Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Variable Overhead Variance: Material Cost Variance Formula
Uploaded by
Bella AyabOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Variable Overhead Variance: Material Cost Variance Formula
Uploaded by
Bella AyabCopyright:
Available Formats
MATERIAL COST VARIANCE FORMULA
Standard Cost – Actual Cost
In other words, (Standard Quantity for actual output x Standard Price) – (Actual Quantity
x Actual Price)
Material Variance is further sub-divided into two heads:
MATERIAL PRICE VARIANCE
MPV = (Standard Price – Actual Price) x Actual Quantity
MATERIAL USAGE VARIANCE
MUV = (Standard Quantity for actual output – Actual Quantity) x Standard Price
LABOR VARIANCE FORMULA
Standard Wages – Actual Wages
In other words,
(Standard Hours for actual output x Standard Rate Per Hour) – (Actual Hours x Actual
Rate Per Hour)
Labor Variance is further sub-divided into two heads:
LABOR RATE VARIANCE
LRV = (Standard Rate Per Hour – Actual Rate Per Hour) x Actual Hours
LABOR EFFICIENCY VARIANCE
LEV = (Standard Hours for Actual Out Put – Actual Hours) x Standard Rate
VARIABLE OVERHEAD VARIANCE
Variable Overhead Variance arises when there is a difference between the actual
variable overhead and the standard variable overhead based on budgets.
VARIABLE OVERHEAD VARIANCE FORMULA
Standard Variable Overhead – Actual Variable Overhead
In other words, (Standard Rate – Actual Rate) x Actual Output
Variable Overhead Variance is further sub-divided into two heads:
VARIABLE OVERHEAD EFFICIENCY VARIANCE
VOEV = (Actual Output – Standard Output) x Standard Rate
VARIABLE OVERHEAD EXPENDITURE VARIANCE
VOEV = (Standard Output x Standard Rate) – (Actual Output x Actual Rate)
FIXED OVERHEAD VARIANCE
1. It arises when there is a difference between the standard fixed overhead for
actual output and the actual fixed overhead.
FIXED OVERHEAD VARIANCE FORMULA
= (Actual Output x Standard Rate per unit) – Actual Fixed Overhead
Fixed Overhead Variance is further sub-divided into two heads:
FIXED OVERHEAD EXPENDITURE VARIANCE
FOEV = Standard Fixed Overhead – Actual Fixed Overhead
FIXED OVERHEAD VOLUME VARIANCE
FOVV = (Actual Output x Standard Rate per unit) – Standard Fixed Overhead
SALES VARIANCE
Sales Variance is the difference between the actual sales and budgeted sales of an
organization.
SALES VARIANCE FORMULA
= (Budgeted Quantity x Budgeted Price) – (Actual Quantity x Actual Price)
Sales Variance is further sub-divided into two heads:
SALES VOLUME VARIANCE
SVV = (Budgeted Quantity – Actual Quantity) x Budgeted Price
SALES PRICE VARIANCE
SPV = (Budgeted Price – Actual Price) x Actual Quantity
Standard Costing and Variance Analysis Formulas:
This is a collection of variance formulas/equations which can help you calculate
variances for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead.
