lung Flukes and OthersJoan Caacbay De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NEMATODES: Hookworms General Info: Hookworm (In General) Strongyloides StercoralisDocument6 pagesNEMATODES: Hookworms General Info: Hookworm (In General) Strongyloides StercoralisMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- Taenia Solium Taenia Saginata Diphyllobotrium Latum Dipylidium Caninum Hymenolepis Nana Hymenolepis Diminuta Echinococcus SPPDocument1 pageTaenia Solium Taenia Saginata Diphyllobotrium Latum Dipylidium Caninum Hymenolepis Nana Hymenolepis Diminuta Echinococcus SPPKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesPlant KingdomInfinite SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom M PDFDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom M PDFAbu SubhanNo ratings yet
- Nema TableDocument3 pagesNema Tableanon_574497805No ratings yet
- بايو نظري محاضرة 6 مترجم PDFDocument16 pagesبايو نظري محاضرة 6 مترجم PDFMatti LaythNo ratings yet
- Hemoflagellates Protozoa: Scientific Name Disease Commune NameDocument6 pagesHemoflagellates Protozoa: Scientific Name Disease Commune Nameaust austNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and treatment of common intestinal parasitesDocument8 pagesCharacteristics and treatment of common intestinal parasitesAlcera JemNo ratings yet
- Snakes, Venom, Effects, AntivenomDocument5 pagesSnakes, Venom, Effects, AntivenomLakshya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Introduction To Nematodes PDFDocument5 pagesWeek 7 Introduction To Nematodes PDFewmedtechNo ratings yet
- Lab 10Document3 pagesLab 10DELOS SANTOS JESSIECAHNo ratings yet
- Nematodes Part 2Document21 pagesNematodes Part 2Grazielle Almazan100% (2)
- Trematode 2021Document46 pagesTrematode 2021ShanmathiNo ratings yet
- Cestodes and Trematodes: A Comparison of Tapeworms and FlukesDocument4 pagesCestodes and Trematodes: A Comparison of Tapeworms and FlukesNatalie EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Snakes - Identification of Poisonous & Non-Poisonous Snakes, Poison Apparatus, Venom & Its EffectDocument6 pagesSnakes - Identification of Poisonous & Non-Poisonous Snakes, Poison Apparatus, Venom & Its EffectAakash VNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Guide QuestionDocument2 pagesParasitology Guide QuestionRoll BiNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFDocument23 pagesPlatyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFAbdulla Hil KafiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 373220677-14e51-Naturalscience02-Unit03-Test PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 3 373220677-14e51-Naturalscience02-Unit03-Test PDFdnaranjo206hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS - Class Notes - SprintDocument35 pagesDIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS - Class Notes - Sprintguptanaina13579No ratings yet
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument36 pagesParasitology ReviewerMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Bio25: Vertebrate Structure & Function: Janice V. NG, MSC Department of Biology, Cas, Upm Sy 2015-2016Document43 pagesBio25: Vertebrate Structure & Function: Janice V. NG, MSC Department of Biology, Cas, Upm Sy 2015-2016Ruby GoNo ratings yet
- Midterms - Clinical ParasitologyDocument19 pagesMidterms - Clinical ParasitologyJyne CatipayNo ratings yet
- Handling and Blood Collection MiceDocument18 pagesHandling and Blood Collection Micerico.daisylynNo ratings yet
- Bio 112 (Phylum Chordata) - 1Document5 pagesBio 112 (Phylum Chordata) - 1Amaan B EydreesNo ratings yet
- 2 Blood and Tissue NematodesDocument1 page2 Blood and Tissue NematodesKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Annelida Platyhelminthes: Manatad, Joy Joy SDocument3 pagesAnnelida Platyhelminthes: Manatad, Joy Joy SJoy ManatadNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive SystemMemes only100% (3)
- Liver FlukeDocument4 pagesLiver FlukecatuiraneljhayyyNo ratings yet
- Parasites by Apple TanDocument16 pagesParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- Scorpions For Kids: Amazing Animal Books For Young ReadersFrom EverandScorpions For Kids: Amazing Animal Books For Young ReadersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- TrematodesDocument30 pagesTrematodesJezzah Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Heterophyid: ST NDDocument3 pagesHeterophyid: ST NDIvan ChuaNo ratings yet
