Professional Documents
Culture Documents
First Year Mathematics
Uploaded by
ViorelBucurOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
First Year Mathematics
Uploaded by
ViorelBucurCopyright:
Available Formats
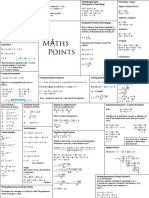
Algebra
Substitution Multiplying Brackets Factorising – 4 types
(the opposite of Factorising)
Calculate the value of 𝑝2 − 3𝑟𝑞 Highest Common Factor
For 𝑝 = 3, 𝑞 = −4 and 𝑟 = 7 3𝑥 + 2 4𝑥 − 3
Simple Equation = 3𝑥 4𝑥 − 3 + 2 4𝑥 − 3 6𝑥 2 − 15𝑥𝑦
Sub in values for p, q and r = 12𝑥 2 − 9𝑥 + 8𝑥 − 6 3𝑥(2𝑥 − 5𝑦)
Simple Equation 3 2 − 3 7 −4 = 12𝑥 2 − 𝑥 − 6
3 2𝑥 − 1 = 4𝑥
3 2𝑥 − 1 = 4𝑥 = 93 Difference of Squares
6𝑥 − 3 = 4𝑥
6𝑥
6𝑥 −−4𝑥
3== 34𝑥 Manipulate Formulae (Rearranging) 4𝑥 2 − 81
6𝑥
2𝑥 = 3 = 3
− 4𝑥 (2𝑥 + 9)(2𝑥 − 9)
2𝑥 3 3
= This is taking a formula and changing its
𝑥= subject (the letter by itself) through rules Quadratics
23
𝑥= of maths. (Multiplication, factorising etc)
2 to get rid of brackets, 𝑥’s to one
Multiply 6𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 − 14
side, numbers to the other…. 1 (3𝑥 − 7)(2𝑥 + 3)
Multiply to get rid of brackets, 𝑥’s to 𝑀=
𝑆+𝑃
one side, numbers to the other…. Grouping
Rearrange the formula to make P its
Inequalities subject. 9𝑎2 − 6𝑎𝑏 + 12𝑎𝑐 − 8𝑏𝑐
3𝑎 3𝑎 − 2𝑏 + 4𝑐(3𝑎 − 2𝑏)
5𝑥 + 1 ≤ 4𝑥 + 3 , 𝑥 ∈ 𝑁 𝑀 𝑆+𝑃 =1 (3𝑎 + 4𝑐)(3𝑎 − 2𝑏)
5𝑥 − 4𝑥 ≤ 3 − 1 𝑀𝑆 + 𝑀𝑃 = 1
Combinations
𝑥≤2 𝑀𝑃 = 1 − 𝑀𝑆
0 1 2 3
Treat this like an equation with 𝑥’s to one 1 − 𝑀𝑆
side and numbers to the other. 𝑃=
𝑀
𝑥 ∈ 𝑁 , 𝑥 ∈ 𝑍 means dots.
𝑥 ∈ 𝑅 means shading
Compound Inequalities
−2 ≤ 5𝑥 + 3 < 18 , 𝑥 ∈ 𝑅 Forming a Quadratic Equation Solving Quadratics −(−4) ± (−4)2 −4(2)(−6)
𝑥=
2(2)
Split into two inequalities and solve as 𝑥 2 − 𝑠𝑢𝑚 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑟𝑜𝑜𝑡𝑠 𝑥 + (𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑟𝑜𝑜𝑡𝑠) = 0 𝑓 𝑥 = 2𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 − 6 = 0
4 ± 16 + 48
before. 𝑥 =
Form the equation with roots 𝑥 = 4 and 𝑥 = 7 factorise 2𝑥 − 6 𝑥 + 1 = 0 4
4 ± 64
−2 ≤ 5𝑥 + 3 5𝑥 + 3 < 18 𝑥 =
𝑥 2 − 4 + 7 𝑥 + (4)(7) = 0 or – 𝑏 formula 4
−2 − 3 ≤ 5𝑥 5𝑥 < 18 − 3 4±8
−5 ≤ 5𝑥 5𝑥 < 15 𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 28 = 0 𝑥 =
4
−1 ≤ 𝑥 𝑥<3 −𝑏 ± 𝑏2 − 4𝑎𝑐 4+8 4−8
Note – ‘roots’ are values for 𝑥 that satisfy the equation. 𝑥= 𝑥 = &
2𝑎 4 4
-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 𝑥 =3 & −1
Laws of Indices Properties of Surds Express as a Single Fraction Simultaneous Equations – 2 unknowns (linear)
Properties of Indices Properties of Surds: Write as a single fraction
1. 𝑎𝑚 . 𝑎𝑛 = 𝑎𝑚+𝑛 3𝑥 − 2 2𝑥 5𝑥 − 1 Solve 4𝑥 + 16𝑦 = 20
+ −
𝑎𝑚 1. 𝑎𝑏 = 𝑎 𝑏 4 3 12 2𝑥 − 3𝑦 = −1
2. = 𝑎𝑚−𝑛
𝑎𝑛
a a
3. 𝑎𝑚 𝑛 = 𝑎𝑚+𝑛 2. = Find a common denominator. Multiply one or both lines to make co-efficients of
𝑛 b b
4. 𝑎𝑏 = 𝑎𝑛 𝑏 𝑛 one of the variables the same. Cancel down and
1 3 3𝑥 − 2 + 4 2𝑥 − 1(5𝑥 − 1) solve.
