Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Major Head Losses in Pipe Flow: Major Head Loss, H Major Head Loss, H
Major Head Losses in Pipe Flow: Major Head Loss, H Major Head Loss, H
Uploaded by
Li ReOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Major Head Losses in Pipe Flow: Major Head Loss, H Major Head Loss, H
Major Head Losses in Pipe Flow: Major Head Loss, H Major Head Loss, H
Uploaded by
Li ReCopyright:
Available Formats
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO
ALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf
A. Darcy-Weisbach Formula (pipe-friction equation) For Turbulent flow:
2. For smooth pipes, Re between 3,000 and 100,000: (Blasius)
Major Head losses in pipe flow
Where:
f = Friction factor 3. For smooth pipes with Re up to about 3,000,000
L = Length of pipe in meter or feet
D = pipe diameter in meter or feet
Reference: V = mean or average velocity of flow in m/s or ft/s
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics 4th Edition by Gillesania
- Mathalino.com
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Head losses in Pipe flow Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf
Head losses in pipes may be classified into two; For non-circular pipes, use D = 4R, where R is the hydraulic radius. 4. For rough pipes, where l < 0.3
the Major head loss, which is caused by pipe friction along straight
sections of pipe of uniform diameter and uniform roughness, and For circular pipes, the head loss may be expressed as:
Minor head loss, which are caused by changes in velocity or direction of
flow and are commonly expressed in terms of Kinetic energy.
Where:
Energy equation between any two points: = absolute roughness, mm
/D = relative roughness
E2 E1 hpump hturb hL, f l = nominal thickness of viscous sublayer
(S.I. units)
p2 V22 p1 V12
z2 z1 hpump hturb hL , f
2g 2g Where:
Q = discharge in m3/s
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Head losses in Pipe flow Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf
Illustration showing the behavior of EGL and HGL Friction factor, f 5. For smooth and rough pipes, turbulent: (Colebrook equation)
For Laminar flow:
For Turbulent flow: The equation was plotted in 1944 by Moody into what is now called
1. For turbulent flow in smooth and rough pipes, universal resistant laws Moody chart for pipe friction.
can be derived from:
Where:
vs = shear velocity or friction velocity
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf
B. Manning formula B. Manning formula
Moody Friction The manning formula is one of the best known open-channel formulas and Values of n to be used with
factor chart is commonly used in pipes. The formula is given by: Manning formula
(S.I. Units)
(English Units)
Where:
n = roughness coefficient
R = hydraulic radius
S = slope of the energy grade line = hf/L
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf
B. Manning formula C. Hazen Williams Formula
Value of Specifc roughness, for pipe materials
Substituting S = hf/L and R = D/4 and solving for hf The Hazen williams formula is widely used in water works industry.
It is used in the design of water pipe systems such as fire sprinkler systems, water supply
networks, and irrigation systems. It is named after Allen Hazen and Gardner Stewart
Williams.
This formula is applicable only to the flow of water in pipes larger than 50 mm(2 in.) and
velocities less than 3m/s. This formula was designed for flow in both pipes and open
channels but is more commonly used in pipes.
square both sides and solve for hf
English units: S.I. units:
(S.I. Units)
For circular pipes flowing full, this formula For circular pipes flowing full, this
becomes formula becomes
For non-circular pipes, use D = 4R
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf Major Head Loss, hf
6. Haaland formula. C. Hazen Williams Formula
For circular pipes:
This is an alternate formula for colebrook equation. S.I. units:
and,
Where:
C1 = Hazen Williams coefficient
D = pipe diameter
R = hydraulic radius
S = slope of the energy grade line = hf/L
(S.I. Units)
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Elev. 100
Major Head Loss, hf Problem #2 Problem #4
C. Hazen Williams Formula Determine the (a) shear stress at the walls of a 300mm diameter pipe when water flowing Solution: Elev. 10
causes a head lost of 5m in 90 m pipe length, (b) the shear velocity, and the (c) shear stress at Q = 12 ft3/s = 0.3401 m3/s
Recommended Value of C1 for Hazen Williams Formula 50mm from the centerline of the pipe. D = 4 = 0.333 ft. = 101.6 mm Elev. 0
Solution: n = 0.013
(a) Shear stress at walls: (c) Shear stress 50 mm from
(b) Shear velocity L = 160 feet = 48.78 m
pipe center (c) Pressure in the tank:
(a) Velocity of flow in the pipe:
Energy equation between A and C:
(b) Head lost in pipe:
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Problem #1 Problem #3 Problem #5
Oil having specific gravity of 0.869 and dynamic viscosity of 0.0814 Pa-s flows through a cast Water flow at the rate of 200 lit/sec through 120-m horizontal pipe having a diameter of Determine the fricion factor for flow having a Rynolds number of 5,000 and relative toughess
iron pipe at a velocity of 1m/s. The pipe is 50m long and 150 mm in diameter/ (a) Find the head 300mm. If the pressure difference between the end points is 280 mmHg, determine the friction off ( /d) of 0.015(transition zone) using colebrook formula.
