Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STUDY GUIDE EXAM 3 - Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics
Uploaded by
Brandice Bradley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pages1. Explain the stages of shock and the positive and negative feedback mechanisms associated with each stage.
2. Describe the effects of increased peripheral resistance on blood pressure and flow. Increased peripheral resistance leads to higher blood pressure and reduced blood flow.
3. Compare and contrast the layers of blood vessel walls for arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries have the most layers for strength, veins have valves to aid return flow, and capillaries are thin-walled for gas/nutrient exchange.
Original Description:
Original Title
SG_Exam 3 Blood vessels (6) (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Explain the stages of shock and the positive and negative feedback mechanisms associated with each stage.
2. Describe the effects of increased peripheral resistance on blood pressure and flow. Increased peripheral resistance leads to higher blood pressure and reduced blood flow.
3. Compare and contrast the layers of blood vessel walls for arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries have the most layers for strength, veins have valves to aid return flow, and capillaries are thin-walled for gas/nutrient exchange.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesSTUDY GUIDE EXAM 3 - Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics
Uploaded by
Brandice Bradley1. Explain the stages of shock and the positive and negative feedback mechanisms associated with each stage.
2. Describe the effects of increased peripheral resistance on blood pressure and flow. Increased peripheral resistance leads to higher blood pressure and reduced blood flow.
3. Compare and contrast the layers of blood vessel walls for arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries have the most layers for strength, veins have valves to aid return flow, and capillaries are thin-walled for gas/nutrient exchange.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
STUDY GUIDE EXAM 3 - Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics
1. Compared to arteries, veins 35. blood pressure
2. Capillaries 36. blood pressure
3. venules. 37. In comparison to a vessel with a large diameter, a vessel with a small
4. veins. diameter has
5. layers of a blood vessel wall 38. cross-sectional area - hemodynamics rule
6. layers of a blood vessel wall 39. The force that moves fluid out of capillaries is ________ pressure whereas
7. fenestrated capillaries the opposing force that moves fluid into capillaries is ________ pressure.
8. capillaries. 40. Blood colloid osmotic pressure
9. Which kind of vessel is also called a resistance vessel? 41. Blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP)
10. Blood flow through a capillary is controlled by the 42. Increased levels of carbon dioxide in the blood
11. The aorta is an example of which type of artery? 43. Aldosterone.
12. The brachial artery is an example of which type of artery? 44. During exercise
13. Arteriosclerosis 45. In response to hemorrhage
14. venules Questions 46-49 refer to the case on shock:
15. Blood moves forward through veins because of 50. If a person stands up suddenly from the prone (lying) position they may feel
16. Which part of the vascular system functions as a blood reservoir and a sudden dizzy or lightheadedness.
contains over 60% of the body's blood? 51. Angiotensin II
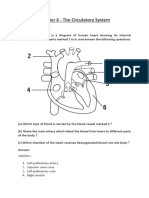
17. List in correct order the sequence of blood vessels that blood would travel in 52. resistance
the systemic circuit starting at the aorta. 53. adaptive anatomy of the aorta
1. venules 5. medium veins 54. autoregulation.
2. arterioles 6. large veins 55. carotid sinus reflex
3. capillaries 7. muscular arteries 56. Which of the following would not be expected from taking a diuretic drug?
4. elastic arteries 57. The velocity and pressure of blood in the capillary beds.
58. blood pressure?
18. The main control of peripheral resistance occurs in the 59. blood pressure
19. Resistance 60. velocity of blood flow
20. Resistance is related to
21. As blood travels from arteries to veins,
22. Blood flow to a tissue will increase if the
23. Blood pressure increases with all of the following, except increased
24. Which of the following factors will increase the net filtration pressure to
move fluid out of capillaries?
25. Pressure trends in the circulatory system
26. Clinically, the term blood pressure usually refers to
27. venous return
28. Blood pressure
29. Factors that affects blood flow
30. cardiac output
31. Edema
32.pulse pressure
33. The blood colloid osmotic pressure mostly depends on the
34. Which of the following statements is false concerning the movement of fluid
between capillaries and interstitial space?
