Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 7 Post Lab (AutoRecovered)
Uploaded by
Maisy BrouilletteOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 7 Post Lab (AutoRecovered)
Uploaded by
Maisy BrouilletteCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 7 Post Lab Assignment
Name: Maisy Brouillette
1. Complete the following tables. Replace the volumes given in each table with the volumes that
you actually recorded in your lab notebook. Note that 1 mmol = 10-3 mol
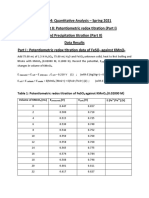
Table 1: Titration of 10 mL of 0.1 M HCl with 0.1 M NaOH
mL NaOH mmol NaOH pH
0.00 0.00 1.65
1.00 0.100 1.84
2.05 0.205 1.94
3.15 0.315 2.02
4.00 0.400 2.08
5.00 0.500 2.20
6.00 0.600 2.35
7.05 0.705 2.82
8.00 0.800 6.26
9.05 0.905 7.75
10.00 1.000 11.21
11.00 1.100 11.51
12.10 1.210 11.64
13.00 1.300 11.74
14.05 1.405 11.85
15.05 1.505 11.89
Table 2: Titration of 10 mL of 0.1 M KHP with 0.1 M NaOH
mL NaOH mmol NaOH pH
0.00 0.00 4.22
1.00 0.100 4.31
2.05 0.205 4.73
3.00 0.300 4.80
4.00 0.40 5.13
5.05 0.505 5.06
6.10 0.610 5.23
7.05 0.705 5.40
8.00 0.800 5.59
9.10 0.910 6.05
10.05 1.005 6.34
11.05 1.105 7.50
12.15 1.215 11.46
13.05 1.305 11.89
14.15 1.415 12.07
15.10 1.510 12.21
Table 3: Titration of 20 mL of Buffer Solution with 0.1 M NaOH
mL NaOH mmol NaOH pH
0.00 0.000 5.05
1.00 0.100 5.12
1.95 0.195 5.27
2.95 0.295 5.42
4.05 0.405 5.68
5.00 0.500 5.95
6.00 0.600 6.75
6.95 0.695 11.29
7.95 0.795 11.94
8.95 0.895 12.18
9.95 0.995 12.32
Table 4: Titration of 20 mL of Buffer Solution with 0.1 M HCl
mL NaOH mmol NaOH pH
0.00 0.000 5.06
1.00 0.100 5.00
2.00 0.200 4.90
3.00 0.300 4.79
4.00 0.400 4.69
5.00 0.500 4.68
6.00 0.600 4.46
7.00 0.700 4.31
8.00 0.800 4.14
9.00 0.900 3.96
10.00 1.000 3.76
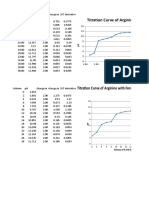
2. For each of these tables, construct a graph of pH vs. amount of titrant in mmol following the
given example. Make sure figure captions accurately reflect what is being shown in graph.
pH
mmol
Figure 1: Titration of 10 mL of M
of 0.1 NaOH
HCl with 0.1 M NaOH.
Figure 2: Titration of 10 mL of 0.1 M KHP with 0.1 M NaOH.
Figure 3: Titration of 20 mL of Buffer Solution with 0.1 M NaOH
Figure 4: Titration of 20 mL of Buffer Solution with 0.1 M HCl
3. Use the pH of the buffer solution to calculate its pK a. Show work.
pH =pKa + log [A-/AH]
pKa=pH - log [A-/AH] = 5.05 – log [0.1/0.1]
pKa=5.05
4. (a) How many moles of NaOH does it take to completely consume the conjugate acid in the
buffer? Show work.
pH =pKa + log [A-/AH]
7=5.05 + log [x/.0075]
x=2.81*10--5
(b) How many moles of HCl does it take to completely consume the conjugate base in the buffer?
Show work.
7=5.05 + log [.0025/x]
X=0.22 mol
5. From a chemistry perspective, explain the trends observed in each graph. Be sure to reference
which figure you’re discussing for clarity (i.e. “In Figure 1, the pH of the solution remains fairly
constant with added NaOH until…”). Make sure you provide a rationale for the shape and trend
for each graph. Do the graphs in Figures 3 and 4 reflect your answers to question 4? Explain.
In 1, 2, and 3, the standard steep jump with most buffers is followed. In one its constant unitl just
over two then jumps to about 11. In 2 and 3 its constant until 7 then jumps to about 11 or 12. In 4
however, the pH steadily decreases with no jump, which is expected for an acid + a buffer.
