Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Acute Appendicitis
Uploaded by
Jane Arian Berzabal100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
6K views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
6K views2 pagesNCP Acute Appendicitis
Uploaded by
Jane Arian BerzabalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Berzabal, Jane Arian I.
NCA2-III Acute Appendicitis June 25, 2021
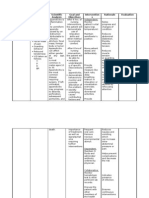
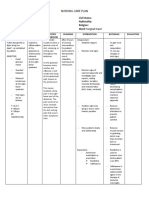
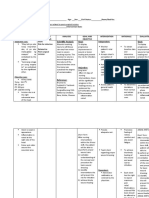
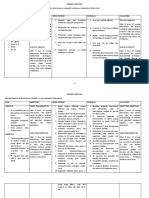
Assessment Explanation of the Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Problem
Short Term: Independent: Short Term:
Subjective:
The creation of surgical Within 8 hours of Monitor vital signs, Fever and pain The goal was met, within
- incision during nursing intervention, the onset of fever with indicate inflammatory 8 hours of nursing
appendectomy disrupts the patient will be able to chills, and pain. responses, which intervention, the patient was
skin integrity of the skin and verbalize and understand contribute to able to verbalize and
Objective: its protective function. the causative/risk factor for infection. understand the causative
Exposure of deep body the infection. and risk factor for the
incised skin @ right tissues to the pathogens in Note risk factors for To evaluate infection.
lower quadrant the environment places the occurrence of presence of infection.
Incision pain patient at risk for infection of infection.
the surgical site, a potentially
threatening complication. Strict compliance to To establish
hospital control mechanism to Long Term:
Factors related to the sterilization and prevent occurrence
surgical procedure include Long Term:
aseptic policies. of infection. The goal was met, after
the method of preoperative After 3 days of nursing
skin preparation, surgical 3 days of nursing
Nursing Diagnosis intervention, the patient will Instruct good hand Reduces the risk for intervention, the patient was
attire of the team, method of be able to achieve timely washing and aseptic infection or cross able to achieved timely
sterile draping, duration of wound healing and be free
Risk for infection related to wound care. contamination of wound healing and free of
surgery and length of of purulent drainage or
surgical incision at right bacteria. purulent drainage or
procedure. erythema.
lower quadrant of the erythema.
abdomen. Inspect incision site. Provides early
Note characteristics detection of infection
Reference: of drainage from process, and
wound. presence of
Hinkle J.L. Cheever K.H. discharges may help
(2017) Brunner an Suddath’s to identify whether
textbook of Medical Surgical there is an infection.
Nursing, Wolters Kluwer,
New York. US. Change wound To reduce existing
dressing as risk factors.
indicated, using
proper technique for
changing/ disposing
of contaminated
materials.
Dependent:
Administer
antibacterial To prevent spreading
medication as of bacteria
ordered.
Educative:
Encourage intake of
fluid and food that is Promotes healing
rich in Vitamin C. and prevents
dehydration.
Reference:
Herdan, H.T., (2020)
NANDA International
Nursing Diagnosis:
Definitions and
Classifications 2018-2020
11th Edition.