1. Direct materials variances formulas
2. Direct labor variances formulas
3. Factory overhead variances formulas
Direct Materials Variances:
Materials purchase price variance Formula:
Materials purchase price variance = (Actual quantity purchased × Actual price) – (Actual
quantity purchased × Standard price)
Materials price usage variance formula:
Materials price usage variance = (Actual quantity used × Actual price) – (Actual quantity
used × Standard price)
materials quantity/usage variance formula:
Materials price usage variance = (Actual quantity used × Standard price) – (Standard
quantity allowed × Standard price)
Materials mix variance formula:
(Actual quantities at individual standard materials costs) – (Actual quantities at weighted
average of standard materials costs)
Materials yield variance formula:
(Actual quantities at weighted average of standard materials costs) – (Actual output
quantity at standard materials cost)
Direct Labor Variances:
Direct labor rate/price variance formula:
(Actual hours worked × Actual rate) – (Actual hours worked × Standard rate)
Direct labor efficiency/usage/quantity formula:
(Actual hours worked × Standard rate) – (Standard hours allowed × Standard rate)
Direct labor yield variance formula:
(Standard hours allowed for expected output × Standard labor rate) – (Standard hours
allowed for actual output × Standard labor rate)
Factory Overhead Variances:
Factory overhead controllable variance formula:
(Actual factory overhead) – (Budgeted allowance based on standard hours allowed*)
Factory overhead volume variance:
(Budgeted allowance based on standard hours allowed*) – (Factory overhead applied or
charged to production**)
Factory overhead spending variance:
(Actual factory overhead) – (Budgeted allowance based on actual hours worked***)
Factory overhead idle capacity variance formula:
(Budgeted allowance based on actual hours worked***) – (Actual hours worked × Standard
overhead rate)
Factory overhead efficiency variance formula:
(Actual hours worked × Standard overhead rate) – (Standard hours allowed for expected
output × Standard overhead rate)
Variable overhead efficiency variance formula:
(Actual hours worked × Standard variable overhead rate) – (Standard hours allowed ×
Standard variable overhead rate)
Variable overhead efficiency variance formula:
(Actual hours worked × Fixed overhead rate) – (Standard hours allowed × Fixed overhead
rate)
Factory overhead yield variance formula:
(Standard hours allowed for expected output × Standard overhead rate) – (Standard hours
allowed for actual output × Standard overhead rate)
Company XYZ produces a product that has the following factory overhead standard costs
per unit. The budgeted production is at the normal capacity of 1,000 units, requiring a
budgeted time of 3,000 hours. The total fixed factory overhead at this capacity is $30,000.
Variable FOH 3 hours at $30 per hour
Fixed FOH 3 hours at $10 per hour
During the month, the company produced 1,100 units and incurred the following actual
factory overhead costs:
Variable FOH 3,250 hours at $29 per hour $ 94,250
Fixed FOH $ 36,500
Total $130,750
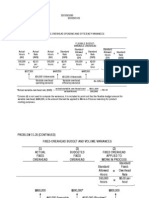
The two-way analysis variances can be computed as follows:
BUDGET VARIANCE
Actual FOH $130,750
Budget allowed on standard hours 129,000
*for variable (1,100 x 3 hours x $30)
*for fixed ($30,000 as budgeted)
Budget variance $ 1,750 UF
VOLUME VARIANCE
Budget allowed on standard hours $129,000
Standard FOH (1,100 x 3 hours x $40) 132,000
Volume variance $ 3,000 F
TOTAL FACTORY OVERHEAD VARIANCE $ 1,250 F
Company XYZ produces a product that has the following factory overhead standard costs
per unit. The budgeted production is at the normal capacity of 1,000 units, requiring a
budgeted time of 3,000 hours. The total fixed factory overhead at this capacity is $30,000.
Variable FOH 3 hours at $30 per hour
Fixed FOH 3 hours at $10 per hour
During the month, the company produced 1,100 units and incurred the following actual
factory overhead costs:
Variable FOH 3,250 hours at $29 per hour $ 94,250
Fixed FOH $ 36,500
Total $130,750
The three-way analysis variances can be computed as follows:
SPENDING VARIANCE
Actual FOH (variable + fixed) $130,750
Budget allowed on actual hours (BAAH) 127,500
*for variable (3,250 hours x $30)
*for fixed ($30,000 as budgeted)
Budget variance $ 3,250 UF
EFFICIENCY VARIANCE
Budget allowed on actual hours (BAAH) $127,500
Budget allowed on standard hours (BASH) 129,000
*for variable (1,100 x 3hours x $30)
*for fixed ($30,000 as budgeted)
Efficiency variance $ 1,500 F
VOLUME VARIANCE
Budget allowed on standard hours (BASH) $129,000
Standard FOH (1,100 x 3 hours x $40) 132,000
Volume variance $ 3,000 F
TOTAL FACTORY OVERHEAD VARIANCE $ 1,250 F
Four-Way Analysis
A more expanded breakdown known as "four-way analysis" simply separates the spending
variance into the variable and fixed components. The four-way analysis consists of: 1.)
variable spending variance, 2.) fixed spending variance, 3.) efficiency variance, and 4.)
volume variance.
