Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Example 1.2: Chapter 1 Introduction
Uploaded by
Carlos SaavedraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Example 1.2: Chapter 1 Introduction
Uploaded by
Carlos SaavedraCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Chapter 1 Introduction
A C A C
B D B D
(a) (b)
C D
A B C D
A B
(c) (d)
C D
A
A B
B
Y Y
C
A C
D
B D
(e) (f)
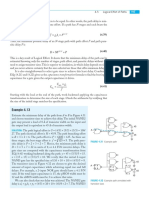
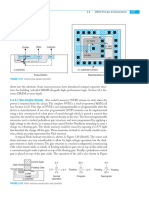
FIGURE 1.18 CMOS compound gate for function Y = (A · B) + (C · D)
This AOI22 gate can be used as a 2-input inverting multiplexer by connecting C = A
as a select signal. Then, Y = B if C is 0, while Y = D if C is 1. Section 1.4.8 shows a way to
improve this multiplexer design.
A
Example 1.2
B Sketch a static CMOS gate computing Y = (A + B + C) · D.
C D
Y SOLUTION: Figure 1.19 shows such an OR-AND-INVERT-3-1 (OAI31) gate. The
D nMOS pull-down network pulls the output low if D is 1 and either A or B or C are 1,
A B C so D is in series with the parallel combination of A, B, and C. The pMOS pull-up net-
work is the conduction complement, so D must be in parallel with the series combina-
FIGURE 1.19 tion of A, B, and C.
CMOS compound gate
for function
Y = (A + B + C) · D 1.4.6 Pass Transistors and Transmission Gates
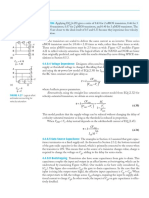
The strength of a signal is measured by how closely it approximates an ideal voltage source.
In general, the stronger a signal, the more current it can source or sink. The power sup-
plies, or rails, (VDD and GND) are the source of the strongest 1s and 0s.
An nMOS transistor is an almost perfect switch when passing a 0 and thus we say it
passes a strong 0. However, the nMOS transistor is imperfect at passing a 1. The high
voltage level is somewhat less than VDD, as will be explained in Section 2.5.4. We say it
passes a degraded or weak 1. A pMOS transistor again has the opposite behavior, passing
strong 1s but degraded 0s. The transistor symbols and behaviors are summarized in Figure
1.20 with g, s, and d indicating gate, source, and drain.
When an nMOS or pMOS is used alone as an imperfect switch, we sometimes call it
a pass transistor. By combining an nMOS and a pMOS transistor in parallel (Figure
1.21(a)), we obtain a switch that turns on when a 1 is applied to g (Figure 1.21(b)) in
which 0s and 1s are both passed in an acceptable fashion (Figure 1.21(c)). We term this a
transmission gate or pass gate. In a circuit where only a 0 or a 1 has to be passed, the appro-
priate transistor (n or p) can be deleted, reverting to a single nMOS or pMOS device.
You might also like
- Sınıflar 2.D.2.Y YazılıDocument2 pagesSınıflar 2.D.2.Y YazılıCihan GöçNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 8: (Electronic Devices)Document7 pagesUnit Test 8: (Electronic Devices)padhi8480No ratings yet
- CAPACITORSDocument34 pagesCAPACITORSshivam bhartiNo ratings yet
- BS8666 2005 WMDocument1 pageBS8666 2005 WMzalzizaNo ratings yet
- Phy JEE Sprint 2019 - SemiConductors PDFDocument15 pagesPhy JEE Sprint 2019 - SemiConductors PDFGaurav SarangiNo ratings yet
- Test 7 - Class 12th 24 09 2022Document9 pagesTest 7 - Class 12th 24 09 2022SabilNo ratings yet
- Indah NHDocument2 pagesIndah NHaiedcellNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: ClassxDocument2 pagesMathematics: ClassxAditya M GuptaNo ratings yet
- 50 Questions For ElectronicsDocument6 pages50 Questions For ElectronicsprateekshivalikNo ratings yet
- 04 GraphicalDocument3 pages04 GraphicalRUSHIKESH ZADENo ratings yet
- OP Answer KEYsDocument5 pagesOP Answer KEYsvenotiw177No ratings yet
- #MOCK JEE Main Practice Test 7 Thermodynamics & Heat TransferDocument5 pages#MOCK JEE Main Practice Test 7 Thermodynamics & Heat TransferApoorv TandonNo ratings yet
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Instrumentation Engineering 2006Document23 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Instrumentation Engineering 2006Meet PatelNo ratings yet
- Advanced - Paper - 2 (Q)Document14 pagesAdvanced - Paper - 2 (Q)Yahoo ManNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Vector: Time: 30 Minutes M. M.: 51Document2 pagesQuiz - Vector: Time: 30 Minutes M. M.: 51AtulNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Assignment - 1: C Q B S A P D R ODocument8 pagesCumulative Assignment - 1: C Q B S A P D R OASHIM GHOSHNo ratings yet
