Professional Documents
Culture Documents
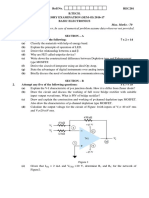
Electronics Engineering 3L:1T:0P 4 Credits
Electronics Engineering 3L:1T:0P 4 Credits
Uploaded by
pcjoshi020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pagekoe 032 electronics engineering
Original Title
electronics eng KOE032
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentkoe 032 electronics engineering
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageElectronics Engineering 3L:1T:0P 4 Credits
Electronics Engineering 3L:1T:0P 4 Credits
Uploaded by
pcjoshi02koe 032 electronics engineering
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Electronics Engineering 3L:1T:0P 4 Credits
Unit Topics Lectures
I PN junction diode: Introduction of semiconductor materials; 8
Semiconductor diode: Depletion layer, V-I characteristics, ideal and
practical, diode resistance, capacitance, diode equivalent circuits, transition
and diffusion capacitance, Zener diodes breakdown mechanism (Zener and
avalanche).
II Diode application: Series, parallel and series, parallel diode configuration, 8
half and full wave rectification, clippers, clampers, Zener diode as shunt
regulator, voltage-multiplier circuits special purpose two terminal devices :
light-emitting diodes, Varactor (Varicap) diodes, tunnel diodes, liquid-
crystal displays.
III Bipolar junction transistors and field effect transistor: Bipolar junction 8
transistor: Transistor construction, operation, amplification action,
common base, common emitter, common collector configuration dc
biasing BJTs: operating point, fixed-bias, emitter bias, voltage-divider bias
configuration. Collector feedback, emitter-follower configuration. Bias
stabilization. CE, CB, CC amplifiers and AC analysis of single stage CE
amplifier (re Model), Field effect transistor: Construction and
characteristic of JFETs. AC analysis of CS amplifier, MOSFET (depletion
and enhancement) type, transfer characteristic.
IV Operational amplifiers: Introduction and block diagram of Op-Amp, ideal 8
& practical characteristics of Op-Amp, differential amplifier circuits,
practical Op-Amp circuits (inverting amplifier, non-inverting amplifier,
unity gain amplifier, summing amplifier, integrator, differentiator), Op-
Amp parameters: input offset voltage, output offset voltage, input biased
current, input offset current differential and common-mode operation.
V Electronic instrumentation and measurements: Digital voltmeter: 8
Introduction, RAMP techniques digital multimeters: Introduction
Oscilloscope: introduction, basic principle, CRT, block diagram of
oscilloscope, simple, measurement of voltage, current phase and frequency
using CRO, introduction of digital storage oscilloscope and comparison of
DSO with analog oscilloscope.
Text /Reference Books:
1. Robert L. Boylestand / Louis Nashelsky, “Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory,” Latest
Edition, Pearson Education.
2. H S Kalsi, “Electronic Instrumentation”, Latest Edition, TMH Publication.
3. Meetidehran/ A.K. singh “fundamental of electronics Engineering”, New age
international publisher.
Course Outcomes:
At the end of this course students will demonstrate the ability to:
