Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanics of Machines Lab: Online Session # 5
Uploaded by
Malik Haider0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThe document provides definitions and concepts related to velocity and discusses drawing a velocity-time graph for a slotted link mechanism. It defines velocity as displacement over time and discusses the concepts of uniform, average, and instantaneous velocity. The procedure involves collecting angular displacement, linear displacement, and time data for a slotted link mechanism and using that data to calculate velocities and plot a velocity-time graph.
Original Description:
velocity time graph and
accelertion time graph
Original Title
5- V-t graph
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides definitions and concepts related to velocity and discusses drawing a velocity-time graph for a slotted link mechanism. It defines velocity as displacement over time and discusses the concepts of uniform, average, and instantaneous velocity. The procedure involves collecting angular displacement, linear displacement, and time data for a slotted link mechanism and using that data to calculate velocities and plot a velocity-time graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesMechanics of Machines Lab: Online Session # 5
Uploaded by
Malik HaiderThe document provides definitions and concepts related to velocity and discusses drawing a velocity-time graph for a slotted link mechanism. It defines velocity as displacement over time and discusses the concepts of uniform, average, and instantaneous velocity. The procedure involves collecting angular displacement, linear displacement, and time data for a slotted link mechanism and using that data to calculate velocities and plot a velocity-time graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Mechanics of Machines Lab
Online Session # 5
To Draw Velocity-Time Graph for Slotted Link Mechanism
Definitions of Velocity
Definition Level of Rigor
Velocity is the ratio of displacement to time.
𝑆
𝑣= More Rigorous, Less Simplified
𝑡
This definition is also known as Uniform or
Constant Velocity.
If an object moves from S1 to S2 in time t1 to t2,
then the ratio of change in displacement to change
in time is called velocity.
𝑆2 − 𝑆1 ∆𝑆
𝑣= =
𝑡2 − 𝑡1 ∆𝑡
This definition is also known as Average Velocity.
An object moves from S1 to S2 in time t1 to t2. We
shorten the time interval t=t2-t1 so that it is near
to zero but not equal to zero. It is also called as
“time approaches zero”. Now, the ratio of change
in displacement to change in time is called
velocity.
∆𝑆
𝑣 = lim
∆𝑡→0 ∆𝑡
This definition is also known as Instantaneous
Velocity.
Derivative of displacement with respect to time is
called velocity.
𝑑𝑆
𝑣=
𝑑𝑡
This definition is also known as Instantaneous
Velocity.
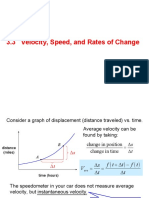
Concept of Tangent and Slope
At a point of a graph, derivative is slope of tangent at that point. So, at any point on S-t graph, velocity is
the slope of tangent at that point.
A (t1, S1)
B (t2, S2)
Slope = Velocity = Rise /Run = S2-S1/t2-t1
Angular Angular Slope or
Linear Time in Rise Run
Displacement Displacement Velocity=
Sr. # Displacement seconds S2-S1 in t2-t1 in
in degrees in radians Rise/Run
(cm) (t) centimeters seconds
(θdeg) (θrad) (cm/s)
1 0 2.5 0 2.7-2.5=0.2 0.01- 0.2/0.01
0=0.01
2 15 2.7 0.01 3.2-2.7=0.5 0.021-
0.1=0.011
3 30 3.2 0.021
4 45 3.85
5 60 4.7
ω= θrad/t
t= θrad/ ω; angular velocity is assumed to be 25 rad/s
θrad = θdeg x π/180
Apparatus Slotted Link Mechanism, Graph Paper, Calculator, Geometry Tools
Theoretical Background
Procedure
Observations and Calculations
Graph
Analysis and Conclusion
You might also like
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- 11 Physics Chapter 2 Comprehensive NotesDocument6 pages11 Physics Chapter 2 Comprehensive NotesKeerthe BalaNo ratings yet
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- 2-Motion in One DimensionDocument20 pages2-Motion in One DimensionAyham SmadiNo ratings yet
- Ce 204a Module 2Document31 pagesCe 204a Module 2EDWARD ANJEILO CACHONo ratings yet
- Unit 2 FlashcardsDocument2 pagesUnit 2 FlashcardsDona MaeNo ratings yet
- CircularMotionExe Unacademy PDFDocument25 pagesCircularMotionExe Unacademy PDFChirag DalwaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3 Rate of ChangeDocument11 pagesLecture 3.3 Rate of ChangeMohd Haffiszul Bin Mohd SaidNo ratings yet
- Graphs Representing Motion: Distance-Time GraphDocument26 pagesGraphs Representing Motion: Distance-Time GraphRandom GuyNo ratings yet
