Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture Material 1: Hilongos National Vocational School Hilongos, Leyte
Uploaded by
Marisa AmboOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Material 1: Hilongos National Vocational School Hilongos, Leyte
Uploaded by
Marisa AmboCopyright:
Available Formats
HILONGOS NATIONAL VOCATIONAL SCHOOL
HILONGOS, LEYTE
LECTURE MATERIAL 1
States of Matter
1. Solid – have definite shape and volume. The particles are tightly packed together;
solids are almost incompressible. Solids have high densities and expand only when
heated.
2. Liquid – have no definite shape but has definite volume. The particles in liquid are
close with one another, but not as close as those in a solid. They generally have
medium densities and tend to expand slightly when heated.
3. Gas – like liquids, take the shape of their container. However, they have no definite
volume. The particles are much farther apart than those in a liquid. They have low
densities and they greatly expand when heated.
4. Plasma – formed by heating and ionizing a gas. They are usually made up of groups
of negatively and positively charged particles. They have neither a definite volume
nor a definite shape.
5. Bose-Einstein Condensate – produced when a cloud of bosons (a type of elementary
particle of matter) is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero such that a
large fraction of the bosons condense. This state of matter includes clod liquid helium
and superconductors like nucleons inside a neutron star.
Properties of Matter
Physical Properties – one that can be observed without changing the composition
of a substance. Physical properties include (but are not limited to): phase, color,
solubility, density, melting and boiling points, volatility, viscosity, and
conductivity.
Chemical Properties – are characteristics that can be observed with an
accompanying change in the chemical composition of a substance. Chemical
properties include (but are not limited to): flammability and chemical reactivity.
Extensive Properties – also known as “Extrinsic Properties” include mass,
length, volume and size. This type of property depend on the amount of matter.
Intensive Properties – also known as “Intrinsic Properties” include, density,
color, physical state, melting, boiling, and freezing points. This type of property
depend on the type of matter.
Classifications of Matter
Matter
Pure Substances Mixtures
Elements Compounds Homogenous Heterogenous
Measurements
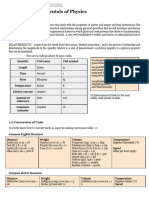
Fundamental SI Units
Quantity Unit Symbol
Length Meter m
Mass Kilogram kg
Time Second s
Electric Current Ampere A
Temperature Kelvin K
Amount of Matter Mole mol
Luminosity Candela cd
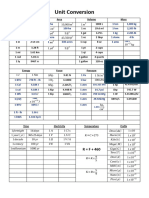
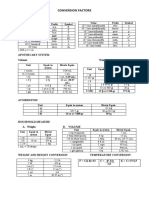
Metric and English Conversion
Quantity Metric English Conversion
1 lb = 454 g
Mass g, kg lb, oz 1 kg = 2.2 lb
1 oz = 28.35 g
1 in = 2.54 cm.
1 m = 39.37 in
Length cm, m, km in, ft, mi 1 ft = 12 in
1 mi = 1.609 km
1 km = 0.62137 mi
1 qt = 946 mL
1 L = 1.057 qt
1 L = 2.12 pints
qt, pints, cups, tsp, 1 L = 4.23 cups
Volume mL, L
tbsp., fl oz, gal 1 tsp = 4.93 mL
1 tbsp = 14.79 mL
1 fl oz = 29. 6 mL
1 gal = 3.79 L
Metric Prefixes and their Equivalents
Prefix Symbol Multiplying Factor
Exa- E 1018
Peta- P 1015
Tera- T 1012
Giga- G 109
Mega- M 106
Kilo K 103
Hecto- h 102
Deca- da 10
Deci- d 10-1
Centi- c 10-2
Milli- m 10-3
Micro- µ 10-6
Nano- n 10-9
Pico- p 10-12
Femto- f 10-15
Atto- a 10-18
You might also like
- Lab Report 2 - Head Loss in Pipe & BendsDocument20 pagesLab Report 2 - Head Loss in Pipe & BendsChris Ang76% (21)
- Tutorial Chapter 02 - AnswerDocument8 pagesTutorial Chapter 02 - AnswerFateh Hakeem100% (4)
- Lecture Material Gen Chem 1Document4 pagesLecture Material Gen Chem 1Marisa AmboNo ratings yet
- Units of MeasurementDocument2 pagesUnits of MeasurementCatherine Joy BesanaNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument3 pagesConversion of UnitsJonn Jhasmir MirNo ratings yet
- AnnouncementsDocument29 pagesAnnouncementsJay-anne CruzNo ratings yet
- General Physics Module 1 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGeneral Physics Module 1 ReviewerIca Safra100% (1)
- Week 1 Phy 1 MeasurementDocument22 pagesWeek 1 Phy 1 MeasurementAngelica Marie DiegoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Lecture 2Document34 pagesGeneral Chemistry Lecture 2Michaela BorjaNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of ChemistryDocument3 pagesSome Basic Concept of ChemistryVikash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: AtomsDocument52 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry: AtomsSuyash A.100% (1)
- Length Weight Capacity Time: MAT082 Conversion Table U. S. Customary UnitsDocument2 pagesLength Weight Capacity Time: MAT082 Conversion Table U. S. Customary UnitsNguyen Tan PhatNo ratings yet
- Basic Laboratory TechniquesDocument9 pagesBasic Laboratory TechniquesannaNo ratings yet
