Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Arts
Uploaded by
Shaira Mica Sanita0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Introduction to Arts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views4 pagesIntroduction To Arts
Uploaded by
Shaira Mica SanitaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
HUMATIES: Introduction to the Arts
FUNCTIONS of the Arts
HUMANITIES 1. Physical Functions
• Humanities came from the word HUMANUS which means to be truly Utility
human. Instructional
• To be truly human is to be culturally enhanced and refined. Historical
• Culture comes from Latin Cultus-Colere, which means to cultivate. Representational
• Culture is the general way of life of a human society. 2. Social Functions
Influential Media
Historical Development of Humanities Interaction(communication)
• MEDIEVAL Period – anything that pertains to man’s cultivation of his 3. Psychological Functions
spirituality. Inspirational
• RENAISSANCE – set of disciplines being taught at the universities.
Relaxation
• MODERN – is equal to ARTS.
Gratification
Art Derivation…
PURPOSES of the Arts
- Aryan root “AR” meaning “join” or “put together”.
1. Arts have moral, educational, social, cultural, and religious purposes
- From this ancient etymon, two Greek verbs are derived:
2. Art for art’s sake
Artizein – to prepare
3. Moments of relaxation
Arkiskein – to put together
4. Imagination is satisfied
- Latin derivation- “ars, artis”- everything artificially made or composed
5. Arts as outlet of our slumbering passions
by man.
6. Powerful means to reform man.
Two Kinds of Man’s Actions
Division of Arts
• There are actions to be done- in relation to man’s ultimate destiny and
1. With respect to purpose:
moral obligations.
Practical arts- directed to produce artifacts and utensils
• There are actions to be made- in relation to man’s practical needs.
which cope with human needs like basket
What an Art is…. Liberal arts-intellectual efforts are considered; take for the case
• Art is the subjective expressions of man’s thought and feelings of AB Course
• Agent: man Fine arts- produce to the human creativity in so far as they
• Importance: expression is an integral part of human being express beauty in different ways and different media like
drawing
Arts vs. Craft Major arts- characterized by their actual and potential
• Art is for appreciation expressiveness like music
• Craft is for utilization Minor arts- connected with the practical uses and purposes like
• Combination: Functional Art interior design
3. PERFORMING ARTS
2. With respect to media and form The performing arts include all forms of art that use the human
Plastic arts- perceived by sense of sight like painting body, face and presence as media
Phonetic arts- based on sounds and words like music 4. DECORATIVE ARTS
Kinetic arts- rhythmic movement like the different kinds of This group of arts deals with the creation of ornamental and
dances functional works using diverse materials like ceramic, wood,
Pure arts- which take only one medium of expression, like color glass, metal, textile etc
in painting. 5. POPULAR ARTS
Mixed Arts – two or more media like opera is a combination of This group of art comprises all forms of popular culture. Pop
music, poetry, and drama culture is the totality of ideas, perspective, attitudes, images and
other phenomena that showcases what is trendy, well-liked, and
Classification of Arts prevalent
1. Space arts- visual arts
2 dimensional(see only in one angle) Hierarchy of Arts
Painting • Immanuel Kant: Music is the lowest of all arts because it gives only
Printing sensible pleasure
Photography • Arthur Schopenhauer: Music is the greatest because is capable of
Drawing/sketching freeing man from his fears and desire
• George Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel: Poetry has the best qualities like
3 dimensional (see in several angles)
immediate perception, creative imagination, development of thoughts
Sculpture
and events.
Architecture
• Gottfried Leibnitz: The Fusion of poetry and music is the highest art
2. Time arts – auditory arts
Music
Origin of the Arts
Dance
• The dance was probably the first art cultivated by man.
combination: Musical Theater/ opera • Music and poetry accompanied dance performances.
• Some scholars also traced the origin of painting and sculpture to dance
GROUPING THE ARTS as seen in many caves of the Neolithic Period where in numerous
1. SPATIAL (VISUAL) ARTS charcoals and color designs of women dancing around idols or men.
These are types of arts that can be perceived by the sense of
• Other authors believe that the origin of these arts is connected with
sight and can be projected into 3-dimensional graphical forms.
sorcery and magic or their superstitious beliefs.
They are primarily visual in nature.
• Religion and superstition , therefore, are the two factors which greatly
which greatly influenced the origin and evolution of arts.
2. LITERARY ARTS (LITERATURE)
What an Art is according to…
Etymologically, it came from the Latin word “ litterae “, which
1. Plato Art imitates nature. Art imitates life.
means letters.