You might also like
- NCP AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP Appendicitisdon-timothy-abenojar-795686% (7)
- NCP (Appendicitis)Document3 pagesNCP (Appendicitis)Jenny Ajoc100% (1)
- NCP AppendicitisDocument8 pagesNCP AppendicitisAaron_Kim_Vela_4636No ratings yet
- NCP-S/P AppendectomyDocument6 pagesNCP-S/P Appendectomytinatin989100% (7)
- NCP AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP Appendicitismnms0708100% (2)
- NCP Appendicitis Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Appendicitis Acute PainMelDred Cajes Bolando33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Appendicitisderic95% (57)
- Nursing Care for Post-Appendectomy PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care for Post-Appendectomy PainChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For AppendicitisMarife Lipana Reyes80% (5)
- Discharge Plan For AppendicitisDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan For Appendicitismclubert100% (3)
- Assess Patient with Suspected AppendicitisDocument6 pagesAssess Patient with Suspected AppendicitisRirin Ajeng Kartiningsih100% (1)
- Appendectomy NCPDocument6 pagesAppendectomy NCPLeah Fe Ariete Adtoon67% (3)
- Appendectomy Nursing Care Plan - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesAppendectomy Nursing Care Plan - Risk For InfectionChebz Zy0% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (1)
- NCP AppendicitisDocument4 pagesNCP AppendicitisAisha LakibulNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy Possible NCPDocument6 pagesAppendectomy Possible NCPIrish Nicole DC100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Appendicitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Appendicitis NCPderic77% (43)
- NCP AppendicitisDocument5 pagesNCP Appendicitismike_steven12100% (2)
- Acute Pain Management Post AppendectomyDocument6 pagesAcute Pain Management Post AppendectomyDaryl Valerio Francisco100% (1)
- Acute Pain NCPDocument4 pagesAcute Pain NCPBea Dela Cena100% (1)
- NCP Acute Pain VaDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain VaKate ClarosNo ratings yet
- NCP Post Op AppendectomyDocument3 pagesNCP Post Op AppendectomyHakam Attawneh100% (2)
- Post Appendectomy NCPDocument1 pagePost Appendectomy NCPJharene BasbañoNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy NCPDocument2 pagesAppendectomy NCPQueency Vanguardia0% (1)
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Post-Operative Acute PainDocument2 pagesCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Post-Operative Acute PainCherald Paul C AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired MobilityDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired MobilityLouis LazaroNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalI Am SmilingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For AppendectomyDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Appendectomyvanessajane0989% (45)
- Final NCP HerniaDocument5 pagesFinal NCP HerniaDenisse Shazz Mae Maret100% (2)
- Orif NCPDocument1 pageOrif NCPLighto Ryusaki100% (1)
- NCP GastroenteritisDocument1 pageNCP GastroenteritisFranchesca PaunganNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie Angelica BilonoNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Skin Integrity Lap CholeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skin Integrity Lap CholeJenny AjocNo ratings yet
- R.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document2 pagesR.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Karen Joy ItoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument4 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageCholecystectomy Nursing Care PlanJor Garcia100% (1)
- Gallstone NCPDocument2 pagesGallstone NCPKelly RiedingerNo ratings yet
- NCP Altered ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP Altered ComfortColleen De la Rosa50% (2)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhel NabosNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJenny Pearl PasalNo ratings yet
- 4 Appendectomy Nursing Care PlansDocument8 pages4 Appendectomy Nursing Care PlansMarin Andrei100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Imbalance Body TemperatureDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Imbalance Body TemperatureCarl J.No ratings yet
- Appendectomy CSDocument30 pagesAppendectomy CSMASIINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For InfectionPatrick Renz TibayanNo ratings yet
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- A Case Study On Acute AppendicitisDocument56 pagesA Case Study On Acute AppendicitisIvy Mae Evangelio Vios92% (13)
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2Angelica OctotNo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- NCP For Ulnar SurgeryDocument5 pagesNCP For Ulnar SurgeryjiloNo ratings yet
