Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Working Stresses and Stress Theories
Uploaded by
ranjithkrajOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Working Stresses and Stress Theories
Uploaded by
ranjithkrajCopyright:
-
Working Stresses 21
Particular Equation Eqn. No.
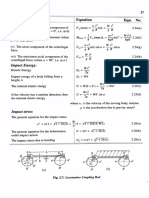
F 2.2
Transverse stress induced around the hole in a CTmax =a-Kn = A Kn
plate of infinite width (Fig. 2.2)
When a plate with a hole is subjected to 2.3
biaxial stresses a-x and a-y acting at right
angles, then the combine d maximum stress
induced (super position)
The notch sensitivity index: 2.4
Estimated fatigue stress concentration factor K,1 = l + q(Kr - l ) 2.5
for normal stress
Estimated combine d fatigue factor for normal 2.6
stress
Estimated fatigue stress concentra tion factor K sf = 1 + q(K5 - 1) 2.7
for shear stress
Theories offailure:
CTx +CTy )
CTe = ( - - - +
(TX - (Ty )2+ ") 2.8(a)
Stress according to the maximum normal 2 ( 2 T X}"
.
stress theory or Rankine theory
= a- 1, maximum principle stress
3.0 -u 1---
F~ F
2.6 ~
F
er= - - -
(B- a)t
2.2
__ _j
t
t
K,
I
'
-~---+ ---+---,,...j 0.2
1.8
1.4 ·+----I - - - - - - - 0.6
L..:::::::::.. ...--____:~_ _,___ ___.,_ __.___ ___.__ _..,____.....J 1.0
1.0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Ratioa/ B - -
Fig. 2.2: Form Stress Factor due to hole in a plate
22 Working Stresses
Particular I Equation Eqn. No.
Stress according to the maximum strain theory or Saint-Vanant's theory
=(l - <rx +<ry ) (<rx -<Fy )2
<Fe µ) (
2
+ (1 + µ)
2
+ T2xy =<rt - µ<r2 2.8(b)
Stress according to the maximum shear stress theory or Guest's theory
<Fe= 2 ..J(<Fx ; <Fy r + Tiy = ✓(<Fx - <Fy)
2 + 4Tiy = (<r1 - <r2) 2.8(c)
Stress according to shear energy theory or the Hencky-von Mises theory
<Fe = ✓(<r;; - <Fx<Fy + <r; + 3Tiy) = ✓c?j + <F~ - <r1<r2 2.8(d)
Maximum total strain energy theory or 2.8(e)
Haigh's theory
Design for strength:
Influence of size:
The elastic limit ~ for any thickness h er'. _ _ (<re - <Fe3 )(h - 12.5) _ B _ (a)
e - <Fe 75 - 12.5 - <Fe 29
between 12.5 mm and 75 mm (Fig. 2.3 and
2.4) where B is the size factor
l/B = 250 2.9(b)
300 - 4h + (<re)<re)(4h - 50)
value of the ratio (<re3 /<re) for a few materials are given in Table. 2.5
N (100) 1000
s OK
Z _ (80) 800
----- \
:::E N'
; ~ (60) 600
:E..... -----
]' (40) 400
u ,,__..
·z __, (20) 200 -----
f .! No 20 1015 Bessemer
~ --------
~ (0) 0
0 25 50 75 100 125 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Size of section, mm Size of section, mm
Fig. 2.3: Influence of Size on E'/astic Li.mit Fig. 2.4: Change of E'/astic Li.mit with Size of
Section
You might also like
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- DDHB Fatigue LoadsDocument6 pagesDDHB Fatigue LoadsranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: Chapter SevenDocument18 pagesStrength of Materials: Chapter SevenBara'ah AlnemrawiNo ratings yet
- Designs 03 00009 PDFDocument26 pagesDesigns 03 00009 PDFDaniel MilosevskiNo ratings yet
- MEMS Assignment 3Document10 pagesMEMS Assignment 3Waqas Aleem KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Exam Vibrations and NoiseDocument6 pagesExam Vibrations and NoisejoaoftabreuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ConductionDocument102 pagesChapter 2 ConductionadlinasirNo ratings yet
- StochasticDocument3 pagesStochasticDan RusherNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Transformation StressDocument34 pagesCh7 Transformation StressDoğukan KurtuluşNo ratings yet
- Ex PDFDocument4 pagesEx PDFAndres AfanadorNo ratings yet
- Chap2 - Analysis of StressDocument37 pagesChap2 - Analysis of StressFuSiang ChorNo ratings yet
- mit8_323_s23_pset_02solDocument12 pagesmit8_323_s23_pset_02solAyham ziadNo ratings yet
- Properties of Quantum Harmonic Oscillator: Study Goal of This LectureDocument6 pagesProperties of Quantum Harmonic Oscillator: Study Goal of This LectureAmina lbrahimNo ratings yet
- Sol 3Document7 pagesSol 3Saif IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- TD Analyse 2Document31 pagesTD Analyse 2عالم السعادة- World HappinessNo ratings yet
- Cob09 3223Document10 pagesCob09 3223HenriqueMassarddaFonsecaNo ratings yet
- Existing Strain at The Soffit - In-Service Analysis of Cracked Concrete SectionsDocument8 pagesExisting Strain at The Soffit - In-Service Analysis of Cracked Concrete SectionsaygunbayramNo ratings yet
- Exam Vibrations and NoiseDocument6 pagesExam Vibrations and NoisejoaoftabreuNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 1617 - Test 1Document4 pagesSem 2 1617 - Test 1Davidz GanNo ratings yet
