Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control System Terminlogy
Control System Terminlogy
Uploaded by
mark amthonyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Control System Terminlogy
Control System Terminlogy
Uploaded by
mark amthonyCopyright:
Available Formats
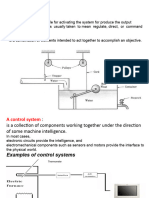
Control System Terminology
Desired Response – the idealised instantaneous behaviour that we would like from the
system.
Transient Response – the gradual change in the system as it approaches its
approximation of the desired response.
Steady-State Response – the response of the system once it has finished changing and is
now approximating the desired response.
Error – the difference between the input and the output of the system.
Steady-State Error – the difference between the steady-state response and the desired
response.
Stability – the ability of the system to settle into a steady-state response.
Controller – the part of the system that generates the input to the plant or process being
controlled.
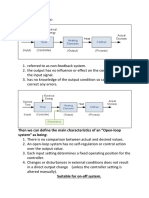
Open-Loop – a system that does not monitor its output. Open-loop systems can not
correct for disturbances.
Closed-Loop – a system that monitors its output and makes corrections to reduce error.
By monitoring the output the system can correct for disturbances.
Disturbance – a signal that is not modelled or calibrated in the system leading to
corruption of the expected behaviour.
Compensator – a system inserted into the controller to improve performance.
Feedback – a path that allows signals from the output of some sub-system to flow back
and affect the input of some sub-system earlier in the system signal path.
Robust – a system that will still work as expected with changes to the system parameters,
as might be caused by wear of components, or a change in behaviour with temperature.
You might also like
- FeedCon (Unit 1) PDFDocument17 pagesFeedCon (Unit 1) PDFAbby MacallaNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument2 pagesCompensationSneha NagarNo ratings yet
- Report SeminarDocument23 pagesReport SeminarpradnyaekadNo ratings yet
- ControllersDocument30 pagesControllersharitha vijiNo ratings yet
- Controller Comparison Close Loop Control SystemDocument4 pagesController Comparison Close Loop Control SystemKristine SecoyaNo ratings yet
- Control System 1Document29 pagesControl System 1Gabriel GalizaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-3Document48 pagesLesson 1-3T ENGANo ratings yet
- Alvarez Johndave Bsece412 Ass#1Document4 pagesAlvarez Johndave Bsece412 Ass#1MelanieNo ratings yet
- Lcs Unit 1 PDFDocument30 pagesLcs Unit 1 PDFRajasekhar AtlaNo ratings yet
- Unit I NotesDocument43 pagesUnit I Notesaravinth69601No ratings yet
- Server Mechanisms in Control TheoryDocument4 pagesServer Mechanisms in Control Theoryhadiakhalid.34No ratings yet
- Topic 1: Introduction To Control System and Mathematical ReviewDocument43 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To Control System and Mathematical ReviewFaez FeakryNo ratings yet
- Control System ModelingDocument24 pagesControl System ModelingSiva Bala KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Introduction PDFDocument7 pagesIntroduction PDFSandeep B RNo ratings yet
- Introduction 23Document16 pagesIntroduction 23Ggfgsgege GegsgsNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop ResponseDocument8 pagesClosed Loop ResponseJoydeep Choudhury 20UCH030No ratings yet
- Unit IDocument42 pagesUnit Irajavelan.mNo ratings yet
- Process Control SystemsDocument6 pagesProcess Control SystemsRae angelo AgonoyNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control Systems: Engr. Joey P. Sarmiento, PECEDocument160 pagesFeedback and Control Systems: Engr. Joey P. Sarmiento, PECERAINIER RamosNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument279 pagesControlNandakishore PradeepNo ratings yet
- Control System OEDocument4 pagesControl System OERanjan MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control SystemDocument45 pagesIndustrial Control Systemyash_ganatraNo ratings yet
