Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
Uploaded by
MIbrahimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
Uploaded by
MIbrahimCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
2
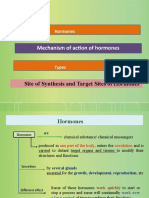
HARMONES
Definition:
Hormones are chemical messengers that
are secreted directly into the blood,
which carries them to organs and tissues
of the body to exert their functions. There
are many types of hormones that act on
different aspects of bodily functions and
processes.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
3
TYPES OF HORMONES
There are three major types of hormones.
Protein hormones (or polypeptide hormones) are
made of chains of amino acids. An example
is ADH (antidiuretic hormone) which decreases
blood pressure.
Steroid hormones are derived from lipids. ...
Amine hormones are derived from amino acids.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
4
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
5
CLASSIFICATION OF HORMONES
Hormones can be classified according to their
chemical nature, mechanism of action, nature of
action, their effects, and stimulation of Endocrine
glands. i. This category of hormones are divided to
six classes, they are hormones steroid; amines;
peptide; protein; glycoprotein
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
6
CLASSIFICATION OF HORMONES
Mechanism of Action: Hormones with Intracellular
Receptors. ... That is to say, the hormone-receptor
complex binds to promoter regions of responsive genes
and stimulate or sometimes inhibit transcription from
those genes. Thus, the mechanism of action of steroid
hormones is to modulate gene expression in target cells.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
7
CLASSIFICATION OF HORMONES
The structure of peptide hormones is that of
a polypeptide chain (chain of amino acids).
The peptide hormones include molecules that are
short polypeptide chains, such as
antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin produced in the
brain and released into the blood in the posterior
pituitary gland.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
8
Cardiac Hormones:
Atrial natriuretic peptide is a hormone that
controls blood pressure in part by increasing the
urinary excretion of sodium. The parathyroid glands
maintain adequate levels of blood calcium.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
9
PINEAL HORMONES:
The pineal gland is a tiny endocrine gland found in
the brain. It produces and secretes the hormone
melatonin, which is a hormone that helps regulate
biological rhythms such as sleep and wake cycles.
The secretion of melatonin is inhibited by light and
triggered by darkness.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
10
GASTROINTESTINAL HORMONES
The gastrointestinal hormones (or gut hormones)
constitute a group of hormones secreted by entero
endocrine cells in the stomach, pancreas, and small
intestine that control various functions of
the digestive organs. ... They exert their autocrine and
paracrine actions that integrate gastrointestinal function.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
11
MODE OF STEROID HORMONE
That is to say, the hormone-receptor
complex binds to promoter regions of
responsive genes and stimulate or
sometimes inhibit transcription from
those genes. Thus, the mechanism of
action of steroid hormones is to
modulate gene expression in target cells.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
12
FOUNCTIONS OF STEROID HORMONE
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
13
MODE OF PEPTIDE HORMONES
Peptide hormones and growth factors initiate
signaling by binding to and activating their cell
surface receptors. The activated receptors
interact with and modulate the activity of cell
surface enzymes and adaptor proteins which
entrain a series of reactions leading to metabolic
and proliferative signals.
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
14
FUNCTIONS OF PEPTIDE HORMONE
Peptide hormones are secreted and function in
an endocrine manner to regulate many
physiological functions, including growth,
appetite and energy metabolism, cardiac
function, stress, and reproductive physiology.
Many signal via G protein-coupled receptors
(GPCRs).
