Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ELECTRICAL MACHINE I Module 1
Uploaded by
kujong agacer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views44 pagesOriginal Title
ELECTRICAL-MACHINE-I-Module-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views44 pagesELECTRICAL MACHINE I Module 1
Uploaded by
kujong agacerCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 44
ELECTRICAL MACHINE I
Denn A. Agatep
Email: denn_agatep@hotmail.com
CP No. 09454821243
Department of Electrical Engineering
College of Engineering
Cagayan State University
For questions and clarification contact the cellphone no. or email me
in the indicated number and email address.
COURSE CONTENT
Module I – (week 1 – 4)
1. INTRODUCTION:
a) Electromechanical Energy Conversion Principles
b) Forces, and Torque in Magnetic Field Systems
c) Energy Balance
d) Energy and Force in a Singly Excited Magnetic Field System
e) Determination of Magnetic Force and Torque Form Energy
f) Energy and Co-energy
e) Multiply-excited Magnetic Field Systems
2. DC GENERATORS
a) Principle of Operation
b) Action of Commutator
c) Constructional Features
d) Armature Windings – Lap and Wave Windings, Simplex and Multiplex Windings
e) Use of Laminated Armature
f) E.M.F. Equation
g) Methods of Excitation - Separately and Self Excited Generators, Shunt, Series, and Compound
Machine
h) Build Up of E.M.F.
i) Critical Field Resistance and Critical Speed
j) Causes for Failure to Self Excite and Remedial Measures
k) Armature Recation
l) Cross Magnetizing and Demagnetizing Ampere Turns/ Pole (AT)
m) Compensating Winding
n) Commutation
o) Reactance Voltage
p) Methods of Improving Commutation – Resistance Commutation, EMF Commutation and Interpoles
and Compoles
3. DC MACHINES CHARACTERISTICS
a) No-load and Load Characteristics of Separately Excited Generator
b) Characteristics of a Shunt Generator
c) Characteristics of Compound Generator
4. PARALLEL OPERATION OF DC GENERATOR
a) Advantages
b) Connecting Shunt Generator in Parallel
c) Equalizer Bar
d) Load Sharing
Module II – (week 5 – 10)
1. DC MOTORS
a) Principle of Operation
b) Back E.M.F.
c) Torque Equation
3. CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATION OF DC MOTORS
a) Shunt Motors
b) Series Motors
c) Compound Motors
4. ARMATURE REACTION AND COMMUTATION
5. STARTING OF DC MOTOR
a) Principle of Operation of 3 and 4 point Starter
b) Drum Controller
c) Constant and Variable Losses
d) Calculation of Efficiency
e) Condition for Maximum efficiency
5. SPEED CONTROL OF DC MOTORS
a) Armature voltage and Field Flux Control Method
b) Ward Leonard Method
6. METHOD OF TESTING IN A DC MOTOR
a) Direct, Indirect, and Regenerative Testing
b) Brake Test
c) Swinburne’s Test
d) Load Test
e) Hopkinson’s Test
f) Field’s Test
g) Retardation Test
h) Separation of Stray Losses in a DC Motor Test.
Module III – (week 11 – 18)
1. SINGLE PHASE TRANSFORMERS
a) Single Phase Transformer Construction Details – Core, Windings and Insulation
b) Principle of Operation – EMF Equation, Magnetizing Current and Core Losses, No Load and On
Load Operation
c) Phasor Diagram and Equivalent Circuit
d) Losses and efficiency, Condition for Maximum Efficiency
e) Voltage Regulation and Approximate Expression for Voltage Regulation
f) Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test
g) Harmonics in Single Phase Transformer
h) Parallel Operation of Transformer
2. THREE PHASE TRANSFORMERS
a) Construction
b) Connections
c) Equal and Unequal Turns Ratio
d) Parallel Operation
e) Load Sharing
f) All Day Efficiency
3. AUTOTRANSFORMERS
You might also like
- 1000 Electrical Machines MCQsDocument458 pages1000 Electrical Machines MCQskibrom atsbha100% (4)
- Free Logical Reasoning Questions AnswersDocument13 pagesFree Logical Reasoning Questions AnswersIdhonna Abihay100% (1)
- Free Logical Reasoning Questions AnswersDocument13 pagesFree Logical Reasoning Questions AnswersIdhonna Abihay100% (1)
- Basic Radio Vol 1-6 - A Rider 1961 TextDocument804 pagesBasic Radio Vol 1-6 - A Rider 1961 TextMariano Alberto Salmón75% (4)
- ME010 508 Electrical & Electronics Lab: StudyDocument1 pageME010 508 Electrical & Electronics Lab: StudyBASIL KUMAR N.KNo ratings yet
- GTU Bachelor of Engineering course on electrical machinesDocument5 pagesGTU Bachelor of Engineering course on electrical machinesjijo123408No ratings yet
- Assesmnet Special Electrical MachinesDocument5 pagesAssesmnet Special Electrical Machinessmugesh012No ratings yet
- MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 18/12/2010 12144 EE/EP5Document6 pagesMSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 18/12/2010 12144 EE/EP5puchughosh972No ratings yet
- DC Machine and TransformerDocument4 pagesDC Machine and TransformermitulNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology CYCLE TEST - III April-2019 15EE232 - EECS PART - A (10 X 1 10 Marks)Document2 pagesSRM Institute of Science and Technology CYCLE TEST - III April-2019 15EE232 - EECS PART - A (10 X 1 10 Marks)skarthikpriyaNo ratings yet