- Schistosomes and Paragonimus Final - GodoyDocument5 pagesSchistosomes and Paragonimus Final - GodoyDanielle Justine GodoyNo ratings yet
- Bio Geo 1 Unit 5Document18 pagesBio Geo 1 Unit 5Luca Bazzi OteroNo ratings yet
- Guide To Internal Parasites of Ruminants: Bunostomum Moniezia Cooperia Ostertagia MonieziaDocument2 pagesGuide To Internal Parasites of Ruminants: Bunostomum Moniezia Cooperia Ostertagia MonieziaShravankumar GaddiNo ratings yet
- Pinworm, Seatworm Enterobiasis, Pinworm InfectionDocument2 pagesPinworm, Seatworm Enterobiasis, Pinworm InfectionJoan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pinworm, Seatworm Enterobiasis, Pinworm InfectionDocument2 pagesPinworm, Seatworm Enterobiasis, Pinworm InfectionJoan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Living PrimatesDocument16 pagesThe Living PrimatesJoan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Living PrimatesDocument16 pagesThe Living PrimatesJoan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fluid Guideline SaTHDocument18 pagesFluid Guideline SaTHpaulito_delgadoNo ratings yet
- Anacardium OrientaleDocument21 pagesAnacardium OrientaleAlexandre Funcia100% (1)
- R-07 Behaviour Policy (1536) PDFDocument1 pageR-07 Behaviour Policy (1536) PDFAmerNo ratings yet
- PT&T Policy Against Married WomenDocument12 pagesPT&T Policy Against Married WomenHershey Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Answer What Are Being Asked ForDocument23 pagesInstructions: Answer What Are Being Asked ForCatlyn Tagala CalzadoNo ratings yet
- Skills Checklist-Critical CareDocument3 pagesSkills Checklist-Critical CareRom Anog100% (4)
- Principles of Paragraph Writing IIIDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Paragraph Writing IIITitiek DwiNo ratings yet
- Hip ExaminationDocument7 pagesHip ExaminationWaqas Haleem100% (1)
- Esthetiques Spa 201005Document134 pagesEsthetiques Spa 201005Kristina0% (1)
- Chocolate: by Jessica SpenceDocument12 pagesChocolate: by Jessica SpenceValéria Oliveira100% (1)
- Natural Disasters and Their Global ImpactDocument17 pagesNatural Disasters and Their Global ImpactgandhialpitNo ratings yet
- Case Studies For PharmacyDocument3 pagesCase Studies For PharmacyMahima Sindhi50% (2)
- Pestel Swot On Dairy IndDocument13 pagesPestel Swot On Dairy Indrudraksha sharmaNo ratings yet
- 서초구 고교기출 4회차Document7 pages서초구 고교기출 4회차ᄋᄋNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument83 pagesMalariasarguss1467% (3)
- Roaduser and Vehicle CharacteristicsDocument62 pagesRoaduser and Vehicle CharacteristicsreashmapsNo ratings yet
- Ruptured Globe Involving Cornea Dictation GuideDocument2 pagesRuptured Globe Involving Cornea Dictation GuideErik Anderson MDNo ratings yet
- TC Electronic M-100 User ManualDocument21 pagesTC Electronic M-100 User Manualzewdaroo9599No ratings yet
- Keys To The Spirit World (Empath U)Document53 pagesKeys To The Spirit World (Empath U)Ruthy Balot100% (1)
- Close Book/Open Book/Open Note : Kerjakan Secara Mandiri, Setiap Kecurangan Berarti Nilai EDocument10 pagesClose Book/Open Book/Open Note : Kerjakan Secara Mandiri, Setiap Kecurangan Berarti Nilai EAlvin FahmiNo ratings yet
- Medication Booklet and TicketDocument3 pagesMedication Booklet and TicketCayanne ChuaNo ratings yet
- What Is MindfulnessDocument4 pagesWhat Is MindfulnessPongal PunithaNo ratings yet
- Soccer Class-Action Complaint - Aug. 27, 2014Document138 pagesSoccer Class-Action Complaint - Aug. 27, 2014Evan Buxbaum, CircaNo ratings yet
- 6Document11 pages6UgaugaaNo ratings yet
- FCPS 1 Radiology + AnswersDocument25 pagesFCPS 1 Radiology + AnswersZahid Qamar100% (2)
- Cystocentesis K4Document24 pagesCystocentesis K4Sze KhayNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Care Bill 2013Document53 pagesMental Health Care Bill 2013Ankit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test SECOND Grading MAPEHDocument10 pagesPeriodical Test SECOND Grading MAPEHLynford A. LagondiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Culture and Quality Management Practices in The Hospital SectorDocument10 pagesOrganizational Culture and Quality Management Practices in The Hospital SectorAaminah BeathNo ratings yet