Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1-Theory-of-Elasticity-PG-Course PDF
Uploaded by
ephOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1-Theory-of-Elasticity-PG-Course PDF
Uploaded by
ephCopyright:
Available Formats
Theory of Elasticity Chapter 1: Intruduction to Basic Terms
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO BASIC TERMS IN THEORY OF ELASTICITY
1.1 Background
1.2 Basic Terms in Elasticity
Theory of elasticity is concerned with the study of the response of elastic
bodies to the action of forces.
Objective of the study: to analyze the stresses and displacements of
structures or machine elements within the elastic range and there by to
check the sufficiency of their strength, stiffness and stability.
Thus, elasticity is the branch of solid mechanics which deals with the
stresses and deformations in elastic solids produced by external force or
changes in temperature.
Theory of elasticity differ form strength of materials by:
Strength of materials deals with stresses and displacements of
structures in the form of a bar system such as truss or rigid frames ,
whereas, when the structure considered is not in the form of a bar
such as blocks, plates, shells, dams and foundations, they are
analyzed only in theory of elasticity.
A thorough and precise analysis of a bar is only possible by theory of
elasticity.
Re- stating; Elasticity deals with mechanical properties of materials under
load particularly, material behavior to retain its original shape
(configuration) after subjection to load as opposed to plasticity.
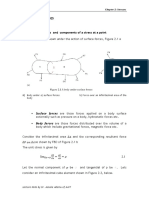
Consider the stress- strain relations of a given body under load as shown
Figure 1-1, below.
Lecture Note by Dr. Asnake Adamu of AAiT 1-1
Theory of Elasticity Chapter 1: Intruduction to Basic Terms
Stress
Permanent set
Strain
Figure 1-1 Stress- strain relation of an elastic body under load
Observation:
Linear relation between a force and deformation up to a point called
elastic limit
Force (stress) increase at a decreasing rate after the elastic limit.
Generally, a perfect elastic material of a body is assumed to
be homogenous and isotopic.
Homogenous refers to condition of a body where the material
continuously distributed over its volume so that the smallest element
cut from the body possesses the same specific physical properties.
Isotropic refers to a body where its elastic properties are same in all
directions
So far, no material as such is perfect elastic or plastic. However, for
practical reason some materials are considered nearly perfect elastic
such as steel and nearly perfect plastic such as rubber.
When the elastic properties of a material become different in different
direction the material of the body is termed as anisotropic.
Lecture Note by Dr. Asnake Adamu of AAiT 1-2
You might also like
- CE2134 (PPT) 1. Basic Concepts of FluidsDocument41 pagesCE2134 (PPT) 1. Basic Concepts of FluidsMiraJo-LingNo ratings yet
- Lab Report # 2Document6 pagesLab Report # 2zainyousafzai100% (1)
- Honors Physics I - Chapter 10: Thermodynamics 2013-2014 ExamDocument7 pagesHonors Physics I - Chapter 10: Thermodynamics 2013-2014 ExamPLAYVONo ratings yet
- Ib Physics ch12 PDFDocument2 pagesIb Physics ch12 PDFHansal Pravin KachharaNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Semi Circular ArchDocument3 pagesExperiment On Semi Circular ArchMukhriz Mansor50% (2)
- Som PDFDocument105 pagesSom PDFanon_10845568100% (1)
- Electrici Ty: Class - XDocument15 pagesElectrici Ty: Class - XHimanshu Garg100% (1)
- Structure Analysis - I Lab Manual: Prepared By: Parveen Berwal Approved By:dr - Arbinda SharmaDocument21 pagesStructure Analysis - I Lab Manual: Prepared By: Parveen Berwal Approved By:dr - Arbinda SharmaSaurabh SahuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics DistributedForcesDocument47 pagesEngineering Mechanics DistributedForcesChamith KarunadharaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Analysis of Statically Determinate StructuresDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Analysis of Statically Determinate StructuresDEEPAKNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Continum MechanicsDocument38 pagesFundamental of Continum MechanicsmssantNo ratings yet