You might also like
- DkaDocument4 pagesDkaAlif Alfarisyi SyahNo ratings yet
- Chem300Quiz 2ChEA LibutlibutDocument15 pagesChem300Quiz 2ChEA LibutlibutEredson LibutlibutNo ratings yet
- CH Lab 3Document8 pagesCH Lab 3Mohammad Fahim NurNo ratings yet
- 25.00 ML of 0.1000M Na2Co3 (Sodium Carbonate) With 0.1000 M HCLDocument3 pages25.00 ML of 0.1000M Na2Co3 (Sodium Carbonate) With 0.1000 M HCLtriple aNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Indicators Lab ReportDocument6 pagesAcid Base Indicators Lab Reportmuskaan0% (2)
- Lab Report BoiDocument7 pagesLab Report BoiNORHIDAYATI BINTI MD GHAZALI MoeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document6 pagesExperiment 2Sinichi IzumiNo ratings yet
- ErlisDocument8 pagesErlisHenry Escorcia AhumadaNo ratings yet
- Estandarización Potenciométrica de Naoh: Masa de Biftalato (G) Gasto V1 (Según 2° Derivada) (ML)Document22 pagesEstandarización Potenciométrica de Naoh: Masa de Biftalato (G) Gasto V1 (Según 2° Derivada) (ML)WILLY DANY MELGAREJO ROMERONo ratings yet
- Acid - Base TitrationDocument21 pagesAcid - Base TitrationketantchaudhariNo ratings yet
- PH V PH V: TitranDocument4 pagesPH V PH V: TitranStephen BagunaNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 Weak Base Strong Acid Lab ReportDocument6 pagesChem 2 Weak Base Strong Acid Lab ReportMohammad Izadi100% (1)
- CHM204 - Lab Report 2Document11 pagesCHM204 - Lab Report 2Romy MansourNo ratings yet
- Informe 7Document6 pagesInforme 7Alonzo Alexandro Manyari DionicioNo ratings yet
- Anthony M. Wachinski - Environmental Ion Exchange - Principles and Design-Taylor & Francis, Chapman and Hall - CRC (2016) (1) (138-157)Document20 pagesAnthony M. Wachinski - Environmental Ion Exchange - Principles and Design-Taylor & Francis, Chapman and Hall - CRC (2016) (1) (138-157)HARDY EDDISONNo ratings yet
- AP CHEM Lab Acid Base Titration PDFDocument4 pagesAP CHEM Lab Acid Base Titration PDFMelnykNo ratings yet
- Report CRE01Document7 pagesReport CRE01munazziliitdNo ratings yet
- How Can I Make A 4N Naoh Solution From Naoh With M 40G/Mol?: Titratable Acidity - TaDocument4 pagesHow Can I Make A 4N Naoh Solution From Naoh With M 40G/Mol?: Titratable Acidity - TaYusiNurmaNo ratings yet
- Buffer Solution ChallengeDocument1 pageBuffer Solution ChallengeRhita TamaleNo ratings yet
- Report - Cation ExchangerDocument5 pagesReport - Cation ExchangerMai HoangNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet Program For Calculating The PH - Coagulant Dosage RelationshipDocument7 pagesSpreadsheet Program For Calculating The PH - Coagulant Dosage RelationshipMohamed TallyNo ratings yet
- Concentración de Equilibrio de Adsorbato Cantidad Específica de Equilibrio de AdsorbatoDocument5 pagesConcentración de Equilibrio de Adsorbato Cantidad Específica de Equilibrio de AdsorbatoDayNo ratings yet
- Report Form PE1Document10 pagesReport Form PE1st19000941No ratings yet
- Grafik PH/V No. Volume Naoh (ML) PH PH/VDocument2 pagesGrafik PH/V No. Volume Naoh (ML) PH PH/VCHERLLIN EVANIANo ratings yet
- V Naoh (ML) PH Volumen Promedio Primera Derivada Volumen PromedioDocument10 pagesV Naoh (ML) PH Volumen Promedio Primera Derivada Volumen PromedioCRISTIAN VILLARRAGA SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Komputasi Kelompok Pert.5Document3 pagesKomputasi Kelompok Pert.5Rodi AnaNo ratings yet
- Strong Acid With Strong Base Titration: Titrant's VolumeDocument9 pagesStrong Acid With Strong Base Titration: Titrant's VolumeKang MustofaNo ratings yet
- Data Results Lab 8Document5 pagesData Results Lab 8Jane RihanNo ratings yet
- Practical Considerations For Conductivity and Total Dissolved Solids MeasurementDocument5 pagesPractical Considerations For Conductivity and Total Dissolved Solids MeasurementVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Disassociation Constant Estimation Using Acetic Acid and Sodium Hydroxide TitrationDocument19 pagesDisassociation Constant Estimation Using Acetic Acid and Sodium Hydroxide Titrationwani280475% (4)
