Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GIS Module 3
Uploaded by
Rose Marie SalazarCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGIS Module 3
Uploaded by
Rose Marie SalazarModule 3
Let’s Get Started (Diagnostic Test)
1. D.
2. D.
3. D.
4. D.
5. D.
6. D.
7. D.
8. D.
9. D.
10. D.
Let’s Get Started (Activity)
1. What is the difference between data and information?
Data does not have any specific purpose whereas Information carries a meaning
that has been assigned by interpreting data.
2. What are the differences between spatial and attribute data?
Spatial data refers to the shape, size and location of the feature while attribute
data is information appended in tabular format to spatial features.
3. Identify each of the files in Table 3.1 according to their extension.
filename.txt - TXT is a file extension for a text file and it indicates the file is a text
document.
filename.doc - is used by the Microsoft Word program.
filename.pdf - stands for the Portable Document Format
filename.jpg - digital image format
filename.tif - stands for “Tagged Image Format File” and used for professional
photography.
filename.html – used to create web pages
filename.xml - stands for Extensible Markup Language.
filename.zip – compressed archive
4. Search for and download three different simple text or flat files. Open them in a word
processor and spreadsheet program. Use the search and replace function to change the
delimiters (e.g., from commas to tabs or vice versa).
5. The US Bureau of Census distributes geospatial data as TIGER files. What are they?
The geodatabases contain national coverage (for geographic boundaries or
features) or state coverage (boundaries within state). These files do not include
demographic data, but they contain geographic entity codes that can be linked
to the Census Bureau’s demographic data
6. Identify resources and websites on the Internet that can help you make sense of file
extensions.
https://www.yourhtmlsource.com/starthere/fileformats.html
Let’s Get Started (Activity)
1. What are the costs and benefits of using primary data instead of secondary data?
Resolve specific research issues.
Better accuracy.
A higher level of control.
Up-to-date information.
You are the owner of the information
2. Refer to the Federal Geographic Data Committee website (http://www.fgdc.gov) and
describe in detail what information should be included in a metadata file. Why are
metadata and standards important?
Metadata helps users find relevant information and discover resources. Using a
standards-based approach, organizing the data helps ensure interoperability
between systems, and also increases data discovery and access.
Let’s Get Started (Activity)
1. Identify five possible sources for data on the gross domestic product (GDP) for the
countries in Africa.
https://www.imf.org/en/Countries/ZAF
https://tradingeconomics.com/country-list/gdp?continent=africa
https://www.statista.com/statistics/240665/gdp-of-africa/
https://data.oecd.org/gdp/gross-domestic-product-gdp.htm
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1120999/gdp-of-african-countries-by-
country/
2. Identify two sources for geographic data (boundary files) for Africa.
https://www.nasa.gov/
https://www.usgs.gov/
3. What kind of geographic data does the United Nations provide?
Spatial data infrastructures provide the institutional and technical foundation of
policies, standards and procedures that enable organizations and information
systems to interact in a way that facilitates spatial data discovery, evaluation and
applications.