lost due to friction, and (b) the shearing stress at the walls of the pipe. factor. Using Moody Diagram: f 0.05
Solution:
Solution: Solution:
(a) Colebrook formula:
For a horizontal pipe, the head lost between the
points is equal to the difference in pressure head
/d
Solve for f using trial and error:
f = 0.0515
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
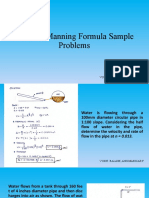
Problem #1 Problem #4 Problem #6
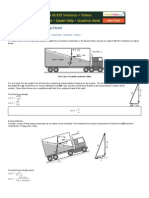
Oil having specific gravity of 0.869 and dynamic viscosity of 0.0814 Pa-s flows through a cast Water flows from a tank through 160 feet of 4 inches diamter Oil of sp.gr. 0.9 and dynamics viscosity = 0.04 Pa-s flows at the rate of 60 liters per second through 50 m of 120
iron pipe at a velocity of 1m/s. The pipe is 50m long and 150 mm in diameter/ (a) Find the head pipe and then discharges into air as shown in the figure. The mm diameter pipe. If the head lost is 6m determine (a) the mean velocity of flow, (b) the type of flow, (c) the
friction factor, f (d) the velocity at the centerline of the pipe, (e) the shear stress at the wall of the pipe and (f) the
lost due to friction, and (b) the shearing stress at the walls of the pipe. flow of water in the pipe is 12 cfs. Assume n = 0.013 and velocity 50mm from the centerline of the pipe.
Solution: neglect minor losses. Determine the following.
(a) The velocity of flow in the ppe in fps. Solution:
(b) (c) Friction factor: (d) Centerline velocity:
(b) The total head lost in the pipe in feet, (a) Mean velocity:
(c) The pressure at the top of the tank in psi.
Solution:
Elev. 100
Q = 12 ft3/s = 0.3401 m3/s
D = 4 = 0.333 ft. = 101.6 mm (b) Type of flow:
n = 0.013
L = 160 feet = 48.78 m Elev. 10
Elev. 0
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Problem #6
Oil of sp.gr. 0.9 and dynamics viscosity = 0.04 Pa-s flows at the rate of 60 liters per second through 50 m of 120
mm diameter pipe. If the head lost is 6m determine (a) the mean velocity of flow, (b) the type of flow, (c) the
friction factor, f (d) the velocity at the centerline of the pipe, (e) the shear stress at the wall of the pipe and (f) the
velocity 50mm from the centerline of the pipe.
