Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 3 Problems: DD TH0 D N OX - 4
Uploaded by
Amir Sharfuddin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesSingle State Design
Original Title
3.Prob
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSingle State Design
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesLecture 3 Problems: DD TH0 D N OX - 4
Uploaded by
Amir SharfuddinSingle State Design
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
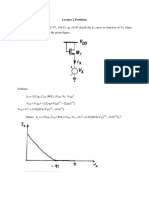
Lecture 3 Problems
Q1. Given VDD=3V, VTH0=0.7V, W/L=50/0.5, RD=2KΩ, µn COX = 1.34225x10-4 for the circuit
shown below
a) What is the small signal gain if M1 is in saturation and ID = 1mA?
b) What input voltage places M1 at the edge of the triode region? What is small signal gain
under this condition?
c) Calculate the input voltage that yield VOUT = 1V and VOUT = 2.5V.
d) Calculate the drain current and the trans-conductance of M1 for both cases.
Solution:
a) AV = - gm RD
gm = = (2µn COX (W/L) ID)1/2
So gm = 5.1812x10-3 mho
And gain AV = - (5.1812x10-3) (2x103) = -10.36
b) Condition for edge of triode region and saturation region is given by VDS = VGS-VTH
Hence VIN-VTH = VDD – RD ID (saturation)
VIN-0.7 = 3-2
VIN = 1.7
c) As VOUT = VDD – (1/2) RD µn COX (W/L) (VIN-VTH)2
VIN = 1.086 (for VOUT =1V) & 0.893 (for VOUT =2.5V)
d) As ID = (VDD - VOUT)/ RD
ID = 1mA (for VOUT =1V) & 0.25mA (for VOUT =2.5V)
As gm = (2µn COX (W/L) ID)1/2
gm = 5.1812m mho (for VOUT =1V) & 2.59m mho (for VOUT =2.5V)
Q2. Given VDD=3V, VTH0=0.7V, W/L=50/0.5, RD=2 KΩ, µn COX = 1.34225x10-4, RS=200 Ω for
the circuit shown below
a) Calculate the small signal gain if M1 is in saturation ID = 0.5 mA.
b) What input voltage places M1 at the edge of the triode region? What is small signal gain
under this condition?
Solution:
a) AV = - (gm RD)/(1+ gm RS)
Now gm = (2µn COX (W/L) ID)1/2 = 3.66m mho
Hence AV = 4.22
b) As we know that VOUT = VDD- RD ID
VOUT =VD = VDD - 2 x 0.5 = 2V
VS = RS ID = 200 x 0.5x 10-3 = 0.1V
Condition for edge of triode region and saturation region is given by VDS = VGS-VTH
VD - VS = VG - VS -VTH
2-0.1 = VG -0.1-0.7
VG = 2.7 or VIN = 2.7
You might also like
- EE213.HW1 SolutionDocument14 pagesEE213.HW1 Solutionkany zhaoNo ratings yet
- 12 Oct Sample Exercises Active Loads-1Document19 pages12 Oct Sample Exercises Active Loads-1MuhammadAliNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- SSED Solved Problems For Chapter 6Document5 pagesSSED Solved Problems For Chapter 6MINH NGUYỄN THẾ100% (1)
- ENEE 3543 - Homework 4 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesENEE 3543 - Homework 4 - SolutionsTSwayNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Resistive Load Mos Inverter: An ExampleDocument41 pages3.1. Resistive Load Mos Inverter: An Exampleerdem10139No ratings yet
- Amec Unit 2 QBDocument23 pagesAmec Unit 2 QBashreen akbar aliNo ratings yet
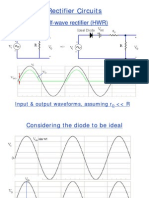
- Rectifier Circuits: Half-Wave Rectifier (HWR)Document18 pagesRectifier Circuits: Half-Wave Rectifier (HWR)Md ArifNo ratings yet
- 2 Stage Amplifiers AssignmentDocument2 pages2 Stage Amplifiers AssignmentShreyaank RaoNo ratings yet
- TUGAS ELEKTRONIKA - Kelompok 2Document11 pagesTUGAS ELEKTRONIKA - Kelompok 2Christine SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2023 - AnsDocument3 pagesTutorial 2023 - Anschetannp121No ratings yet
- HW 3 SolutionDocument10 pagesHW 3 Solutionblatant01No ratings yet
- Sol 3Document22 pagesSol 3ee206023No ratings yet
- Sol 3Document23 pagesSol 3akakameyNo ratings yet
- Lect 9,10 - MOSFET DC AnalysisDocument17 pagesLect 9,10 - MOSFET DC Analysisshashikala kotiNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FDocument44 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- ECE102 - F12 ProSet 7 PDFDocument37 pagesECE102 - F12 ProSet 7 PDFlokeshwarrvrjcNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 - SolutionDocument10 pagesSheet 3 - SolutionMajid HelmyNo ratings yet
- EC238 Electronics I: MOSFET DC and BiasingDocument9 pagesEC238 Electronics I: MOSFET DC and BiasingSara El-GendyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-3 With SolutionsDocument3 pagesTutorial-3 With SolutionsSandesh RSNo ratings yet
- EeeDocument15 pagesEeeSoma SinhaNo ratings yet
- Example 2.1: 2.2 Long-Channel I-V CharacteristicsDocument1 pageExample 2.1: 2.2 Long-Channel I-V CharacteristicsCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Differential AmplifierDocument24 pagesDifferential AmplifierT H ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryDocument25 pagesChapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryrasheeenNo ratings yet
- 320 Lecture 29Document8 pages320 Lecture 29Kirubel MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of MIcroelectronics, Razavi Chapter 7 SolutionsDocument85 pagesFundamental of MIcroelectronics, Razavi Chapter 7 SolutionsTaís LaurindoNo ratings yet
- Models Analog Design 9Document65 pagesModels Analog Design 9api-3750190No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 2 PDFAiffah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Mosfet-3: DC Analysis of FETDocument9 pagesMosfet-3: DC Analysis of FETKomay Abo ShakraNo ratings yet