You might also like
- Variance Analysis 2 Way To 4 Way With NotesDocument3 pagesVariance Analysis 2 Way To 4 Way With NotesAceeNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument8 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisSaad RebelNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing or Variance AnalysisDocument11 pagesStandard Costing or Variance Analysisgull skNo ratings yet
- Variance AnalysisDocument18 pagesVariance Analysiskittyshukla100% (1)
- CH 15 SolDocument4 pagesCH 15 SolAnonymous MSetY7IczNo ratings yet
- Variance AnalysisDocument19 pagesVariance AnalysisMishael MainaNo ratings yet
- Overhead Variance - PinnacleDocument2 pagesOverhead Variance - PinnacleMagadia Mark JeffNo ratings yet
- Variable Cost Variances Direct Material Variances: Variance AnalysisDocument21 pagesVariable Cost Variances Direct Material Variances: Variance AnalysisKuldeep GargvanshiNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument137 pagesStandard CostingMuhammad azeem100% (1)
- Chap 010 ADocument11 pagesChap 010 AEdraNo ratings yet
- Variance Analysis With The Reasons of VariancesDocument19 pagesVariance Analysis With The Reasons of Variancesmohamed Suhuraab100% (1)
- Factory Overhead Application Methods High-Low Point MethodDocument8 pagesFactory Overhead Application Methods High-Low Point MethodtrisNo ratings yet
- Factory Overhead Cost Variances AnalysisDocument11 pagesFactory Overhead Cost Variances AnalysisKabobo Han0% (2)
- Chapter 5 Variance AnalysisDocument21 pagesChapter 5 Variance AnalysisPoonam SharmaNo ratings yet
- VariancesDocument45 pagesVariancesanonNo ratings yet
- Factory Overhead Variance AnalysisDocument3 pagesFactory Overhead Variance AnalysisKabobo HanNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance Analysis BreakdownDocument26 pagesStandard Costing & Variance Analysis BreakdownAnuruddha RajasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7,8Document9 pagesChapter 7,8Hesham AhmedNo ratings yet
- FORMULA: UNDERSTANDING EXPENSESDocument24 pagesFORMULA: UNDERSTANDING EXPENSESRedgie Mark UrsalNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budgeting and Overhead Cost ManagementDocument11 pagesFlexible Budgeting and Overhead Cost ManagementUmair Ayaz60% (5)
- VARIANCE ANALYSIS_084249Document20 pagesVARIANCE ANALYSIS_084249Adams JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Budgeted quantity varianceDocument3 pagesBudgeted quantity varianceHappyPurpleNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 AnswerDocument7 pagesTutorial 4 AnswernajihahNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9-10: Solutions (12/01)Document8 pagesExercise 9-10: Solutions (12/01)ppaulyni33No ratings yet
- HbjhjhjhujuhjDocument14 pagesHbjhjhjhujuhjnjkjhNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument36 pagesStandard CostingParamjit Sharma96% (24)
- 7 - Variance AnalysisDocument15 pages7 - Variance AnalysisRakeysh RakyeshNo ratings yet
- Variable Overhead Variance AnalysisDocument30 pagesVariable Overhead Variance Analysismohammed azizNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Tutorial WorkingsDocument51 pagesWeek 11 Tutorial WorkingsKwang Yi JuinNo ratings yet
- Flexible & Standard Costing Tutorial ExercisesDocument2 pagesFlexible & Standard Costing Tutorial ExercisesToni BuiNo ratings yet
- Cost Lesson 8.variancesDocument4 pagesCost Lesson 8.variancessanagustinveramaeNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing Variance Formulas & ExamplesDocument12 pagesStandard Costing Variance Formulas & ExamplesCh Sam100% (1)
- Standard CostingDocument9 pagesStandard CostingRoselyn LumbaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Homework MADocument13 pagesChapter 8 Homework MAErvin Jello Rosete RagonotNo ratings yet
- Variable overhead and fixed overhead variancesDocument3 pagesVariable overhead and fixed overhead variancesAdi PhasaNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Standard CostDocument31 pagesGroup 7 Standard CostChristian Acab GraciaNo ratings yet
- Cost ManagementDocument18 pagesCost ManagementGeo Rublico ManilaNo ratings yet
- Variance Analysis - Overhead CostsDocument32 pagesVariance Analysis - Overhead CostsTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Financial - Performance ReportDocument29 pagesAnalyzing Financial - Performance ReportjatimTV webNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument8 pagesSummarySittiehaina GalmanNo ratings yet
- Hilton CH 10 Select SolutionsDocument24 pagesHilton CH 10 Select SolutionsRaza Ze0% (1)