- 11 Math - Chap.12Document1 page11 Math - Chap.12Chauhdary AkashNo ratings yet
- GATE ECE 2003 Actual PaperDocument24 pagesGATE ECE 2003 Actual Paperkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Phy Eng Umeed (Laxman Sir) 3.ODocument52 pagesPhy Eng Umeed (Laxman Sir) 3.Oshivamkumar821101.nNo ratings yet
- Gt-4 PCB: Multiple Correct QuestionsDocument25 pagesGt-4 PCB: Multiple Correct QuestionsrushiNo ratings yet
- Three Phase ConvertersDocument8 pagesThree Phase ConvertersrotluNo ratings yet
- Date Questions 09.10.2016 100Document10 pagesDate Questions 09.10.2016 100Sagar DesaiNo ratings yet
- II Mid Bits For StudentsDocument9 pagesII Mid Bits For StudentsSurya MukeshNo ratings yet
- Maths QuizDocument4 pagesMaths Quiznaman.bahal09No ratings yet
- Chapter6 Ex SolDocument26 pagesChapter6 Ex SolShivani YadavNo ratings yet
- New DLP Answer-Sheet-Template For-All-Assignments 09.08.18Document1 pageNew DLP Answer-Sheet-Template For-All-Assignments 09.08.18PNo ratings yet
- P Xe DX, Is Equal To : Q. No. 1 - 25 Carry One Mark EachDocument17 pagesP Xe DX, Is Equal To : Q. No. 1 - 25 Carry One Mark EachPartha Sarathi MannaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic PDFDocument52 pagesMagnetic PDFdivyanshjoshidpsjkpNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Transformer Delta Star Connection PDFDocument6 pagesThree Phase Transformer Delta Star Connection PDFkaresanikas2004No ratings yet
- Vectors - Question PaperDocument4 pagesVectors - Question PaperCelestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- Gate 2006 PDFDocument16 pagesGate 2006 PDFMahendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Bs8666 ShapesDocument2 pagesBs8666 ShapesMahaveer Janapala50% (2)
- 3A. BS 8666 2005 ShapesDocument2 pages3A. BS 8666 2005 Shapes小月No ratings yet
- NTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Document16 pagesNTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Apex Institute100% (1)
- Power ElectonicsDocument189 pagesPower ElectonicsTUFAN GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Dao's Theorem On Six Circumcenters AssociatedDocument4 pagesDao's Theorem On Six Circumcenters AssociatedNam Vu PhươngNo ratings yet
- Ufe Fseu C6 CGUam 3 K Ta X9Document16 pagesUfe Fseu C6 CGUam 3 K Ta X9Gingka HaganeNo ratings yet
- F Hours: KF) - (I) (Ii)Document2 pagesF Hours: KF) - (I) (Ii)Nayinala Satya KiranNo ratings yet
- MA1511 Cheat Sheet V1.3 3Document2 pagesMA1511 Cheat Sheet V1.3 3AlfrescoNo ratings yet
- Rev B - Neet - Aipmt-Physics-30years Chapterwise SolutionsDocument2 pagesRev B - Neet - Aipmt-Physics-30years Chapterwise SolutionsPankaj Mishra0% (1)
- GATE ECE 2004 Actual PaperDocument24 pagesGATE ECE 2004 Actual Paperkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Constraint SolvingDocument30 pagesGeometric Constraint Solvingmszlazak4179No ratings yet
- Vectors PDFDocument3 pagesVectors PDFtrannyNo ratings yet
- Analog 2018Document3 pagesAnalog 2018Aparajita NathNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structures - Lecture 28, 29Document24 pagesDiscrete Structures - Lecture 28, 29Aman WastiNo ratings yet
- Solution Ee Set C 2018Document16 pagesSolution Ee Set C 2018Dharmender KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Full Test) Mains - Paper 1Document7 pagesChemistry (Full Test) Mains - Paper 1Ravi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engg 2013Document16 pagesElectrical Engg 2013Srimannarayana NandamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engg 2013Document16 pagesElectrical Engg 2013JADDUNo ratings yet
- 10 Jan 2019 Shift 1 English PhysicsDocument11 pages10 Jan 2019 Shift 1 English PhysicsShobhit KumarNo ratings yet
- Paper Urdu 12Document3 pagesPaper Urdu 12AdilNo ratings yet
- 43-th Math Paper 2nd FinalDocument5 pages43-th Math Paper 2nd FinalOjasNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument5 pagesQuestion BankDhaya VNo ratings yet
- 6 JSG4 P Ss WT KN AWJh Eq 68Document22 pages6 JSG4 P Ss WT KN AWJh Eq 68Gingka HaganeNo ratings yet
- 1682585215Document22 pages1682585215asmaa.khaledmhammed789No ratings yet