- EE333 Electrical Machines Lab IIDocument2 pagesEE333 Electrical Machines Lab IIvpzfarisNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. III Year I Semester Supplementary Examinations, Nov/Dec., 2018 (EEE)Document2 pagesB.Tech. III Year I Semester Supplementary Examinations, Nov/Dec., 2018 (EEE)Namaswini SureshNo ratings yet
- EE232 Electrical Machines Lab IDocument3 pagesEE232 Electrical Machines Lab ISREEHARI S J100% (1)
- Sy Ee Sem IV Cne 22418 Qp Model Answers (1)Document39 pagesSy Ee Sem IV Cne 22418 Qp Model Answers (1)1345Pranmya LadEENo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Magnetic Fields and Magnetic CircuitsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Magnetic Fields and Magnetic CircuitsDarshit KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical (09) /power Electronics (24) : Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesElectrical (09) /power Electronics (24) : Gujarat Technological UniversityKeyur PatelNo ratings yet
- R. Valunjkar (Total Load: 209+120 Part-A 329) : (Old 63hrs. & New 63hrs.) 126 Hrs in 4 MonthsDocument8 pagesR. Valunjkar (Total Load: 209+120 Part-A 329) : (Old 63hrs. & New 63hrs.) 126 Hrs in 4 MonthsRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy Conversion Lab ManualDocument61 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversion Lab Manualprathyush srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Ee8301 Em1 Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulDocument2 pagesEe8301 Em1 Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulSK ŠañđyNo ratings yet
- Manual EEE2003Document64 pagesManual EEE2003rishanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-I (Alternator)Document2 pagesAssignment-I (Alternator)debipraasadNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument350 pagesIlovepdf MergedJulius BoitizonNo ratings yet
- EEE2003 SyllabusDocument2 pagesEEE2003 SyllabusRAKESH K 20BEE1177No ratings yet
- Electric Circuit LabDocument9 pagesElectric Circuit LabKhetrimayum Robert SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology PDFDocument1 pageElectrical Technology PDFBibi Shama ShaikNo ratings yet
- Electromech Energy Conversion QDocument4 pagesElectromech Energy Conversion QAngon BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- ACMDocument4 pagesACMPoopNo ratings yet
- Cycle 1 Experiment No. 4 Study of The Steady State Performance of A Separately Excited DC GeneratorDocument4 pagesCycle 1 Experiment No. 4 Study of The Steady State Performance of A Separately Excited DC GeneratorVIJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Ait 225Document2 pagesAit 225Oscar I. ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- EE-422-Final-Examination PETE 2207Document6 pagesEE-422-Final-Examination PETE 2207Christian Rogel De TorresNo ratings yet
- Eee2003 SLBDocument2 pagesEee2003 SLBBiselary FinahNo ratings yet
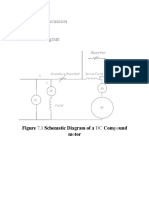
- Results and Discussion Schematic Diagram: Schematic Diagram of A Com Und M TorDocument8 pagesResults and Discussion Schematic Diagram: Schematic Diagram of A Com Und M TorJaniel MalitNo ratings yet
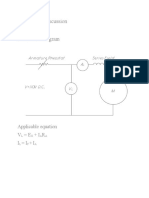
- Results and Discussion Schematic Diagram: Applicable Equation V E + I R I I + IDocument8 pagesResults and Discussion Schematic Diagram: Applicable Equation V E + I R I I + IJaniel MalitNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engg Semester 4Document18 pagesElectrical Engg Semester 4Ravi Raj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Project Plan - ConquestDocument7 pagesProject Plan - ConquestSarath TejaNo ratings yet
- Btech Ee 3 Sem Transformers and Direct Current Machines A1135 Dec 2018Document2 pagesBtech Ee 3 Sem Transformers and Direct Current Machines A1135 Dec 2018Raj KamalNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Constructional Features of Rotating Electrical MachinesDocument17 pagesQuestions & Answers On Constructional Features of Rotating Electrical Machineskibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Summer Model Answer PaperDocument22 pages2017 Summer Model Answer PaperAbhishek ChavanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines - 1Document241 pagesElectrical Machines - 1Moshood AdeleyeNo ratings yet
- Btech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Document2 pagesBtech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Raj KamalNo ratings yet
- R07aec13 - Electrical TechnologyDocument5 pagesR07aec13 - Electrical TechnologymdabdulhaqNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On DC GeneratorsDocument17 pagesQuestions & Answers On DC Generatorskibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- EEE 6th Sem Electrical DrivesDocument3 pagesEEE 6th Sem Electrical DrivesSandip MandalNo ratings yet