- DampingDocument7 pagesDampingTrangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document3 pagesTutorial 4snoozermanNo ratings yet
- Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesPhiladelphia University Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringTamer JafarNo ratings yet
- StructuresDocument22 pagesStructuresNandan HegdeNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strain CalculationDocument3 pagesStress and Strain CalculationThuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress Transformation PDFDocument23 pagesPlane Stress Transformation PDFDel MarNo ratings yet
- Murakami - Analysis of Stress Intensity Factors of Modes I, II and III For Inclined Surface Cracks of Arbitrary ShapeDocument14 pagesMurakami - Analysis of Stress Intensity Factors of Modes I, II and III For Inclined Surface Cracks of Arbitrary ShapeDavid C HouserNo ratings yet
- Multiple Hypotesis TestingDocument4 pagesMultiple Hypotesis Testingfrapass99No ratings yet
- Diffraction of LightDocument12 pagesDiffraction of LightAnkit UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 24 June 2022 Shift I PhysicsDocument6 pages24 June 2022 Shift I PhysicsArav IyerNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Pass YearDocument4 pagesTest 1 Pass Yearnik naimNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Theory Guide for EngineersDocument52 pagesTransmission Line Theory Guide for EngineersKallu kaliaNo ratings yet
- Department of Food Engineering Ned University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument11 pagesDepartment of Food Engineering Ned University of Engineering and TechnologySahar Batool QaziNo ratings yet
- ME2121 Finals ReviewDocument4 pagesME2121 Finals ReviewSherman LiamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24: Steady State LEQR and The S-Procedure: t+1 T T T T T TDocument9 pagesLecture 24: Steady State LEQR and The S-Procedure: t+1 T T T T T TMayur BhiseNo ratings yet
- Test 11p Full Syllabus Latest Pattern SolutionDocument12 pagesTest 11p Full Syllabus Latest Pattern SolutionHardik ChhabraNo ratings yet
- HW6Document8 pagesHW6Duna areny molneNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis and ModellingDocument3 pagesVibration Analysis and ModellingTom ReitsmaNo ratings yet
- Classical Least Squares TheoryDocument35 pagesClassical Least Squares TheoryAnonymous tsTtieMHDNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales Parciales y Series de Fourier: Ejercicios de Tercer ParcialDocument3 pagesEcuaciones Diferenciales Parciales y Series de Fourier: Ejercicios de Tercer ParcialLizz CardenasNo ratings yet
- Wall Loads For Trench DesignDocument3 pagesWall Loads For Trench DesigndantevariasNo ratings yet
- CM 17 Small OscillationsDocument6 pagesCM 17 Small Oscillationsosama hasanNo ratings yet
- Exam Vibrations and NoiseDocument5 pagesExam Vibrations and NoisejoaoftabreuNo ratings yet
- ASM AssignmentsDocument10 pagesASM AssignmentsGulshan DewanganNo ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions in A Graduate Course in Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument64 pagesProblems and Solutions in A Graduate Course in Classical Electrodynamicsfiroz khanNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument1 pagePhysics FormulasspinfxNo ratings yet
- MIET1076 - Lec 9 - 2020 With Handwritten NotesDocument21 pagesMIET1076 - Lec 9 - 2020 With Handwritten NotesPhyo Marn Hone LinNo ratings yet
- MOM I - Module 21 PDFDocument9 pagesMOM I - Module 21 PDFAriel Toño Vaquera ZeballosNo ratings yet
- MOM I - Module 21Document9 pagesMOM I - Module 21Muhammad HabibNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS EQUATIONSDocument11 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS EQUATIONSAnthony MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Stress and Strain - Axial LoadingDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Stress and Strain - Axial Loadingtaymar18No ratings yet
- Experiment 7: StatementDocument4 pagesExperiment 7: StatementabubakarNo ratings yet
- Fe Statics Review: October 1, 2013 J. LiuDocument16 pagesFe Statics Review: October 1, 2013 J. LiumiladNo ratings yet
- I Yr PHYSICS 8 MARKS EMDocument2 pagesI Yr PHYSICS 8 MARKS EMsksnjgamingNo ratings yet