Solution:
(e) Shear stress at the wall of the pipe: (f) Velocity at 50mm from the centerline:
Squaring both sides:
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
City of Dasmariñas,Cavite
Thank you for listening
God Bless
VIRTUE EXCELLENCE SERVICE
You might also like
- EVAL 4 pt.1 - XPERTZ CE REVIEWDocument22 pagesEVAL 4 pt.1 - XPERTZ CE REVIEWSteven ValerioNo ratings yet
- Api 598Document2 pagesApi 598Nitin Aggarwal78% (9)
- Reference List For Urea Plants0306Document5 pagesReference List For Urea Plants0306lalitbadheNo ratings yet
- WITH SOLUTIONS Pipe Connection and Three ReservoirDocument46 pagesWITH SOLUTIONS Pipe Connection and Three ReservoirMark PulongbaritNo ratings yet
- MEEN 20052 - Week 2 - Salamat, Andre Agassi D.Document4 pagesMEEN 20052 - Week 2 - Salamat, Andre Agassi D.andreagassiNo ratings yet
- Gis Located Above B)Document10 pagesGis Located Above B)Apple AterradoNo ratings yet
- BernaulliDocument6 pagesBernaulliCamille SemillaNo ratings yet
- Hyd - 7Document2 pagesHyd - 7SamNo ratings yet
- p γ υ z H p γ υ z H: Problem 7Document4 pagesp γ υ z H p γ υ z H: Problem 7Ariel GamboaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids: Sample Problems ADocument3 pagesProperties of Fluids: Sample Problems AFronda Jerome BlasNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 11Document1 pageCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 11Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- WEIRSDocument4 pagesWEIRSJovy AndoNo ratings yet
- Exam in Fluids1Document4 pagesExam in Fluids1Prince Winderic Gaza AclanNo ratings yet
- Head Losses LectureDocument1 pageHead Losses Lecturebang sieNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Rest: Common Liquid PropertiesDocument13 pagesFluid Mechanics Rest: Common Liquid PropertiesJericho Alfred Rullog SapitulaNo ratings yet
- Psad - 2Document25 pagesPsad - 2Mary Ann Toni N. RasonabeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6.1-6.2 Reynolds NumberDocument5 pagesMODULE 6.1-6.2 Reynolds NumberFrancis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 EXERCISE PROBLEMSDocument6 pagesChapter 9 EXERCISE PROBLEMSSAUCEJO. Ferd Anthony C,No ratings yet
- WITH SOLUTIONS Open Channel and Alternate Stages of FlowDocument43 pagesWITH SOLUTIONS Open Channel and Alternate Stages of FlowMark PulongbaritNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Hydrostatic Forces & BuoyancyDocument9 pagesModule 3 Hydrostatic Forces & BuoyancyJuan HeroNo ratings yet
- Math Samples PDFDocument1 pageMath Samples PDFArwin VillegasNo ratings yet
- Permeability Test in The Field by Pumping From WellsDocument16 pagesPermeability Test in The Field by Pumping From WellsGed CudiamatNo ratings yet
- PRELIM EXAM - Docx QuestionnaireDocument1 pagePRELIM EXAM - Docx QuestionnaireLian HebronNo ratings yet
- Given That Length of Pipe1, 2 3: Pipe 1 Length 1800 M: SolutionDocument4 pagesGiven That Length of Pipe1, 2 3: Pipe 1 Length 1800 M: SolutionDiecon Irish ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 First Law-Closed System ProblemsDocument11 pagesUnit 2 First Law-Closed System Problemspiravi66No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 2Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics Lesson 2Harold RondillaNo ratings yet
- BatteryExam MathDocument6 pagesBatteryExam MathjadeNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Fluid Flow Measurement - Pitot Tube and Venturi MeterDocument14 pages2.1 Fluid Flow Measurement - Pitot Tube and Venturi MeterMaria Ysabel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDocument25 pagesLesson 7 - Fundamentals of Fluid FlowJenuine LimonNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 3 DiscussionDocument19 pagesHydraulics 3 DiscussionRaymund PertudoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5.1-5.5 Coefficients To TubesDocument18 pagesMODULE 5.1-5.5 Coefficients To TubesFrancis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - Written ReportDocument7 pagesHydraulics - Written ReportChristian ConsignaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics: Principles of Hydrostatics Pressure or Unit Pressure, PDocument11 pagesFluid Statics: Principles of Hydrostatics Pressure or Unit Pressure, PJustin Paul VallinanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Orifices Weirs and Tubes Practice ProblemsDocument14 pagesChapter Six Orifices Weirs and Tubes Practice ProblemsJerle ParondoNo ratings yet
- PS2Document1 pagePS2ChristianNo ratings yet