You might also like
- Big Data AnalyticsDocument64 pagesBig Data AnalyticsSameer MemonNo ratings yet
- Internal 1Document19 pagesInternal 1TKKNo ratings yet
- Organizing Data and Information in DatabasesDocument7 pagesOrganizing Data and Information in DatabasesJulienne SisonNo ratings yet
- Topic 3-4 Information Systems ArchitectureDocument13 pagesTopic 3-4 Information Systems Architecturevincent waithakaNo ratings yet
- BIG DATA 1 Unit.docxDocument17 pagesBIG DATA 1 Unit.docxIshika SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 DSDocument12 pagesUnit 2 DSMalik SahabNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 1Document10 pagesUnit 1 1Sahil DhakadNo ratings yet
- Basic of Intelligence BusinessDocument5 pagesBasic of Intelligence BusinessDhivena JeonNo ratings yet
- Fake VideoDocument25 pagesFake VideoSalman AwanNo ratings yet
- Unit-1-Part1-Big Data Analytics and ToolsDocument12 pagesUnit-1-Part1-Big Data Analytics and ToolsAlekhya AbbarajuNo ratings yet
- GIS Database Creation and DesignDocument24 pagesGIS Database Creation and DesignAbubakar Aminu UsmanNo ratings yet
- Tutorials For TRI and QGISDocument24 pagesTutorials For TRI and QGISDoddy Pratama PNo ratings yet
- Updated Unit-2Document55 pagesUpdated Unit-2sc0% (1)
- Data and Business Intelligence Module OverviewDocument17 pagesData and Business Intelligence Module OverviewClariza PascualNo ratings yet
- Pasion, Kaye Lianne G. Relos, Yella Mae P. Santos, Monica Sophia LDocument32 pagesPasion, Kaye Lianne G. Relos, Yella Mae P. Santos, Monica Sophia LYella Mae Pariña RelosNo ratings yet
- Database Design and ComponentsDocument11 pagesDatabase Design and ComponentsPurnima GoyalNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram for Mahindra Sona Dispatch DatabaseDocument10 pagesER Diagram for Mahindra Sona Dispatch Databasesagarvk70No ratings yet
- Files Yedai Handout # 1Document10 pagesFiles Yedai Handout # 1Jersel MitchellNo ratings yet
- DB Managment Ch1Document4 pagesDB Managment Ch1Juan Manuel Garcia NoguesNo ratings yet
- Recode 5 DHSDocument144 pagesRecode 5 DHSMiguel CrisNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Data Preprocessing and VisualizationDocument15 pagesModule 2 - Data Preprocessing and VisualizationRaiza AnancaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document6 pagesHomework 2Fatih OlukNo ratings yet
- Korallys Rodríguez October 15, 2021. Prof. Donato COMP 4400Document2 pagesKorallys Rodríguez October 15, 2021. Prof. Donato COMP 4400Korallys RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ModuleDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Modulejhell dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Data, fields, records and files explainedDocument6 pagesData, fields, records and files explainedaim_nainaNo ratings yet
- HW-1 Answers DBMT KeyDocument9 pagesHW-1 Answers DBMT Keykarthikeyan RNo ratings yet
- Data Science IntroductionDocument82 pagesData Science IntroductionAbhi GiriNo ratings yet
- 1 Theories and Applications of Database ManagementDocument7 pages1 Theories and Applications of Database ManagementShad Mad Stephen CakirNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Unit-I Why We Need Data Mining?Document21 pagesSyllabus: Unit-I Why We Need Data Mining?Pradeepkumar 05No ratings yet
- Big Data: Presented By, Nishaa RDocument24 pagesBig Data: Presented By, Nishaa RNishaaNo ratings yet
- Big Data NotesDocument68 pagesBig Data NotesDrKrishna Priya ChakireddyNo ratings yet
- Data StructureDocument4 pagesData Structureamaravathi RNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document19 pagesUnit 1thakursahabonhunt1No ratings yet
- DBMS Total NotesDocument283 pagesDBMS Total NotesSpandana SpandanaNo ratings yet
- Geodata Management: Responsible Persons: Andreas Neumann Helen Freimark Andreas WehrleDocument26 pagesGeodata Management: Responsible Persons: Andreas Neumann Helen Freimark Andreas WehrleSyed Shadab Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Hand Book: Ahmedabad Institute of TechnologyDocument103 pagesHand Book: Ahmedabad Institute of TechnologyBhavik SangharNo ratings yet
- BigData, Data Mining and Machine Learning Ch1&2Document5 pagesBigData, Data Mining and Machine Learning Ch1&2aswagadaNo ratings yet
- Types of digital data and Big Data characteristicsDocument136 pagesTypes of digital data and Big Data characteristicsVani MittalNo ratings yet
- DataspacesDocument4 pagesDataspaceskatherine976No ratings yet
- CH 9Document23 pagesCH 9ankita_malik_2No ratings yet
- Unit-1 DWDMDocument20 pagesUnit-1 DWDMsanjayktNo ratings yet
