0% found this document useful (0 votes)
370 views5 pagesEngineering Method Statement Overview
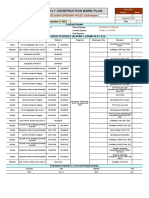
The document provides details on the conceptual design for a project including foundation work, structural works, civil works, design approach, design criteria, proposed specifications, and engineering codes and guidelines to be used. Foundation work will include soil investigation and testing. Structural works will use reinforced concrete and steel. Civil works include roads, drainage, sewerage, and water reticulation. Design criteria are also outlined.
Uploaded by
aimkcl90Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
370 views5 pagesEngineering Method Statement Overview
The document provides details on the conceptual design for a project including foundation work, structural works, civil works, design approach, design criteria, proposed specifications, and engineering codes and guidelines to be used. Foundation work will include soil investigation and testing. Structural works will use reinforced concrete and steel. Civil works include roads, drainage, sewerage, and water reticulation. Design criteria are also outlined.
Uploaded by
aimkcl90Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd