Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Potassium-Sparing Diuretics: Drug Name Clinical Use Phacmacodynamics Toxicity Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist
Uploaded by
SalomeSibashvili0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views1 pagePotassium-sparing diuretics work by reducing sodium absorption in the collecting tubules and ducts of the kidney, thereby reducing loss of potassium in the urine. The two main types are mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists like spironolactone and eplerenone, which bind to receptors to blunt aldosterone activity, and ENAC channel blockers like amiloride and triamterene, which directly interfere with sodium entry through epithelial sodium channels. Toxicities can include hyperkalemia, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, and kidney stones.
Original Description:
Original Title
POTASSIUM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPotassium-sparing diuretics work by reducing sodium absorption in the collecting tubules and ducts of the kidney, thereby reducing loss of potassium in the urine. The two main types are mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists like spironolactone and eplerenone, which bind to receptors to blunt aldosterone activity, and ENAC channel blockers like amiloride and triamterene, which directly interfere with sodium entry through epithelial sodium channels. Toxicities can include hyperkalemia, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, and kidney stones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views1 pagePotassium-Sparing Diuretics: Drug Name Clinical Use Phacmacodynamics Toxicity Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist
Uploaded by
SalomeSibashviliPotassium-sparing diuretics work by reducing sodium absorption in the collecting tubules and ducts of the kidney, thereby reducing loss of potassium in the urine. The two main types are mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists like spironolactone and eplerenone, which bind to receptors to blunt aldosterone activity, and ENAC channel blockers like amiloride and triamterene, which directly interfere with sodium entry through epithelial sodium channels. Toxicities can include hyperkalemia, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, and kidney stones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
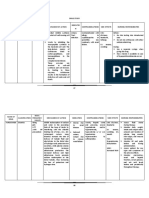
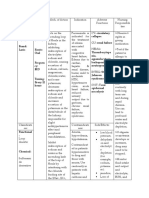
POTASSIUM-SPARING DIURETICS
Drug Name Clinical Use Phacmacodynamics Toxicity
Mineralocorticoid
receptor antagonist
Spironolactone --Primary aldosteronism (Conn’s -reduce Na + absorption in the collecting Hyperkalemia
syndrome, tubules and ducts. Hyperchloremic Metabolic Acidosis
ectopic adrenocorticotropic -Potassium absorption (and K + secretion) Gynecomastia
hormone production) at this site is regulated by aldosterone Acute Renal Failure
Eplerenone --secondary hyperaldosteronism -Spironolactone and eplerenone bind to Kidney Stones
(evoked by heart failure, hepatic mineralocorticoid receptors and blunt Contraindications:
cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, or aldosterone activity. Hyperkalemia
other conditions associated with Chronic renal insufficiency
diminished effective intravascular Liver diseases—impaired metabolism of
volume). triamterene/spironolactone
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
(Erythromycin, fluconazole, diltiazem
and grapefruit juice) can markedly
increase blood level of eplerenone but
not spironolactone
ENAC Channel blockers
Amiloride -Amiloride and triamterene do not block
aldosterone, but instead directly interfere
with Na + entry through the epithelial Na +
Triamterene
channels (ENaC) in the apical membrane
of the collecting tubule.
-reduce Na + absorption in the collecting
tubules and ducts
-Potassium absorption (and K + secretion)
at this site is regulated by aldosterone
You might also like
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 pagesPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- Ninja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1Document42 pagesNinja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1pp100% (1)
- Classification of DiureticDocument3 pagesClassification of DiureticJanice Malafu De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Table of AntidotesDocument5 pagesTable of Antidotesangelotisbe1120No ratings yet
- Drugs and The Kidney: Continuing Medical EducationDocument6 pagesDrugs and The Kidney: Continuing Medical EducationJANINE PASIONNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs Acting On Renal SystemDocument20 pagesPharmacology of Drugs Acting On Renal SystemBestha Chakri100% (2)
- Renal PharmacologyDocument7 pagesRenal PharmacologywanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- Table of Antidotes PDFDocument2 pagesTable of Antidotes PDFAmirah AndresNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and AntidotesDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and AntidotesreynoldNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionPiny CesarNo ratings yet
- Toxi Lab AntidotesDocument4 pagesToxi Lab AntidotesMariz VillaNo ratings yet
- Table of Antidotes PDFDocument2 pagesTable of Antidotes PDFhassen zabalaNo ratings yet