Possible Essays:
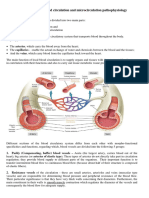
1. List 6 causes of hypovolemic shock as given in your lecture notes
2. RAA pathway. Name the components and function where appropriate.
3. Explain why each of the symptoms of shock occurs.
4. Stages of Shock - be able to name each stage and give an example of a positive and negative feedback mechanism as it applies to the stages
of shock.
For each of the following situations, describe the anticipated effect on blood pressure and the physiological basis of the response:
Situation Effect on BP Physiological basis of the response
(write
increase or
decrease)
High salt diet
A blow on the head that damages
or disables the vasomotor center
An attack by a mugger
A hypothalamic tumor resulting in
excess ADH production
Increased renin production
Increased peripheral resistance
A bee sting causes vasodilation
of almost all of the body's
arterioles
You might also like
- Blood Flow PhysicsDocument17 pagesBlood Flow PhysicsAhmad Haikal0% (1)
- Central Venous Pressure: Its Clinical Use and Role in Cardiovascular DynamicsFrom EverandCentral Venous Pressure: Its Clinical Use and Role in Cardiovascular DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Cicrulatory and Immune Workbook KEYDocument32 pagesCicrulatory and Immune Workbook KEYgeorgia robinsonNo ratings yet
- Human Cardiac Information Questions WorksheetDocument5 pagesHuman Cardiac Information Questions Worksheetgardereynoso14No ratings yet
- Circulatory System TerminologiesDocument4 pagesCirculatory System TerminologiesavduqueNo ratings yet
- Pathology LE 1Document13 pagesPathology LE 1Joshua HonoridezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Capillary Circulation, Edema FormationDocument24 pagesLecture 13 - Capillary Circulation, Edema Formationmurtada gubaNo ratings yet
- IHA-Chap. 5-Circulatory SystemDocument18 pagesIHA-Chap. 5-Circulatory SystemVarsha SNo ratings yet
- Shock: Dr. P. Manoj Kumar Asst. Professor, Dep. of Gen. Surgery, CaimsDocument61 pagesShock: Dr. P. Manoj Kumar Asst. Professor, Dep. of Gen. Surgery, CaimsManoj Kumar PasunooriNo ratings yet
- CVS L1Document4 pagesCVS L1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- GCSE Mammalian Transport System - VesselsDocument104 pagesGCSE Mammalian Transport System - Vesselspranavsantosh13No ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY by Kanze Ul EmanDocument11 pagesPHYSIOLOGY by Kanze Ul EmanMuhammad Farhan100% (1)
- What Makes Blood Flow pdf1Document3 pagesWhat Makes Blood Flow pdf1blackruiner2008No ratings yet
- Hemodynamics (Copy)Document41 pagesHemodynamics (Copy)BerihunNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 1: Transport)Document10 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 1: Transport)Gerard Selvaraj88% (26)
- Control of Blood Tissue Blood Flow: Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PHDDocument25 pagesControl of Blood Tissue Blood Flow: Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PHDNermeinKhattabNo ratings yet
- Circulation: Chapter OutlineDocument7 pagesCirculation: Chapter OutlineKaye Selene Raphaelle SyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PDFDocument12 pagesCardiovascular System PDFVon Valentine MhuteNo ratings yet
- Arterial, Arteriolar, Capillary, Venous & Lymphatic Circulations Feyitimi AaDocument67 pagesArterial, Arteriolar, Capillary, Venous & Lymphatic Circulations Feyitimi Aaintarebatinya32No ratings yet
- Name: Grade: SubjectDocument5 pagesName: Grade: SubjectvinaNo ratings yet
- VAN MHUTE - Human Physiology Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument4 pagesVAN MHUTE - Human Physiology Cardiovascular PhysiologyTapiwa KugodaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesCirculatory System2015.562fatimazaherakhanumNo ratings yet
- Final Exam PracticeDocument6 pagesFinal Exam PracticeErvin T MileNo ratings yet
- Important Questions: I. NameDocument5 pagesImportant Questions: I. Namesamhi96No ratings yet
- Lecture 14-Oct.23 Haemodynamics of Circulation, Circulatory Mechanics, ResistanceDocument29 pagesLecture 14-Oct.23 Haemodynamics of Circulation, Circulatory Mechanics, ResistanceAparmitNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 TransportDocument12 pagesForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 TransportMohdAmerAhmadNo ratings yet