- Exer 2 Post-Lab ReportDocument6 pagesExer 2 Post-Lab ReportKin DemoticaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Titration CurveDocument3 pagesGroup 4 Titration CurveEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Δ Ph Δ vol naoh Δ pH/ Δ vol naohDocument3 pagesΔ Ph Δ vol naoh Δ pH/ Δ vol naohJoel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Results and Data CMT 463 Exp 3Document7 pagesResults and Data CMT 463 Exp 3IzzyanIsaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Btech 10687 21 - Hitesh - Rathi 1Document4 pagesExperiment 3 - Btech 10687 21 - Hitesh - Rathi 1gvjbhknlkmNo ratings yet
- Foster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Document7 pagesFoster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Cole FosterNo ratings yet
- TItrasi Potensiometri PH MetriDocument19 pagesTItrasi Potensiometri PH MetriNabila Putri SabilaNo ratings yet
- Chem 2673 Lab 7CDocument6 pagesChem 2673 Lab 7CManda BaboolalNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 SBLDocument13 pagesLab 2 SBLapi-384770852No ratings yet
- Graficas Acido.Document3 pagesGraficas Acido.jessica valenciaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kimia AnalitikDocument6 pagesTugas Kimia AnalitikIbal LaodeNo ratings yet
- CH Lab 6Document7 pagesCH Lab 6Mohammad Fahim NurNo ratings yet
- Curva de Valoración Ácido-BaseDocument9 pagesCurva de Valoración Ácido-BaseMadgiel Adriano MallquiNo ratings yet
- Purcei Prestarter2017Document4 pagesPurcei Prestarter2017Luca GrigorasNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios AnalisisDocument9 pagesEjercicios AnalisisAndrea Frias AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Report: Standardization of A Strong Acid (HCL) With A Strong Base (Naoh) .Document7 pagesPost Lab Report: Standardization of A Strong Acid (HCL) With A Strong Base (Naoh) .Mohammad Fahim NurNo ratings yet
- Batch ReactorDocument16 pagesBatch ReactorZharifah Bari'ah Basa'ahNo ratings yet
- Titration Curve of Aspartic Acid Against 0.2M NaohDocument3 pagesTitration Curve of Aspartic Acid Against 0.2M NaohEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Ka Lab Extra Material DoneDocument12 pagesKa Lab Extra Material DoneAbu Sufyan ButtNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 PH and BufferDocument7 pagesExperiment 2 PH and Bufferjayco sonNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Formulasi Dan Teknologi Sediaan Solida Formulasi Tablet Ibuprofen Metode Granulasi BasahDocument5 pagesLaporan Praktikum Formulasi Dan Teknologi Sediaan Solida Formulasi Tablet Ibuprofen Metode Granulasi BasahiraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Ternary Phase Diagram (Liquid-Liquid Extraction)Document15 pagesExperiment 3: Ternary Phase Diagram (Liquid-Liquid Extraction)Noor Nasuha Noor Ariffin100% (1)
- Titrimetric Analysis of An Amino AcidDocument15 pagesTitrimetric Analysis of An Amino Acidapi-535149918No ratings yet
- Tarea E L-LDocument4 pagesTarea E L-LRoco neluNo ratings yet
- Physical Organic 1 Post-LabDocument7 pagesPhysical Organic 1 Post-LabsamNo ratings yet
- SpecDocument8 pagesSpecJirapat ThonglekpechNo ratings yet
- Grafik UtsDocument8 pagesGrafik UtsRodi AnaNo ratings yet
- Unknown Analysis LabDocument9 pagesUnknown Analysis LabTrixie LeNo ratings yet
- Tabla de FrecuenciasDocument14 pagesTabla de FrecuenciasAiner ShuanNo ratings yet
- Math Practice Simplified: Decimals & Percents (Book H): Practicing the Concepts of Decimals and PercentagesFrom EverandMath Practice Simplified: Decimals & Percents (Book H): Practicing the Concepts of Decimals and PercentagesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- DS - Senna ConcentrateDocument7 pagesDS - Senna ConcentrateFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- 7088-Unit 1 A Guide To The IALA MBS 1 An Introduction To The IALA MBSDocument5 pages7088-Unit 1 A Guide To The IALA MBS 1 An Introduction To The IALA MBSZuri MpowerNo ratings yet