- DIURETICS LECTURE ZebDocument52 pagesDIURETICS LECTURE ZebPROF DR SHAHMURAD100% (2)
- Diuretics NewDocument21 pagesDiuretics NewPawan RajNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument3 pagesAntidotedeanelaylayNo ratings yet
- Renal Pharma 3Document14 pagesRenal Pharma 3Pranjali WeladiNo ratings yet
- ADH & Potassium Sparing Diuretics BDSDocument18 pagesADH & Potassium Sparing Diuretics BDSDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.DDocument28 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.Dmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Wuolah-Free-Topic 27Document2 pagesWuolah-Free-Topic 27Moldovan Maria TatianaNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument9 pagesExcretory Products and Their Eliminationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument5 pagesAntidoteMaynard ArandaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, KemdDocument46 pagesAdrenal Gland: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, KemdZahra AstriantaniNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Common Drugs and AntidotesDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Common Drugs and AntidotesAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- Toxicology and AntidoteDocument6 pagesToxicology and AntidoteVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Their AntidotesDocument6 pagesCommon Drugs and Their AntidotesShun Reigh SumilangNo ratings yet
- Ph'cology of Diuretics (RZH)Document48 pagesPh'cology of Diuretics (RZH)beby febyola siagianNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Agents: Dept. of Pharmacology & TherapeuticDocument44 pagesDiuretic Agents: Dept. of Pharmacology & Therapeuticangelica gloryNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes LecDocument4 pagesElectrolytes LecMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Animal Toxins and Renal Ion Transport: Another Dimension in Tropical NephrologyDocument8 pagesAnimal Toxins and Renal Ion Transport: Another Dimension in Tropical NephrologyMiguel SierraNo ratings yet
- PHS CVSDocument25 pagesPHS CVStewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument8 pagesAntidotedeanelaylayNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Drugs: Thiazides Sites of ActionDocument52 pagesDiuretic Drugs: Thiazides Sites of Actionuzzal ahmedNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- Over 13 Years of Age Are As Follows:: Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme InteractionDocument2 pagesOver 13 Years of Age Are As Follows:: Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme InteractionMbali MabuzaNo ratings yet
- K10 Kuliah NefrourologiDocument170 pagesK10 Kuliah NefrourologimarinanananaNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument4 pagesDiureticsdhainey100% (3)
- Anti-Coagulant (Vte in Obstetrics) - Madam LiewDocument10 pagesAnti-Coagulant (Vte in Obstetrics) - Madam LiewNana YunusNo ratings yet
- Plant Species Epidemiology Mechanism of Action Clinical SignsDocument1 pagePlant Species Epidemiology Mechanism of Action Clinical SignsmariaNo ratings yet
- Approach Blood GasesDocument1 pageApproach Blood GasesEmilyNo ratings yet
- HPT DDX (Sarah)Document3 pagesHPT DDX (Sarah)Maisarah RepinNo ratings yet
- Rta PDFDocument4 pagesRta PDFtraceyNo ratings yet
- Diana's Renal DiseasesDocument9 pagesDiana's Renal DiseasesdhyltonNo ratings yet
- CH11-Amino Acid MetabolismDocument106 pagesCH11-Amino Acid MetabolismChatchawinNo ratings yet
- (Printed) Pass Medicine Notes - Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology (Edited)Document53 pages(Printed) Pass Medicine Notes - Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology (Edited)Joanne HoNo ratings yet
- CC2 PREMILS To FINALS MERGED PDFDocument65 pagesCC2 PREMILS To FINALS MERGED PDFAlecx LipatanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DoneDocument12 pagesDrug Study DoneSheila Mae PanisNo ratings yet
- What Is Diuretic? Classify Diuretics? A Diuretic Is DefinedDocument3 pagesWhat Is Diuretic? Classify Diuretics? A Diuretic Is DefinedSujan Bose100% (1)
- USMLE Step 1 JournalDocument167 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Journalmed studentNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants: Elisabeth F. BildenDocument14 pagesAntidepressants: Elisabeth F. BildenSNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Urinary System (2020)Document55 pagesFundamental of Urinary System (2020)Nadya PutriNo ratings yet
- Video 4: Ahorradores de K: Amilorida y TriamterenoDocument2 pagesVideo 4: Ahorradores de K: Amilorida y TriamterenoCarlos Rodríguez AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Effects Adrenal Hormones RegebDocument7 pagesEffects Adrenal Hormones RegebPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- 2ND Se Mid Note 116Document2 pages2ND Se Mid Note 116Jonathan MangawiliNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Board Recall Must ReadDocument8 pagesBoard Recall Must ReadSarahSalvanNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument3 pagesPharmacologyDuy LuuNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument75 pagesAcute Renal FailureAshwin Raghav SankarNo ratings yet