- Module 10 Standard CostsDocument28 pagesModule 10 Standard Costsi_kostadinovicNo ratings yet
- Variance Analysis (Practice Problems)Document7 pagesVariance Analysis (Practice Problems)Godwin De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Managerial Accounting Quiz (Online)Document5 pagesAnswer:: Managerial Accounting Quiz (Online)Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Solutions - Inclass ExercisesDocument12 pagesChapter 10 Solutions - Inclass ExercisesSummerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Chapter 6Document3 pagesLecture Notes - Chapter 6Saint BakemonoNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis FormulasDocument5 pagesStandard Costing and Variance Analysis FormulasKaran OberoiNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing Quiz PrintingDocument9 pagesStandard Costing Quiz PrintingLovErsMaeBasergoNo ratings yet
- Direct Cost Variances Chapter 10Document15 pagesDirect Cost Variances Chapter 10Ahsan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Labour Cost VarianceDocument30 pagesLabour Cost VarianceSunita BasakNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Standard Costs and VariancesDocument84 pagesManagerial Accounting Standard Costs and VariancesSyed Atiq TurabiNo ratings yet
- SMA Chapter Four - Variance AnalysisDocument86 pagesSMA Chapter Four - Variance Analysisngandu100% (1)
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Types of Reconciling Items in Bank Reconciliation: Type ADocument3 pagesTypes of Reconciling Items in Bank Reconciliation: Type ABella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Is Taxable Income?: Key TakeawaysDocument4 pagesWhat Is Taxable Income?: Key TakeawaysBella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Is Bad Debt?: Fiscal Period Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesWhat Is Bad Debt?: Fiscal Period Financial StatementsBella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Is A Bank Reconciliation StatementDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Bank Reconciliation StatementYassi CurtisNo ratings yet
- What Is The Percentage of Completion Method?: Gross ProfitDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Percentage of Completion Method?: Gross ProfitBella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Is Accumulated Depreciation?: Contra Asset AccountDocument2 pagesWhat Is Accumulated Depreciation?: Contra Asset AccountBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Bad Debt 2Document3 pagesBad Debt 2Bella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Is Cash Accounting?Document2 pagesWhat Is Cash Accounting?Jonhmark AniñonNo ratings yet
- Examples of Assets AreDocument2 pagesExamples of Assets AreBella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Is A Franchisee?: FranchiseDocument1 pageWhat Is A Franchisee?: FranchiseBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Variable Overhead Variance: Material Cost Variance FormulaDocument6 pagesVariable Overhead Variance: Material Cost Variance FormulaBella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Is A Partnership?: Types of Partnership Arrangements Limited LiabilityDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Partnership?: Types of Partnership Arrangements Limited LiabilityBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Definition of 'Accounts Receivable': Definition: Accounts Receivable (AR) Is The Proceeds or Payment Which The CompanyDocument1 pageDefinition of 'Accounts Receivable': Definition: Accounts Receivable (AR) Is The Proceeds or Payment Which The CompanyBella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Are Cash Equivalents?Document3 pagesWhat Are Cash Equivalents?Bella AyabNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 test results, beds and cases summaryDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 test results, beds and cases summaryBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Costs Involved: TrademarksDocument2 pagesCosts Involved: TrademarksBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Scrib 1Document2 pagesScrib 1Bella AyabNo ratings yet
- Understanding control risk and audit proceduresDocument4 pagesUnderstanding control risk and audit proceduresBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Questions 1 & 2 Are Based On The Following InformationDocument3 pagesQuestions 1 & 2 Are Based On The Following InformationBella AyabNo ratings yet
