Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Work and Energy: Part A. Vocabulary Review
Uploaded by
ForeignnX Phayy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
943 views2 pages1. The document is a worksheet about work and energy concepts including vocabulary terms, equations, and example problems. It contains a vocabulary review matching section to define terms like kinetic energy, work, potential energy, and efficiency.
2. The concept review section asks students to complete sentences using these terms and define concepts like the law of conservation of energy. Example problems calculate kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy using the given equations.
3. The questions at the end ask students to explain how a hammer's kinetic energy would change if dropped from a higher roof and how machines can be useful even if their efficiency is less than 100%.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chapter_Review_Work_and_Energy_Editable_1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document is a worksheet about work and energy concepts including vocabulary terms, equations, and example problems. It contains a vocabulary review matching section to define terms like kinetic energy, work, potential energy, and efficiency.
2. The concept review section asks students to complete sentences using these terms and define concepts like the law of conservation of energy. Example problems calculate kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy using the given equations.
3. The questions at the end ask students to explain how a hammer's kinetic energy would change if dropped from a higher roof and how machines can be useful even if their efficiency is less than 100%.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
943 views2 pagesWork and Energy: Part A. Vocabulary Review
Uploaded by
ForeignnX Phayy1. The document is a worksheet about work and energy concepts including vocabulary terms, equations, and example problems. It contains a vocabulary review matching section to define terms like kinetic energy, work, potential energy, and efficiency.
2. The concept review section asks students to complete sentences using these terms and define concepts like the law of conservation of energy. Example problems calculate kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy using the given equations.
3. The questions at the end ask students to explain how a hammer's kinetic energy would change if dropped from a higher roof and how machines can be useful even if their efficiency is less than 100%.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
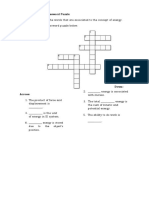
Name Date Class
Work and Energy
Part A. Vocabulary Review
Directions: Match the description in the first column with the term in the second column by writing the correct
letter in the space provided.
1. total amount of kinetic and potential energy
in a system a. energy
b. work
2. the ability to cause change
c. kinetic energy
3. stored energy due to position d. law of conservation of
4. energy in the form of motion energy
e. gravitational potential
5. Energy cannot be created or destroyed energy
6. does work with only one movement of the machine f. mechanical energy
7. energy stored in chemical bonds g. potential energy
h. simple machine
8. ratio of output work to input work
i. efficiency
9. energy stored by things that are above earth
j. chemical potential
10. SI unit of energy energy
11. force applied through a distance k. joule
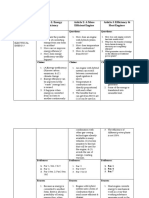
Part B. Concept Review
Directions: Complete the following sentences using the correct terms.
1. The amount of kinetic energy a moving object has depends
on its mass and its .
2. The potential energy of an object depends on its .
3. The energy stored in foods and fuels is
potential energy.
4. The law of states that energy cannot be created
or destroyed.
5. A compound machine is a combination of two or more .
6. The number of times a machine multiplies the effort force is the
of the machine.
7. You convert kinetic energy into thermal energy when you
rub two sticks together because of .
Work and Energy 31
Name Date Class
8. The total energy of a system remains .
9. Screws and wedges are modified .
10. A car engine changes chemical potential energy into the
energy of the moving car.
2
11. Use the equation KE = 12 m × v to calculate the kinetic energy of a 100 kg cart moving at a
speed of 7 m/s?
12. Use the equation GPE = m 9.8 m/s h to calculate the gravitational potential of a 10-kg
2
sack of groceries on a shelf 1 m above the floor?
Directions: Answer the following questions on the lines provided.
13. A hammer falls off a roof top and strikes the ground with a certain kinetic energy. If it fell
from a roof twice as tall, how would its kinetic energy compare? Explain.