5. 𝑎 −𝑛 = 3. 𝑎 𝑎=𝑎
1
𝑎𝑛 12
𝑛 12𝑥 − 5 4𝑥 + 16𝑦 = 20 4𝑥 + 16𝑦 = 20
6. 𝑎𝑛 = 𝑎
Surds Example 12 2𝑥 − 3𝑦 = −1 × −2 −4𝑥 + 6𝑦 = 2
7. 𝑎0 =1
22𝑦 = 22
Indices Example 𝑥+ 𝑥 𝑥− 𝑥 =6 Equations Using Fractions 4𝑥 + 16𝑦 = 20 𝑦=1
2 1 1 4𝑥 + 16(1) = 20
8𝑥 − =
𝑥 𝑥− 𝑥 + 𝑥 𝑥− 𝑥 =6 3𝑥 − 4 2𝑥 + 1 2 4𝑥 + 16 = 20
= 42𝑥+1
2 4𝑥 = 4 Also occurs in co-ordinate
2 Similar to above but we can drop the denominator. 𝑥=1 geometry to find where
𝑥2 −𝑥 𝑥+𝑥 𝑥− 𝑥 =6 Remember to put any whole number over 1.
23 𝑥 lines intersect
1 = 22 2𝑥+1
22 𝑥2 − 𝑥 = 6 2(2) 2𝑥 + 1 − 1(2) 3𝑥 − 4 = 1(3𝑥 − 4)(2𝑥 + 1) Algebra Division
2(3𝑥 − 4)(2𝑥 + 1)
23𝑥 𝑥2 − 𝑥 − 6 = 0 Divide 2𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 − 13𝑥 + 6 by 𝑥 + 3
1 = 24𝑥+2
22 8𝑥 + 4 − 6𝑥 + 8 = 6𝑥 2 − 8𝑥 + 3𝑥 − 4
𝑥−3 𝑥+2 =0 2𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 + 2
0 = 6𝑥 2 − 8𝑥 − 8𝑥 + 6𝑥 + 3𝑥 − 8 − 4 − 4
1 6𝑥 2 − 7𝑥 − 16 = 0 𝑥+3 2𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 − 13𝑥 + 6
23𝑥−2 = 24𝑥+2 𝑥=3 𝑥 = −2 2𝑥 3 + 6𝑥 2
not a solution −5𝑥 2 − 13𝑥 + 6
1 −𝑏 ± 𝑏 2 − 4𝑎𝑐
3𝑥 − = 4𝑥 + 2 𝑥= −5𝑥 2 − 15𝑥
2 Verify 2𝑎 2𝑥 + 6
1 This means check your solutions. −(−7) ± (−7)2 −4(6)(−16) 2𝑥 + 6
2 − = 4𝑥 − 3𝑥 𝑥=
2 From above: 2(6) 0
1 𝑥=3
1 =𝑥 7 ± 433
2 3+ 3 3− 3 =6 𝑥= Writing Expressions/ Solving Problems II
12
2 𝑥 is a real number.
9+3 3−3 3− 3 =6 One new number is formed by increasing 𝑥 by 1.
9−3= 6 Verified 7 + 433 7 − 433
𝑥= 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥 = A second new number is formed by decreasing 𝑥 by 2.
12 12
The product of the 2 new numbers is 1
Writing Expressions/ Solving Problems
𝑥 = 2.3 & − 1.2 Find 𝑥.
The length of a rectangle is 5 times its width. The perimeter
(𝑥 + 1) 𝑥 − 2 = 1
of the rectangle is 120m.