- BIG Data AnalyticsDocument17 pagesBIG Data AnalyticsPawanNo ratings yet
- CC Becse Unit 4 PDFDocument32 pagesCC Becse Unit 4 PDFRushikesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Fbda Unit-1Document17 pagesFbda Unit-1Anonymous iWeSkVpNo ratings yet
- Metadata To Support Archived Data Management Systems: Standard Practice ForDocument64 pagesMetadata To Support Archived Data Management Systems: Standard Practice Fordannychacon27No ratings yet
- Data Structures, Database Models, and Concepts ExplainedDocument3 pagesData Structures, Database Models, and Concepts ExplainedGary0% (1)
- Module 2 Review Questions PDFDocument2 pagesModule 2 Review Questions PDFWilson LohNo ratings yet
- National Spatial Data Infrastructure: Concepts and ComponentsDocument46 pagesNational Spatial Data Infrastructure: Concepts and Componentsholasa666No ratings yet
- MSTK Tool 10d: Data Management Best PracticesDocument2 pagesMSTK Tool 10d: Data Management Best PracticesNaveed UllahNo ratings yet
- Big Data AnalyticsDocument21 pagesBig Data AnalyticsAasim SaifiNo ratings yet
- Managing Knowledge For Strategic Business Analysts: The Executive Information PortalDocument18 pagesManaging Knowledge For Strategic Business Analysts: The Executive Information PortalVarun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument14 pagesChapter TwoTade GaromaNo ratings yet
- Database ConceptsDocument27 pagesDatabase ConceptsIrfanullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introductory To Data AnalyticsDocument11 pagesLecture 1 - Introductory To Data AnalyticsZakwan WanNo ratings yet
- Recode6 DHS 22march2013 DHSG4Document171 pagesRecode6 DHS 22march2013 DHSG4Mawasumi Ayu AndiniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Database System: October 2019Document31 pagesFundamentals of Database System: October 2019Oh Den NiNo ratings yet
- DatabasesDocument31 pagesDatabasesFaraz HumayunNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Big Data Analytics in The IndustryDocument15 pagesThe Influence of Big Data Analytics in The IndustrymikhailovaelyaNo ratings yet
- Data Science and Big Data overviewDocument6 pagesData Science and Big Data overviewDaniel VasconcellosNo ratings yet
- Pre-Proposal Project Title & Statements Name: Subject Code & Description / Time & DayDocument2 pagesPre-Proposal Project Title & Statements Name: Subject Code & Description / Time & DayRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Health & Safety: Equipment/Task NameDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Health & Safety: Equipment/Task NameRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
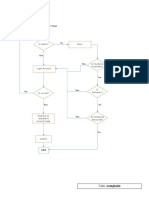
- Flowchart Case 5Document1 pageFlowchart Case 5Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- CommodityCodes For WebsiteDocument344 pagesCommodityCodes For WebsiteRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document4 pagesLesson 2Rose Marie Salazar100% (2)
- ThreeDocument2 pagesThreeRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- ReviseDocument4 pagesReviseRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- InfoDocument3 pagesInfoRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Does entrepreneurship involve entrepreneurs with unique characteristicsDocument3 pagesDoes entrepreneurship involve entrepreneurs with unique characteristicsRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document5 pagesModule 2Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Entrep Lesson 2Document4 pagesEntrep Lesson 2Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Let's Get Started! (Think and Recall) : Activity 1Document8 pagesLet's Get Started! (Think and Recall) : Activity 1Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Introduction ProposalDocument1 pageIntroduction ProposalRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
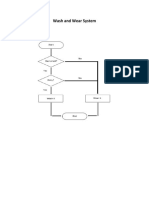
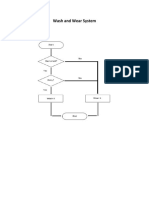
- Wash & Wear Care SystemDocument1 pageWash & Wear Care SystemRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Case 1Document2 pagesFlowchart Case 1Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Case 3Document1 pageFlowchart Case 3Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- GISDocument4 pagesGISRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
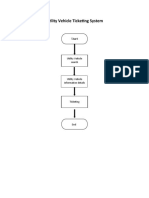
