Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ansys Lecture: R.M. Shahbab Lecturer, Dept. of IPE, BUET
Uploaded by
RM ShahbabOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ansys Lecture: R.M. Shahbab Lecturer, Dept. of IPE, BUET
Uploaded by
RM ShahbabCopyright:
Available Formats
R.M.
Shahbab
Lecturer,
Dept. of IPE, BUET.
Ansys Lecture
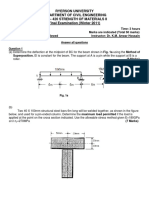
1. Finite Element Analysis: The finite element analysis (FEA) is the most popularly used
method for solving problems of engineering and mathematical models. Areas of interest
include structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic
potential. The FEA is actually a numerical method for solving partial differential
equations in two or three space variables. FEA solves a problem by subdividing a large
system into smaller, simpler parts that are called Finite Elements.
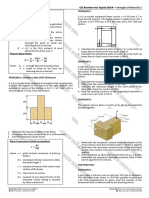
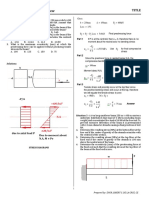
2. Illustration of Distributed load on a simply supported Beam.
w = 5 N/mm
a = 40 mm
L = 1m
a = 40 mm
Material Structural Steel
Theoretical max. deflection 1.453 mm
Theoretical max. bending stress 58.59Pa
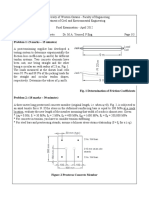
3. Illustration of point load on a simply supported beam.
P = 5000 N
a = 40 mm
L = 1m
a = 40 mm
Material Stainless Steel
Theoretical max. deflection 2.33 mm
Theoretical max. bending stress 117 MPa
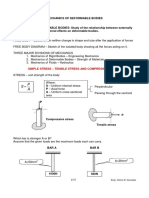
4. Illustration of uniformly varying load on a cantilever beam
P = 500 N
a = 40 mm
a = 70 mm
L = 500 mm
Material Structural Steel
5. Illustration of torsional shear stress and factor of safety calculation.
Max. allowable shear stress, 𝜏max 13,200 MPa
You might also like
- Ansys Lecture: R.M. Shahbab Lecturer, Dept. of IPE, BUETDocument4 pagesAnsys Lecture: R.M. Shahbab Lecturer, Dept. of IPE, BUETRM ShahbabNo ratings yet
- 2 Simple StrainDocument21 pages2 Simple StrainFrances Louise LariosaNo ratings yet
- Mos PPT (Ame004) (18 19 16)Document95 pagesMos PPT (Ame004) (18 19 16)Muhammad Rizwan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Sectional AnalysisDocument24 pagesLecture 8 - Sectional AnalysisKhaled AlregebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Axial Stress and Strain - 3Document26 pagesLecture 1 - Axial Stress and Strain - 3Alvin DeliroNo ratings yet
- Tensile TestDocument15 pagesTensile Testrakan454ssNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanics of Def. Bodies + Normal StressDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Mechanics of Def. Bodies + Normal StressJQNo ratings yet
- Mech 30a March 21 2022 Eteeap ModuleDocument65 pagesMech 30a March 21 2022 Eteeap ModuleGibson DiangoNo ratings yet
- 2 1-Simplestrain PDFDocument21 pages2 1-Simplestrain PDFMarkVincentTulinaoNo ratings yet
- 0050 - Cantilever Under Torsion Without Warping: DescriptionDocument3 pages0050 - Cantilever Under Torsion Without Warping: DescriptionjohnNo ratings yet
- Ecv 203: Strength of Materials I: C.A.T Ii DATE: 10/08/21 To Be Submitted On 10/09/21 Instructions Attempt ALL QuestionsDocument11 pagesEcv 203: Strength of Materials I: C.A.T Ii DATE: 10/08/21 To Be Submitted On 10/09/21 Instructions Attempt ALL QuestionsRobertNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. StressDocument5 pagesLesson 1. Stressrobin roldanNo ratings yet
- Cub Surg Lesson02 Presentation v2 Tedl DWCDocument15 pagesCub Surg Lesson02 Presentation v2 Tedl DWCHarendra Singh Rathore DoultpuraNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Simulation Using Abaqus: Internship OnDocument24 pagesFinite Element Simulation Using Abaqus: Internship OnranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- CVL Final Exam Past YearDocument3 pagesCVL Final Exam Past YearApril SkyNo ratings yet
- Apr 2024 - Strength of Materials 5Document2 pagesApr 2024 - Strength of Materials 5isnainsalman3No ratings yet
- Simple Stress: Fundamentals of Deformable BodiesDocument3 pagesSimple Stress: Fundamentals of Deformable Bodiesreymart cereneoNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 5: Theories of Failure: Safe If Brittle Fails If DuctileDocument4 pagesProblem Sheet 5: Theories of Failure: Safe If Brittle Fails If DuctileDivyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 01Document8 pagesElectrical Machines 01saghiram8071No ratings yet
- Lab Hardness MemoDocument4 pagesLab Hardness MemoJan YsNo ratings yet
- Mohr Gary2007 - Article - M shapedSpecimenForTheHigh STRDocument12 pagesMohr Gary2007 - Article - M shapedSpecimenForTheHigh STRradheNo ratings yet
- Beam AnalysisDocument273 pagesBeam AnalysisJeffry VargasNo ratings yet
- Strength 5 May 2021Document2 pagesStrength 5 May 2021Jon SnowNo ratings yet
- T03 - Magnetic Circuits (Complete)Document31 pagesT03 - Magnetic Circuits (Complete)rvjf8bwrj2No ratings yet
- Mem-402-Mos Final QB-2015Document9 pagesMem-402-Mos Final QB-2015Rohit DiwakarNo ratings yet