𝑥 𝑥−2 +1 𝑥−2 =1
𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 + 𝑥 − 2 − 1 = 0
𝑤𝑖𝑑𝑡ℎ = 𝑥 𝑙𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑡ℎ = 5𝑥
𝑥2 − 𝑥 − 3 = 0
𝑥 + 𝑥 + 5𝑥 + 5𝑥 = 120
𝑥 = 10
Use –b to finish to give 𝑥 = 2.303 & 𝑥 = −1.303
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Simple Equation 3 2 1 4 6 3 4 6 4 3 2 3 3 2 Multiply To Get Rid of Brackets, 'S To One Side, Numbers To The OtherDocument2 pagesSimple Equation 3 2 1 4 6 3 4 6 4 3 2 3 3 2 Multiply To Get Rid of Brackets, 'S To One Side, Numbers To The OtherViorelBucurNo ratings yet
- 2c. Integration by Partial FractionDocument47 pages2c. Integration by Partial FractionMildred Cardenas BañezNo ratings yet
- Differentiation NotesDocument2 pagesDifferentiation NotesdheekshaNo ratings yet
- CBSE G+10 Pair+of+Linear+Equations+in+Two+Variables NotesDocument8 pagesCBSE G+10 Pair+of+Linear+Equations+in+Two+Variables NotesyeahmevaibhaviNo ratings yet
- The Order of Operations (PEMDAS) : Parentheses or or - Exponents 5)Document82 pagesThe Order of Operations (PEMDAS) : Parentheses or or - Exponents 5)jack barensNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Pair of Linear Equations Study NotesDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Pair of Linear Equations Study NotesbhuvaninfosystemsNo ratings yet
- As Pure Maths Revision NotesDocument15 pagesAs Pure Maths Revision NotesAbd Elrhman MohamedNo ratings yet
- Points of Intersection - Merry ChrismayantiDocument10 pagesPoints of Intersection - Merry ChrismayantiCalista Valencia BudiNo ratings yet
- MA112 - Makeup - Test 1 - S2 - 2020 - SolutionsDocument3 pagesMA112 - Makeup - Test 1 - S2 - 2020 - Solutionsnomaan7804No ratings yet
- Precalculus Week3 Day1Document24 pagesPrecalculus Week3 Day1dwayneNo ratings yet
- W2 Ex 5D 5E 5F 5G LogarithmsDocument3 pagesW2 Ex 5D 5E 5F 5G LogarithmsJessicaNo ratings yet
- Math 9 ReviewerDocument9 pagesMath 9 ReviewerAleah Tungbaban100% (3)
- Mathematics Grade 9 To Complete Algebraic ExpressionsDocument5 pagesMathematics Grade 9 To Complete Algebraic Expressionskatlegodikgetsi60No ratings yet
- Handout SolvingapempeDocument1 pageHandout SolvingapempeLyn MacabulitNo ratings yet
- As QuadraticsDocument11 pagesAs QuadraticsLucas RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Partial DerivDocument3 pagesPartial Derivq237680No ratings yet
- Higher Mathematics Checklist ZETA MATHSDocument22 pagesHigher Mathematics Checklist ZETA MATHSbrunaalvesbento.1997No ratings yet
- Yr10 SimultaneousEquationsDocument18 pagesYr10 SimultaneousEquationsfaridaisme2009No ratings yet
- Scheme Answer DiamiondDocument11 pagesScheme Answer DiamiondKin Chen TeeNo ratings yet
- Sequences: Arithmetic Sequence Quadratic SequenceDocument4 pagesSequences: Arithmetic Sequence Quadratic SequencerawadNo ratings yet
- Technique of Integration by Partial FractionsDocument7 pagesTechnique of Integration by Partial FractionsRinae SadikiNo ratings yet
- Modulus and Graph of Logarithms&Exponentials Functions (Ans)Document9 pagesModulus and Graph of Logarithms&Exponentials Functions (Ans)EphraimNo ratings yet
- Week 2 AS Rational FunctionDocument4 pagesWeek 2 AS Rational FunctionTrsitan lisolaNo ratings yet
- M9 (19) Simplifying Radical ExpressionDocument7 pagesM9 (19) Simplifying Radical ExpressionClaude de alger ObeliaNo ratings yet
- Module I Lessons 3 and 4Document9 pagesModule I Lessons 3 and 4Paul Stephen SorianoNo ratings yet
- Genmath 3Document4 pagesGenmath 3Jere MyNo ratings yet
- Diff Calculus SECTION 5Document19 pagesDiff Calculus SECTION 5ParthasarathiNo ratings yet
- 1 To 8Document9 pages1 To 8Hannah Julia A. NgNo ratings yet
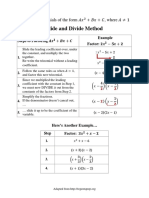
- Slide and Divide Method: Factoring Trinomials of The Form + +, Where 1Document1 pageSlide and Divide Method: Factoring Trinomials of The Form + +, Where 1lisa grinbergNo ratings yet