2. Aristotle Art imitates men and nature in action
3. Oscar Wilde, Irish Author(The Importance of Being Earnest) Where does beauty lie?
It is life that imitates art. • Beauty is out there; it is objective. It is a primary quality that resides
4. Henri-Louis Bergson (Noble Prize in Literature, 1927) It is not reason in the object.
that enables us to imitate; art is not imitation; art is made from intuition. • Beauty is not there. It is a secondary quality that resides in the
5. G.E Moore Art is both imitation and intuition perceiver. (John Locke)
6. Sigmund Freud, Austrian Psychiatrist Art is a wish-fulfillment; an • Beauty is neither primary nor secondary; it is tertiary in nature. It
excellent work of art results from frustration depends on the appropriate situational perspective
7. Jose Ortega Y Gasset, Spanish Philosopher
Art is a form of escape; escape from human negative elements Is everything in nature and art beautiful? Why certain things are called
8. Leo Tolstoy, Russian Novelist “ugly” ?
Art is communication; it infects our feelings Everything in nature and art is beautiful for everything is created
9. Benedetto Croce, Italian writer perfect according to its nature and form. All things are beautiful and
Art is merely an expression regardless if it is understood or not perfect in themselves, but not in relation to us. The reasons ?
10. Albert Camus; French Philosopher and writer - Objects which we see every day lose their significance to us. People
Art is rebellion who have in the Banawe
11. John Dewey, American Philosopher Rice Terraces for a long time will not see beauty of their mountains as in the
Art is not limited in the gallery and museum eyes of a tourist.
12. Dante Leoncini - Certain things are dangerous to our lives like snakes, and other wild
When man beautifies himself, he becomes a human art animals.
13. Margarette Macdonald’s Art is esoteric. It is mysterious. It is indefinable. - Certain conditions in human life such as poverty and disease are
It is only describable. referred to as ugly but once painted in a novel, they become meaningful and
beautiful.
Is art an Imitation or a Creation?
• Art tends not simply to imitate, but to express nature with clarity and Categories of Beautiful
meaning. Arts therefore, is not mere copying of things and nature, but 1. The Sublime
a creative activity. enjoyment is aroused by astonishment and awe, like looking at
• Are there any criteria to determine the excellence of the works of art? the starry heavens, the majesty of mountain ranges, the heroic
• Art depends on individual feelings and opinions; tastes are relative acts of heroes and saints.
and personal. It may vary according to different periods and culture.
• How do we form good standards for art appreciation and judgment?
• Successive EXPERIENCES reveal to us the insight of beauty and the
meaning of art. 2. The Nice
enjoyment is aroused by sympathy, love, benevolence,
When do we say an art is BEAUTIFUL? tenderness and modesty like children, flowers , flower
• Beautiful is that which a source of pleasure. Thus, if an art is the reason arrangement, artifacts.
of our pleasure, it is then really beautiful. 3. The Comic
enjoyment because it makes us laugh like satire and irony, the 2. Non-representational- has no definite subjects, only ideas attached.
exaggerated, the repetitious, the ridiculous, and the playful. Product of imagination
The Role of Art Criticism Sources of Art Subjects
• Criticism is a method of verifying or testing artistic works. It is a 1. Mythology- one of the richest source of arts subjects
technique to stimulate the understanding of art and to develop artistic 2. Heroes and Patriots
sensibility. 3. Religion
4. Nature
OBJECTIVITY OF ART a. persons
If the appreciation of arts is subjective, can it be somehow objective? b. animals
YES, it can be objective as well. C. inanimate objects
5. Rural and Urban ecology
1. Through critical study of the properties of beauty
Order
Proportion
Clarity
Unity
Balance
Dominance
2. Through the general consensus of the experts .
3. The final arbiter in the judgment of the works of arts is TIME. Good art
last long, if not immortal. Bad art is ephemeral and transitory.