14. Explain how machines can be useful if the output work is always less than the input work.
32 Work and Energy
You might also like
- A Tale of Two CitiesDocument111 pagesA Tale of Two CitiesMohamed SultanNo ratings yet
- BeowulfDocument2 pagesBeowulfJesa EscoberNo ratings yet
- (Gilman) TP-CASTT FrankensteinDocument3 pages(Gilman) TP-CASTT FrankensteinA ThingNo ratings yet
- Final Test The Miracle WorkerDocument7 pagesFinal Test The Miracle WorkerLawrence QuimboNo ratings yet
- Heep Yunn School - Mid-Year Examinations (2021 - 2022) : Syllabus (F.2)Document3 pagesHeep Yunn School - Mid-Year Examinations (2021 - 2022) : Syllabus (F.2)YIN CHONGNo ratings yet
- Uniformly Accelerated Motion (Horizontal and Vertical)Document27 pagesUniformly Accelerated Motion (Horizontal and Vertical)Seth DelfinNo ratings yet
- A Good Man Is Hard To Find Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesA Good Man Is Hard To Find Lesson PlanCharles AbelNo ratings yet
- AgamemnonDocument28 pagesAgamemnonBahadur BiswasNo ratings yet
- Cpe 0900Document7 pagesCpe 0900Ranuk AbeylathNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Gen Physics 2017-2018Document2 pages2nd Grading Gen Physics 2017-2018Mariel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 17 1+energy An+overviewDocument3 pages17 1+energy An+overviewjessielaine80No ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Test - Physical ScienceDocument4 pages2nd Quarter Test - Physical ScienceArven DulayNo ratings yet
- Types of Energy (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and WorksheetsDocument1 pageTypes of Energy (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheetsnareman100% (6)
- Types of Energy Answer KeyDocument1 pageTypes of Energy Answer Keynareman100% (1)
- Envi WorkDocument2 pagesEnvi WorkjerellNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument14 pagesEnergyosama100% (1)
- Energy Conversions and Energy Sources TASK Davina MoralesDocument3 pagesEnergy Conversions and Energy Sources TASK Davina MoralesDavina MoralezNo ratings yet
- Science9 Quarter 4 Module 5Document16 pagesScience9 Quarter 4 Module 5Joan D. Roque80% (5)
- S9 Q4 Enhanced Hybrid Module 3 Week 4Document16 pagesS9 Q4 Enhanced Hybrid Module 3 Week 4Sheeromae SabalaNo ratings yet
- Energy and ChemistryDocument27 pagesEnergy and Chemistry中村カズハNo ratings yet
- Long QuizDocument4 pagesLong QuizSteffe Mitch GarciaNo ratings yet
- Work, Power, Energy WorksheetDocument6 pagesWork, Power, Energy WorksheetDato Dato DatoNo ratings yet
- QUIZ LRMDS Work Power EnergyDocument1 pageQUIZ LRMDS Work Power Energyambermikaela.siNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Gen Physics 2017-2018 EditedDocument3 pages2nd Grading Gen Physics 2017-2018 EditedMariel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Gen Physics 2017-2018 EditedDocument3 pages2nd Grading Gen Physics 2017-2018 EditedMariel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Conservation of EnergyDocument2 pagesConservation of EnergyChristine BelaleNo ratings yet
- 0 BooksDocument26 pages0 BooksSakhawat AliNo ratings yet
- Diamond Stone International School IGCSE Weekly Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesDiamond Stone International School IGCSE Weekly Lesson PlanjanithaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: The Characteristics of ElectricityDocument38 pagesUnit 4: The Characteristics of ElectricitysaminbansalprogamerNo ratings yet
- Test - Introduction To EnergyDocument12 pagesTest - Introduction To EnergyAxia LlanosNo ratings yet
- Introduction-To-Energy KeyDocument2 pagesIntroduction-To-Energy KeyAngel JaimesNo ratings yet
- c05d9 Naturalscience04 Unit08 Diagnostic PDFDocument2 pagesc05d9 Naturalscience04 Unit08 Diagnostic PDFFaty Berir Martinez100% (1)
- Lesson Plan (Potential and Kinetic)Document10 pagesLesson Plan (Potential and Kinetic)Ace Arciaga75% (4)
- 2nd Semester Activity 1 STUDENT VERSIONDocument2 pages2nd Semester Activity 1 STUDENT VERSIONAn NguyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction of Energy Sources and Its Conversion: Strength of Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction of Energy Sources and Its Conversion: Strength of Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsMahesh DhopeNo ratings yet
