Professional Documents
Culture Documents
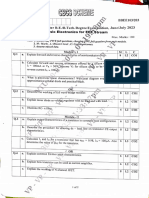
First Semester M.Tech. Power Electronics Degree (Autonomous) Semester End Examination, SEE, Jan2019
Uploaded by
mallikarjun aradhyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
First Semester M.Tech. Power Electronics Degree (Autonomous) Semester End Examination, SEE, Jan2019
Uploaded by
mallikarjun aradhyaCopyright:
Available Formats
(Page 1 of 8)
USN 18EPE 13
First Semester M.Tech. Power Electronics Degree (Autonomous) Semester End Examination, SEE, Jan2019
Solid State Power Controllers
(Model Question Paper – 1)
Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100
Instructions to students:
1. Answer FIVE FULL Questions.
2. Answer ONE full question from each module.
3. All questions carry equal marks.
Mar COs RBT*
ks
With a neat circuit diagram and relevant output voltage waveforms, explain the 10 CO1
L2
a) operation of single ø semi converter feeding R-L load.
1.
With a neat circuit diagram and output voltage waveforms, Justify the 10 CO1
L4
b) suitability of 3 ø Full converter for high power conversion.
OR
With a neat labeled diagram & relevant waveforms, explain the working of a 10 CO1
a single phase dual converter. L2
A 3 phase half wave converter is operated from a 3-phase star connected 208- 10 CO2
V, 60 Hz supply and the load resistance is R = 10Ω. If it is required to obtain
2 an average output voltage of 50% of the maximum possible output voltage,
b) calculate (a) the delay angle α. b) The rms and average output currents, c) The L3
average and rms thyristor currents, d) the rectification efficiency, e) the TUF
and
f) the input PF
With a neat labeled diagram and relevant waveforms, explain the working of a 10 CO1
a) L2
single ø current source, ASCI type inverter.
3.
With a neat circuit diagram explain the operation of three ø voltage source 10 CO1
b) L2
bridge inverter operating with 180°mode of operation.
OR
Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560056
(An Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum & Aided by Govt. of Karnataka, India)
(Page 2 of 8)
With a neat labeled diagram and relevant waveforms, explain the working of a 10 CO1
a) L2
single-ø full bridge voltage source inverter.
4
With a neat circuit diagram explain the operation of three ø voltage source 10 CO1
b) L2
bridge inverter operating with 120°mode of operation.
Discuss the different harmonic reduction methods of inverters. 10 CO1 L2
a)
5.
With a neat circuit diagram explain the operation of sinusoidal pulse width 10 CO3
modulation technique voltage control of 3- phase inverter. L2
b)
OR
Discuss with waveform, voltage control of 3 ø inverters by third harmonic 10 CO3
L2
a) PWM technique
6.
Explain with waveform, the single phase voltage control of inverter using 10 CO3
L2
b) SPWM technique.
Explain the basic concept and features of a multilevel inverters. 10 CO1
a) L2
7.
Describe the operation of a diode clamped multilevel inverter. State its merits 10 CO1
b) L2
and demerits.
OR
With a neat circuit diagram, explain the operation of a cascaded H-bridge 10 CO1
L2
a) multilevel inverter.
8.
With a neat circuit diagram, explain the operation of a Capacitor clamped 10 CO1
b) L2
multilevel inverter.
The buck dc dc converter has the following parameters. Input voltage = 50 V; 10 CO2
D= 0.4; L= 400 µH; C= 100 µF; f= 20 kHz; R= 20Ω. Assuming ideal
L3
a) components, calculate a) output voltage b) Maximum and Minimum inductor
9. current c) the output voltage ripple.
With neat circuit diagram and waveforms explain the principle of step up 10 CO3
b) L2
converters.
Explain the transformer model for DC –DC converter with advantages. 10 CO3 L2
a)
10. With neat circuit diagram and waveforms explain the principle of step 10 CO1
b) L2
down converters.
Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560056
(An Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum & Aided by Govt. of Karnataka, India)
(Page 3 of 8)
Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560056
(An Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum & Aided by Govt. of Karnataka, India)
(Page 4 of 8)
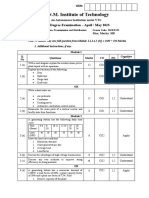
USN 18EPE 13
First Semester M.Tech. Power Electronics Degree (Autonomous) Semester End Examination, SEE, Jan2019
Solid State Power Controllers
(Model Question Paper – II)
Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100
Instructions to students:
1. Answer FIVE FULL Questions.
2. Answer ONE full question from each module.
3. All questions carry equal marks.
COs RBT*
Marks
With a neat circuit diagram and relevant waveforms, explain the 10 CO1
L2
a) operation of 3 ø semi converter.
1.
With a neat labeled diagram & relevant waveforms, explain the 10 CO1
L2
b) working of a single phase dual converter.
OR
With a neat circuit diagram and output voltage waveforms, explain the 10 CO1
a operation of 1-ø full converter. Obtain the expression of average value L4
2 of resultant output voltage.
With a neat circuit diagram and relevant waveforms, explain the 10 CO1
b) L2
operation of 3 ø full converter.
With a neat labeled diagram and relevant waveforms, explain the 10 CO1
a) L2
working of a 1 ø half bridge voltage source inverter.
3.
With a neat circuit diagram explain the operation of three ø bridge 10 CO1
b) L2
voltage source inverter operating with 180°mode of operation.
OR
With a neat labeled diagram and relevant waveforms, explain the 10 CO1
a) L2
working of a single-ø full bridge voltage source inverter.
4
b) Write a note on resonant inverters discussing the importance. 10 CO1 L2
Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560056
(An Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum & Aided by Govt. of Karnataka, India)
(Page 5 of 8)
Discuss with waveform, voltage control of 3 ø inverters by third 10 CO3
L2
a) harmonic PWM technique.
5.
With a neat circuit diagram explain the operation of sinusoidal pulse 10 CO1
L2
b) width modulation technique voltage control of 3- phase inverter.
OR
Discuss the different harmonic reduction techniques of inverters. 10 CO3 L2
a)
6.
Explain with waveform, the single phase voltage control of inverter 10 CO3
L2
b) using SPWM technique.
Explain the basic concept and features of multilevel inverters. 10 CO1
a) L2
7.
With a neat circuit diagram, explain the operation of a cascaded H- 10 CO1
b) L2
bridge multilevel inverter.
OR
Describe the operation of a diode clamped multilevel inverter. State its 10 CO1
L2
a) merits and demerits.
8.
With a neat circuit diagram, explain the operation of a Capacitor 10 CO1
b) L2
clamped multilevel inverter.
The buck dc dc converter has the following parameters. Input voltage = 50 10 CO2
V; D= 0.4; L= 400 µH; C= 100 µF; f= 20 kHz; R= 20Ω. Assuming ideal
L4
a) components, calculate a) output voltage b) Maximum and Minimum inductor
9. current c) the output voltage ripple.
With neat circuit diagram and waveforms explain the principle of step 10 CO3
b) L2
down converters.
OR
Explain the transformer model for DC –DC converter with advantages. 10 CO3 L2
a)
10. With neat circuit diagram and waveforms explain the principle of step 10 CO3
b) L2
up converters.
Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560056
(An Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum & Aided by Govt. of Karnataka, India)
(Page 6 of 8)
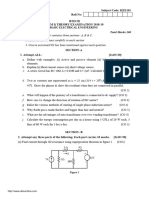
USN 18EPE 13
First Semester M.Tech. Power Electronics Degree (Autonomous) Semester End Examination, SEE, Jan2019
Solid State Power Controllers
(Model Question Paper – III)
Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100
Instructions to students:
1. Answer FIVE FULL Questions.
2. Answer ONE full question from each module.
3. All questions carry equal marks.
Marks COs RBT*
With a neat circuit diagram and relevant output voltage source current 10 CO1
waveforms, explain the operation of single ø semi converter feeding L2
a)
R-L load.
1.
With a neat circuit diagram and output voltage waveforms, explain the 10 CO2
operation of 3 ø converter. Obtain the expression of average value of L4
b)
resultant output voltage.