- A01628 CH19Document36 pagesA01628 CH19Yannis ZoldenbergNo ratings yet
- 1st Year PhysiologyDocument15 pages1st Year PhysiologyMaheen AnwaarNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument60 pagesBlood VesselsJerick Sevilla SearesNo ratings yet
- CBSE CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 - Body Fluids and Circulation Important Questions 2023-24Document15 pagesCBSE CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 - Body Fluids and Circulation Important Questions 2023-24susilmaji92No ratings yet
- MCQs On Circulation Physiology With KeyDocument6 pagesMCQs On Circulation Physiology With KeyMudassar Roomi91% (34)
- Practice Test: Biology: Body Fluids & Circulation For Live Session On 17-Nov-2018 On Neetprep Youtube ChannelDocument4 pagesPractice Test: Biology: Body Fluids & Circulation For Live Session On 17-Nov-2018 On Neetprep Youtube ChannelSamprita DuttaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Hemodynamic EdemaDocument57 pages3 - Hemodynamic Edemaaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Faal-Blok14-3BDocument18 pagesPraktikum Faal-Blok14-3BKelompok 5A Semester 4No ratings yet
- Neuro Anatomy & Pathophysiology Laboratory Manual - 2 Semester, S. Y 2019 - 2020Document6 pagesNeuro Anatomy & Pathophysiology Laboratory Manual - 2 Semester, S. Y 2019 - 2020cris baligodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - The Circulatory System - ICSE - Class 8Document17 pagesChapter 6 - The Circulatory System - ICSE - Class 8Amita Wahi100% (1)
- Human System 2 ReviewDocument14 pagesHuman System 2 Reviewn.misovicNo ratings yet
- Norepinephrine and Vasopressin in Hemorrhagic Shock A Focus On RenalDocument13 pagesNorepinephrine and Vasopressin in Hemorrhagic Shock A Focus On RenalKatherine Poma RamosNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Biology - Lesson Note April 8,2020Document10 pagesGrade 9 Biology - Lesson Note April 8,2020micahxNo ratings yet
- 46.1 The Circulatory SystemDocument15 pages46.1 The Circulatory Systemapi-520057338No ratings yet
- T2 Ans PDFDocument53 pagesT2 Ans PDFMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - Anatomy and Physiology of For PhlebotomyDocument54 pagesUNIT 3 - Anatomy and Physiology of For PhlebotomyorionsiguenzaNo ratings yet
- For Class Students Circulatory System: Name The FollowingDocument14 pagesFor Class Students Circulatory System: Name The FollowingMehar ShreeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Transport of Substances in Humans: Learning ObjectivesDocument18 pagesChapter 9 - Transport of Substances in Humans: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation - 2023.editedDocument13 pagesBlood Circulation - 2023.editedrislariyas13No ratings yet
- Iadt03i5p345 PDFDocument15 pagesIadt03i5p345 PDFSudhit SethiNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 Biology Selina Solution Chapter 6 The Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesICSE Class 8 Biology Selina Solution Chapter 6 The Circulatory SystemAmmolh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Vascular Events in Acute InflammationDocument21 pagesVascular Events in Acute InflammationPOPCULTUREFAMNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System and Gas Exchange Powerpoint CUMMULATIVEDocument55 pagesCirculatory System and Gas Exchange Powerpoint CUMMULATIVEAjay N. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow ECMDocument31 pagesBlood Flow ECMirene :]No ratings yet
- Physiology of Circulation SystemDocument52 pagesPhysiology of Circulation SystemReni TeeWeeNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: College of Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument8 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: College of Medical Laboratory ScienceBianca Cielo BalabagNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Heart & Circulation KeyDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Heart & Circulation KeyJenn YumulNo ratings yet
- ВР PDFDocument73 pagesВР PDFikokalariNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PhysiologyDocument102 pagesCardiac PhysiologyPeter Larsen100% (1)