- Eee2003 Electromechanical-Energy-Conversion Eth 1.0 37 Eee2003Document2 pagesEee2003 Electromechanical-Energy-Conversion Eth 1.0 37 Eee2003Nathan ShankarNo ratings yet
- Cycle 2 Electrical Machines Lab IiDocument1 pageCycle 2 Electrical Machines Lab IishahanmalikkvNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, April - 2018 Electrical Machines-IiDocument8 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, April - 2018 Electrical Machines-Iianon_176479687No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesElectrical Machines II Exam Questionsanon_176479687No ratings yet
- EE6365 Electrical Engineering Lab Course PlanDocument3 pagesEE6365 Electrical Engineering Lab Course Plansimman83No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2015 Electrical Machiens-IDocument5 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2015 Electrical Machiens-IniharikaNo ratings yet
- Questions On DC MachinesDocument42 pagesQuestions On DC Machineskibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Thirumalai Engineering College Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Cat - Ii Electrical Machines - IDocument4 pagesThirumalai Engineering College Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Cat - Ii Electrical Machines - IVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- MSBTET Model Answers for Electric Motors and TransformersDocument15 pagesMSBTET Model Answers for Electric Motors and Transformers29 Sidram BirajdarNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives Experiment List Cycle 1Document1 pageElectric Drives Experiment List Cycle 1Ashish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- meoetIV 4001Document3 pagesmeoetIV 4001Bharathi ManoNo ratings yet
- BEEE - Unit - II - QBDocument6 pagesBEEE - Unit - II - QBSweetlineSoniaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Todays Technician Automotive Electricity and Electronics Classroom and Shop Manual Pack 6th EditionDocument9 pagesSolution Manual For Todays Technician Automotive Electricity and Electronics Classroom and Shop Manual Pack 6th EditionPaulPaynermyd100% (34)
- Scheme - I Sample Question PaperDocument4 pagesScheme - I Sample Question Paperjijo123408No ratings yet
- Introduction To Machine 2020 - 21Document1 pageIntroduction To Machine 2020 - 21martazemeduNo ratings yet
- Assignment-6 DC MotorDocument3 pagesAssignment-6 DC MotornikunjNo ratings yet
- Review 13 Rural ElectrificationDocument17 pagesReview 13 Rural Electrificationdongzkie100% (1)
- Questions & Answers On Synchronous Machine StabilityDocument20 pagesQuestions & Answers On Synchronous Machine Stabilitykibrom atsbha50% (2)
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- FCS+Chapter+3 (3 1-3 3)Document11 pagesFCS+Chapter+3 (3 1-3 3)kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Ecological Concepts: Unit IDocument14 pagesEcological Concepts: Unit Ikujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Course DetailsDocument2 pagesCourse Syllabus Course Detailskujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument60 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversionkujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document1 pageActivity 2kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument60 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversionkujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control Systems: Rezel A. Sto. Tomas, Ece 1Document10 pagesFeedback and Control Systems: Rezel A. Sto. Tomas, Ece 1kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document1 pageActivity 2kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuit FundamentalsDocument40 pagesMagnetic Circuit Fundamentalskujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Components v2Document32 pagesSymmetrical Components v2Carlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 3.) Magnetic+circuitDocument40 pages3.) Magnetic+circuitkujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Switching Theory and Logic Circuits 1Document184 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic Circuits 1kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- 1.) Magnetic+Field+and+Self+InductanceDocument23 pages1.) Magnetic+Field+and+Self+Inductancekujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Magneticcircuits 140916102412 Phpapp02Document19 pagesMagneticcircuits 140916102412 Phpapp02Madhan Kumar ChNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuit FundamentalsDocument40 pagesMagnetic Circuit Fundamentalskujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFkujong agacerNo ratings yet