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
15
Thank You
Benazir College of Nursing Larkana
You might also like
- Genetics (Biol 105) Linkage and Recombination Exercises: Progeny Phenotype Progeny NumberDocument4 pagesGenetics (Biol 105) Linkage and Recombination Exercises: Progeny Phenotype Progeny NumberAngelica GeneraleNo ratings yet
- NKTI Laboratory - Scheme Model (Revised - Track)Document1 pageNKTI Laboratory - Scheme Model (Revised - Track)nerinel coronadoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesThe Endocrine SystemОксана КрасильниковаNo ratings yet
- Hormones, ClassificationDocument10 pagesHormones, ClassificationMenoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)Document31 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)arun231187No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Endocrine SystemDocument53 pagesLecture 2 Endocrine SystemLouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Endrocrinology - PPTX Version 1Document40 pagesEndrocrinology - PPTX Version 1Abishek BhadraNo ratings yet
- Overview of Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesOverview of Endocrine System2023ph17No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine Systempranutan739No ratings yet
- 1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineDocument36 pages1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- THE Endocrine System: 10th GradeDocument19 pagesTHE Endocrine System: 10th GradeKyle OrlanesNo ratings yet
- Under The Guidance Of:: Dr. Sandeep Tandon Professor and Head of Dept. of PedodonticsDocument79 pagesUnder The Guidance Of:: Dr. Sandeep Tandon Professor and Head of Dept. of PedodonticsMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problem On EndocrineDocument48 pagesCare of Clients With Problem On EndocrineAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action of Hormones: Site of Synthesis and Target Sites of HormonesDocument26 pagesMechanism of Action of Hormones: Site of Synthesis and Target Sites of HormonesAbdul MoqeetNo ratings yet
- Endocrine-System 20231001 220830 0000Document33 pagesEndocrine-System 20231001 220830 0000murlastaceytormisNo ratings yet
- 6 Group Phsiology.....Document14 pages6 Group Phsiology.....Ayat ChaudaryNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument45 pagesDocumentPrajwal PatilNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument95 pagesEndocrine SystemUmar Ilyasu JibrilNo ratings yet
- Introduction - CC3: Mechanism of Hormonal ActionDocument40 pagesIntroduction - CC3: Mechanism of Hormonal ActionAl-hadad AndromacheNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument114 pagesReproductive SystembookaccountNo ratings yet
- PHR 121 Anatomy & Physiology: Diploma in PharmacyDocument51 pagesPHR 121 Anatomy & Physiology: Diploma in PharmacyAzmi ArifinNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument37 pagesThe Endocrine SystemM Shafique SadiqeeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument4 pagesEndocrine Glandakash_zizouNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-1)Document11 pagesMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-1)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument55 pagesHormonesAvinashNo ratings yet
- Sheena Khan: Biochemistry Generiic Bs NursingDocument22 pagesSheena Khan: Biochemistry Generiic Bs NursingsharmeenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System OutlineDocument17 pagesEndocrine System OutlineEsthermae PanadenNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of HormonDocument16 pagesBiochemistry of HormonMuhamad SdeqNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-1Document90 pagesEndocrine System-1markmuiruri581No ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument74 pagesEndocrinologysyedahaleemajunaidsNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Management of Male InfertilityDocument22 pagesHormonal Management of Male Infertilitydranibalurologoencancun.mxNo ratings yet
- Hormone GroupDocument35 pagesHormone GroupNeph VargasNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Part 1Document64 pagesThe Endocrine System Part 1rizwanbasNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Courselink NotesDocument27 pagesUnit 1 Courselink NotesLauren StamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PDFDocument38 pagesEndocrine System PDFUlfat NiazyNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 DiplomaDocument6 pagesLec 1 DiplomaEman saadiNo ratings yet
- Hormones 859645Document34 pagesHormones 859645Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Assessment of The Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesMODULE 1 Assessment of The Endocrine SystemLorraine GambitoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction EndocrinologyDocument40 pages1 - Introduction EndocrinologyBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 20231110 222858 0000Document87 pagesDrugs Acting On The Endocrine System 20231110 222858 0000Sameera DahamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument5 pagesChapter 10 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology IntroductionDocument43 pagesEndocrinology IntroductionDICKSONNo ratings yet