- Yuktiana Kharisma Bagian Farmakologi FK UNISBA 2017Document55 pagesYuktiana Kharisma Bagian Farmakologi FK UNISBA 2017Nurul PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agents: University of Negros Occidental-RecoletosDocument66 pagesAdrenergic Agents: University of Negros Occidental-Recoletosmary grace trinidadNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentFrom EverandFast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Type I and Type IIDocument27 pagesHypersensitivity Type I and Type IISalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Scleroderma, Sjogren's SyndromeDocument31 pagesScleroderma, Sjogren's SyndromeSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Spinal SurgeryDocument19 pagesSpinal SurgerySalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Type I and Type IIDocument27 pagesHypersensitivity Type I and Type IISalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Normal Function of AnorectumDocument2 pagesNormal Function of AnorectumSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Rectal Prolapse: RectumDocument5 pagesRectal Prolapse: RectumSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Indication ContraindicatDocument2 pagesIndication ContraindicatSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Spread & Contagion by SlidesgoDocument7 pagesCOVID-19 Spread & Contagion by SlidesgoSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Anorectal Abscesses and FistulaDocument3 pagesAnorectal Abscesses and FistulaSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors: Drug Name Clinical Use Pharmacokineti Cs Cautions Adverse Effect Interactions HyperkalemiaDocument1 pageAce Inhibitors: Drug Name Clinical Use Pharmacokineti Cs Cautions Adverse Effect Interactions HyperkalemiaSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Emulsion LectureDocument30 pagesEmulsion LectureRay YangNo ratings yet
- Poster PresentationDocument3 pagesPoster PresentationNipun RavalNo ratings yet
- What Role Does Imagination Play in Producing Knowledge About The WorldDocument1 pageWhat Role Does Imagination Play in Producing Knowledge About The WorldNathanael Samuel KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems: Management Information Systems, 4 EditionDocument27 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Expert Systems: Management Information Systems, 4 Editionabhi7219No ratings yet
- English 9 Week 5 Q4Document4 pagesEnglish 9 Week 5 Q4Angel EjeNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Group 11 RRL, Proposed Title and Answers To The QuestionsDocument14 pagesPractical Research 2 Group 11 RRL, Proposed Title and Answers To The QuestionsFeby Margaret AngNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Educational Background Certification Major Name of Institute PeriodDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Educational Background Certification Major Name of Institute PeriodTHEVINESHNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument12 pagesJurnalSandy Ronny PurbaNo ratings yet
- TextdocumentDocument254 pagesTextdocumentSaurabh SihagNo ratings yet
- Th-Sunday Magazine 6 - 2Document8 pagesTh-Sunday Magazine 6 - 2NianotinoNo ratings yet
- GRADE 302: Element Content (%)Document3 pagesGRADE 302: Element Content (%)Shashank Saxena100% (1)
- 60 Plan of DepopulationDocument32 pages60 Plan of DepopulationMorena Eresh100% (1)
- System Administration ch01Document15 pagesSystem Administration ch01api-247871582No ratings yet
- Module 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentDocument19 pagesModule 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentRoxan Binarao-Bayot60% (5)
- TDS-11SH Top Drive D392004689-MKT-001 Rev. 01Document2 pagesTDS-11SH Top Drive D392004689-MKT-001 Rev. 01Israel Medina100% (2)
- Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyDocument15 pagesFaculty of Engineering & TechnologyGangu VirinchiNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebDocument4 pagesActivity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers DSPs S10Document16 pagesMicrocontrollers DSPs S10Suom YnonaNo ratings yet
- Jmac TempDocument5 pagesJmac TempDan GerNo ratings yet
- Bethelhem Alemayehu LTE Data ServiceDocument104 pagesBethelhem Alemayehu LTE Data Servicemola argawNo ratings yet
- Claudia Maienborn, Semantics, 381Document34 pagesClaudia Maienborn, Semantics, 381robert guimaraesNo ratings yet
- Chapter5A TorqueDocument32 pagesChapter5A TorqueShuq Faqat al-FansuriNo ratings yet
- His 101 Final ReportDocument15 pagesHis 101 Final ReportShohanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Online Games To The AcademicDocument20 pagesThe Impact of Online Games To The AcademicJessica BacaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 4 PDFMeloy ApiladoNo ratings yet
- The Hot Aishwarya Rai Wedding and Her Life.20130105.040216Document2 pagesThe Hot Aishwarya Rai Wedding and Her Life.20130105.040216anon_501746111100% (1)
- Major Chnage at Tata TeaDocument36 pagesMajor Chnage at Tata Teasheetaltandon100% (1)
- Chapter 5: Current and Resistance: 5.1 The Motion of Electric ChargeDocument11 pagesChapter 5: Current and Resistance: 5.1 The Motion of Electric Chargeayunna ayunniNo ratings yet
- Traulsen RHT-AHT Reach in Refrigerator WUT Glass DoorDocument2 pagesTraulsen RHT-AHT Reach in Refrigerator WUT Glass Doorwsfc-ebayNo ratings yet
- Porsche Dealer Application DataDocument3 pagesPorsche Dealer Application DataEdwin UcheNo ratings yet