- R13 Jntua Mechanical Engineer Question PaperDocument2 pagesR13 Jntua Mechanical Engineer Question PaperChandrika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Closed-Book Practice-Ch 06 (2016!07!31)Document8 pagesClosed-Book Practice-Ch 06 (2016!07!31)JuanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document4 pagesTutorial 9TOS CCLNo ratings yet
- 3 Mec32-1 Simple Stress and Thin Walled CylindersDocument38 pages3 Mec32-1 Simple Stress and Thin Walled CylindersAlex JavierNo ratings yet
- MEGA Review-Module-32-Strength-of-Materials-3Document1 pageMEGA Review-Module-32-Strength-of-Materials-3Study BuddiesNo ratings yet
- R7220103 Strength of Materials - IIDocument1 pageR7220103 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- MOSDocument366 pagesMOSMr.S UpenderNo ratings yet
- 20-1-16 LS Dyna - SHPB Analysis FinalDocument7 pages20-1-16 LS Dyna - SHPB Analysis FinalJayDeep KhajureNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Simple StrainDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Simple StrainYnah Marie BoragayNo ratings yet
- Module 30 - Stress-Strain RIDocument3 pagesModule 30 - Stress-Strain RIClark Sibi100% (1)
- Mec 610 Lab 1 29032023Document5 pagesMec 610 Lab 1 29032023Aqil AimanNo ratings yet
- 2012 ExamDocument3 pages2012 ExamJagannathanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Mecvina PDFDocument37 pagesMicrosoft Word Mecvina PDFErvin GohNo ratings yet
- TensileDocument11 pagesTensileNicholas ChanNo ratings yet
- Lesson I - SIMPLE STRESS - Part IDocument34 pagesLesson I - SIMPLE STRESS - Part Iemsebial29No ratings yet
- Simple StrainDocument13 pagesSimple StrainJacob Aquino100% (1)
- ExamsDocument8 pagesExamsJoy CeeNo ratings yet
- Som Assignments PDFDocument12 pagesSom Assignments PDFLaxmi HattiholiNo ratings yet
- Contact Force Models Including Electric Contact deDocument5 pagesContact Force Models Including Electric Contact de46k2dgs2sjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document8 pagesChapter 5Ali MadkNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument31 pagesChapter Three: Mechanical Properties of MaterialsOmar AlzoubiNo ratings yet
- ≤ σ is the allowable stress for the material used. Substituting σ in theDocument4 pages≤ σ is the allowable stress for the material used. Substituting σ in theJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- SEC MODULE 06 SolDocument4 pagesSEC MODULE 06 Solkenji belanizoNo ratings yet
- Contribution119 FinalDocument8 pagesContribution119 FinalPhúc DuyNo ratings yet
- Coupling Parallel Buildings by Supplemental Viscous Damper DeviceDocument6 pagesCoupling Parallel Buildings by Supplemental Viscous Damper Devicemina refaatNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Chapter 3Document22 pagesStrength of Material Chapter 3naserunnNo ratings yet
- Ce 429st Pre-Final Exam - KeyDocument9 pagesCe 429st Pre-Final Exam - KeyAl-fin KaytingNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Stress Analysis ProjectDocument22 pagesMechanics of Materials Stress Analysis ProjectDaffa SudianaNo ratings yet
- ER 05M 145 ER 05M 145: Hi-Power YPEDocument1 pageER 05M 145 ER 05M 145: Hi-Power YPEjuliofelixNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet No 5Document2 pagesProblem Sheet No 5akbarNo ratings yet
- NIMS PosterDocument1 pageNIMS Posterアスリアナ イブラヒムNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 pages1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1onenoteforlocadNo ratings yet
- FLEXURAL 12 (Autosaved)Document42 pagesFLEXURAL 12 (Autosaved)Ezen ChiNo ratings yet
- Magneto-Resistive and Spin Valve Heads: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandMagneto-Resistive and Spin Valve Heads: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Chapter - 4 Functional Decomposition: Step 1: Finding The Most General Function Which Has To Be AccomplishedDocument6 pagesChapter - 4 Functional Decomposition: Step 1: Finding The Most General Function Which Has To Be AccomplishedRM ShahbabNo ratings yet
- AsssignmentDocument1 pageAsssignmentRM ShahbabNo ratings yet
- Incorporating The Voice of Customer in Product Design With Quality Function Deployment (QFD)Document3 pagesIncorporating The Voice of Customer in Product Design With Quality Function Deployment (QFD)RM ShahbabNo ratings yet
- IPE 303 Product Design: Chapter 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting From Variable LoadingDocument6 pagesIPE 303 Product Design: Chapter 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting From Variable LoadingRM ShahbabNo ratings yet
- IPE 303 Product Design: Chapter 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting From Variable LoadingDocument11 pagesIPE 303 Product Design: Chapter 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting From Variable LoadingRM ShahbabNo ratings yet
- IPE 303 Lecture - 16sept2020Document14 pagesIPE 303 Lecture - 16sept2020RM ShahbabNo ratings yet
- Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design - Chapter 8 - Part 1Document71 pagesShigley's Mechanical Engineering Design - Chapter 8 - Part 1RM ShahbabNo ratings yet
- IPE 303 Lecture - 30sept2020Document21 pagesIPE 303 Lecture - 30sept2020RM ShahbabNo ratings yet