OR
With a neat labeled diagram & relevant waveforms, explain the 10 CO1 L2
a
working of a single phase semi controlled series converter.
A 3 phase half wave converter is operated from a 3-phase star 10 CO2 L3
connected 208-V, 60 Hz supply and the load resistance is R = 10Ω. If
2 it is required to obtain an average output voltage of 50% of the
b) maximum possible output voltage, calculate (a) the delay angle α. b)
The rms and average output currents, c) The average and rms thyristor
currents, d) the rectification efficiency, e) the TUF and
f) the input PF
With a neat labeled diagram and relevant waveforms, explain the 10 CO1 L2
a)
working of a 1 ø full bridge inverter.
3.
With a neat circuit diagram explain the operation of three ø bridge 10 CO1 L2
b)
inverter operating with 180°mode of operation.
Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560056
(An Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum & Aided by Govt. of Karnataka, India)
(Page 7 of 8)
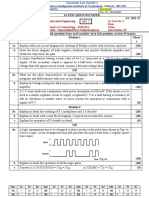
OR
a) Discuss the differences between CSI and VSI with applications. 10 CO1 L2
4
With a neat labeled diagram and relevant waveforms, explain the 10 CO1
b) L2
working of a single ø current source, ASCI type inverter.
Explain with waveform, the single phase voltage control of inverter 10 CO3
L2
a) using SPWM technique.
5.
With a neat circuit diagram explain the operation of sinusoidal pulse 10 CO3
L2
b) width modulation technique voltage control of 3- phase inverter.
OR
Discuss with waveform, voltage control of 3 ø inverters by third 10 CO3
L2
a) harmonic PWM technique
6.
Discuss the different harmonic reduction methods of inverters. 10 CO2 L2
b)
Explain the basic concept and features of multilevel inverters. 10 CO1
a) L2
7.
Explain with circuit diagram, the operation of a diode clamped 10 CO1
b) L2
multilevel inverter.
OR
With a neat circuit diagram, explain the operation of a cascaded H- 10 CO1
L2
a) bridge multilevel inverter.
8.
With a neat circuit diagram, explain the operation of a Capacitor 10
b) L2
clamped multilevel inverter.
The buck dc dc converter has the following parameters. Input voltage 10 CO3
= 50 V; D= 0.4; L= 400 µH; C= 100 µF; f= 20 kHz; R= 20Ω. Assuming
L3
a) ideal components, calculate a) output voltage b) Maximum and
9. Minimum inductor current c) the output voltage ripple.
With neat circuit diagram and waveforms explain the principle of step 10
b) L2
up converters.
OR
Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560056
(An Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum & Aided by Govt. of Karnataka, India)
(Page 8 of 8)
Explain the transformer model for DC –DC converter with advantages. 10 CO3 L2
a)
The buck dc dc converter has the following parameters. Input voltage 10 CO3
10. = 50 V; D= 0.4; L= 400 µH; C= 100 µF; f= 20 kHz; R= 20Ω. Assuming
b) L3
ideal components, calculate a) output voltage b) Maximum and
Minimum inductor current c) the output voltage ripple.
Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560056
(An Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum & Aided by Govt. of Karnataka, India)
You might also like
- 16MT12303 - ApcDocument10 pages16MT12303 - ApcNmg KumarNo ratings yet
- BBEE103 Set 1Document2 pagesBBEE103 Set 1Sachin K PNo ratings yet
- 22 BEE13 Set 1Document2 pages22 BEE13 Set 1Abdulkhaliq NasherNo ratings yet
- BBEE103 Set 1Document2 pagesBBEE103 Set 1samanth0404No ratings yet
- I B.Tech. II Semester Regular Examinations October 2021Document10 pagesI B.Tech. II Semester Regular Examinations October 2021AmarnathNo ratings yet
- BEC303 Set1Document3 pagesBEC303 Set1vedd22eceNo ratings yet
- 22 BEE13 Set 1Document2 pages22 BEE13 Set 1PRABHANJANNo ratings yet
- 19eec44 - Analog Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsDocument2 pages19eec44 - Analog Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsKarunakaran M,47No ratings yet
- Basic Electroincs 1st IADocument2 pagesBasic Electroincs 1st IARachana MedehalNo ratings yet
- USN 18EEEE62: High Voltage EngineeringDocument2 pagesUSN 18EEEE62: High Voltage Engineering1DA18EE013Gagana B.RNo ratings yet
- Instructions To The Candidates I. Answer Five Full QuestionsDocument3 pagesInstructions To The Candidates I. Answer Five Full QuestionsKaran JagannathNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Electronics: M.Tech. (Integrated Power System) First SemesterDocument1 pageAdvanced Power Electronics: M.Tech. (Integrated Power System) First SemesterMahesh ShendeNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 2018 (Cbcs Scheme) 18EE53Document2 pagesModel Question Paper 2018 (Cbcs Scheme) 18EE53Mohana M ReddyNo ratings yet
- GTD Model QP 2Document3 pagesGTD Model QP 2Jeevan N BNo ratings yet
- 19eec42 - Generation Transmission and DistributionDocument3 pages19eec42 - Generation Transmission and DistributionKarunakaran M,47No ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Page 1 of 2 Sub Code: KEE302Document2 pagesTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Page 1 of 2 Sub Code: KEE302AvinäshShärmaNo ratings yet
- BEEE103 Set 1Document3 pagesBEEE103 Set 1pruthvichougule21No ratings yet
- 18 Ee 432Document3 pages18 Ee 432AnushkaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Engineering (Model Question Paper - 3)Document1 pageHigh Voltage Engineering (Model Question Paper - 3)1DA18EE013Gagana B.RNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical 1st Year 2021 T101ADocument5 pagesBasic Electrical 1st Year 2021 T101ASukanta MallickNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Modeling: M. Tech. First Semester (Integrated Power System / Power Elect. & Power System) (C.B.C.S.)Document2 pagesPower Systems Modeling: M. Tech. First Semester (Integrated Power System / Power Elect. & Power System) (C.B.C.S.)Mahesh ShendeNo ratings yet
- Ism - MQ-1Document2 pagesIsm - MQ-1aravindNo ratings yet
- 15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering1Document2 pages15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering1jagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits IIDocument2 pagesAnalog Circuits IIVictor SealNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 31-Oct-2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 31-Oct-2023rakshithvittla1234No ratings yet
- MQ - 2 - HVE - May - June-20 - 18EE62Document1 pageMQ - 2 - HVE - May - June-20 - 18EE621DA18EE013Gagana B.RNo ratings yet
- NR 310204 Power ElectronicsDocument8 pagesNR 310204 Power ElectronicsSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Subject Title: Analog Circuits: 18EC42 Model Question Paper-2 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme)Document3 pagesSubject Title: Analog Circuits: 18EC42 Model Question Paper-2 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme)VijaykumarPatilNo ratings yet