- 053 - CE8021, CE6701 Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering - 2 Marks 2Document116 pages053 - CE8021, CE6701 Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering - 2 Marks 2Ankit Jose Antony0% (1)
- Problem Set No.1-MidtermDocument31 pagesProblem Set No.1-MidtermROYCE1983No ratings yet
- Stresses in BeamsDocument9 pagesStresses in BeamsAyad SlabyNo ratings yet
- Concrete Structures: Temesgen Wondimu, PHD Chapter 2: Strain-Compatibility Analysis of RC Sections Under BendingDocument25 pagesConcrete Structures: Temesgen Wondimu, PHD Chapter 2: Strain-Compatibility Analysis of RC Sections Under BendingAbrehaAbayNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-1 - 2-Mark Question and AnswersDocument10 pagesMechanics of Materials-1 - 2-Mark Question and AnswersSrikant PotluriNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Problems PDFDocument122 pagesStrength of Materials Problems PDF172Raisa Amilah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Collision of Elastic BodiesDocument19 pagesCollision of Elastic Bodiesviveksp99No ratings yet
- Fea QBDocument11 pagesFea QBPradeepNo ratings yet
- 2019 CE5320 Assignment 2Document2 pages2019 CE5320 Assignment 2sayan mukherjee0% (1)
- General Physics WorksheetDocument6 pagesGeneral Physics WorksheetDanielNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - DeflectionsDocument101 pagesUnit 4 - DeflectionsksrsunilNo ratings yet
- Overviews of StaticsDocument70 pagesOverviews of StaticsJacous Wcy100% (1)
- StrengthDocument5 pagesStrengthMUHAMMAD NURNAJMINo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument37 pagesEngineering Mechanicser_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics - SDOF - PpsDocument13 pagesStructural Dynamics - SDOF - PpsSai KumarNo ratings yet
- Time Series AnalysisDocument5 pagesTime Series AnalysisMaged Al-BarashiNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion - AurinoDocument38 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion - AurinoEngr AurinoNo ratings yet
- Som All Theory Question and Answers Shaikh Sir NotesDocument7 pagesSom All Theory Question and Answers Shaikh Sir NotesSwapnil JadhavNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument14 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodiesrachelle rivadullaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Slope and Deflection Strength of Materials - Part 1Document14 pagesChapter 8 Slope and Deflection Strength of Materials - Part 1Abhijith ShettyNo ratings yet
- PPT4. PlasticityIITKDocument70 pagesPPT4. PlasticityIITKKartik Shankar KumbhareNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Forces, Equilibrium: Chapter HighlightsDocument87 pagesIntroduction - Forces, Equilibrium: Chapter HighlightsJagannath MandalNo ratings yet
- Deflection by Energy MethodsDocument10 pagesDeflection by Energy MethodsMfonobong John EkottNo ratings yet
- Frequency of Free Damped Vibrations (Viscous Damping)Document8 pagesFrequency of Free Damped Vibrations (Viscous Damping)ذوالفقار علي حسينNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodsDocument14 pagesFinite Element MethodspriyaankNo ratings yet
- Rillej: Portlan'D Cement AssociationDocument328 pagesRillej: Portlan'D Cement AssociationCarlos PEREZ NEYRANo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Orifice Flow Lesson 1Document5 pagesModule 3 - Orifice Flow Lesson 1Aica AtendidoNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis LabDocument29 pagesStructural Analysis Labsamiee_meNo ratings yet
- جميع سلايدات الاستاتيكاDocument129 pagesجميع سلايدات الاستاتيكاDanaabdurNo ratings yet
- NIT - DURGAPUR Part-Time Admission To PHD ProgrammeDocument3 pagesNIT - DURGAPUR Part-Time Admission To PHD Programmeanne_sibiusNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of MaterialsDocument18 pagesMechanics of MaterialsSaad FaheemNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods and Computer ProgrammingDocument19 pagesNumerical Methods and Computer ProgrammingSabby OnindoNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of A Particle Part 1Document18 pagesEquilibrium of A Particle Part 1Casalta KennethNo ratings yet