- Flowchart Case 2Document2 pagesFlowchart Case 2Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- L5 Processing ActivityDocument1 pageL5 Processing ActivityRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Case 4Document2 pagesFlowchart Case 4Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- L4 Processing ActivityDocument1 pageL4 Processing ActivityRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- BSIT Student Explains Key IS TermsDocument1 pageBSIT Student Explains Key IS TermsRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Case 5Document1 pageFlowchart Case 5Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- AlcibiadesDocument1 pageAlcibiadesRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- $ - Server & $ - RequestDocument10 pages$ - Server & $ - RequestRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Vagrant CheatsheetDocument11 pagesVagrant CheatsheetRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Based On Your Answers in The Learner Engagement Activity, Provide A Brief Description of Each Word About The SDLCDocument1 pageBased On Your Answers in The Learner Engagement Activity, Provide A Brief Description of Each Word About The SDLCRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sir LagonoyDocument1 pageAssignment Sir LagonoyRose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- $server 1Document21 pages$server 1Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- PHP Global Variables1Document1 pagePHP Global Variables1Rose Marie SalazarNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource WasSara AlbogamiNo ratings yet
- Actup ElgDocument2 pagesActup ElgsaikiranvaddiNo ratings yet
- College Computing Final Exam Software TestingDocument17 pagesCollege Computing Final Exam Software TestingHarveen VelanNo ratings yet
- Ed I Module Users GuideDocument474 pagesEd I Module Users Guide791987100% (1)
- Flexible Web App Penetration Tester RoleDocument2 pagesFlexible Web App Penetration Tester RoleChaitanyaVallurupalliNo ratings yet
- SAP Data ArchivingDocument29 pagesSAP Data Archivingdeepak.bishtNo ratings yet
- Sap c4c DemoDocument23 pagesSap c4c DemoSourabh Bhardwaj0% (1)
- Remote Method Invocation (RMI)Document29 pagesRemote Method Invocation (RMI)AnikNo ratings yet
- Social NetworkingDocument53 pagesSocial NetworkingSrikanth Nadella50% (2)
- Advance DatabaseDocument7 pagesAdvance DatabaseChariz Legaspi100% (1)
- Security Threats: A Guide For Small and Medium BusinessesDocument9 pagesSecurity Threats: A Guide For Small and Medium BusinessesmasimnaseerNo ratings yet
- Data Centre Security Policy (ITT CourseDocument23 pagesData Centre Security Policy (ITT CourseAditya Patadia0% (1)
- RQ TrackerDocument6 pagesRQ TrackersyedNo ratings yet
- S9L28 Anatomy of A Secure ConnectionDocument6 pagesS9L28 Anatomy of A Secure ConnectionMireki VallaNo ratings yet
- MS Access January Exam 2022 PDFDocument4 pagesMS Access January Exam 2022 PDFthe hubcompsNo ratings yet
- Secure Software Notes On Operating SystemsDocument6 pagesSecure Software Notes On Operating SystemsVarun MohunahNo ratings yet
- Git CommandsDocument10 pagesGit CommandsbanuNo ratings yet
- AWS Analytics, Data, & Application Services GuideDocument59 pagesAWS Analytics, Data, & Application Services GuideJohana KellyNo ratings yet
- UCS1412 - Database Lab Assignment - 7 Name:Prakash R ROLL NO:185001108Document4 pagesUCS1412 - Database Lab Assignment - 7 Name:Prakash R ROLL NO:185001108prakashNo ratings yet
- SQL SequencesDocument3 pagesSQL SequencesShobha Kumari ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Security Profiles 56Document220 pagesFortigate Security Profiles 56GregoryNo ratings yet
- Software Test Metric: UNIT 10 Planning ManagementDocument24 pagesSoftware Test Metric: UNIT 10 Planning ManagementKimberly DosadoNo ratings yet
- 10982C Supporting and Troubleshooting Windows 10Document9 pages10982C Supporting and Troubleshooting Windows 10Chris Buenaventura100% (1)
- Module 1 - Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument15 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Operations ManagementXehdrickke FernandezNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Models ExplainedDocument50 pagesSoftware Quality Models ExplainedLearning StrengthNo ratings yet
- CIS Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Benchmark v2.2.0Document205 pagesCIS Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Benchmark v2.2.0César Medina CoronaNo ratings yet
- Audit TrailDocument3 pagesAudit Trailsapan.pan0% (1)
- Cache Backup and RestoreDocument32 pagesCache Backup and RestoreMike PappasNo ratings yet
- ITIL Framework for Academic Information System Incident ManagementDocument10 pagesITIL Framework for Academic Information System Incident ManagementDimas Kusuma Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
- SAQ IndiaDocument9 pagesSAQ Indiarahullpk87No ratings yet