- Subject Title: Analog Circuits: 18EC42 Model Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme)Document3 pagesSubject Title: Analog Circuits: 18EC42 Model Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme)VijaykumarPatilNo ratings yet
- EC QuestionBank 1Document2 pagesEC QuestionBank 1lubnaNo ratings yet
- MST 2 P1 (Ex-502)Document36 pagesMST 2 P1 (Ex-502)ASHISH SINGH SENGARNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits Module 5Document53 pagesAnalog Circuits Module 5Ranjith AcharyaNo ratings yet
- GTD Model QP 1Document3 pagesGTD Model QP 1Jeevan N BNo ratings yet
- Pse Supple 2021Document2 pagesPse Supple 2021Aditya JhaNo ratings yet
- Beee GGCT Mid Term 2 Paper 2023Document2 pagesBeee GGCT Mid Term 2 Paper 2023ShirishNo ratings yet
- Psa1 MQP 3 2021Document3 pagesPsa1 MQP 3 20211DA18EE013Gagana B.RNo ratings yet
- 9A02504 Power ElectronicsDocument4 pages9A02504 Power ElectronicsMohan Krishna100% (1)
- Kee101t Ee Aktu QP-2020-21Document14 pagesKee101t Ee Aktu QP-2020-21Sudhir ChandNo ratings yet
- PRN No. Total No. of Questions: 07: (An Autonomous Institute Affiliated To Savitribai Phule Pune University)Document3 pagesPRN No. Total No. of Questions: 07: (An Autonomous Institute Affiliated To Savitribai Phule Pune University)cpt.ghostNo ratings yet
- 18 Ee 461Document2 pages18 Ee 461anonymusNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: 71778: Reg. NoDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper Code: 71778: Reg. NokarthickpjceNo ratings yet
- Kings: Question BankDocument6 pagesKings: Question Bankapi-19951707No ratings yet
- Basic Eln-2021-IA-1-Set 2 - ModifiedDocument2 pagesBasic Eln-2021-IA-1-Set 2 - ModifiedProf. Nikhil KulkarniNo ratings yet
- J.B. Institute of Engineering and Technology R20Document2 pagesJ.B. Institute of Engineering and Technology R20hidhanaaNo ratings yet
- Ee 6 Sem Power Electronics Winter 2017Document2 pagesEe 6 Sem Power Electronics Winter 2017pankaj mobile zoneNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Engineering Kamaraju and NaiduDocument2 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering Kamaraju and NaiduAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledSoorya Priya Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- KSR Institute For Engineering and Technology TIRUCHENGODE - 637 215Document5 pagesKSR Institute For Engineering and Technology TIRUCHENGODE - 637 215Karthikeyan SelvaNo ratings yet
- 18 Ec 421Document3 pages18 Ec 421Srujana PurohitNo ratings yet
- Btech 1 Sem Basic Electrical Engineering Kee 101 2018 19Document4 pagesBtech 1 Sem Basic Electrical Engineering Kee 101 2018 19Viraj RuhelaNo ratings yet
- PUE Question Paper Format - 100 MarksDocument3 pagesPUE Question Paper Format - 100 MarksnupurnehaNo ratings yet
- Ism - MQ-4Document3 pagesIsm - MQ-4aravindNo ratings yet
- An Active Inductor-Based VCO With Wide Tuning Range and High DC-to-RF Power EfficiencyDocument5 pagesAn Active Inductor-Based VCO With Wide Tuning Range and High DC-to-RF Power EfficiencyOmarFaruqeNo ratings yet
- Q.No. MarksDocument2 pagesQ.No. MarksCharandeep TirkeyNo ratings yet
- CIA-III 2018-19 Even Kee 201Document2 pagesCIA-III 2018-19 Even Kee 201amit621988No ratings yet
- 13A99101 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering PDFDocument1 page13A99101 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering PDFsubbuNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper: Unit - I Questions Marks BLL CODocument2 pagesModel Question Paper: Unit - I Questions Marks BLL COViju JigajinniNo ratings yet
- (Affiliated To JNTUA & Approved by AICTE) (Accredited by NAAC With A'Grade & Accredited by NBA (EEE, ECE & CSE) )Document2 pages(Affiliated To JNTUA & Approved by AICTE) (Accredited by NAAC With A'Grade & Accredited by NBA (EEE, ECE & CSE) )aravindNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsFrom EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bengaluru - 56 Applied MathematicsDocument3 pagesDr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology, Bengaluru - 56 Applied Mathematicsmallikarjun aradhyaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Wind - PVDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Wind - PVmallikarjun aradhyaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurement - Ph.D.-dissertation - April-2001 PDFDocument195 pagesInstrumentation and Measurement - Ph.D.-dissertation - April-2001 PDFmallikarjun aradhyaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument11 pagesReportmallikarjun aradhyaNo ratings yet