- C. Conservation and Dissipation of Energy: Fiberglass Insulation Wool InsulationDocument3 pagesC. Conservation and Dissipation of Energy: Fiberglass Insulation Wool InsulationGUSADHIAoNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Work, Energy, Power and MachinesDocument44 pagesModule 11 Work, Energy, Power and MachinesMarjorie Brondo100% (1)
- K 12 Exam 4th Quarter Science 9Document5 pagesK 12 Exam 4th Quarter Science 9Julie Ann Pineda BalichaNo ratings yet
- Module Sample Format For Math and ScienceDocument44 pagesModule Sample Format For Math and Sciencetees cNo ratings yet
- Es TG Module 2 Climate RevisedDocument23 pagesEs TG Module 2 Climate RevisedNikkieIrisAlbañoNovesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document4 pagesUnit 4АА-11-21 Руденко ДмитроNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q1 Module 3 PE - KE Activity SheetsDocument12 pagesScience 8 Q1 Module 3 PE - KE Activity SheetsJilyan Stephanie AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Guided Generalization Essential Article 1: Energy Efficiency Article 2: A More Efficient Engine Article 3: Efficiency & Heat EnginesDocument3 pagesGuided Generalization Essential Article 1: Energy Efficiency Article 2: A More Efficient Engine Article 3: Efficiency & Heat EnginesEdzborbonNo ratings yet
- Potential Vs Kinetic Energy Worksheet - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesPotential Vs Kinetic Energy Worksheet - Answer KeyFlamingXedNo ratings yet
- Energy SourcesDocument14 pagesEnergy Sourceshjjpt4ycrgNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceDonna Lyn BorjaNo ratings yet
- Stem ProjectDocument6 pagesStem ProjecthourNo ratings yet
- Re 4.3 (Mio)Document6 pagesRe 4.3 (Mio)Angel PerezNo ratings yet
- P1 Revision OverviewDocument3 pagesP1 Revision Overviewian McMillanNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceBeverly Joyce BarettoNo ratings yet
- Aviral Classes - Khandari Crossing Bypass Road, Agra Contact No-8755228920Document4 pagesAviral Classes - Khandari Crossing Bypass Road, Agra Contact No-8755228920Madhukar BhagatNo ratings yet
- Science 3 PTDocument3 pagesScience 3 PTMARY ROVELYN CABRALESNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms and Changes IncompleteDocument4 pagesEnergy Forms and Changes IncompletePhilip Moore100% (1)
- Energy Separate 1Document55 pagesEnergy Separate 1Alisha KhanNo ratings yet
- Class - 8 Physics Chapter - 4 Energy (Solutions) : A. Choose The Correct OptionDocument4 pagesClass - 8 Physics Chapter - 4 Energy (Solutions) : A. Choose The Correct Optionankurstudypoint4No ratings yet
- Module in PhysicsDocument41 pagesModule in PhysicsJeje NutNo ratings yet
- Energy Quiz Key 2Document2 pagesEnergy Quiz Key 2Queenie maunaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Energy and ChemistryDocument94 pages2 - Energy and ChemistryKenny Jay LabianoNo ratings yet
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument3 pagesIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionMuhammad barakatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Energy: Energy at A Glance, 2015Document4 pagesIntroduction To Energy: Energy at A Glance, 2015Balanuța IanaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Project!: Chem4Kids Israel Science and TechnologyDocument3 pagesPeriodic Table Project!: Chem4Kids Israel Science and TechnologyForeignnX PhayyNo ratings yet
- The Story of JezebelDocument1 pageThe Story of JezebelForeignnX PhayyNo ratings yet
- Anticipation Guide William ShakespeareDocument1 pageAnticipation Guide William ShakespeareForeignnX PhayyNo ratings yet
- Congress in A Flash New Reading FillableDocument2 pagesCongress in A Flash New Reading FillableForeignnX PhayyNo ratings yet
- 4051 Manuscript 10825 1 10 20220331Document12 pages4051 Manuscript 10825 1 10 20220331Chandra MouliNo ratings yet
- 13 - Wool-And-Coir-Fiber-Reinforced-Gypsum-Ceiling-Tiles-Wit - 2021 - Journal-of-BuilDocument9 pages13 - Wool-And-Coir-Fiber-Reinforced-Gypsum-Ceiling-Tiles-Wit - 2021 - Journal-of-BuilJenifer TejadaNo ratings yet
- Astm F 16Document5 pagesAstm F 16Maki Salim HussainNo ratings yet