- Johanna Jane H. Macasero - Endocrine System TranscriptDocument13 pagesJohanna Jane H. Macasero - Endocrine System TranscriptJohanna MacaseroNo ratings yet
- Sample TransDocument5 pagesSample TransNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrineHoney Mie MorenoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Study of The Endocrine SystemDocument225 pagesStudy of The Endocrine SystemHuzaifa RashidNo ratings yet
- Hormones:: Signaling MoleculesDocument20 pagesHormones:: Signaling MoleculesSangeeta DwivediNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesEndocrine SystemMerrin EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ResonanceDocument51 pagesEndocrine ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- HORMONES Melanie DacuyaDocument16 pagesHORMONES Melanie DacuyaMaria BernalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 PhysiologyDocument49 pagesChapter - 17 PhysiologyAhsanullah PathanNo ratings yet
- 4 Endocrine 1Document18 pages4 Endocrine 1ShenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Vertebrate) : HomeostasisDocument7 pagesEndocrine System (Vertebrate) : HomeostasisKaleem UllahNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMary Christelle100% (1)
- Chapter 6 The Endocrine SystemDocument37 pagesChapter 6 The Endocrine SystemReikooNo ratings yet
- PD22 Hap1 L03Document33 pagesPD22 Hap1 L03Ka Yan LAUNo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument65 pagesHORMONESsoumya palavalasaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM, Hormones (Reviewer)Document4 pagesBIOCHEM, Hormones (Reviewer)michaelamontanielNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument17 pagesEndocrine SystemSoumik MallickNo ratings yet
- Classification of Hormones: By. Dr. Luna PhukanDocument13 pagesClassification of Hormones: By. Dr. Luna Phukanacrehell8No ratings yet
- Hormonal and Alkaline Diet For Women: Reverse Ailments and Heal the Body Naturally Inspired By Barbara Oneill Self Heal By DesignFrom EverandHormonal and Alkaline Diet For Women: Reverse Ailments and Heal the Body Naturally Inspired By Barbara Oneill Self Heal By DesignNo ratings yet
- Culture, Health and Society SyllabusDocument7 pagesCulture, Health and Society SyllabusMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Title: Principles and Methods of EvaluationDocument2 pagesTitle: Principles and Methods of EvaluationMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Curriculum, Planning and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesCurriculum, Planning and DevelopmentMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Curriculum, Planning and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesCurriculum, Planning and DevelopmentMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Culture, Health and Society SyllabusDocument7 pagesCulture, Health and Society SyllabusMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Title: Principles and Methods of EvaluationDocument2 pagesTitle: Principles and Methods of EvaluationMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Planning and Development (CPD) : Muhammad IbrahimDocument14 pagesCurriculum Planning and Development (CPD) : Muhammad IbrahimMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Online Classes ScheduleDocument5 pagesOnline Classes ScheduleMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- CPDDocument9 pagesCPDMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Pharma Unit 8 - Anti - Adrenergic Drugs - 2 of 2Document21 pagesPharma Unit 8 - Anti - Adrenergic Drugs - 2 of 2MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agent & Mechanism of Resistance: Muhammad Ibrahim AnsariDocument29 pagesAntimicrobial Agent & Mechanism of Resistance: Muhammad Ibrahim AnsariMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- ACN-CHN SyllabusDocument4 pagesACN-CHN SyllabusMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- CPDDocument9 pagesCPDMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Organic ChemistryDocument40 pagesBasic Concepts of Organic ChemistryMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 7Document34 pages7MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Health, Planning and DevelopmentDocument14 pagesHealth, Planning and DevelopmentMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Proteins and Lipids: Bio ChemistryDocument19 pagesCarbohydrates, Proteins and Lipids: Bio ChemistryMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Online Classes ScheduleDocument5 pagesOnline Classes ScheduleMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 5Document8 