- 1.) Magnetic+Field+and+Self+InductanceDocument23 pages1.) Magnetic+Field+and+Self+Inductancekujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Magneticcircuits 140916102412 Phpapp02Document19 pagesMagneticcircuits 140916102412 Phpapp02Madhan Kumar ChNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Components v2Document32 pagesSymmetrical Components v2Carlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table ProofsDocument20 pagesLaplace Table Proofskujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self: Course Outline Unit 1: The Self From Various PerspectivesDocument1 pageUnderstanding The Self: Course Outline Unit 1: The Self From Various Perspectiveskujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Advance MathematicsDocument94 pagesAdvance Mathematicskujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Current & Resistance: - Current and Current Density - Ohm's Law - Resistivity - ResistanceDocument17 pagesCurrent & Resistance: - Current and Current Density - Ohm's Law - Resistivity - ResistancePedroNo ratings yet
- BME 595 - Medical Imaging Applications Part 2: Introduction To Mri Fundamentals of Magnetic Resonance Feb. 16, 2005Document42 pagesBME 595 - Medical Imaging Applications Part 2: Introduction To Mri Fundamentals of Magnetic Resonance Feb. 16, 2005Jo Hn VengzNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Formulas and Numerical ProblemsDocument11 pagesElectrostatics Formulas and Numerical ProblemsManish kumar100% (2)
- Quiz On InductorsDocument3 pagesQuiz On InductorsMahmoud OsamaNo ratings yet
- Name: Sajeel Khan Roll#: M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: Magnetism in Condensed Matter Submitted To: Dr. Imran Sadiq SBDocument10 pagesName: Sajeel Khan Roll#: M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: Magnetism in Condensed Matter Submitted To: Dr. Imran Sadiq SBAnonymous f7wV1lQKRNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Intensity (H)Document5 pagesMagnetic Field Intensity (H)M HASIN ISHMAM JEETNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of Coordination ComplexesDocument14 pagesMagnetic Properties of Coordination ComplexesbnkjayaNo ratings yet
- Gcse Physics Answers and Mark Schemes: ChargeDocument8 pagesGcse Physics Answers and Mark Schemes: ChargeChristina T Z-chYnNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II - Unit 11 - Week 8Document3 pagesElectrical Machines II - Unit 11 - Week 8Prathap VuyyuruNo ratings yet
- NG Compass General Questions 12p 109qDocument12 pagesNG Compass General Questions 12p 109qAds Lyf INNo ratings yet
- Wcanrrersru: 6650 Bingle Road Houston, Texas ' 1 1 0 9 2Document10 pagesWcanrrersru: 6650 Bingle Road Houston, Texas ' 1 1 0 9 2OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Crystallography: Classification of Crystal Systems and DefectsDocument54 pagesCrystallography: Classification of Crystal Systems and DefectsSaad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Apc B MC12Document6 pagesApc B MC12Sagar KumarNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Rating and Loss DissipationDocument25 pagesQuestions & Answers On Rating and Loss Dissipationkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- How Does A Van de Graaff Generator OperateDocument8 pagesHow Does A Van de Graaff Generator OperateTimberlyNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Compensation For Transmission and Distribution SystemsDocument4 pagesReactive Power Compensation For Transmission and Distribution SystemsSuranjana DasNo ratings yet
- Superparamagnetism: Limits and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesSuperparamagnetism: Limits and ApplicationsNguyen VuNo ratings yet
- Wet Magnetic Particle Testing and Dry Magnetic Particle TestingDocument2 pagesWet Magnetic Particle Testing and Dry Magnetic Particle TestingLlewellyn AspaNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Protection Vol 3 PDFDocument479 pagesPower Systems Protection Vol 3 PDFlaser2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NMR TheoryDocument63 pagesChapter 1 NMR TheoryabhiNo ratings yet
- Physics Project - Mapping The Magnetic FieldDocument26 pagesPhysics Project - Mapping The Magnetic Fieldmohammadumair2006No ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-05: Magnetism and MatterDocument2 pagesCBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-05: Magnetism and MatterabcdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 11 Q2 M2Document13 pagesChemistry 1 11 Q2 M2Jessie CandawanNo ratings yet
- N35UH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN35UH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Leviation Train ProjectDocument7 pagesMagnetic Leviation Train ProjectMd.Sameul IslamNo ratings yet
- BobiSoft Short Description 2017Document12 pagesBobiSoft Short Description 2017Masum uddin mondolNo ratings yet
- Catapult ForceDocument5 pagesCatapult Forcemohammad narmiNo ratings yet
- Mineral Processing-II SlidesDocument138 pagesMineral Processing-II SlidesAli Wassan100% (2)
- DC Machine Lectures PDFDocument131 pagesDC Machine Lectures PDFSarthakNo ratings yet