- EN13480-3 Chap12 ModificationsDocument37 pagesEN13480-3 Chap12 ModificationsPrashant ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Course Covers Time-Dependent HamiltoniansDocument44 pagesQuantum Mechanics Course Covers Time-Dependent HamiltoniansMaurin PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Linear Stochastic Models: Least Squares, Regression, and Residual AnalysisDocument12 pagesLinear Stochastic Models: Least Squares, Regression, and Residual AnalysismarioasensicollantesNo ratings yet
- Strain Rosette Analysis BeamDocument7 pagesStrain Rosette Analysis Beammuhammad haroonNo ratings yet
- Bohr & Wheeler Fission Theory Calculation 4 March 2009: Z A 2 A ADocument22 pagesBohr & Wheeler Fission Theory Calculation 4 March 2009: Z A 2 A AAlexandre PereiraNo ratings yet
- 2 LectDocument21 pages2 LectkazimmehdiNo ratings yet
- Webinar 30 Rectangular PlatesDocument37 pagesWebinar 30 Rectangular PlatesJason DrakeNo ratings yet
- Internship Report on Finite Element Simulation Using ABAQUSDocument32 pagesInternship Report on Finite Element Simulation Using ABAQUSranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument7 pagesDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Internship Finite Element Simulation of Titanium Welded Specimens Using ABAQUSDocument24 pagesInternship Finite Element Simulation of Titanium Welded Specimens Using ABAQUSranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- First PhaseDocument14 pagesFirst PhaseranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- A Project Seminar On Structural Weight Optimization Analysis of CNC LatheDocument11 pagesA Project Seminar On Structural Weight Optimization Analysis of CNC LatheranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: Modal Analysis of Sandvik PDJN/L Cutting ToolDocument9 pagesAbstract:: Modal Analysis of Sandvik PDJN/L Cutting ToolranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Low Velocity Impact Behaviour and Modelling of FRP CompositesDocument17 pagesLow Velocity Impact Behaviour and Modelling of FRP CompositesranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Final - Seminar - Updated Report - FinalDocument16 pagesFinal - Seminar - Updated Report - FinalranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- CNC Programming: NC Addresses Characteristics (G and M Codes) : - G Preparing CodesDocument50 pagesCNC Programming: NC Addresses Characteristics (G and M Codes) : - G Preparing CodesranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Study of Free Vibration Characteristics of Cantilever Beams Through Modal Testing and Analysis 2017-18Document70 pagesStudy of Free Vibration Characteristics of Cantilever Beams Through Modal Testing and Analysis 2017-18ranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Units for Stress Concentration FactorsDocument3 pagesSymbols and Units for Stress Concentration FactorsranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual 2016 PDFDocument62 pagesWorkshop Manual 2016 PDFgiridharrajeshNo ratings yet
- Finite element simulation of tensile test using AbaqusDocument24 pagesFinite element simulation of tensile test using AbaqusranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Low Velocity Impact Behaviour and Modelling of FRP CompositesDocument7 pagesLow Velocity Impact Behaviour and Modelling of FRP Compositesranjithkraj100% (1)
- DDHB Keys and CouplingsDocument12 pagesDDHB Keys and CouplingsranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Study of Free Vibration Characteristics of Cantilever Beams Through Modal Testing and Analysis 2017-18Document70 pagesStudy of Free Vibration Characteristics of Cantilever Beams Through Modal Testing and Analysis 2017-18ranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- DDHB Impact LoadsDocument2 pagesDDHB Impact LoadsranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- DDHB - Design of ShaftsDocument6 pagesDDHB - Design of ShaftsranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Advanced Theory of Vibration Nonlinear Vibration ADocument3 pagesAdvanced Theory of Vibration Nonlinear Vibration AranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Units for Stress Concentration FactorsDocument3 pagesSymbols and Units for Stress Concentration FactorsranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- DDHB Riveted JointsDocument7 pagesDDHB Riveted JointsranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- LinesDocument26 pagesLinesnitte5768No ratings yet
- Civil III Strength of Materials (10cv33) NotesDocument74 pagesCivil III Strength of Materials (10cv33) NotesSaiSowmithGoudNaramala0% (1)