4. Get rid of our prejudices and personal sentiments.
Art: Subjects, Medium and Technique
• Subject- the object matter
• Medium- materials and equipments that the artist utilizes in his
expression
• Technique- the manner in which the artist utilizes his medium
Art Subjects (person, scene or event)
1. Representational- has definite subjects.
- Natural (from nature)
- Conventional (man-made)
You might also like
- Renaissance ArtDocument42 pagesRenaissance Artapi-269480354No ratings yet
- The Essential Nature of Art and Its Social ImportanceDocument16 pagesThe Essential Nature of Art and Its Social ImportanceGilda Keziah TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Elements and Principles of DesignDocument53 pagesLesson 6 - Elements and Principles of DesignJerick FernandezNo ratings yet
- Understanding the General View of ArtDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the General View of ArtReginabel AnsilNo ratings yet
- BalanceDocument7 pagesBalanceapi-180230978No ratings yet
- Art Appreciation 1Document15 pagesArt Appreciation 1ryan panerejen100% (1)
- Subject and Content of Art Dan JustineDocument18 pagesSubject and Content of Art Dan JustineRaymundo CanizaresNo ratings yet
- One Point Perspective Drawing WorksheetDocument7 pagesOne Point Perspective Drawing WorksheetLadunca MihaiNo ratings yet
- METHODS OF PRESENTING ARTDocument65 pagesMETHODS OF PRESENTING ARTBpNo ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of ArtDocument100 pagesElements and Principles of ArtBea SeloterioNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument24 pagesArt AppreciationRajz UyNo ratings yet
- Styles of ArtDocument30 pagesStyles of ArtCyra Jane DianaNo ratings yet
- ELEMENTS AND PRINCIPLES OF VISUAL ARTDocument14 pagesELEMENTS AND PRINCIPLES OF VISUAL ARTEllain CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Subject of ArtDocument41 pagesSubject of ArtThal ThalNo ratings yet
- The Movement of People Assessment TaskDocument2 pagesThe Movement of People Assessment Taskapi-420688546No ratings yet
- Van Gogh's Mental Health & Starry NightDocument37 pagesVan Gogh's Mental Health & Starry NightsebastianNo ratings yet
- Vincent Van GoghDocument17 pagesVincent Van GoghRafa BelliniNo ratings yet
- Mona Lisa AnalysisDocument5 pagesMona Lisa AnalysisWan Ahmad Iman ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- The elements of visual artsDocument30 pagesThe elements of visual artsAbigail Faye RoxasNo ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection PuzzleDocument29 pagesOrthographic Projection PuzzleCharlon MamacosNo ratings yet
- 6 - Art CriticismDocument19 pages6 - Art CriticismGenesis Maylar David100% (2)
- The Starry NightDocument3 pagesThe Starry Nightapi-297082627No ratings yet
- Act.2 - Art of Emerging EuropeDocument10 pagesAct.2 - Art of Emerging EuropeRafael Lopez CargoNo ratings yet
- Medium of Arts PDFDocument47 pagesMedium of Arts PDFJessadel Capirol CapinNo ratings yet
- What Is Abstract ArtDocument36 pagesWhat Is Abstract ArtAldren Pagui-en BonaobraNo ratings yet
- Roland Barthes-Rhetoric of The ImageDocument11 pagesRoland Barthes-Rhetoric of The Images_arioglu100% (2)
- ImpressionismDocument1 pageImpressionismapi-286865403No ratings yet
- Art Criticism and Formal Analysis OutlineDocument6 pagesArt Criticism and Formal Analysis Outlineapi-212612789No ratings yet
- LESSON 2.1 - Methods of Pressenting Arts Subjects PDFDocument39 pagesLESSON 2.1 - Methods of Pressenting Arts Subjects PDFChena Berna RolloNo ratings yet
- Gec 006 ReviewerDocument6 pagesGec 006 ReviewerLEARSI ISRAELNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation Lesson 5Document66 pagesArt Appreciation Lesson 5Khrystinne Jem RoseteNo ratings yet
- Print MakingDocument4 pagesPrint MakingHon Su SeanNo ratings yet
- What is PaintingDocument49 pagesWhat is PaintingLeire JacutanNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Fixtures: Alcala Dalit Jose Sangco Sacbibit ARC183Document34 pagesPlumbing Fixtures: Alcala Dalit Jose Sangco Sacbibit ARC183Nicole Steve Callo SacbibitNo ratings yet
- Design Theory, Gestalt and CompositionDocument231 pagesDesign Theory, Gestalt and CompositionJojomay2100% (1)
- Abstract ArtDocument9 pagesAbstract Artapi-193496952No ratings yet
- ArtCriticism V20 N01 PDFDocument108 pagesArtCriticism V20 N01 PDFsamilorNo ratings yet
- SurrealismDocument3 pagesSurrealismapi-340026463No ratings yet
- Visual Arts Explained-Aidan ObrienDocument44 pagesVisual Arts Explained-Aidan Obrienapi-267019518No ratings yet
- The Principles of DesignDocument5 pagesThe Principles of DesignSubhod KotianNo ratings yet