- DanielJacobs QuestionsDocument79 pagesDanielJacobs QuestionsJimena MedinaNo ratings yet
- SHORT REPORT - 606 - Liner DisplacementDocument26 pagesSHORT REPORT - 606 - Liner DisplacementwongpeisenNo ratings yet
- I. Melc.: Perpetual Succour Academy, Inc. National Rd. Poblacion Dos, Malabuyoc, Cebu Science 10Document4 pagesI. Melc.: Perpetual Succour Academy, Inc. National Rd. Poblacion Dos, Malabuyoc, Cebu Science 10Cry BeroNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentdola indupriyaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular Biology Module (Lecture and Laboratory)Document200 pagesCell and Molecular Biology Module (Lecture and Laboratory)RM Montemayor100% (2)
- Aplied Thermodynamics Tutorial 1, Revision of Isentropic Efeciency Advanced Steam Cycles.Document80 pagesAplied Thermodynamics Tutorial 1, Revision of Isentropic Efeciency Advanced Steam Cycles.Moch Bagus BahtiarNo ratings yet
- Particle Size and Shape - CompleteDocument26 pagesParticle Size and Shape - CompleteNitin MauryaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2150 Lab 03 - The Hall EffectDocument6 pagesPhysics 2150 Lab 03 - The Hall EffectJeet Saurav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 - THERMODYNAMICSDocument37 pagesChapter-9 - THERMODYNAMICSJoanne SohNo ratings yet
- Dye Laser: Navigation SearchDocument6 pagesDye Laser: Navigation SearchselvakanmaniNo ratings yet
- SPM Phy Quantity of Heat IDocument13 pagesSPM Phy Quantity of Heat ICHINEMEREM EZEHNo ratings yet
- Jgeot.21.00089 OffprintDocument11 pagesJgeot.21.00089 OffprintBrian SheilNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 1 EEE-466, Power Electronics Lab: Design and Simulation of Bridge RectifiersDocument9 pagesLab Assignment 1 EEE-466, Power Electronics Lab: Design and Simulation of Bridge RectifiersKhairulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Magnetic Materials: EXERCISES (PAGES 263 - 264)Document14 pagesChapter 11: Magnetic Materials: EXERCISES (PAGES 263 - 264)sagarshivnathsingh18818No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Differentiation: StructureDocument30 pagesUnit 6 Differentiation: StructuretapansNo ratings yet
- Steps To Improve Roads On Black Cotton SoilsDocument9 pagesSteps To Improve Roads On Black Cotton SoilsAmrutha SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Board (Tantalum Less) : Solidworks Drawing: All Changes Must Be Done in Solidworks DatabaseDocument2 pagesPower Supply Board (Tantalum Less) : Solidworks Drawing: All Changes Must Be Done in Solidworks DatabasezizouhicheNo ratings yet
- Flange Management Rev 1 160216081830Document31 pagesFlange Management Rev 1 160216081830Ali100% (1)
- Q1.An Electrical Circuit Is Shown in The Figure Below.: ST Thomas More Catholic SchoolDocument54 pagesQ1.An Electrical Circuit Is Shown in The Figure Below.: ST Thomas More Catholic SchooljsNo ratings yet
- Green Adeptness in The Synthesis and Stabilization of Copper Nanoparticles: Catalytic, Antibacterial, Cytotoxicity, and Antioxidant ActivitiesDocument15 pagesGreen Adeptness in The Synthesis and Stabilization of Copper Nanoparticles: Catalytic, Antibacterial, Cytotoxicity, and Antioxidant ActivitiesWindah AnisyahNo ratings yet
- Right Triangle TrigonometryDocument19 pagesRight Triangle TrigonometryJohnNo ratings yet
- Draft - 8 - WAP - 5 - 200 KMPH - Finalyzing The SpecificationDocument75 pagesDraft - 8 - WAP - 5 - 200 KMPH - Finalyzing The Specificationsrikanth potnuruNo ratings yet
- Turbomachinery: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocument86 pagesTurbomachinery: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsBabita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document2 pagesUnit 2Rohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- 3D Numerical Modelling of Open Channel Flow With Submerged VegetationDocument9 pages3D Numerical Modelling of Open Channel Flow With Submerged VegetationIhtesham KhanNo ratings yet
- Solved 2024 Specimen Paper ICSE Class 10 ChemistryDocument11 pagesSolved 2024 Specimen Paper ICSE Class 10 ChemistrymmroyalethegreatNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Reciprocating COMPRESSORDocument30 pagesModule 6 Reciprocating COMPRESSORSylvesterNo ratings yet