- 1st QE Answer Key Plate No. 1Document7 pages1st QE Answer Key Plate No. 1Hubert Jay Fedalino YubatNo ratings yet
- Cee 117 Sim SDL CompleteDocument234 pagesCee 117 Sim SDL CompleteRyan DelicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 Shear DesignDocument14 pagesChapter-7 Shear DesignAngelo RosNo ratings yet
- HF Using Manning Formula Sample Problems: Voice: Balase, Ann Maricar FDocument11 pagesHF Using Manning Formula Sample Problems: Voice: Balase, Ann Maricar FKyohai RinggoNo ratings yet
- Irrigation EngineeringDocument18 pagesIrrigation EngineeringUmar NaveedNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI-Fluid MeasurementDocument75 pagesChapter VI-Fluid MeasurementArah Louise ApostolNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 4Document3 pagesActivity Sheet 4Shiebastian ArietaNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Week 3Document18 pagesData Analysis Week 3Christian John Paul LijayanNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICS TOPIC 1 FLUID PROPERTIES UNIT PRESSURE 23 May 2022Document41 pagesHYDRAULICS TOPIC 1 FLUID PROPERTIES UNIT PRESSURE 23 May 2022samera salihNo ratings yet
- 12 16Document10 pages12 16Aboalmaail AlaminNo ratings yet
- Final Quiz Problems To Be MadeDocument16 pagesFinal Quiz Problems To Be MadeRyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics LectureDocument12 pagesEngineering Mechanics LectureMeverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- A. Force Acting On The Gate:: SolutionDocument3 pagesA. Force Acting On The Gate:: SolutionFiel Ericson SolaresNo ratings yet
- Highway and Railroad Engineering: Reversed CurvesDocument8 pagesHighway and Railroad Engineering: Reversed CurvesDirect XNo ratings yet
- P7 3B Bernardo KathryneDocument4 pagesP7 3B Bernardo KathryneKATHRYNE BERNARDONo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDocument17 pagesTopic 5 Fundamentals of Fluid FlowJohn Rey Galendez LaviñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DamsDocument46 pagesChapter 3 Damsace pedroNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear Translation - Moving Vessel - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument2 pagesRectilinear Translation - Moving Vessel - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument2 pagesFluidsPatrick AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document10 pagesModule 3Niño YbañezNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Hyd 13Document2 pagesHyd 13Luna RonquilloNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow - Bernoulli's Energy TheoremDocument12 pages1.2 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow - Bernoulli's Energy TheoremTeodolfo Delos Trino Balanay100% (1)
- Anghel A Open ChannelsDocument32 pagesAnghel A Open ChannelsJovan Bucol100% (1)
- CharlesDocument5 pagesCharlesreniel fabroNo ratings yet
- Print 3Document2 pagesPrint 3Li ReNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningFrom EverandHandbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- 6.3 Functions: Chapter 6 Functions and LoopsDocument4 pages6.3 Functions: Chapter 6 Functions and LoopsLi ReNo ratings yet
- 14-Scilab FunctionsDocument12 pages14-Scilab FunctionsLi ReNo ratings yet
- 11-2D Animation and Multiple PlotsDocument7 pages11-2D Animation and Multiple PlotsLi ReNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - Technopreneurship - Strategic Information System (W11)Document59 pagesWeek 13 - Technopreneurship - Strategic Information System (W11)Li ReNo ratings yet
- Technopreneurship: Understanding of Marketplace and Customer NeedsDocument55 pagesTechnopreneurship: Understanding of Marketplace and Customer NeedsLi ReNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Technopreneurship - Value PropositionDocument27 pagesWeek 10 - Technopreneurship - Value PropositionLi ReNo ratings yet
- Week 14 - Technopreneurship - Operations Management (W14)Document56 pagesWeek 14 - Technopreneurship - Operations Management (W14)Li Re100% (1)
- Functions and Loops: Programming. It Is The Most Popular Way of Programming Since It Is QuiteDocument7 pagesFunctions and Loops: Programming. It Is The Most Popular Way of Programming Since It Is QuiteLi ReNo ratings yet
- Rizals Travel Timeline in 1887 Bohemia Brunn Vienna Germany Switzerland and ItalyDocument3 pagesRizals Travel Timeline in 1887 Bohemia Brunn Vienna Germany Switzerland and ItalyLi ReNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Measurement (Orifices and Tubes) : Device Coefficient Device CoefficientDocument3 pagesFluid Flow Measurement (Orifices and Tubes) : Device Coefficient Device CoefficientLi ReNo ratings yet