pages5MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 7Document34 pages7MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Benazir College of Nursing LarkanaDocument15 pagesBenazir College of Nursing LarkanaMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1Document38 pages1MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agent & Mechanism of Resistance: Muhammad Ibrahim AnsariDocument29 pagesAntimicrobial Agent & Mechanism of Resistance: Muhammad Ibrahim AnsariMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 5Document8 pages5MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Proteins and Lipids: Bio ChemistryDocument19 pagesCarbohydrates, Proteins and Lipids: Bio ChemistryMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Online Classes ScheduleDocument5 pagesOnline Classes ScheduleMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1Document38 pages1MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Organic ChemistryDocument40 pagesBasic Concepts of Organic ChemistryMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Glucose BCDocument17 pagesGlucose BCAditya ChawlaNo ratings yet
- BK 15.7 CheDocument62 pagesBK 15.7 CheVenkata RamananNo ratings yet
- I Can : © Pearson Education LTD 2014. Copying Permitted ForDocument2 pagesI Can : © Pearson Education LTD 2014. Copying Permitted Forghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- Chapters Summary (Biology by Solomon)Document10 pagesChapters Summary (Biology by Solomon)edomin00No ratings yet
- Noah Loya - Cell Study GuideDocument3 pagesNoah Loya - Cell Study GuideNoah LoyaNo ratings yet
- Enterobacter Sakazakii: General MicrobiologyDocument25 pagesEnterobacter Sakazakii: General MicrobiologyMasNo ratings yet
- (RM) 1 Non Invasive Ultrasound NeuromodulationDocument15 pages(RM) 1 Non Invasive Ultrasound NeuromodulationOak TreeNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes ChecklistDocument2 pagesCell Processes Checklistapi-324166624No ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesReview QuestionsAR EddingNo ratings yet
- SOL Review Biochemistry and WaterDocument1 pageSOL Review Biochemistry and WaterAlayna SheltonNo ratings yet
- CTB Indonesia - Operational Research - Guidelines - Roadmap (Bahasa)Document66 pagesCTB Indonesia - Operational Research - Guidelines - Roadmap (Bahasa)Shely NoviaNo ratings yet
- Oeq 2Document7 pagesOeq 2Sara JosephNo ratings yet
- Biology NTSE Stage-1Document5 pagesBiology NTSE Stage-1Sonal Gupta100% (5)
- Gene Therapy: Science, Technology & SocietyDocument25 pagesGene Therapy: Science, Technology & SocietyNicki Lyn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Salmonella: Methods and ProtocolsDocument303 pagesSalmonella: Methods and ProtocolsHesham AbdelmonemNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology Week 3. ABCDDocument21 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology Week 3. ABCDohsehuns wifeuNo ratings yet
- General Bacteriology 23.04.2020Document99 pagesGeneral Bacteriology 23.04.2020N Ganapathi KumarNo ratings yet
- Zheng Hong 郑 红 Department of Medical Genetics & Cell BiologyDocument63 pagesZheng Hong 郑 红 Department of Medical Genetics & Cell BiologyinakiNo ratings yet
- Name Atul Pati Tripathi Collected Received Lab No. Age: Gender: Reported A/c Status Ref By: Report StatusDocument2 pagesName Atul Pati Tripathi Collected Received Lab No. Age: Gender: Reported A/c Status Ref By: Report StatusAtul TripathiNo ratings yet
- Split GenesDocument56 pagesSplit GenesMithun RajNo ratings yet
- EVALUATE - Quiz 1 (Intro To Bio, Cell Theory, Cell Types, Structure and Function) - General Biology 1Document16 pagesEVALUATE - Quiz 1 (Intro To Bio, Cell Theory, Cell Types, Structure and Function) - General Biology 1gcjar vllnNo ratings yet
- Mind Map: Chemical Substances Found in The OrganismsDocument5 pagesMind Map: Chemical Substances Found in The OrganismsMaharajan McsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Mechanism of Action of All Drugs - +Document4 pagesPharmacology - Mechanism of Action of All Drugs - +Sahal ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Virtual Laboratory Worksheet-Cellular Transport MechanismDocument2 pagesVirtual Laboratory Worksheet-Cellular Transport MechanismKeizzhia Alleonah T. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Andre FE (2008) - Vaccination Greatly Reduces Disease, Disability, Death and Inequity Worldwide PDFDocument7 pagesAndre FE (2008) - Vaccination Greatly Reduces Disease, Disability, Death and Inequity Worldwide PDFHoa NắngNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesNCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell The Unit of LifeShanthamurthy ShanthalaNo ratings yet
- PCR Testing Centers in The PhilippinesDocument36 pagesPCR Testing Centers in The Philippineskhrayzie bhoneNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Antar SelDocument39 pagesKomunikasi Antar SelMOCHILNo ratings yet