1. Understand the concept of PN junction and special purpose diodes.
2. Study the application of conventional diode and semiconductor diode.
3. Analyse the I-V characteristics of BJT and FET.
4. Analyzethe of Op-Amp, amplifiers, integrator, and differentiator.
5. Understand the concept of digital storage oscilloscope and compare of DSO with analog
oscilloscope
You might also like
- Power Factor CorrectionDocument3 pagesPower Factor CorrectionAsfand HaroonNo ratings yet
- Articolo SWR EngDocument4 pagesArticolo SWR EngLuis Enrique Castillejo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lead Acid Battery ChargerDocument2 pagesLead Acid Battery ChargermuaazgujjarNo ratings yet
- EE2203-Electronic Device and Circuits Question BankDocument11 pagesEE2203-Electronic Device and Circuits Question BankAnbarasan Annamalai100% (1)
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated CircuitsDocument6 pagesLinear Integrated CircuitsRanganathan ThambirajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document48 pagesChapter 17MahmoudKhedrNo ratings yet
- Digital Phase Selector: A Mini-Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Requirements For The Award ofDocument53 pagesDigital Phase Selector: A Mini-Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Requirements For The Award ofdondbNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument8 pagesLVDTAnirban GhoshNo ratings yet
- AC PotentiometerDocument3 pagesAC PotentiometerNh Chuminda Yapa100% (1)
- Power Electronics Lab Manual PDFDocument41 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual PDFSudhakar MarojuNo ratings yet
- Delta B Drive Short Manual PDFDocument32 pagesDelta B Drive Short Manual PDFAshok SahuNo ratings yet
- Induction CookersDocument5 pagesInduction CookersVăn LinNo ratings yet
- SCR, Traic, Diac ReportDocument19 pagesSCR, Traic, Diac ReportPravin Gareta60% (5)
- Solar-Powered Battery Charging With Highly Efficient Buck ConverterDocument20 pagesSolar-Powered Battery Charging With Highly Efficient Buck ConverterSusanNo ratings yet
- Designing Planar Magnetics DixonDocument26 pagesDesigning Planar Magnetics Dixonarulsrini77No ratings yet
- Introduction To ProteusDocument8 pagesIntroduction To ProteusateeqshaheenNo ratings yet
- On IgbtDocument19 pagesOn IgbtSayanta Saha100% (1)
- Diac CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesDiac CharacteristicsSourabh100% (1)
- Major ProjectDocument10 pagesMajor ProjectDebeshNo ratings yet
- Smps InverterDocument5 pagesSmps Invertersami_yNo ratings yet
- Common Base Transistor Characteristics PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Base Transistor Characteristics PDFTravis50% (2)
- Transistor Test Using An Analogue Multi MeterDocument3 pagesTransistor Test Using An Analogue Multi MeterryinejanNo ratings yet
- 16ee401 Devices and Circuits 3/0/0/3Document2 pages16ee401 Devices and Circuits 3/0/0/3Divya Priyadharshini MohanNo ratings yet
- What Is An "M7" Diode?: Sherrellbc Jan 16 '15 at 15:45Document2 pagesWhat Is An "M7" Diode?: Sherrellbc Jan 16 '15 at 15:45Jai Ho100% (1)
- Boost DesignDocument4 pagesBoost DesignmuthukumartharaniNo ratings yet
- LVDT: Basic Principle, Theory, Working, Explanation & Diagram - Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument2 pagesLVDT: Basic Principle, Theory, Working, Explanation & Diagram - Linear Variable Differential TransformerAtul NagarkarNo ratings yet
- Digital Voltmeters Can Be Classified in To The Following Broad CategoriesDocument22 pagesDigital Voltmeters Can Be Classified in To The Following Broad CategoriesSysu KumarNo ratings yet
- EDC Question BankDocument13 pagesEDC Question BankvenzkrishNo ratings yet
- Transistor and Amplifier Formulas: Appendix FDocument5 pagesTransistor and Amplifier Formulas: Appendix FPrashant BabuNo ratings yet
- CRT AssignmentDocument21 pagesCRT AssignmentRittika RatawaNo ratings yet
- Proteuslab 01Document3 pagesProteuslab 01Sanjid ElahiNo ratings yet
- University Institute of Engineering Department Au-1Document40 pagesUniversity Institute of Engineering Department Au-1Manveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Transformer: Rapid ElectronicsDocument5 pagesTransformer: Rapid ElectronicsMayaa KhanNo ratings yet