- C9789810694364SM PDFDocument34 pagesC9789810694364SM PDFJohnrey FlandezNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 2015 by S K MondalDocument471 pagesStrength of Materials 2015 by S K MondalNaman Jain100% (1)
- Composite - Design ProjectDocument6 pagesComposite - Design ProjectSomen DasNo ratings yet
- Analysis of TrussesDocument2 pagesAnalysis of TrussesMelvin Esguerra50% (2)
- Formula Sheet For Exam 1Document1 pageFormula Sheet For Exam 1chris ricaNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain DiagramDocument4 pagesStress Strain DiagramMartine CastroNo ratings yet
- Statics and Strength of Materials Intro Beam AnalysisDocument69 pagesStatics and Strength of Materials Intro Beam AnalysisSam SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Machine ElementsDocument18 pagesStresses in Machine ElementsthirumalaikumaranNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument8 pagesElasticityGuru GuroNo ratings yet
- Plates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and AnalysisFrom EverandPlates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- My Days in Court: Travails and Hullabaloos in a UniversityFrom EverandMy Days in Court: Travails and Hullabaloos in a UniversityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Mechanical Properties of Materials ClassNoteDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties of Materials ClassNoteTousik IqbalNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Biomechanics SolutionDocument12 pagesModule 2 Biomechanics SolutionSnehasis RoutrayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Viscoelastic PropertiesDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Viscoelastic PropertiesGarry TaylorNo ratings yet
- 02 Strength of Materials IntroDocument19 pages02 Strength of Materials IntroEricka HuseñaNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. Physics - I Year: Djk1A: Properties of MatterDocument79 pagesB.Sc. Physics - I Year: Djk1A: Properties of MatterThatOneGuyNo ratings yet
- Elasticity (Mech Prop of Solids)Document30 pagesElasticity (Mech Prop of Solids)Jawan DiwaniiNo ratings yet
- Stress StrainDocument22 pagesStress StrainRinku RinkuNo ratings yet
- What Is ElasticityDocument2 pagesWhat Is Elasticityzhungjian586No ratings yet
- Current Changes To The Strength Grading of UK Softwoods-European HarmonisationDocument11 pagesCurrent Changes To The Strength Grading of UK Softwoods-European HarmonisationephNo ratings yet
- STL-01 Manufacturing and Fabrication of Steel 2020.21 I PDFDocument9 pagesSTL-01 Manufacturing and Fabrication of Steel 2020.21 I PDFephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Theory-of-Elasticity-PG-Course PDFDocument15 pagesChapter 2-Theory-of-Elasticity-PG-Course PDFephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Theory-of-Elasticity-PG-Course PDFDocument15 pagesChapter 4-Theory-of-Elasticity-PG-Course PDFephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Theory-of-Elasticity-PG-Course PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 3-Theory-of-Elasticity-PG-Course PDFephNo ratings yet
- CE6507 Steel Structures - Course Outline 2020.21 I MOD P4 PDFDocument1 pageCE6507 Steel Structures - Course Outline 2020.21 I MOD P4 PDFephNo ratings yet
- Slab Es en 1992-2015 PDFDocument4 pagesSlab Es en 1992-2015 PDFephNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Beam Slab and Staircase de PDFDocument4 pagesApproaches To Beam Slab and Staircase de PDFephNo ratings yet
- STL-02ii Plastic AnalysisDocument13 pagesSTL-02ii Plastic AnalysisephNo ratings yet
- One-Way Shear in Wide Concrete Beams With Narrow Supports: AuthorsDocument10 pagesOne-Way Shear in Wide Concrete Beams With Narrow Supports: AuthorsephNo ratings yet
- 62 Effect PDFDocument9 pages62 Effect PDFephNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Cost Variation in Solid and Hollow Floor Construction in Lagos StateDocument12 pagesAssessment of Cost Variation in Solid and Hollow Floor Construction in Lagos StateephNo ratings yet
- Beam Splice Worked Example PDFDocument5 pagesBeam Splice Worked Example PDFephNo ratings yet