- B. Surgical ManagementDocument20 pagesB. Surgical ManagementNickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionEllenare Racion100% (1)
- NCP Risk of InfectionDocument5 pagesNCP Risk of InfectionPaolo UyNo ratings yet
- Assessme NT Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesDocument3 pagesAssessme NT Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesTricia100% (1)
- NCP 3 Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesNCP 3 Risk For Infectionbrian.dulatreNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAvery LabawigNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Factors: INFECTION Is Define AsDocument7 pagesFactors: INFECTION Is Define AsJessica GlitterNo ratings yet
- NCP CASE PRES Potential Risk InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP CASE PRES Potential Risk InfectionKuda Gene LorenNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care ActivityDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Care ActivityJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Velasco Journal - Maam Abby - PediaDocument2 pagesVelasco Journal - Maam Abby - PediaJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Academic Integrity: You As The Student MustDocument2 pagesAcademic Integrity: You As The Student MustJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Velasco Journal - Maam Abby - PediaDocument2 pagesVelasco Journal - Maam Abby - PediaJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- FI JournalDocument12 pagesFI JournalJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- ComplicationsDocument1 pageComplicationsJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care Activity Converted EditedDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Care Activity Converted EditedJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Surgery JournalDocument7 pagesSurgery JournalJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care ActivityDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Care ActivityJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Unstable AnginaDocument31 pagesUnstable AnginaJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- What Is Nursing and Communication SkillsDocument37 pagesWhat Is Nursing and Communication SkillsSareno PJhēa100% (1)
- Intubation ChecklistDocument3 pagesIntubation ChecklistJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care ActivityDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Care ActivityJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Journal #3 Berzabal, Jane Arian I.Document2 pagesJournal #3 Berzabal, Jane Arian I.Jane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Stigma and Discrimination During COVID-19 Pandemic: Divya Bhanot, Tushar Singh, Sunil K. Verma and Shivantika SharadDocument11 pagesStigma and Discrimination During COVID-19 Pandemic: Divya Bhanot, Tushar Singh, Sunil K. Verma and Shivantika SharadJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care Activity Converted EditedDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Care Activity Converted EditedJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Submitted By: Jane Arian Berzabal Nbb2Document14 pagesCase Study: Submitted By: Jane Arian Berzabal Nbb2Jane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Journal. SchizoDocument1 pageJournal. SchizoJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Discrimination Among The Notre Dame de Chartres Medical Staffs During The COVID-19 PandemicDocument16 pagesDiscrimination Among The Notre Dame de Chartres Medical Staffs During The COVID-19 PandemicJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- September 12, 2020: Gulanick, Meg. "Nursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Intervention." Apple BooksDocument9 pagesSeptember 12, 2020: Gulanick, Meg. "Nursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Intervention." Apple BooksJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Movie Review 3 (Enough)Document1 pageMovie Review 3 (Enough)Jane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Journal #1 Berzabal, Jane Arian I.Document2 pagesJournal #1 Berzabal, Jane Arian I.Jane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- FI JournalDocument12 pagesFI JournalJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Journal #2 Berzabal, Jane Arian I.Document2 pagesJournal #2 Berzabal, Jane Arian I.Jane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Journal. SchizoDocument1 pageJournal. SchizoJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- 13Document28 pages13didiNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Fecal IncontinenceDocument2 pagesManagement of Patients With Fecal IncontinenceJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure: Guidelines For The Primary Care Physician and The Heart Failure SpecialistDocument12 pagesTreatment of Congestive Heart Failure: Guidelines For The Primary Care Physician and The Heart Failure SpecialistJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Child discipline and bullying roles for nursesDocument2 pagesChild discipline and bullying roles for nursesJane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Gec 3 Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesGec 3 Finals ReviewerYam KayeNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Advantages and Disadvantages of VolunteeringDocument6 pagesDiscuss The Advantages and Disadvantages of Volunteeringaidil islamNo ratings yet