- Matsuki-Me4435 C145078Document5 pagesMatsuki-Me4435 C145078Nguyễn Nhật MinhNo ratings yet
- I) Ii) Iii) Iv) I) Ii) Iii) Iv) V) Vi) : Bangladesh Power Development Board Marks DistributionDocument3 pagesI) Ii) Iii) Iv) I) Ii) Iii) Iv) V) Vi) : Bangladesh Power Development Board Marks DistributionsadmanNo ratings yet
- Study On Electricity Distribution, Substation Operation & Maintenance of DESCODocument46 pagesStudy On Electricity Distribution, Substation Operation & Maintenance of DESCOSarwer Hussain Faisal100% (5)
- Ha 25 74 Nxair 50ka enDocument46 pagesHa 25 74 Nxair 50ka engerardo.aquinoNo ratings yet
- ABB DC Power - Supplies - Catalog PDFDocument118 pagesABB DC Power - Supplies - Catalog PDFAdnan Naeem MalikNo ratings yet
- 18s266-Pr-Vp-2000-Po006-10002 VTDocument347 pages18s266-Pr-Vp-2000-Po006-10002 VTAlia RedhaNo ratings yet
- Head - Lamps LED CatalogueDocument20 pagesHead - Lamps LED CatalogueJuris MickēvičsNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 2 - EE 421Document5 pagesModule 1 - Part 2 - EE 421Mirasol JavierNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Magnetic VS Thermal MagneticDocument2 pagesHydraulic Magnetic VS Thermal MagneticLakshmi Pathi100% (1)
- EXPERIMENT 6:observation of The V-I Characteristic of A DiodeDocument5 pagesEXPERIMENT 6:observation of The V-I Characteristic of A DiodeShubham waghmareNo ratings yet
- 1N5221A To 1N5272DDocument3 pages1N5221A To 1N5272DlavinelllNo ratings yet
- P19 ArduinoDocument1 pageP19 ArduinoSanto MulyonoNo ratings yet
- Test Machine Sesi 1718 Sem 2 Second VersionDocument3 pagesTest Machine Sesi 1718 Sem 2 Second VersionaimamNo ratings yet
- TUGASAN KUMPULAN (DC Generator)Document43 pagesTUGASAN KUMPULAN (DC Generator)Zainuddin BusuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Study of 3-Phase Induction Motor Starting Transients Submitted By: Group 1 (Tuesday Batch)Document4 pagesExperiment 2: Study of 3-Phase Induction Motor Starting Transients Submitted By: Group 1 (Tuesday Batch)Anonymous a10IpLym4rNo ratings yet
- Itm - Codigos SiemensDocument234 pagesItm - Codigos SiemensSantiago FarfanNo ratings yet
- Sinexcel PresentationDocument33 pagesSinexcel Presentationapi-582917436No ratings yet
- March Power Report - 2020Document70 pagesMarch Power Report - 2020Gyan chandraNo ratings yet
- Proposal PaperDocument13 pagesProposal Paperapi-331985309No ratings yet
- Bulletin 2881BDocument2 pagesBulletin 2881Bsylvi293No ratings yet
- Electrical Assignment 1 2016-17Document2 pagesElectrical Assignment 1 2016-17Anonymous Xf6rRynzNo ratings yet
- Compalarm CatalogDocument4 pagesCompalarm CatalogXuân Thuỷ PhạmNo ratings yet
- Guide Lines: Field Component ManualDocument21 pagesGuide Lines: Field Component ManualOsman ElmaradnyNo ratings yet
- Diode V-I Characteristics Curve, Diode in Series ConnectionDocument17 pagesDiode V-I Characteristics Curve, Diode in Series ConnectionShuvodip Das100% (1)
- (DDS)Document12 pages(DDS)minhtutran1983No ratings yet
- MRU1 WoodWArdDocument28 pagesMRU1 WoodWArdYago PereiraNo ratings yet
- SMPS Laboratory InstructionsDocument28 pagesSMPS Laboratory InstructionsM.Seddik DOUARNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage (V) #61-340 #61-342 Ranges & Accuracies: Digital Multimeter Instruction ManualDocument6 pagesAC Voltage (V) #61-340 #61-342 Ranges & Accuracies: Digital Multimeter Instruction Manualtallerleo551No ratings yet
- Data Sheet 3VA9988-0AA11: ModelDocument6 pagesData Sheet 3VA9988-0AA11: ModelRurizwan Syahru WibisanaNo ratings yet