- Loops: Reference: - Sandeep Nagar, Introduction To Scilab For Engineers and ScientistsDocument19 pagesLoops: Reference: - Sandeep Nagar, Introduction To Scilab For Engineers and ScientistsLi ReNo ratings yet
- 10-Special PlotsDocument22 pages10-Special PlotsLi ReNo ratings yet
- Autocad CommandsDocument6 pagesAutocad CommandsLi ReNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Measurement (Other Devices and Unsteady Flow) : Venturi Meter NozzleDocument3 pagesFluid Flow Measurement (Other Devices and Unsteady Flow) : Venturi Meter NozzleLi ReNo ratings yet
- Weirs: Classification of Weirs Definition of TermsDocument4 pagesWeirs: Classification of Weirs Definition of TermsLi ReNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Problems and Pipe NetworksDocument3 pagesReservoir Problems and Pipe NetworksLi ReNo ratings yet
- Non Uniform Flow Open Channel & Hydraulic JumpDocument3 pagesNon Uniform Flow Open Channel & Hydraulic JumpLi ReNo ratings yet
- Print 3Document2 pagesPrint 3Li ReNo ratings yet
- Open Channel: Classification of Open-Channel Flows Classification of Open-Channel FlowsDocument4 pagesOpen Channel: Classification of Open-Channel Flows Classification of Open-Channel FlowsLi ReNo ratings yet
- Baldwin-Hydraulic-Heads CABEÇOTE DE FILTRODocument2 pagesBaldwin-Hydraulic-Heads CABEÇOTE DE FILTROEduardo CramerNo ratings yet
- Water HammerDocument20 pagesWater HammerAJITKp90No ratings yet
- 4) Design of Pumping Machinery - Head CalculationsDocument7 pages4) Design of Pumping Machinery - Head CalculationsNaveen NagisettiNo ratings yet
- YFA48C Safety Valve For Steam - YongyiDocument17 pagesYFA48C Safety Valve For Steam - YongyidanangNo ratings yet
- CIM - 10 PolyhydronDocument2 pagesCIM - 10 PolyhydronJindal HydraulicsNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Centrifugal Pump: Course ProjectDocument16 pagesDesign and Analysis of Centrifugal Pump: Course ProjectJay MahajanNo ratings yet
- Price YutaDocument5 pagesPrice YutaArtlanNo ratings yet
- Api Spec 6D: API - The American Petroleum InstituteDocument3 pagesApi Spec 6D: API - The American Petroleum Institutenrd9771100% (1)
- Chapter 1. INTRODUCTION: 1.0. BackgroundDocument37 pagesChapter 1. INTRODUCTION: 1.0. Backgrounddelta conceptNo ratings yet
- Appendix E Sizing of Water Piping System: (Continued)Document1 pageAppendix E Sizing of Water Piping System: (Continued)MARONo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Institute Standards For Rotodynamic PumpsDocument5 pagesHydraulic Institute Standards For Rotodynamic Pumpseduin100% (1)
- Modul Elektro Pneumatik 1Document26 pagesModul Elektro Pneumatik 1AdhitNo ratings yet
- Masterflex PS Tubing PDFDocument2 pagesMasterflex PS Tubing PDFAnonymous 1oWzM3No ratings yet
- KITZ VLV Install-Operation Trouble Shooting 20151116 PDFDocument44 pagesKITZ VLV Install-Operation Trouble Shooting 20151116 PDFFahmi HaidiNo ratings yet
- Listado de Todos Los Materiales en HanaDocument2,398 pagesListado de Todos Los Materiales en Hanamery ruizNo ratings yet
- BS en 1671Document23 pagesBS en 1671vincze_szilardNo ratings yet
- Needle Valves (MS 01 69) R4Document4 pagesNeedle Valves (MS 01 69) R4herysyam1980No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Symbols: Service Training Manual CM 760/780Document23 pagesHydraulic Symbols: Service Training Manual CM 760/780victor lara100% (1)
- 16 Manometarski Razvodni Ventili 134Document2 pages16 Manometarski Razvodni Ventili 134Dejan DejanovicNo ratings yet
- Safety ValveDocument5 pagesSafety ValvesridharNo ratings yet
- P39 Standard Gas Regulators: Applications SpecificationsDocument4 pagesP39 Standard Gas Regulators: Applications SpecificationsAlexander Charry GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6ADocument22 pagesChapter 6Amaninder_khasria100% (3)
- Compressor GAR 5Document10 pagesCompressor GAR 5moisesNo ratings yet
- Course Introduction:: Advanced Pump TechnologyDocument9 pagesCourse Introduction:: Advanced Pump TechnologyMoucha JustdoitNo ratings yet
- Hydro Calc WebDocument8 pagesHydro Calc WebAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power Units Vertical Mount Fixed DisplacementDocument32 pagesHydraulic Power Units Vertical Mount Fixed DisplacementSujata Roy100% (1)
- Pump CatalogDocument10 pagesPump Cataloggreatwallshipping.indNo ratings yet