- Anti Sleep Alarm RDocument31 pagesAnti Sleep Alarm RPrints Bindings100% (1)
- Bob Blue2 Ring TesterDocument4 pagesBob Blue2 Ring Testerbybu74No ratings yet
- Synchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesSynchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersJoseph Harindranath67% (3)
- Brake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 PhaseDocument7 pagesBrake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 Phasejassisc100% (1)
- PWM Off-Line Switching Regulator Ics: Str-A6000H SeriesDocument13 pagesPWM Off-Line Switching Regulator Ics: Str-A6000H SeriesAnonymous Lfgk6vygNo ratings yet
- Eye Blink Sensorensor Accident Prevention ReportDocument20 pagesEye Blink Sensorensor Accident Prevention ReportAyushi Jain0% (1)
- 17ee82 - Ida - Mod 3 NotesDocument38 pages17ee82 - Ida - Mod 3 NotesManish Kumar SahaniNo ratings yet
- Car Battery Charger Circuit DiagramDocument3 pagesCar Battery Charger Circuit DiagramJaiNo ratings yet
- Water Level ControllerDocument7 pagesWater Level ControllerYudi Mahato0% (1)
- Single Phase SPWM InverterDocument46 pagesSingle Phase SPWM Inverternitin aryaNo ratings yet
- Design and Develop An IGBT Inverter For AC Motor Drive ApplicationsDocument40 pagesDesign and Develop An IGBT Inverter For AC Motor Drive Applicationselectron1999100% (1)
- Ch7 Induction MotorDocument82 pagesCh7 Induction MotorMuhammad R ShihadehNo ratings yet
- LVDT - Linear Variable Displacement Transducers/TransformersDocument10 pagesLVDT - Linear Variable Displacement Transducers/TransformersNandhinee DeviNo ratings yet
- Exp 9 Boost ConverterDocument8 pagesExp 9 Boost ConverterusmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistor: UNIT-4Document70 pagesField Effect Transistor: UNIT-4I am FineNo ratings yet
- Voltage Doubler ADocument2 pagesVoltage Doubler AErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument4 pagesCapacitorsJohn David YermoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Unit 1 PDFDocument27 pagesTransformer Unit 1 PDFtinkudhullNo ratings yet
- Automatic Battery Charger CircuitsDocument25 pagesAutomatic Battery Charger Circuitsrowell ramosNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier.Document37 pagesPower Electronics Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier.Hassan technologist0% (1)
- Study of LVDT and Precision RectifierDocument10 pagesStudy of LVDT and Precision RectifierDivyam Gupta 1373 -12th BNo ratings yet
- Electric Piano: Adam Estes and Yukimi MorimotoDocument21 pagesElectric Piano: Adam Estes and Yukimi MorimotoBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Workshop ON Ltspice: Fabrice WATEAUDocument60 pagesWorkshop ON Ltspice: Fabrice WATEAUkalimbaloNo ratings yet
- Electrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsFrom EverandElectrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)Document27 pagesConvolutional Neural Network (CNN)pcjoshi02No ratings yet
- 1 STDocument6 pages1 STpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Balwinder Sir 1st ClassDocument6 pagesBalwinder Sir 1st Classpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- CNN 1Document23 pagesCNN 1pcjoshi02No ratings yet
- B.Tech EC Syllabus 3rd YearDocument35 pagesB.Tech EC Syllabus 3rd Yearpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- 7 Limbs of StateDocument8 pages7 Limbs of Statepcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Attempt All Sections. If Require Any Missing Data Then Choose SuitablyDocument3 pagesAttempt All Sections. If Require Any Missing Data Then Choose Suitablypcjoshi02No ratings yet
- B.Tech EC Final YearDocument18 pagesB.Tech EC Final Yearpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not ProvidedDocument2 pagesTime: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not Providedpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Suraj PDFDocument8 pagesSuraj PDFpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Rec 101 2016 17Document4 pagesBasic Electronics Rec 101 2016 17pcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Advance Digital Design Using VeilogDocument99 pagesAdvance Digital Design Using Veilogpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument50 pagesBipolar Junction Transistorspcjoshi02No ratings yet