- Measurements Used in Analytical ChemistryDocument8 pagesMeasurements Used in Analytical ChemistryCHRISTINE JOY RETARDONo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry BSMTDocument5 pagesInorganic Chemistry BSMTjulianneNo ratings yet
- DistanceDocument2 pagesDistanceMike Raphy T. VerdonNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction, Matter & MeasurementDocument29 pagesChapter One: Introduction, Matter & MeasurementThanh LanNo ratings yet
- Physical Constants: Quantity Symbol Traditional Units SI UnitsDocument4 pagesPhysical Constants: Quantity Symbol Traditional Units SI UnitssureshNo ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 2 Part 1 Review of General ChemistryDocument44 pages02 Chapter 2 Part 1 Review of General ChemistryAko si GianNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument101 pagesGeneral ChemistryNohelia Fer GavNo ratings yet
- 0 Review of MeasurementDocument27 pages0 Review of MeasurementJustin MenorasNo ratings yet
- Conversions Between Imperial Metric PDFDocument4 pagesConversions Between Imperial Metric PDFJoselyn MessinaNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chem. (Module) - 1Document14 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chem. (Module) - 1mujeebc 1972No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1 - Chemical HistoryDocument9 pagesLecture Notes 1 - Chemical HistoryannmarieNo ratings yet
- Formulas in PhysicsDocument2 pagesFormulas in PhysicsChristine Irish Yebes MacaliNo ratings yet
- Scramble D: WordsDocument39 pagesScramble D: WordsSheanneNo ratings yet
- Matter HomeworkDocument32 pagesMatter HomeworkJames PerriamNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Units Physical Quantities Measurement Errors and UncertaintiesDocument19 pagesLAS 1 Units Physical Quantities Measurement Errors and UncertaintiesFlor de AldaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1Document9 pagesGen Chem 1Chennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - 11th NCERTDocument25 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry - 11th NCERTThe Boring CompanyNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document2 pagesModule 2Hazel MuñozNo ratings yet
- UNIT - CONVERSION FACTOR - Unit Operations in Food Processing - R. L. Earle - Appendix 2 - Units and Conversion FactorsDocument2 pagesUNIT - CONVERSION FACTOR - Unit Operations in Food Processing - R. L. Earle - Appendix 2 - Units and Conversion FactorsPief GustidaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document17 pagesModule 1Kenth Godfrei DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- General Physics ReviewerDocument12 pagesGeneral Physics ReviewerfelixiefairyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 1 NotesErin olinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1Annie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsVikash Rao khatodiyaNo ratings yet
- Essential Ideas: CHEM 1211K / Chapter 1Document4 pagesEssential Ideas: CHEM 1211K / Chapter 1Sreenivasa ReddyNo ratings yet
- Physical Science International Ed 12Th Edition Stephanie J Slater Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesPhysical Science International Ed 12Th Edition Stephanie J Slater Download PDF Chapterkate.hawkins778100% (4)
- Quantities Are Symbolised by Italic Letters!: Measurement. Si Quantities and UnitsDocument2 pagesQuantities Are Symbolised by Italic Letters!: Measurement. Si Quantities and UnitsDane BosevNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Units and ConstantsDocument3 pagesConversion of Units and ConstantsLopez D NikkoNo ratings yet
- Precision Refers To How Close Each Measurement Is To One AnotherDocument3 pagesPrecision Refers To How Close Each Measurement Is To One AnotherBethwaine VicenteNo ratings yet
- 01 Handout 1Document10 pages01 Handout 1Brent Gabrielle TarapeNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument2 pagesConversion of UnitsDrenzxkyNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Calculation EditedDocument7 pagesMeasurement and Calculation EditedJenna MarianoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument90 pagesReviewer in PhysicsLouise RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ProblemsDocument5 pagesUnit 1 ProblemsFrederick NakosNo ratings yet
- CLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFDocument57 pagesCLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFSarah RashidNo ratings yet
- Base Quantities & Derived QuantitiesDocument1 pageBase Quantities & Derived Quantitiesjgd2080No ratings yet
- Conversion FactorsDocument1 pageConversion Factorsanise santosNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of ChemistryDocument16 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistryharshit pandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Unit and MeasurementDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Unit and MeasurementAmar Danial100% (1)
- Measurement and ConversionDocument24 pagesMeasurement and Conversionaika smithNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors PDFDocument1 pageConversion Factors PDFTrixie IsiderioNo ratings yet