- What Is The Corporate Governance CodeDocument12 pagesWhat Is The Corporate Governance CodeBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Questions 11 and 12 Are Based On The Following InformationDocument2 pagesQuestions 11 and 12 Are Based On The Following InformationBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Second PreboardDocument6 pagesSecond PreboardBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Net income corrections for 2021Document1 pageNet income corrections for 2021Bella AyabNo ratings yet
- Second PB Acctg 203BDocument12 pagesSecond PB Acctg 203BBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Second PreboardDocument6 pagesSecond PreboardBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Second PB Acctg 203BDocument12 pagesSecond PB Acctg 203BBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Auditing TheoDocument4 pagesAuditing TheoBella AyabNo ratings yet
- Ap 59 PW - 5 06 PDFDocument18 pagesAp 59 PW - 5 06 PDFJasmin NgNo ratings yet
- Construction ContractDocument17 pagesConstruction ContractYvonne Gam-oyNo ratings yet
- Structure: Industrial Policy: Objectives & EvolutionDocument33 pagesStructure: Industrial Policy: Objectives & EvolutionSujeet SinghNo ratings yet
- CVEN90045 - Stakeholders 2 CompleteDocument19 pagesCVEN90045 - Stakeholders 2 Completeakas84No ratings yet
- Minimum Efficient ScaleDocument1 pageMinimum Efficient ScaleJohnlene Louise SaitonNo ratings yet
- DOH Administrative Order 2019-0036 Establishment of F1 Plus BNB and BNBi ProgramDocument65 pagesDOH Administrative Order 2019-0036 Establishment of F1 Plus BNB and BNBi ProgramAngelica BolosNo ratings yet
- Accounting Techniques Used in A Fraud Investigation: Mary Anne Basilone Diane A. Matthews Carlow UniversityDocument39 pagesAccounting Techniques Used in A Fraud Investigation: Mary Anne Basilone Diane A. Matthews Carlow UniversityDicky AndryNo ratings yet
- Group 5: Statistical Analysis With Software ApplicationDocument6 pagesGroup 5: Statistical Analysis With Software ApplicationMitch Tokong MinglanaNo ratings yet
- Casebook 2.2 Semi FinalDocument1,015 pagesCasebook 2.2 Semi FinalCarol AnnNo ratings yet
- Project Execution Plan (Brief)Document13 pagesProject Execution Plan (Brief)Dilip Kumar0% (1)
- SWMS 71 - Use of Curing ChemicalDocument2 pagesSWMS 71 - Use of Curing ChemicaleastNo ratings yet
- Gap Analysis ISO 9001-2015Document17 pagesGap Analysis ISO 9001-2015Yudi ArkanantaNo ratings yet
- EasyBiz Alliances Final PRDocument2 pagesEasyBiz Alliances Final PRCity PRNo ratings yet
- What is a brand? Perspectives on meaningDocument13 pagesWhat is a brand? Perspectives on meaningFlorrNo ratings yet
- Ethical Dillema in BusinessDocument2 pagesEthical Dillema in BusinesscharlesNo ratings yet
- Barton, D 2012 Business Skills 7 - Cross Cultural CommunicationDocument4 pagesBarton, D 2012 Business Skills 7 - Cross Cultural Communicationnickw43No ratings yet
- LC3 AnalysisDocument21 pagesLC3 AnalysistimothyNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Rawash: Sr. Oracle HCM Techno-Functional Consultant (EBS - Fusion)Document3 pagesAhmed Rawash: Sr. Oracle HCM Techno-Functional Consultant (EBS - Fusion)hamdy20017121No ratings yet
- TechNip Italy pressure vessel rulesDocument14 pagesTechNip Italy pressure vessel rulespraveenvelath100% (1)
- The Central Park Apartment Owners Association - Bye LawsDocument25 pagesThe Central Park Apartment Owners Association - Bye Lawskjacobgeorge1242100% (6)
- Company Registration Status As On 10.12.2019Document1 pageCompany Registration Status As On 10.12.2019Vishav JindalNo ratings yet
- General Motors Transactional Translational ExposuresDocument5 pagesGeneral Motors Transactional Translational ExposuresRaghavendra Somasundaram100% (3)
- Personal Liability of Officer for Debts of Defectively Incorporated BusinessDocument2 pagesPersonal Liability of Officer for Debts of Defectively Incorporated BusinessDorothy PuguonNo ratings yet
- Operate A Pencil Grinder Rev 2Document3 pagesOperate A Pencil Grinder Rev 2grantNo ratings yet
- Brochure Netherlands 30% RulingDocument16 pagesBrochure Netherlands 30% RulingZafer TurhanNo ratings yet
- Item PicDocument4 pagesItem PicMukesh MakadiaNo ratings yet
- 4319 12366 1 PBDocument10 pages4319 12366 1 PBMaulida FathiaNo ratings yet
- BrandZ 2015 LATAM Top50 ReportDocument83 pagesBrandZ 2015 LATAM Top50 ReportmperdomoqNo ratings yet
- Project Report On AdvertisingDocument90 pagesProject Report On AdvertisingfakrhaNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Strategy OMDocument8 pagesCh-2 Strategy OMAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- IFM SyllabusDocument17 pagesIFM Syllabussagarzawar1No ratings yet
- ch#5 of CFDocument2 pagesch#5 of CFAzeem KhalidNo ratings yet