- Teaching Short Stories in the ClassroomDocument10 pagesTeaching Short Stories in the ClassroomNoor AzielaNo ratings yet
- Linear and Aerial PerspectiveDocument8 pagesLinear and Aerial PerspectiveAbdul Ghafoor BhattiNo ratings yet
- Semiotic AnalysisDocument20 pagesSemiotic AnalysisRAAM100% (1)
- 7 ColorsDocument39 pages7 Colorspratima1823100% (1)
- 305lesson Plan Format 1Document10 pages305lesson Plan Format 1api-655554957No ratings yet
- MEDIUMDocument37 pagesMEDIUMXXXNo ratings yet
- Elements of Art GuideDocument4 pagesElements of Art GuideKaryl AarientosNo ratings yet
- Methods of Presenting The Art SubjectsDocument40 pagesMethods of Presenting The Art SubjectsLeo OydaNo ratings yet
- Mona LisaDocument8 pagesMona LisaSindoori NaguleswaranNo ratings yet
- Design Elements and Principles ExplainedDocument50 pagesDesign Elements and Principles ExplainedJaivikas ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Teacher's guide evaluates OBTL approach in solid mensurationDocument10 pagesTeacher's guide evaluates OBTL approach in solid mensurationChris Paul Pre100% (1)
- What Does Art MeanDocument3 pagesWhat Does Art MeanMohsin AzizNo ratings yet
- Impressionism 1Document35 pagesImpressionism 1joeric1No ratings yet
- LP - Warm and Cool ColoursDocument3 pagesLP - Warm and Cool Coloursapi-450688909No ratings yet
- Expressionism Movement Guide: Distorted Forms, Bold Colors, Emotional ForceDocument24 pagesExpressionism Movement Guide: Distorted Forms, Bold Colors, Emotional ForceGäbrïèl LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument4 pagesArt AppreciationBianca SophiaNo ratings yet
- Art AppDocument14 pagesArt AppRijohnna Moreen RamosNo ratings yet
- Hum 1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesHum 1 ReviewerAlyssa Mae MendozaNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument8 pagesArt Appreciationgayle limusNo ratings yet
- MASECO ReportingDocument24 pagesMASECO ReportingShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- 11 Sunday: Ordinary TimeDocument188 pages11 Sunday: Ordinary TimeShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Ais 2 Act 2Document1 pageAis 2 Act 2Shaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Chalice-Ariel Cruets - Jay-Allen Lavabo/Towel - Perlita-Ailyn Ciborium - Jaspher Water - LhynDocument1 pageChalice-Ariel Cruets - Jay-Allen Lavabo/Towel - Perlita-Ailyn Ciborium - Jaspher Water - LhynShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Sanita, Shaira Micav V.Document1 pageSanita, Shaira Micav V.Shaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Marley CompanyDocument13 pagesMarley CompanyShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Brunei Darussalam: An Overview of the Geography, Culture, and Legal SystemDocument3 pagesBrunei Darussalam: An Overview of the Geography, Culture, and Legal SystemShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- DaisyDocument1 pageDaisyShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document1 pageActivity 3Shaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Sculpture and Photography: Reporter: Sanita, Shaira Mica, V.-BSA 2ADocument57 pagesSculpture and Photography: Reporter: Sanita, Shaira Mica, V.-BSA 2AShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document1 pageActivity 3Shaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Sanita, Shaira Mica, V.Document1 pageSanita, Shaira Mica, V.Shaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Ais 2 Act 2Document1 pageAis 2 Act 2Shaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Sanita, Shaira Mica, V.Document1 pageSanita, Shaira Mica, V.Shaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Stone Carving Is An Activity Where Pieces of Rough Natural Stone Are Shaped byDocument4 pagesStone Carving Is An Activity Where Pieces of Rough Natural Stone Are Shaped byShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ArtsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To ArtsShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
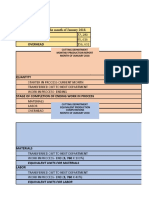