- Body Fluid and Circulation - Board Pattern Test (BPT)Document2 pagesBody Fluid and Circulation - Board Pattern Test (BPT)Dr-Atin Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Shock and Metabolic Response To TraumaDocument114 pagesSeminar Shock and Metabolic Response To TraumaA. TivieanNo ratings yet
- Cluster 4 Close Door 2022Document53 pagesCluster 4 Close Door 2022RadTech ReviewerNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument28 pagesClinical ChemistryialegnaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, Tenth Edition (PDFDrive) - 100 - 100Document10 pagesChemistry, Tenth Edition (PDFDrive) - 100 - 100Ezat JrNo ratings yet
- The NahtwaithiaDocument2 pagesThe NahtwaithiascopsNo ratings yet
- Selective Red Cell Variables in Chippiparai Hound Breeds of Tamil Nadu - A Pilot Study in 30 DogsDocument6 pagesSelective Red Cell Variables in Chippiparai Hound Breeds of Tamil Nadu - A Pilot Study in 30 DogsIndian Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences RNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Case Study: Pre-InternshipDocument6 pagesGroup 7 Case Study: Pre-InternshipTrish ShangNo ratings yet
- Methods For Reticulocyte CountingDocument52 pagesMethods For Reticulocyte CountingAri EcheverríaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology MCQ - Answer KeyDocument54 pagesCSEC Biology MCQ - Answer KeyDark PlaceNo ratings yet
- PMLS 1 LEC 3 StudentsDocument50 pagesPMLS 1 LEC 3 StudentsThynee Gamalong TagoNo ratings yet
- Casualty Simulation TechniquesDocument61 pagesCasualty Simulation TechniquesKath Glover100% (1)
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDocument4 pagesErythrocyte Sedimentation RateCarlos LemosNo ratings yet
- Discipline Grid 1. Programme:: Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy BucharestDocument5 pagesDiscipline Grid 1. Programme:: Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy BucharestAbdallah DarwishNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document25 pagesUnit 3senthilNo ratings yet
- Hematologic Test TherapyDocument71 pagesHematologic Test Therapyyasin shifaNo ratings yet
- Coatron M2 01 - 16 PDFDocument48 pagesCoatron M2 01 - 16 PDFBymbasuren SaturdayNo ratings yet
- Grappling With The Monster The Curse and The Cure of Strong Drink by Arthur, T. S. (Timothy Shay), 1809-1885Document131 pagesGrappling With The Monster The Curse and The Cure of Strong Drink by Arthur, T. S. (Timothy Shay), 1809-1885Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- MCQ Exam 2011 PDFDocument22 pagesMCQ Exam 2011 PDFBranka Kurtovic80% (10)
- Stem Cell - MD: The Ultimate Stroke Rehabilitation Program!Document4 pagesStem Cell - MD: The Ultimate Stroke Rehabilitation Program!David A. SteenblockNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document3 pagesDrug Study 2Roland YusteNo ratings yet
- Mnjy MPR 2024Document22 pagesMnjy MPR 2024RambabuNo ratings yet
- Bilirrubina Total y Fraccionada - SPINDREACTDocument2 pagesBilirrubina Total y Fraccionada - SPINDREACTPatrick BradyNo ratings yet
- SYCDW 2011 Coag Made EasyDocument17 pagesSYCDW 2011 Coag Made EasyRose KasidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Overview of The CirculationDocument26 pagesChapter 14 - Overview of The Circulationmuna sNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- 2nd Periodical Test in Science 6Document6 pages2nd Periodical Test in Science 6Jonniza AlbitNo ratings yet
- Blood Typing Activity For Lab Practical 2Document11 pagesBlood Typing Activity For Lab Practical 2Liliana PerezNo ratings yet
- BPT Syllabus PDFDocument99 pagesBPT Syllabus PDFAbhishek NegiNo ratings yet
- Tableofbloodgroupsystemsv10030 JUN 2021withLRGandrevisedantigensDocument3 pagesTableofbloodgroupsystemsv10030 JUN 2021withLRGandrevisedantigensManuel Perez GomezNo ratings yet
- L89 - Muzaffar Nagar Cc3 Shop No. 11, Near Dr. Dharampal Singh Sadar Bazar Muzaffarnagar 251001Document4 pagesL89 - Muzaffar Nagar Cc3 Shop No. 11, Near Dr. Dharampal Singh Sadar Bazar Muzaffarnagar 251001shivang ranaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 QuestionDocument9 pagesChapter 3 QuestionShila KaurNo ratings yet
- Dr. Bruce Fogle - DogsDocument344 pagesDr. Bruce Fogle - DogsZana Maric67% (3)
- And Its: Dr. V.PushkarDocument92 pagesAnd Its: Dr. V.PushkarMudit MisraNo ratings yet