- PM Equations PDFDocument6 pagesPM Equations PDFfifak44760No ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Manual For Bridging (Summer 2019) : Algebra - Part 2Document10 pagesPre-Calculus Manual For Bridging (Summer 2019) : Algebra - Part 2Kristine VirgulaNo ratings yet
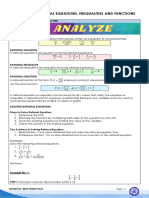
- Module 3: Rational Equations, Inequalities and Functions: Page - 1Document6 pagesModule 3: Rational Equations, Inequalities and Functions: Page - 1RexTheKingNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Class 9th (KPK) Chapter # 7 Linear Equations & InequealitesDocument25 pagesMathematics: Class 9th (KPK) Chapter # 7 Linear Equations & Inequealitessalma khanNo ratings yet
- First Order ODE Forced OscillationsDocument2 pagesFirst Order ODE Forced OscillationsDerek WangNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions (Autosaved)Document27 pagesPartial Fractions (Autosaved)Imaya SenuriNo ratings yet
- As Pure Maths Revision Notes: 1 SurdsDocument14 pagesAs Pure Maths Revision Notes: 1 SurdsM.Usama MustafaNo ratings yet
- As Pure Maths Revision NotesDocument14 pagesAs Pure Maths Revision NotesSundarNo ratings yet
- Axioms of Equality and EquationsDocument6 pagesAxioms of Equality and EquationsPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Polynomials, Cubic Equations, and Partial Fractions LectureDocument8 pagesPolynomials, Cubic Equations, and Partial Fractions LectureAdwin JY LowNo ratings yet
- Module General Mathematics 2Document9 pagesModule General Mathematics 2sherilyn palacayNo ratings yet
- Continuation of AntidifferentiationDocument11 pagesContinuation of AntidifferentiationAeriel May PliegoNo ratings yet
- GM Lesson 3 Rational Equations and InequalitiesDocument20 pagesGM Lesson 3 Rational Equations and Inequalitiescha618717No ratings yet
- A. Solving Linear EquationsDocument6 pagesA. Solving Linear EquationsHiba WasimNo ratings yet
- #3 - Linear Systems - SubstitutionDocument4 pages#3 - Linear Systems - SubstitutionmbuswellNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Rational Equations and InequalitiesDocument7 pagesLesson 7 Rational Equations and InequalitiesBaby Jean CoronelNo ratings yet
- P3-Topic 3.4Document47 pagesP3-Topic 3.4Devilish LuciferNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Day 3Document30 pagesGen Math Day 3KC KayeNo ratings yet
- Y10 Maths - Algebra - I Can ListDocument2 pagesY10 Maths - Algebra - I Can ListMicah SharpNo ratings yet
- Non HomoDocument12 pagesNon HomoMisha ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Advanced Differentiation: Example 1 SolutionDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Advanced Differentiation: Example 1 SolutionNur amirahNo ratings yet
- BS Caculus2Document4 pagesBS Caculus2Ayesha NasirNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Simultaneous Equations FoundationDocument4 pagesYear 10 Simultaneous Equations FoundationSamanpol PalasingNo ratings yet
- PMT Mock MSDocument25 pagesPMT Mock MSsaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two NewDocument56 pagesChapter Two NewDana S. Hama AminNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Worksheet Do All Work On Your Own Paper!Document5 pages2.3 Worksheet Do All Work On Your Own Paper!princess nesrin milicanNo ratings yet
- Bridge 2 Linear and Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesBridge 2 Linear and Quadratic EquationsDearly Niña OsinsaoNo ratings yet
- Solving Rational Equations and InequalitiesDocument9 pagesSolving Rational Equations and Inequalitiestishvill18No ratings yet
- Week 10-11 - CalcDocument5 pagesWeek 10-11 - CalcFlorenceNo ratings yet
- Art Craft Design - : ProjectDocument8 pagesArt Craft Design - : ProjectViorelBucurNo ratings yet
- Art Craft Design - : DrawingDocument8 pagesArt Craft Design - : DrawingViorelBucurNo ratings yet
- Art Craft Design - : DrawingDocument8 pagesArt Craft Design - : DrawingViorelBucurNo ratings yet
- Installation Programming Operating: Keyfob Operated Alarm SystemDocument20 pagesInstallation Programming Operating: Keyfob Operated Alarm SystemViorelBucurNo ratings yet