- Blank 4NA Sci (Phy) Revision NotesDocument33 pagesBlank 4NA Sci (Phy) Revision NotesFrancine TheophilaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Forces and Motion 2017Document13 pagesCHAPTER 2 Forces and Motion 2017Pikachu AlsalehNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight LineDocument8 pagesMotion in Straight Linearyaanuragyadav24No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiestempestNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Forces and Motion Chapter 2: Forces and Motion: Physics SPM 2018Document13 pagesChapter 2: Forces and Motion Chapter 2: Forces and Motion: Physics SPM 2018The Tech DeveloperNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Physics NotesDocument60 pagesYear 11 Physics NotesFaustina ConfuciousNo ratings yet
- Computational Methods - CFD Lecture 4Document31 pagesComputational Methods - CFD Lecture 4Morteza KhashehchiNo ratings yet
- Nehakumari BEdrollno 43Document29 pagesNehakumari BEdrollno 43Anubhav KumarNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument49 pagesTheoryAman kumarNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument96 pagesKinematicsAnkur Jyoti Sarma100% (1)
- Graphs of MotionDocument80 pagesGraphs of Motionrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- 01 ES203 Dynamics W01 W02 DDLRDocument22 pages01 ES203 Dynamics W01 W02 DDLRyhanie salvadorNo ratings yet
- Velocity Time Graphs PDFDocument42 pagesVelocity Time Graphs PDFAk R71No ratings yet
- Rotations of Rigid ObjectsDocument14 pagesRotations of Rigid ObjectsJackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Rate of Change and LimitsDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 1 Rate of Change and Limitsjustinelabucay067No ratings yet
- Y3 Physics Notes EOYDocument27 pagesY3 Physics Notes EOYumairahNo ratings yet
- Physics: Kinematics - Describing MotionDocument25 pagesPhysics: Kinematics - Describing MotiontonyNo ratings yet
- Notes-Motion From BYjusDocument12 pagesNotes-Motion From BYjusSidra JamilNo ratings yet
- Blank 4E5N Sci (Phy) Revision NotesDocument42 pagesBlank 4E5N Sci (Phy) Revision NotesFrancine TheophilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Rotation Rotation:: Solid BodyDocument25 pagesChapter 10: Rotation Rotation:: Solid BodyHanifah IntaniaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 MotionDocument31 pagesUnit 2 MotionDenise WUNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Lesson 11& 12Document11 pagesDynamics - Lesson 11& 12Vimukthi LakshanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 MotionDocument31 pagesUnit 2 MotionJackiequeencess TentadoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics L2Document11 pagesKinematics L2BAISHALI NAGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Kinematic in 1D (Part 1) (PHY130)Document26 pagesChapter 2 Kinematic in 1D (Part 1) (PHY130)FiqajasmeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Part 1 - MSK SirDocument56 pagesUnit 1 - Part 1 - MSK SirShadowツNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 NotesDocument3 pagesCHP 2 NotesFasihNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7 (Inclined - Plane)Document3 pagesExperiment No 7 (Inclined - Plane)Arfa aNo ratings yet
- W10 Kinematics of A Particle: Kns1633 Engineering Mechanics Semester 1 2011-2012 MR Abdul Azim AbdullahDocument59 pagesW10 Kinematics of A Particle: Kns1633 Engineering Mechanics Semester 1 2011-2012 MR Abdul Azim AbdullahSek Chin JiNo ratings yet
- Physics Module 2Document8 pagesPhysics Module 2Brille Adrian FernandoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in One DimensionDocument38 pagesKinematics in One DimensionQassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- PDF - Chapter 1 - Particle Kinematic - BMCG - FullDocument92 pagesPDF - Chapter 1 - Particle Kinematic - BMCG - FullTakip MatNo ratings yet
- Share '1. Physics (1) .PPT'Document216 pagesShare '1. Physics (1) .PPT'Joanna BinanNo ratings yet
- Induction MachineDocument16 pagesInduction MachineUsama RaoNo ratings yet
- 2019 NMAT Physics LectureDocument114 pages2019 NMAT Physics Lecturekingwinter13.officialNo ratings yet
- Circular Notes 2023Document28 pagesCircular Notes 2023tingtong3141No ratings yet
- GP2 MotionDocument6 pagesGP2 Motiontmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Kinematics in One DimensionDocument17 pagesKinematics in One DimensionSandra MeruNo ratings yet
- Country's Best Online Test PlatformDocument74 pagesCountry's Best Online Test PlatformSubhrasankar RaychaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Instantaneous Velocity: Class #2Document7 pagesInstantaneous Velocity: Class #2Mayank GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Velocity Time Graph NoteDocument3 pagesLesson 5 - Velocity Time Graph Notebinuk wNo ratings yet
- Motion Physics KinematicsDocument96 pagesMotion Physics KinematicsMadhurima MaityNo ratings yet