- Chapter (5) Part (2) (Long Channel MOSFET)Document22 pagesChapter (5) Part (2) (Long Channel MOSFET)Ahmed SalehNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering: American University of BeirutDocument10 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering: American University of BeirutadgjkinghackNo ratings yet
- Lecturer On Mos InverterDocument24 pagesLecturer On Mos InvertersoumikbhNo ratings yet
- Transistor Mosfet: Dr. Pham Nguyen Thanh LoanDocument77 pagesTransistor Mosfet: Dr. Pham Nguyen Thanh LoanhajjkaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetdomingouclarayNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-Module1: Gowra P SDocument5 pagesAnalog Electronic Circuits Lab-Module1: Gowra P SReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Ee618 PDFDocument39 pagesEe618 PDFfilmfilmfNo ratings yet
- ESC201T L28 MOS CircuitsDocument15 pagesESC201T L28 MOS CircuitsRachit MahajanNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 - SolutionsDocument14 pagesHomework 3 - SolutionsYahya Salam SalehNo ratings yet
- Famini Pelon Quizon Elecs FetDocument7 pagesFamini Pelon Quizon Elecs FetPatrick FaminiNo ratings yet
- Cur Mir 1Document1 pageCur Mir 1amiglaniNo ratings yet
- Current Mirror DesignDocument17 pagesCurrent Mirror DesignQãzí HamzaNo ratings yet
- Inverter VTC With Cadence VirtuosoDocument7 pagesInverter VTC With Cadence VirtuosoAbhishek Kumar0% (1)
- Experiment No. 1: ObjectiveDocument9 pagesExperiment No. 1: ObjectiveNitin RajputNo ratings yet
- Problems Solution MOSFET at DCDocument9 pagesProblems Solution MOSFET at DCMd. Nymur Rahman HemelNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 B (MOSShortTransistors)Document8 pagesLecture03 B (MOSShortTransistors)Yuichi SegawaNo ratings yet
- Current Sources and Sinks: V V V V V V VDocument7 pagesCurrent Sources and Sinks: V V V V V V VSyed HyderNo ratings yet
- Midterm CircuitosDocument7 pagesMidterm CircuitosSantiago G. TorresNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Assignment 1 SolvedDocument17 pagesVlsi Assignment 1 SolvedNilesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Class Test: C W K G KV V L KIDocument2 pagesClass Test: C W K G KV V L KIIndranilNo ratings yet
- TP GG 0v SG TP SG GS DDocument2 pagesTP GG 0v SG TP SG GS DGurpreet Singh DhindsaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Digital Integrated Circuit Design: N-Channel MOSFET EQUATIONDocument3 pagesHomework 2 Digital Integrated Circuit Design: N-Channel MOSFET EQUATIONKhánh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Voltage Reference 23Document25 pagesVoltage Reference 23api-3750190No ratings yet
- ECE 1312 IIUM L16 FET DC AnalysisDocument20 pagesECE 1312 IIUM L16 FET DC AnalysisFatihah AinaNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Problems: DD TH0 F X X X DDDocument2 pagesLecture 2 Problems: DD TH0 F X X X DDAmir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- Babu Banarasi Das University, Lucknow: B. Sc. (Honours) Electronic Science Course Structure (Under CBCS)Document12 pagesBabu Banarasi Das University, Lucknow: B. Sc. (Honours) Electronic Science Course Structure (Under CBCS)Amir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- Pomodoro Technique For Time Management: Based On Our Brain Plan-Do-Check-ActDocument3 pagesPomodoro Technique For Time Management: Based On Our Brain Plan-Do-Check-ActAmir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Srinagar Electronics & Communication Engineering DepartmentDocument18 pagesNational Institute of Technology Srinagar Electronics & Communication Engineering DepartmentAmir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- M.Tech Admissions Brochure: 2-Year and 3-Year Programs Session: July, 2020Document7 pagesM.Tech Admissions Brochure: 2-Year and 3-Year Programs Session: July, 2020Amir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- 3Document9 pages3Amir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- 2016 25-2 Tomato Increase ProductivityDocument4 pages2016 25-2 Tomato Increase ProductivityAmir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- 2016 25-2 Tomato Increase ProductivityDocument4 pages2016 25-2 Tomato Increase ProductivityAmir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- Etf 2005Document6 pagesEtf 2005Nashat OsmanNo ratings yet
- The Gist of NCERT - Geography PDFDocument119 pagesThe Gist of NCERT - Geography PDFmadhu100% (1)
- Etf 2005Document6 pagesEtf 2005Nashat OsmanNo ratings yet
- 07 03 2018 Delhi TH Amir 1803070758 PDFDocument18 pages07 03 2018 Delhi TH Amir 1803070758 PDFAmir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 1 1Document136 pagesDigital Electronics 1 1Amir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- Leep 203Document23 pagesLeep 203sanagavarapuNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Symbols: Good Problems: March 25, 2008Document2 pagesMathematical Symbols: Good Problems: March 25, 2008John TingNo ratings yet
- 07 03 2018 Delhi TH Amir 1803070758 PDFDocument18 pages07 03 2018 Delhi TH Amir 1803070758 PDFAmir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 110914075241 Phpapp02Document33 pagesLecture5 110914075241 Phpapp02Amir SharfuddinNo ratings yet