- Natural NumbersDocument2 pagesNatural NumbersViorelBucurNo ratings yet
- Integers: Addition and Subtraction ProblemsDocument2 pagesIntegers: Addition and Subtraction ProblemsViorelBucurNo ratings yet
- FIRSTYEARMATHEMATICSEXAM2015FINALDocument12 pagesFIRSTYEARMATHEMATICSEXAM2015FINALViorelBucurNo ratings yet
- Reseller Handbook 2019 v1Document16 pagesReseller Handbook 2019 v1Jennyfer SantosNo ratings yet
- F07 hw07Document2 pagesF07 hw07rahulNo ratings yet
- Sonnet WorksheetDocument3 pagesSonnet WorksheetMary Cris EspirituNo ratings yet
- Natural Language Processing Projects: Build Next-Generation NLP Applications Using AI TechniquesDocument327 pagesNatural Language Processing Projects: Build Next-Generation NLP Applications Using AI TechniquesAnna BananaNo ratings yet
- Explicit and Implicit Grammar Teaching: Prepared By: Josephine Gesim & Jennifer MarcosDocument17 pagesExplicit and Implicit Grammar Teaching: Prepared By: Josephine Gesim & Jennifer MarcosJosephine GesimNo ratings yet
- Pugh MatrixDocument18 pagesPugh MatrixSulaiman Khan0% (1)
- Transportation Research Part F: Andreas Lieberoth, Niels Holm Jensen, Thomas BredahlDocument16 pagesTransportation Research Part F: Andreas Lieberoth, Niels Holm Jensen, Thomas BredahlSayani MandalNo ratings yet
- Adobe Voice Assessment Tool-FinalDocument1 pageAdobe Voice Assessment Tool-Finalapi-268484302No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Simulation of HVDC SystemDocument24 pagesUnit 5 - Simulation of HVDC Systemkarthik60% (10)
- TLG 82201Document7 pagesTLG 82201beatmymeat100% (2)
- Quantile Regression (Final) PDFDocument22 pagesQuantile Regression (Final) PDFbooianca100% (1)
- Parallels of Stoicism and KalamDocument95 pagesParallels of Stoicism and KalamLDaggersonNo ratings yet
- Dcat2014 - Simulated Set B - Section 3 - Reading Comprehension - Final v.4.7.2014Document6 pagesDcat2014 - Simulated Set B - Section 3 - Reading Comprehension - Final v.4.7.2014Joice BobosNo ratings yet
- Zoe LeonardDocument9 pagesZoe LeonardSandro Alves SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Cleric Spell List D&D 5th EditionDocument9 pagesCleric Spell List D&D 5th EditionLeandros Mavrokefalos100% (2)
- HR Recruiter Interview Question & AnswerDocument6 pagesHR Recruiter Interview Question & AnswerGurukrushna PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Use of ICT in School AdministartionDocument32 pagesUse of ICT in School AdministartionSyed Ali Haider100% (1)
- Media Kit (Viet)Document2 pagesMedia Kit (Viet)Nguyen Ho Thien DuyNo ratings yet
- Makalsh CMDDocument22 pagesMakalsh CMDMaudy Rahmi HasniawatiNo ratings yet
- Armor MagazineDocument56 pagesArmor Magazine"Rufus"100% (2)
- Oral Abstract PresentationDocument16 pagesOral Abstract Presentationapi-537063152No ratings yet
- NHÓM ĐỘNG TỪ BẤT QUY TẮCDocument4 pagesNHÓM ĐỘNG TỪ BẤT QUY TẮCNhựt HàoNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma of PenisDocument13 pagesCarcinoma of Penisalejandro fernandezNo ratings yet
- Educational Metamorphosis Journal Vol 2 No 1Document150 pagesEducational Metamorphosis Journal Vol 2 No 1Nau RichoNo ratings yet
- Anthropology Chapter 2 ADocument17 pagesAnthropology Chapter 2 AHafiz SaadNo ratings yet
- BS Assignment Brief - Strategic Planning AssignmentDocument8 pagesBS Assignment Brief - Strategic Planning AssignmentParker Writing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Form Aplikasi CCAI GTP 2011Document5 pagesForm Aplikasi CCAI GTP 2011Tomo SiagianNo ratings yet
- Operations Management and Operations PerformanceDocument59 pagesOperations Management and Operations PerformancePauline LagtoNo ratings yet
- Ingles Nivel 2Document119 pagesIngles Nivel 2Perla Cortes100% (1)
- Capital Structure: Meaning and Theories Presented by Namrata Deb 1 PGDBMDocument20 pagesCapital Structure: Meaning and Theories Presented by Namrata Deb 1 PGDBMDhiraj SharmaNo ratings yet