- Materials Labor Overhead: Equivalent Units For MaterialsDocument25 pagesMaterials Labor Overhead: Equivalent Units For MaterialsShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Cost Production Report AnalysisDocument33 pagesCost Production Report AnalysisShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet for Unadjusted and Adjusted Trial BalancesDocument2 pagesWorksheet for Unadjusted and Adjusted Trial BalancesShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Cost Production Report AnalysisDocument33 pagesCost Production Report AnalysisShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Stone Carving Is An Activity Where Pieces of Rough Natural Stone Are Shaped byDocument4 pagesStone Carving Is An Activity Where Pieces of Rough Natural Stone Are Shaped byShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Process CostingDocument2 pagesProcess CostingShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle ProblemDocument2 pagesAccounting Cycle ProblemShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- F Unadjusted Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Statement of IncomeDocument1 pageF Unadjusted Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Statement of IncomeShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- Acct TutorDocument22 pagesAcct TutorKthln Mntlla100% (1)
- F Unadjusted Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Statement of IncomeDocument1 pageF Unadjusted Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Statement of IncomeShaira Mica SanitaNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument1 pageAccountingRajashekar ReddyNo ratings yet
- REFLECTIONDocument6 pagesREFLECTIONjericho azul100% (1)
- Wiliam (2018) - Chapter 5 (Providing Feedback That Moves Learning Forward)Document32 pagesWiliam (2018) - Chapter 5 (Providing Feedback That Moves Learning Forward)JalNo ratings yet
- The Self Various PerspectiveDocument68 pagesThe Self Various PerspectiveKristine Anne IgotNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument43 pagesAnxietyام محمد القحطانيNo ratings yet
- Carrom BasicsDocument3 pagesCarrom Basicssurefooted10% (1)
- 50 Books To Read in 2024 To Master 5 SkillsDocument6 pages50 Books To Read in 2024 To Master 5 SkillsAvina NigNo ratings yet
- Educational Implication of Individual DifferencesDocument4 pagesEducational Implication of Individual DifferencesShiera GannabanNo ratings yet
- The Belle ȂmeDocument4 pagesThe Belle Ȃmesei gosaNo ratings yet
- Types and Importance of CommunicationDocument32 pagesTypes and Importance of CommunicationzameerNo ratings yet
- Background Music and TV Screens Should Be Banned in Public PlacesDocument2 pagesBackground Music and TV Screens Should Be Banned in Public PlacesFelipe GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Work ImmersionDocument2 pagesWork Immersioncharmsonin12No ratings yet
- TVL LAS Practical Research 1 1Document4 pagesTVL LAS Practical Research 1 1Erika Joyce ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Communication: (Verbal and Non Verbal)Document18 pagesCommunication: (Verbal and Non Verbal)Dr. Honeylou Az. OpondaNo ratings yet
- Client Attachment To TherapistDocument11 pagesClient Attachment To Therapistjherrero22100% (2)
- Jalen Rose GDocument26 pagesJalen Rose GkloNo ratings yet
- Asperger's Syndrome in AdulthoodDocument7 pagesAsperger's Syndrome in AdulthoodWillyOaksNo ratings yet
- FS002 - Module 1.1 - 1.2Document7 pagesFS002 - Module 1.1 - 1.2Devine Erika S. Vitasa100% (6)
- Management - Repor On Rondell DataDocument7 pagesManagement - Repor On Rondell DataHaji AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Final YLTC Project LP 3Document15 pagesFinal YLTC Project LP 3KeonKNo ratings yet
- Final PaperDocument38 pagesFinal PaperYoj EisNo ratings yet
- Proverbs 29:18a: Corporate Social Responsibility and Good Governance Second EditionDocument8 pagesProverbs 29:18a: Corporate Social Responsibility and Good Governance Second EditionLouelie Jean AlfornonNo ratings yet
- 03 Dessler - HRM12e - PPT - 03Document54 pages03 Dessler - HRM12e - PPT - 03Brian GiriNo ratings yet
- RPP Pendidikan Kependudukan SDDocument29 pagesRPP Pendidikan Kependudukan SDerianNo ratings yet
- Project Problem Based Learning Grp. 5Document44 pagesProject Problem Based Learning Grp. 5LaarnieNo ratings yet
- Jaspers Resume 4Document1 pageJaspers Resume 4api-531828040No ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence and COUNSELOR TRAINEES' SELF DEVELOPMENTDocument9 pagesThe Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence and COUNSELOR TRAINEES' SELF DEVELOPMENTTan Li LiNo ratings yet
- Engaging English Lesson on Outwitting a CrocodileDocument5 pagesEngaging English Lesson on Outwitting a Crocodileandres corpuzNo ratings yet
- ARCH 400 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesARCH 400 Lecture Notesrida.haider2002No ratings yet
- Rogers Gloria Interview AnalysisDocument8 pagesRogers Gloria Interview AnalysisJon100% (1)
- Understanding Older Adults' Wellbeing From A Philosophical PerspectiveDocument39 pagesUnderstanding Older Adults' Wellbeing From A Philosophical PerspectiveNESLİHAN ORALNo ratings yet