- 002 PDFDocument9 pages002 PDFTrisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Control Engineering & Instrumentation Assignment # 01 Submitted By: Syed Hamza Zulfiqar Reg # 620/BSME/f16 (B)Document12 pagesControl Engineering & Instrumentation Assignment # 01 Submitted By: Syed Hamza Zulfiqar Reg # 620/BSME/f16 (B)Hamza zulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control Systems - Part 2Document9 pagesIntroduction To Control Systems - Part 2Trisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Open Loop SystemDocument4 pagesOpen Loop Systemumar almoqidNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignDocument14 pagesTopic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignxREDCivicCometxNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics NotesDocument90 pagesMechatronics NotesSanskar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 EditDocument5 pagesChapter 1 EditMohd Farhan SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Topic 5-Types of FeedbackDocument31 pagesTopic 5-Types of FeedbackBautista, Aljhon G.No ratings yet
- Control Systems Two Marks QuestionDocument41 pagesControl Systems Two Marks QuestionSk WajuddinNo ratings yet
- controlICS CH1Document5 pagescontrolICS CH1Magarsaa Qana'iiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control Chapter 1Document19 pagesIndustrial Control Chapter 1Qayyum AqasyahNo ratings yet
- Obor - Prelim-Exam-for-Feedback-and-Control-SystemDocument5 pagesObor - Prelim-Exam-for-Feedback-and-Control-SystemDhikbuttNo ratings yet
- Ingeniería de Control: 1. Examen Unidad 1Document3 pagesIngeniería de Control: 1. Examen Unidad 1Luis Fernando Mena HernándezNo ratings yet
- 001 Feedback and CONTROL SYSTEMS - NotesDocument10 pages001 Feedback and CONTROL SYSTEMS - NotesJeremiahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automatic ControlDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Automatic ControlFatih YıldızNo ratings yet
- LESSON1 IntroToControlSystemDocument10 pagesLESSON1 IntroToControlSystemalexancog456No ratings yet
- Prelim-MODULE 4Document5 pagesPrelim-MODULE 4Celimen, John Renz C.No ratings yet
- Linear Control System: Presented by Imran Basha SyedDocument35 pagesLinear Control System: Presented by Imran Basha SyedSyed Imran BashaNo ratings yet
- Ec3351 Control SystemsDocument18 pagesEc3351 Control SystemsParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Control Systems PPT 1Document27 pagesControl Systems PPT 1sad soulNo ratings yet
- EE2253 - Control Systems PDFDocument124 pagesEE2253 - Control Systems PDFaduveyNo ratings yet
- First Order Control System: Module Name: Industrial Processes Module Code: Etu 08201 Group MembersDocument8 pagesFirst Order Control System: Module Name: Industrial Processes Module Code: Etu 08201 Group MembersGhubaida HassaniNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Assignment - 1Document6 pagesMechatronics Assignment - 1SARTHAK JAINNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control SystemDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Assignment Control 615.Document12 pagesAssignment Control 615.Hamza zulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Rev. in Auto Contol SystemDocument2 pagesRev. in Auto Contol SystemChristopher AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Assignment Understanding Servomechanism in Control TheoryDocument3 pagesAssignment Understanding Servomechanism in Control Theoryhadiakhalid.34No ratings yet
- IntroDocument2 pagesIntroJoe Marie ValcarcelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control Systems: Unit - 1Document19 pagesIntroduction To Control Systems: Unit - 1Vimala ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- Examples of Control Systems:: Lecture OneDocument4 pagesExamples of Control Systems:: Lecture OnemornyNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - 1Document3 pagesLab 1 - 1ahmed elesilyNo ratings yet
- Close & Open Loop SystemDocument6 pagesClose & Open Loop SystemAdonis NicolasNo ratings yet
- اسس هندسة السيطرة النظري-مرحلة ثالثة-قسم هندسة تقنيات الحاسوبDocument80 pagesاسس هندسة السيطرة النظري-مرحلة ثالثة-قسم هندسة تقنيات الحاسوبطيبه محمد احمد حمد هندسة تقنيات الحاسوبNo ratings yet
- Week1 KendaliDocument71 pagesWeek1 KendaliChairul FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives - Motor Controllers and Control SystemsDocument11 pagesElectric Drives - Motor Controllers and Control SystemsRam KumarNo ratings yet
- University of Mindanao, Matina, Davao CityDocument3 pagesUniversity of Mindanao, Matina, Davao CityJohn Carlo PagaraNo ratings yet
- Semi-Markov Models: Control of Restorable Systems with Latent FailuresFrom EverandSemi-Markov Models: Control of Restorable Systems with Latent FailuresNo ratings yet