- 00 FEM Part 1Document26 pages00 FEM Part 1ephNo ratings yet
- A Comparitive Study of Solid Slab With Ribbed Slab in Bale Robe Town Ethiopia PDFDocument8 pagesA Comparitive Study of Solid Slab With Ribbed Slab in Bale Robe Town Ethiopia PDFeph100% (2)
- A Study On Pushover Analysis Using Capacity Spectrum Method Based On Eurocode 8Document13 pagesA Study On Pushover Analysis Using Capacity Spectrum Method Based On Eurocode 8ephNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Flat Slab Vs Post Tensioned Flat SlabDocument4 pagesA Comparative Study of Flat Slab Vs Post Tensioned Flat SlabephNo ratings yet
- The Theory of The Strip Method For DesignDocument16 pagesThe Theory of The Strip Method For DesignephNo ratings yet
- Long-Term de Ections of Reinforced Concrete Elements: Accuracy Analysis of Predictions by Different MethodsDocument18 pagesLong-Term de Ections of Reinforced Concrete Elements: Accuracy Analysis of Predictions by Different MethodsephNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Redox Reactions Student VersionDocument34 pagesUnit 6 - Redox Reactions Student VersionAmadu sallieuNo ratings yet
- DC Corona Characteristics Derived From Corona Cage Tests and SimulationsDocument9 pagesDC Corona Characteristics Derived From Corona Cage Tests and SimulationsDimension JovenNo ratings yet
- L 5 The Normal CurveDocument37 pagesL 5 The Normal CurveAiza mae MontiagodoNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Factors Influencing Mycelium Based CompositesDocument9 pagesFabrication Factors Influencing Mycelium Based CompositesSander BroersNo ratings yet
- FLEXOGUM - Ver 2.0Document3 pagesFLEXOGUM - Ver 2.0Query TANo ratings yet
- FSC Physics 2 Year: Chapter 15: Electromagnetic InductionDocument15 pagesFSC Physics 2 Year: Chapter 15: Electromagnetic InductionAdeela UmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19-23 EHL Elliptical Conjunctions - ThermoHDL & ThermoEHLDocument86 pagesChapter 19-23 EHL Elliptical Conjunctions - ThermoHDL & ThermoEHLsatoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ADocument10 pagesModule 3 AProdyot SinhaNo ratings yet
- Bashir Et Al. 2019Document11 pagesBashir Et Al. 2019HariPJaishiNo ratings yet
- ZG NuclearDocument16 pagesZG NuclearSaad ChoukriNo ratings yet
- Terrameter-VES Rev5b CompressedDocument2 pagesTerrameter-VES Rev5b CompressedO6U Pharmacy RecordingsNo ratings yet
- Instruction Sheet: ExampleDocument5 pagesInstruction Sheet: ExampleMohammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Tuesday 12 May 2020: PhysicsDocument28 pagesTuesday 12 May 2020: Physicshanthi winkoNo ratings yet
- PG M.sc. Chemistry 344 21 Inorganic Chemistry-II MSC ChemistryDocument394 pagesPG M.sc. Chemistry 344 21 Inorganic Chemistry-II MSC ChemistryinuperuvaikalaNo ratings yet
- Batra Ring: DescriptionDocument2 pagesBatra Ring: DescriptionxzarrandikoNo ratings yet
- Consumer Schedule of TariffDocument2 pagesConsumer Schedule of TariffAbdullah NaeemNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements - Practice Sheet - (NSEC)Document4 pagesP Block Elements - Practice Sheet - (NSEC)aryanNo ratings yet
- Motion in A PlaneDocument15 pagesMotion in A PlaneLokeshNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics I (Math 1041) Worksheet IDocument2 pagesApplied Mathematics I (Math 1041) Worksheet IEphrata M MulualemNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 1Document2 pagesProblems Set 1suby0% (1)
- PH PDQ R ToyDocument22 pagesPH PDQ R ToysuchitchattiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Generation of High VoltageDocument20 pagesChapter-2 Generation of High VoltageYuusuf AbdirizakNo ratings yet
- Cable EntryDocument4 pagesCable EntryJandri JacobNo ratings yet
- Physics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensDocument16 pagesPhysics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensHemnathpalaniNo ratings yet
- Generator 61a88ffeadbc7Document307 pagesGenerator 61a88ffeadbc7jpkNo ratings yet
- MATRICESDocument18 pagesMATRICESPushkar GawadeNo ratings yet
- New Holland Excavator E70bsr Rops Tier3 en Service ManualDocument20 pagesNew Holland Excavator E70bsr Rops Tier3 en Service Manualphyliss100% (44)