- R1807005-SCE Monthly Disconnect Data Report January 2024Document23 pagesR1807005-SCE Monthly Disconnect Data Report January 2024Rob NikolewskiNo ratings yet
- BEKS - Annual Report - 2017 - Revisi PDFDocument596 pagesBEKS - Annual Report - 2017 - Revisi PDFWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- TDS - Paper WS - Lecta Creaset HWS - ENDocument2 pagesTDS - Paper WS - Lecta Creaset HWS - ENSundar MoorthiNo ratings yet
- Stated ModulDocument3 pagesStated Modulweldy kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of Date PalmDocument12 pagesProduction Technology of Date PalmAkash Tahir100% (2)
- Coach Bud WinterDocument4 pagesCoach Bud WinterPasquale Belluscifotografo100% (1)
- VAKSINDocument29 pagesVAKSINLeonardo LiswojoNo ratings yet
- 24 - Metor 6E DatasheetDocument2 pages24 - Metor 6E DatasheetCharles LiNo ratings yet
- Tabel-Thermo Gas Hasil Pmbakaran Cengel (SI-18 HLM)Document18 pagesTabel-Thermo Gas Hasil Pmbakaran Cengel (SI-18 HLM)rasid redNo ratings yet
- (Anita E. Kelly (Auth.) ) The Psychology of SecretsDocument268 pages(Anita E. Kelly (Auth.) ) The Psychology of SecretsYsa CatNo ratings yet
- Cadbury Operations ProjectDocument28 pagesCadbury Operations Projectparulhrm80% (5)
- Wheat Crop Development in Central Punjab (Faisalabad, 2020 - 21)Document32 pagesWheat Crop Development in Central Punjab (Faisalabad, 2020 - 21)Fuzail KhanNo ratings yet
- Pune CME 2011 BrochureDocument4 pagesPune CME 2011 BrochuredrpajaniNo ratings yet
- An Exercise On Cost-Benefits Analysis: Category Details Cost in First YearDocument3 pagesAn Exercise On Cost-Benefits Analysis: Category Details Cost in First YearPragya Singh BaghelNo ratings yet
- Final Annual Report 2018Document31 pagesFinal Annual Report 2018Nirmal Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Boiler & Turbine Efficiency: Rohit Verma Dy - Director NPTI, FaridabadDocument77 pagesBoiler & Turbine Efficiency: Rohit Verma Dy - Director NPTI, FaridabadLakshya Soni100% (3)
- RQ - RP - RPT & FBNDocument35 pagesRQ - RP - RPT & FBNSlim.B100% (2)
- Love Always, Kate (Love Always - D.Nichole King PDFDocument763 pagesLove Always, Kate (Love Always - D.Nichole King PDForquesta110% (1)
- 01 Rev C Brochure Tissue Tek Cryo3 Flex CryostatDocument5 pages01 Rev C Brochure Tissue Tek Cryo3 Flex CryostatRuben ArismendiNo ratings yet
- Adjectives - ED or - ING Exercise: A Fill The Gaps With The Adjectives in BracketsDocument2 pagesAdjectives - ED or - ING Exercise: A Fill The Gaps With The Adjectives in BracketsYoNo ratings yet
- (L) Io 360 M1a Parts Catalog PC Lio 360 M1aDocument81 pages(L) Io 360 M1a Parts Catalog PC Lio 360 M1aMo HoNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid 0808Document72 pagesBasic First Aid 0808BS AnilKumarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Different Extraction Methods On Some PropertiesDocument13 pagesEffects of Different Extraction Methods On Some PropertiesDizon, Sean Andrei S.No ratings yet
- FP - FPX Fristam FP742 Curvebook R4Document48 pagesFP - FPX Fristam FP742 Curvebook R4Chemikal EngineerNo ratings yet
- 15 - 16 Lean Management (Final)Document63 pages15 - 16 Lean Management (Final)Aquilando David Mario SimatupangNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industry of PakistanDocument30 pagesSugar Industry of Pakistanadnaneconomist100% (9)
- Jewish Standard, February 26, 1016Document56 pagesJewish Standard, February 26, 1016New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System & Major Organs (1-4)Document6 pagesEndocrine System & Major Organs (1-4)april lou andrea sorillaNo ratings yet