- Units and Conversion Factors: AppendixDocument2 pagesUnits and Conversion Factors: AppendixAcelora AzulNo ratings yet
- Che 1000 Stoichiometry Lecture Notes 2020 Academic Year 09 Mar 2021Document27 pagesChe 1000 Stoichiometry Lecture Notes 2020 Academic Year 09 Mar 2021Nathan MulunguNo ratings yet
- FinalestDocument76 pagesFinalestKristen Janna BulaNo ratings yet
- Las 1Document33 pagesLas 1ShernanNo ratings yet
- Foundations of College Chemistry 14th Edition Hein Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesFoundations of College Chemistry 14th Edition Hein Solutions ManualJosephWebbemwiy100% (48)
- Lesson 2 - Conversion of Units 2023Document14 pagesLesson 2 - Conversion of Units 2023yhaelguan77No ratings yet
- Handbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningFrom EverandHandbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Surface Production OperationsDocument23 pagesSurface Production OperationsСергей ВельдяксовNo ratings yet
- General Material Balance For Gas Condensate Reservoir and Its Giipestimations 2157 7463 1000270Document5 pagesGeneral Material Balance For Gas Condensate Reservoir and Its Giipestimations 2157 7463 1000270Marcelo AyllonNo ratings yet
- 3 Ways To Turn Salt Water Into Drinking Water - WikiHowDocument12 pages3 Ways To Turn Salt Water Into Drinking Water - WikiHowMuhamad Rahim WasesaNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Ultrasound and Its Application IDocument10 pagesThe Principles of Ultrasound and Its Application ICao Sang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Knovel Charts For Water & Steam, SI & English Units, 2006, Norwich, 26pgDocument26 pagesKnovel Charts For Water & Steam, SI & English Units, 2006, Norwich, 26pgVlad ElenaNo ratings yet
- P MMHG: Constantes de Antoine Parámetros Binarios: (G - G) (Cal/Mol K) Parámetros Binarios: AlfaDocument14 pagesP MMHG: Constantes de Antoine Parámetros Binarios: (G - G) (Cal/Mol K) Parámetros Binarios: AlfaXiime WalburgNo ratings yet
- GROUP VIIA (17) - The HalogensDocument13 pagesGROUP VIIA (17) - The HalogensOlamide AyindeNo ratings yet
- Key Homework 3 11th Gas LawDocument5 pagesKey Homework 3 11th Gas LawTai PanNo ratings yet
- Final Examination-Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesFinal Examination-Fluid MechanicsPel Martine AilesNo ratings yet
- Modular Skid SystemsDocument16 pagesModular Skid SystemsFWICIP100% (1)
- Agar50series MPFM SpecDocument4 pagesAgar50series MPFM SpecJADNo ratings yet
- Bhetg / SOLVENT 1009: Jan. 4., 1972 Yatarq - H - Kawa Etal 3,632,830Document10 pagesBhetg / SOLVENT 1009: Jan. 4., 1972 Yatarq - H - Kawa Etal 3,632,830Al RammohanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 1 - Xii - Liquid Solutions (Concentration Terms and Henry-S Law) - 27416162Document9 pagesTutorial Sheet - 1 - Xii - Liquid Solutions (Concentration Terms and Henry-S Law) - 27416162Sparsh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Carburation in Theory Practice A Manual of Reference For Automobile Engineers Owners 1913Document306 pagesCarburation in Theory Practice A Manual of Reference For Automobile Engineers Owners 1913Juan CalfulcuraNo ratings yet
- Controlling Ejector Performance: BY C. G. Blatchley Schutte & KoertingDocument9 pagesControlling Ejector Performance: BY C. G. Blatchley Schutte & KoertingCan YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Ch14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic TheoryDocument54 pagesCh14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic TheorysugarfootgalNo ratings yet
- BCZT Crystallo-GjitDocument8 pagesBCZT Crystallo-GjitRachna SelvamaniNo ratings yet
- Tank Design As Per IS803 and API650Document36 pagesTank Design As Per IS803 and API650Vikash Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Cyclone Separators: Learner GuideDocument14 pagesCyclone Separators: Learner GuideRobson DE Freitas WerlingNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nodal AnalysisDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Nodal AnalysisPaola Andrea RoaNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Magnet HandbookDocument39 pagesHitachi Magnet HandbookSilverio AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Design of Safety ValvesDocument19 pagesDesign of Safety ValvesJoyNo ratings yet
- Influence of Gas Temperature On Electrical Breakdown in Cylindrical ElectrodesDocument5 pagesInfluence of Gas Temperature On Electrical Breakdown in Cylindrical ElectrodesDaniel Rodrigo FalconiNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument8 pagesAbstractfaramarzkazemiNo ratings yet
- Viscosity Correction Factor For Rotameter: J. WojtkowiakDocument5 pagesViscosity Correction Factor For Rotameter: J. WojtkowiakHasan RabyNo ratings yet
- BlowerDocument3 pagesBlowerRaman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gas DehydrationDocument67 pagesGas DehydrationmohamedNo ratings yet
- Boyle's LawDocument4 pagesBoyle's LawRacel M. Benico100% (1)