- 31 Analysis Design Asynchronous Sequential Circuits PDFDocument72 pages31 Analysis Design Asynchronous Sequential Circuits PDFpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- ECD Lab NEC 752Document17 pagesECD Lab NEC 752pcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Steps For Simulating VHDL Programs in OrCADDocument8 pagesSteps For Simulating VHDL Programs in OrCADpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Biquad Filter PDFDocument5 pagesBiquad Filter PDFpcjoshi02100% (1)
- Assembling and Running An 8051 ProgramDocument5 pagesAssembling and Running An 8051 Programpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Cad Lab Cmos Inverter PDFDocument4 pagesCad Lab Cmos Inverter PDFpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Integrated CircuitDocument160 pagesIntegrated Circuitpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Ac 800 PDFDocument344 pagesAc 800 PDFJose Vicente CentellesNo ratings yet
- PG Diploma in Vlsi Soc Design and Verification Course StructureDocument16 pagesPG Diploma in Vlsi Soc Design and Verification Course Structurepitcheswarrao mrNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computer 1Document4 pagesFundamentals of Computer 1Holsworth WilsonNo ratings yet
- How LTE Stuff Works?Document1 pageHow LTE Stuff Works?subbaNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Diode: 1N4148/1N4448/1N914B 500mW High Speed Switching DiodeDocument2 pagesSmall Signal Diode: 1N4148/1N4448/1N914B 500mW High Speed Switching DiodeRaju VemulaNo ratings yet
- Centrecom Micro Transceivers: At-Mx10 At-Mx10S At-Mx20T At-210T At-210TsDocument2 pagesCentrecom Micro Transceivers: At-Mx10 At-Mx10S At-Mx20T At-210T At-210TsCarlos DuranNo ratings yet
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiDocument10 pagesChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiPradeep Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Trunk Switching (LAB#13) : NameDocument3 pagesTrunk Switching (LAB#13) : NameUsairumNo ratings yet
- Industrial PC IPC 6110Document4 pagesIndustrial PC IPC 6110Arthur TalibulinNo ratings yet
- gf6 bk1 OverallDocument1 pagegf6 bk1 OverallJvr SeeNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument6 pagesEmbedded SystemsShuvoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Storage Devices and MediaDocument21 pages3.1 Storage Devices and MediaAqilah HasmawiNo ratings yet
- Overview Data Sheets: F 8652: Central ModuleDocument2 pagesOverview Data Sheets: F 8652: Central ModuleDNo ratings yet
- MIOT Project Report - MergedDocument25 pagesMIOT Project Report - MergedKunal maneNo ratings yet
- Computing Funda - Midterm ExamDocument10 pagesComputing Funda - Midterm ExamMark JamesNo ratings yet
- TV101WXM NF0Document38 pagesTV101WXM NF0Harward StarkNo ratings yet
- Co PDFDocument123 pagesCo PDFSitaNo ratings yet
- Ecografo Resoan PDFDocument357 pagesEcografo Resoan PDFalejandra ruizNo ratings yet
- VO3150A 0.5 A Output Current IGBT and MOSFET Driver: Vishay SemiconductorsDocument11 pagesVO3150A 0.5 A Output Current IGBT and MOSFET Driver: Vishay Semiconductorsnhatnam06dt1No ratings yet
- Ic 695 Cpu 315Document14 pagesIc 695 Cpu 315Dilyalew DebreworkNo ratings yet
- RT NAGAR - Laptop ReportDocument1 pageRT NAGAR - Laptop ReportAshwin PanditNo ratings yet
- Dell Dock wd19s 180w Data SheetDocument5 pagesDell Dock wd19s 180w Data Sheetsunilkhairnar38No ratings yet
- MCQ Bank For Computer FundamentalsDocument4 pagesMCQ Bank For Computer FundamentalsEgeru JosephNo ratings yet
- Part No. Product Name/Description Received Date QTY UnitDocument8 pagesPart No. Product Name/Description Received Date QTY Unitvicente tanNo ratings yet
- Streamlined Productivity & Simplified Lifestyle: Benq Gw2480Document2 pagesStreamlined Productivity & Simplified Lifestyle: Benq Gw2480sundaraNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Model Paper XI (Paper I)Document16 pagesComputer Science Model Paper XI (Paper I)Muhammad ZahooruddinNo ratings yet
- IEC20091118133046Document5 pagesIEC20091118133046SEANMNo ratings yet
- SM#Limitatore CLG-SL - v102 (PCLGLxE) - eDocument6 pagesSM#Limitatore CLG-SL - v102 (PCLGLxE) - eJaime Basquez PaccoNo ratings yet
- Maximite Hardware ManualDocument7 pagesMaximite Hardware ManualAlfonso Hernández MagdalenoNo ratings yet