- PHS 05b-1a48 PDFDocument1 pagePHS 05b-1a48 PDFranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- I C Engines and Fluid Machinery LabDocument39 pagesI C Engines and Fluid Machinery LabranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering PDFDocument23 pagesCivil Engineering PDFranjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Problem 1 SolutionDocument24 pagesProblem 1 Solutionnitte5768No ratings yet
- Experimental modal analysis of cantilever beam using wireless sensor nodeDocument4 pagesExperimental modal analysis of cantilever beam using wireless sensor noderanjithkrajNo ratings yet
- Civil III Strength of Materials (10cv33) NotesDocument74 pagesCivil III Strength of Materials (10cv33) NotesSaiSowmithGoudNaramala0% (1)
- DOCS-#165539-v8-Technical Manual FOB4 TS Section 5 - MaintenanceDocument108 pagesDOCS-#165539-v8-Technical Manual FOB4 TS Section 5 - MaintenanceBME AOHNo ratings yet
- (Nano and Energy) Gavin Buxton - Alternative Energy Technologies - An Introduction With Computer Simulations-CRC Press (2014) PDFDocument302 pages(Nano and Energy) Gavin Buxton - Alternative Energy Technologies - An Introduction With Computer Simulations-CRC Press (2014) PDFmarcosNo ratings yet
- Kak MhamadDocument1 pageKak MhamadAyub Anwar M-SalihNo ratings yet
- Ndeb Bned Reference Texts 2019 PDFDocument11 pagesNdeb Bned Reference Texts 2019 PDFnavroop bajwaNo ratings yet
- M HNDTL SCKT Imp BP RocDocument2 pagesM HNDTL SCKT Imp BP RocAhmed Abd El RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/41Document24 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/41jesslynaureliaNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying Factors Behind Patient Safety IncidentsDocument5 pagesRoot Cause Analysis: Identifying Factors Behind Patient Safety IncidentsPrabhas_Das7No ratings yet
- CotomDocument8 pagesCotommuangawaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris RanggaDocument3 pagesBahasa Inggris RanggaArdiyantoNo ratings yet
- Stockholm Acc A300 600 2278Document164 pagesStockholm Acc A300 600 2278tugayyoungNo ratings yet
- Façade Lift PerformanceDocument2 pagesFaçade Lift PerformanceIgor DzuklevskiNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review: Constructive Analysis in English and Filipino 1 SEMESTER 2021-2022Document4 pagesA Critical Review: Constructive Analysis in English and Filipino 1 SEMESTER 2021-2022roseNo ratings yet
- Epoxy HRDocument5 pagesEpoxy HRMuthuKumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ESPDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in ESPkaren daculaNo ratings yet
- The Facility Manager's HandbookDocument362 pagesThe Facility Manager's HandbookLuân Châu100% (14)
- Biokimia - DR - Maehan Hardjo M.biomed PHDDocument159 pagesBiokimia - DR - Maehan Hardjo M.biomed PHDHerryNo ratings yet
- The History of Coins and Banknotes in Mexico: September 2012Document35 pagesThe History of Coins and Banknotes in Mexico: September 2012Mladen VidovicNo ratings yet
- Teaching English as a Second Language in Four PhasesDocument18 pagesTeaching English as a Second Language in Four PhasesVia Johnson100% (1)
- Pertanyaan Dan Jawaban Interview Dengan Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesPertanyaan Dan Jawaban Interview Dengan Bahasa Inggrissan_idrus_sip99No ratings yet
- Wave Optics - I: Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreDocument16 pagesWave Optics - I: Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreNitesh Gupta100% (1)
- AquaMatic Price List 2018Document102 pagesAquaMatic Price List 2018milesNo ratings yet
- 4 Types and Methods of Speech DeliveryDocument2 pages4 Types and Methods of Speech DeliveryKylie EralinoNo ratings yet
- Difference between Especially and SpeciallyDocument2 pagesDifference between Especially and SpeciallyCarlos ValenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08-Borrowing Costs-Tutorial AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter 08-Borrowing Costs-Tutorial AnswersMayomi JayasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4a Presentation: Types of PatrolDocument4 pagesTopic 4a Presentation: Types of PatrolGesler Pilvan SainNo ratings yet
- Fit Friend Business Game StrategiesDocument7 pagesFit Friend Business Game StrategiesSanchit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- BLADED - Theory Manual PDFDocument134 pagesBLADED - Theory Manual PDFdavidlokito100% (2)
- Ebola Research ProposalDocument10 pagesEbola Research ProposalChege AmbroseNo ratings yet
- USA Gas TurbineDocument4 pagesUSA Gas TurbineJustin MercadoNo ratings yet