- Ad 1Document138 pagesAd 1Simran Jeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Lect1 Ccts and LayoutDocument43 pagesLect1 Ccts and LayoutJonitha KruthikaNo ratings yet
- Basic Matrix Analysis and Synthesis: With Applications to Electronic EngineeringFrom EverandBasic Matrix Analysis and Synthesis: With Applications to Electronic EngineeringNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 192Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 192Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 4.4.6.4 Voltage Dependence: Chapter 4 DelayDocument1 page4.4.6.4 Voltage Dependence: Chapter 4 DelayCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls and Fallacies: Targeting A Bleeding-Edge ProcessDocument1 pagePitfalls and Fallacies: Targeting A Bleeding-Edge ProcessCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 191Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 191Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Cmos Vlsi Design 198Document1 pageCmos Vlsi Design 198Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Logical Effort of Paths: A and C Begin To Rise (Figure 4.28 (C) ) - at First, Both Nodes See ApproximatelyDocument1 pageLogical Effort of Paths: A and C Begin To Rise (Figure 4.28 (C) ) - at First, Both Nodes See ApproximatelyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Cmos Vlsi Design 162Document1 pageCmos Vlsi Design 162Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Circuit Elements: 3.4.3.1 CapacitorsDocument1 pageCircuit Elements: 3.4.3.1 CapacitorsCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Cmos Vlsi Design 149Document1 pageCmos Vlsi Design 149Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Circuit Extraction: CONNECT Layer1 Layer2Document1 pageCircuit Extraction: CONNECT Layer1 Layer2Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 140Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 140Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Issues: Antenna RulesDocument1 pageManufacturing Issues: Antenna RulesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Layer Density Rules: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 pageLayer Density Rules: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CMOS Processing Technology: 3.4.3.4 Transmission LinesDocument1 pageChapter 3 CMOS Processing Technology: 3.4.3.4 Transmission LinesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4.3.7 Non-Volatile Memory: P+ Diode N+ Well Contact Collector Base EmitterDocument1 page3.4.3.7 Non-Volatile Memory: P+ Diode N+ Well Contact Collector Base EmitterCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- MOSIS Scalable CMOS Design RulesDocument1 pageMOSIS Scalable CMOS Design RulesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.2 Silicon On Insulator: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 page3.4.1.2 Silicon On Insulator: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4 CMOS Process Enhancements: 3.4.3.3 InductorsDocument1 page3.4 CMOS Process Enhancements: 3.4.3.3 InductorsCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.5 Plastic Transistors: InterconnectDocument1 page3.4.1.5 Plastic Transistors: InterconnectCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Micron Design Rules: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 pageMicron Design Rules: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS Process Enhancements: Layer Rule Description 65 NM Rule (M) TABLE 3.1Document1 pageCMOS Process Enhancements: Layer Rule Description 65 NM Rule (M) TABLE 3.1Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.4 Higher Mobility: High-K Gate Stack TEM (© IEEE 2007.)Document1 page3.4.1.4 Higher Mobility: High-K Gate Stack TEM (© IEEE 2007.)Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Silicon Dioxide (Sio) : Well-Edge Proximity EffectDocument1 pageSilicon Dioxide (Sio) : Well-Edge Proximity EffectCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Mask Summary: The Masks Encountered For Well Specification May Include N-WellDocument1 pageMask Summary: The Masks Encountered For Well Specification May Include N-WellCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Mask Summary: The Only Mask Involved With Contacts To Active or PolyDocument1 pageMask Summary: The Only Mask Involved With Contacts To Active or PolyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CMOS Processing Technology: PassivationDocument1 pageChapter 3 CMOS Processing Technology: PassivationCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Gate Oxide: 3.2 CMOS TechnologiesDocument1 pageGate Oxide: 3.2 CMOS TechnologiesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Gate and Source/Drain Formations: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 pageGate and Source/Drain Formations: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 138Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 138Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Isolation: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 pageIsolation: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- List of Documents: ZPMC FOR Ceres Terminal AmsterdamDocument17 pagesList of Documents: ZPMC FOR Ceres Terminal AmsterdamAdan Rodríguez SoaresNo ratings yet
- Specification of TokensDocument17 pagesSpecification of TokensSMARTELLIGENT0% (1)
- KIPWindows Driver GuideDocument36 pagesKIPWindows Driver GuidePBTS CORPNo ratings yet
- Technical Data - Trendsetter FamilyDocument7 pagesTechnical Data - Trendsetter FamilyRogerio FerracinNo ratings yet
- 200 Indiabix IT Question - M A Latif LimonDocument17 pages200 Indiabix IT Question - M A Latif LimonMohammodMosaddakShovonNo ratings yet
- BmbbhaaevvvjusbstdDocument1 pageBmbbhaaevvvjusbstdbmbbhaaevvvjusbstdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Introduction To The Management of Information SecurityDocument12 pagesChapter 01 Introduction To The Management of Information Securityغسان الشليف100% (1)
- Oracle Implementing Goal ManagementDocument68 pagesOracle Implementing Goal ManagementamrsihNo ratings yet
- MS-SSIS Lab Material: Select FromDocument6 pagesMS-SSIS Lab Material: Select FromachudharamNo ratings yet
- By Sachin Vasantrao Inkane PGT, AECS, IndoreDocument13 pagesBy Sachin Vasantrao Inkane PGT, AECS, IndoreErnie AcunaNo ratings yet
- PD ChecklistDocument6 pagesPD Checklistsat100% (1)
- A Multidimensional Performance Model For Consolidating Balanced ScorecardDocument11 pagesA Multidimensional Performance Model For Consolidating Balanced ScorecardTiago100% (1)
- My Script of Title Defense - EditedDocument3 pagesMy Script of Title Defense - EditedNoor Alam Abir 181-15-933No ratings yet
- Cimon XpanelDesigner User ManualDocument377 pagesCimon XpanelDesigner User ManualJuan LuisNo ratings yet
- BaocaovxlDocument8 pagesBaocaovxlNAMNo ratings yet
- Advance Steel and Robot Structural AnalysisDocument18 pagesAdvance Steel and Robot Structural AnalysisSibil DavidNo ratings yet
- Wolfdale1333-D667 multiQIGDocument97 pagesWolfdale1333-D667 multiQIGJorge LaglaiveNo ratings yet
- Cloaking Training - FacebookDocument8 pagesCloaking Training - FacebookGabriel SantosNo ratings yet
- Halstead's Software MetricsDocument7 pagesHalstead's Software MetricsLokdeep SalujaNo ratings yet
- 5G Basic Architecture and Log AnalysisDocument20 pages5G Basic Architecture and Log AnalysisAvinash sanasNo ratings yet
- JIRA Dumps - Merged FullDocument28 pagesJIRA Dumps - Merged FullVijay KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Multi Camera Adapter Module V2.2 User Guide: Rev 1.0 Nov. 2019Document7 pagesRaspberry Pi Multi Camera Adapter Module V2.2 User Guide: Rev 1.0 Nov. 2019Brayan Boyer ZuritaNo ratings yet
- IT8075-Software Project ManagementDocument10 pagesIT8075-Software Project ManagementHarishwaran R VNo ratings yet
- Textbook CatalogDocument24 pagesTextbook CatalogOney David Correa ZapataNo ratings yet
- (Ebook - Asp - Net) Introducing ASP - NET 2.0 PDFDocument446 pages(Ebook - Asp - Net) Introducing ASP - NET 2.0 PDFVales RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Sony Chassis Ae5 PDFDocument94 pagesSony Chassis Ae5 PDFadhrianneNo ratings yet
- Asitrade 2Document53 pagesAsitrade 2eduardoNo ratings yet
- Implementing Infrastructure As A Code Using Terraform: Case StudyDocument4 pagesImplementing Infrastructure As A Code Using Terraform: Case StudyMax Lee100% (1)
- Synopsis of Library Management SystemDocument26 pagesSynopsis of Library Management SystemSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- TX Notary Business-Startup (SOS)Document29 pagesTX Notary Business-Startup (SOS)Ebony Pollard100% (1)