- Vote Ryan Aldred For Usdaw ECDocument2 pagesVote Ryan Aldred For Usdaw ECUSDAWactivistNo ratings yet
- Detection of Marine Microalgae (Phytoplankton) Quality To Support Seafood Health: A Case Study On The West Coast of South Sulawesi, IndonesiaDocument8 pagesDetection of Marine Microalgae (Phytoplankton) Quality To Support Seafood Health: A Case Study On The West Coast of South Sulawesi, IndonesiaIndah AdeliaNo ratings yet
- Microbank™-Dry: Product Code Pl.172Document2 pagesMicrobank™-Dry: Product Code Pl.172Fadhlan ArifinNo ratings yet
- Defining MasculinityDocument9 pagesDefining Masculinityapi-572228483No ratings yet
- Title:: Zarah Adriel A. ManaloDocument9 pagesTitle:: Zarah Adriel A. ManaloDana LeiNo ratings yet
- Department of Social Welfare and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesDepartment of Social Welfare and DevelopmentJhana May PayatNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Physical Fitness ActivitiesDocument27 pagesPhysical Education: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Physical Fitness ActivitiesKeith Tristan RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Carcedo vs. Maine Marine PhilsDocument21 pagesCarcedo vs. Maine Marine PhilsDani McstNo ratings yet
- Hip Pain in Pregnancy GTPS - Oct19-1Document3 pagesHip Pain in Pregnancy GTPS - Oct19-1Ryan CrossNo ratings yet
- Mohammadi 202. Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Among A Iranian Computer UsersDocument6 pagesMohammadi 202. Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Among A Iranian Computer UsersFioriAmeliaHathawayNo ratings yet
- HEARING IMPAIRMENT GUIDEDocument29 pagesHEARING IMPAIRMENT GUIDEAPRILYN REFENDOR BCAEd - 4DNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Should Not Be Provided For Free Regardless of A PersonDocument1 pageHealthcare Should Not Be Provided For Free Regardless of A PersonLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- Practising and Changing Health BehavioursDocument2 pagesPractising and Changing Health BehavioursM. Amebari NongsiejNo ratings yet
- Zombie Apocalypse Synthesis Group EssayDocument4 pagesZombie Apocalypse Synthesis Group Essayapi-514832443No ratings yet
- Dehlendorf2021 PCC DevelopmentDocument6 pagesDehlendorf2021 PCC Developmentinggar ratnakusumaNo ratings yet
- Bonardi2017 - Cópia PDFDocument11 pagesBonardi2017 - Cópia PDFRENATO SUDATINo ratings yet
- Innovative Use of Virtual Reality in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Case-StudyDocument12 pagesInnovative Use of Virtual Reality in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Case-StudyomenpkuNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 3 QPDocument11 pagesNutrition 3 QPRizwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 5E Lesson PlanDocument7 pages5E Lesson PlanGary WilliamsNo ratings yet
- ORGS 1136 - Week 4 Notes ORGS 1136 - Week 4 NotesDocument3 pagesORGS 1136 - Week 4 Notes ORGS 1136 - Week 4 NotesTara FGNo ratings yet
- Hiv and Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission (PMTCT) : by Gebremaryam TDocument100 pagesHiv and Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission (PMTCT) : by Gebremaryam THambal AhamedNo ratings yet
- NobelEsthetic Proc&Prod - 2010 - GBDocument116 pagesNobelEsthetic Proc&Prod - 2010 - GBNiaz AhammedNo ratings yet
- Hospital Architecture As An Active Medicine: Bilyana DochevaDocument146 pagesHospital Architecture As An Active Medicine: Bilyana DochevaGIANELLA NAJARRONo ratings yet
- FCCS Course Advert 22.09.2022 - FinalDocument2 pagesFCCS Course Advert 22.09.2022 - FinalShaneabbas JafferNo ratings yet
- MHN MUHS External and InternalDocument5 pagesMHN MUHS External and Internalanupa sukalikarNo ratings yet
- Safety ManualDocument21 pagesSafety ManualAli ImamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28: Nutrition and Fluids Student Assignment: Match Each Nutrient With Its Function in The BodyDocument2 pagesChapter 28: Nutrition and Fluids Student Assignment: Match Each Nutrient With Its Function in The BodyMA. OLIVIA LINAONo ratings yet
- 1.BSBDIV501 Student Assessment Tasks RedoneDocument28 pages1.BSBDIV501 Student Assessment Tasks RedoneÇrox Rmg PunkNo ratings yet