- KNS1633 Engineering Mechanics: Kinematics of A Particle: Week 9Document55 pagesKNS1633 Engineering Mechanics: Kinematics of A Particle: Week 9Sek Chin Ji100% (1)
- SHORT NOTES Force and Motion 1Document1 pageSHORT NOTES Force and Motion 1YARSHANA A/P SIVAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Ap PhysicsDocument16 pagesChapter 6 Ap Physicsapi-664002484No ratings yet
- L 3 Motion Physics F 1920Document48 pagesL 3 Motion Physics F 1920Zeynep BayramNo ratings yet
- Average Acceleration and Instantaneous AccelerationDocument14 pagesAverage Acceleration and Instantaneous AccelerationCherry Pie Renon0% (1)
- F4C2 (Part 1)Document10 pagesF4C2 (Part 1)7cj996jtkcNo ratings yet
- Grpahs StudentDocument33 pagesGrpahs StudentAftab NadafNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 KinematicsDocument49 pagesChapter-2 KinematicsAgustinus Aldi Irawan RahardjaNo ratings yet
- Slides Acceleration Wk4Document9 pagesSlides Acceleration Wk4Nathaniel GoggansNo ratings yet
- Kinematics SolDocument125 pagesKinematics Soldebasmitabera5947No ratings yet
- Divided by The PermittivityDocument1 pageDivided by The PermittivityVasanth Kumar NainalaNo ratings yet
- (Answer) Assignment For Physics 1 PDFDocument8 pages(Answer) Assignment For Physics 1 PDFTake IchiruNo ratings yet
- 03 Deflection of Beta Particles in A Magnetic Field PDFDocument4 pages03 Deflection of Beta Particles in A Magnetic Field PDFPriya RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Physics Mid Topic Test Revision 2023 SOLUTIONSDocument4 pagesPhysics Mid Topic Test Revision 2023 SOLUTIONSRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- What Is A Force? How Do Forces Combine? How Does Friction Affect Motion?Document15 pagesWhat Is A Force? How Do Forces Combine? How Does Friction Affect Motion?Gaurav SwamiNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument2 pagesDynamicsJosef EdrickNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Work Energy and PowerDocument13 pagesIGCSE Work Energy and PowerErrol WaltersNo ratings yet
- P2.3 Triple Forces in Action: Add Notes and Diagrams To Make It UsefulDocument1 pageP2.3 Triple Forces in Action: Add Notes and Diagrams To Make It UsefulOliviaNo ratings yet
- 12indf IntegrationDocument65 pages12indf IntegrationPrantik SealNo ratings yet
- Mga Halimbawa NG Anapora at KataporaDocument3 pagesMga Halimbawa NG Anapora at KataporaRoxanie Ranido43% (7)
- TRANSFORMERDocument10 pagesTRANSFORMERarunkumarNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Potential Energy On Shelves: Prior Knowledge Questions (Do These BEFORE Using The GizmoDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Potential Energy On Shelves: Prior Knowledge Questions (Do These BEFORE Using The GizmoMaryam ShiriNo ratings yet
- Physics Free-Fall Lab ReportDocument12 pagesPhysics Free-Fall Lab Reportapi-462581860No ratings yet
- Elite Medics October Physics ClassDocument80 pagesElite Medics October Physics ClassApollo WongNo ratings yet
- Ascham 2014 Physics Trials & SolutionsDocument31 pagesAscham 2014 Physics Trials & SolutionsNhan LeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/42Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/42SarveshNo ratings yet
- MCQ Paper - 02: LD, H # Meh 01 Hs (G 10 MS)Document9 pagesMCQ Paper - 02: LD, H # Meh 01 Hs (G 10 MS)Kumari KarunanayakeNo ratings yet
- E4. Torque Second Condition of EquilibriumDocument4 pagesE4. Torque Second Condition of EquilibriumPaulo Remulla50% (2)
- Chapter05 Circular Motion SDocument9 pagesChapter05 Circular Motion SeltytanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear WebQuestDocument2 pagesNuclear WebQuestBridget OppeltNo ratings yet
- Jee+main+2021 +physics+most+important+topicsDocument26 pagesJee+main+2021 +physics+most+important+topicsHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- Work - Energy Theorem and PowerDocument33 pagesWork - Energy Theorem and PowerAh RainNo ratings yet
- Cart Lab Report PREAP PhysicsDocument5 pagesCart Lab Report PREAP Physicsgongsterr0% (3)
- Sim in Grade 8 ScienceDocument13 pagesSim in Grade 8 ScienceDen Gesiefer Pambid Lazaro100% (5)
- Work, Energy and Power Circular Motion: UNIT 03, 04Document31 pagesWork, Energy and Power Circular Motion: UNIT 03, 04Haris khanNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body Dynamics Theory - EDocument45 pagesRigid Body Dynamics Theory - Ethinkiit100% (3)
- Resolution and CompositionDocument84 pagesResolution and CompositionSilvers RayleighNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic InductionJohn Hugo100% (1)
- L M VR: M (Ball) 2 KG V (Ball) 3.2 M/s M (Bar) 4 KGDocument4 pagesL M VR: M (Ball) 2 KG V (Ball) 3.2 M/s M (Bar) 4 KGJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet