Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9th Century: When It Started Branch of Science
Uploaded by
riza amores0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
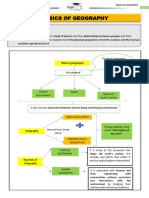
28 views4 pagesPhysics is the study of how physical systems interact with one another. Gravity, light, and time are among the topics studied by physicists. The Theory of Relativity was created by Albert Einstein, a famous physicist. Chemistry is the study of matter's composition, properties, reactions, and structure. Pasteurization is the practice of heating liquids such as milk and orange juice to destroy hazardous microorganisms. It was discovered by chemist Louis Pasteur. Astronomy is the study of anything outside of Earth's atmosphere in the universe. Galileo's observations prompted the beginning of modern astronomy.
Original Description:
Intro to STS
Original Title
IntroSTS_RAmores
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhysics is the study of how physical systems interact with one another. Gravity, light, and time are among the topics studied by physicists. The Theory of Relativity was created by Albert Einstein, a famous physicist. Chemistry is the study of matter's composition, properties, reactions, and structure. Pasteurization is the practice of heating liquids such as milk and orange juice to destroy hazardous microorganisms. It was discovered by chemist Louis Pasteur. Astronomy is the study of anything outside of Earth's atmosphere in the universe. Galileo's observations prompted the beginning of modern astronomy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pages9th Century: When It Started Branch of Science
Uploaded by
riza amoresPhysics is the study of how physical systems interact with one another. Gravity, light, and time are among the topics studied by physicists. The Theory of Relativity was created by Albert Einstein, a famous physicist. Chemistry is the study of matter's composition, properties, reactions, and structure. Pasteurization is the practice of heating liquids such as milk and orange juice to destroy hazardous microorganisms. It was discovered by chemist Louis Pasteur. Astronomy is the study of anything outside of Earth's atmosphere in the universe. Galileo's observations prompted the beginning of modern astronomy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Instructions: Fill in the table with the following information need (At least 10 but you can go
overboard). Definition must be concise and up to 3 sentences only.
Paper Size: A4
Can be handwritten or type written
When uploading/posting in G.classroom it should be in PDF format with a file name of:
IntroSTS_fist name initial and complete surname (example: IntroSTS_KJDapula)
When it started Branch of Science Definition
4th century BCE Physics is the study of how physical
systems interact with one
another. Gravity, light, and
time are among the topics
studied by physicists. The
Theory of Relativity was
created by Albert Einstein,
a famous physicist.
9th century Chemistry Is the study of matter's
composition, properties,
reactions, and structure.
Pasteurization, for
example, is the practice of
heating liquids such as milk
and orange juice to destroy
hazardous microorganisms.
It was discovered by
chemist Louis Pasteur.
6th century BC Astronomy is the study of anything
outside of Earth's
atmosphere in the universe.
This includes objects visible
with the naked eye, such as
the Sun, Moon, planets, and
stars. Galileo's observations
of the Moon, Venus' phases,
Jupiter's moons, sunspots,
and the knowledge that the
Milky Way Galaxy is made
up of seemingly
uncountable individual
stars prompted the
beginning of modern
astronomy.
4th century BC Geology is the study of Earth—its
interior and exterior
surfaces, the rocks and
other materials that
surround us, the processes
that have resulted in their
formation, the water that
flows over the surface and
lies beneath it, the changes
that have occurred over
geological time, and the
changes that we can expect
to occur in the near future.
Geology is a science, and to
understand geological
problems, we employ
deductive reasoning and
scientific procedures. The
founder of modern geology
is James Hutton, a Scottish
farmer and naturalist.
371–287 BCE Botany The study of plants,
including their structure,
characteristics, and
biochemical activities, is a
discipline of biology. Plant
taxonomy and the study of
plant diseases and
interactions with the
environment are also
covered. Botany is credited
to Theophrastus, a Greek
philosopher who studied
with Plato before becoming
an Aristotelian student.
12th century Zoology (also known as animal
science) is a branch of
biology concerned with
animal life. It encompasses
everything from the
structure of organisms to
the cellular level of life.
Aristotle is known as the
"Father of Zoology"
because of his significant
contributions to the field,
which include a vast
amount of information
about the diversity,
structure, and behavior of
animals, as well as the
analysis of many elements
of living things and the
beginnings of taxonomy
science.
350 BC Meteorology is a field of atmospheric
science that covers
atmospheric chemistry and
physics, with a strong
emphasis on weather
forecasting. Meteorology is
a branch of science that use
physics and chemistry,
among other tools, to better
understand the Earth's
atmosphere, its processes,
and its structure.
Meteorology was written by
Aristotle in 350 BC.
Aristotle is often considered
to be the father of
meteorology.
late 19th century Oceanography Oceanography is the study
of the ocean using
chemistry, geology,
meteorology, biology, and
other fields of science.
Climate change, pollution,
and other causes are
endangering the ocean and
its marine life, so it's
especially vital now. Walter
Munk was an Austrian-
born American
oceanographer who laid the
groundwork for modern
oceanography with his
pioneering investigations of
ocean currents and wave
propagation.
1866 Genetics is the study of how features
like hair color, eye color,
and illness risk are passed
down (“inherited”) from
one generation to the next.
Genetics has an impact on
how these inherited
qualities vary from person
to person. Gregor Mendel,
known as the "Father of
Genetics," discovered the
fundamental laws of
inheritance while working
on pea plants.
1879 Psychology is a science and a profession
dedicated to figuring out
how people think, feel, act,
and learn. The study of
conscious and unconscious
events, as well as feelings
and thinking, is included in
psychology. In 1879,
Wilhelm Wundt founded
the Institute for
Experimental Psychology at
Leipzig University in
Germany. In
fact, Wundt is commonly
considered
the father of psychology.
You might also like
- Definition of ScienceDocument19 pagesDefinition of Sciencejay ann delaNo ratings yet
- Definition of ScienceDocument19 pagesDefinition of Sciencejay ann delaNo ratings yet
- Tugas AS1 HaniLutfianaFebrianiOde 16023436Document2 pagesTugas AS1 HaniLutfianaFebrianiOde 16023436Cuttie BunnyNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument2 pagesAstronomyCassandra UyNo ratings yet
- Semester 5 Open Course - I: (Problems Not Required)Document12 pagesSemester 5 Open Course - I: (Problems Not Required)kcameppadi123No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument30 pagesPhysicsPolNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledFish SauceNo ratings yet
- SHS Q3 - Las Eval - Diss 11 W1 7Document39 pagesSHS Q3 - Las Eval - Diss 11 W1 7Gerard LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument29 pagesChapter1 PDFsgw67No ratings yet
- Phy Ch-1 The Physical WorldDocument15 pagesPhy Ch-1 The Physical Worldjanhavi.patil200175No ratings yet
- CNewton's Laws of MotionDocument27 pagesCNewton's Laws of MotionLhai Dizon CawiganNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam: Grade 3 Science, 1st Quarter Long TestDocument3 pagesMock Exam: Grade 3 Science, 1st Quarter Long TestJoyceNo ratings yet
- Konsep Kosmologi Dalam Filsafat: Fathur RahmanDocument11 pagesKonsep Kosmologi Dalam Filsafat: Fathur RahmanFajar FijeyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Notes Lesson 1-11Document12 pagesEarth Science Notes Lesson 1-11Joshua PerlasNo ratings yet
- Natural Science - WikipediaDocument25 pagesNatural Science - WikipediaDamilare Daniel OlaniyiNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument1 pageAstronomyEleazar MelchiahNo ratings yet
- LLKKDocument1 pageLLKKanandphilipkurianNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Astronomy and Astrology?Document1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between Astronomy and Astrology?Yuri De VeraNo ratings yet
- Zoology: DescriptionDocument3 pagesZoology: DescriptionGamingWithCharlesPHNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument3 pagesAstronomyAngelo Otañes GasatanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Is ADocument1 pageEarth and Life Science Is ARyan CortezNo ratings yet
- ASTROPHYSICSDocument5 pagesASTROPHYSICSgopika mohanNo ratings yet
- ch1 Physical WorldDocument15 pagesch1 Physical WorldPriyanshi PanwarNo ratings yet
- Merge 03Document248 pagesMerge 03yogesh yogNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument1 pageAstronomyJhapaul LlaneraNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 11Document234 pagesPhysics Class 11Afrin FirdusNo ratings yet
- Physical WorldDocument15 pagesPhysical Worldschand280No ratings yet
- IDP - Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesIDP - Earth ScienceRichelle MasingNo ratings yet
- What Is AstronomyDocument6 pagesWhat Is AstronomyRonnie PastranaNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument127 pagesEarth ScienceMina TzuzukiNo ratings yet
- Space ScienceDocument55 pagesSpace ScienceHrid 2100% (1)
- Student Booklet: For Use by Students and Teachers, During The Examination and Real-Time Investigative Project WorkDocument55 pagesStudent Booklet: For Use by Students and Teachers, During The Examination and Real-Time Investigative Project WorkPrisha Gupta50% (2)
- Astronomy: This Article Is About The Scientific Study of Celestial Objects. For Other Uses, SeeDocument1 pageAstronomy: This Article Is About The Scientific Study of Celestial Objects. For Other Uses, SeeDean Joyce AlborotoNo ratings yet
- Note Taking ExerciseDocument1 pageNote Taking ExerciseLailla MarlinaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - MC Science 5 AstronomyDocument3 pagesModule 2 - MC Science 5 AstronomyLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Goals and Scope of AstronomyDocument16 pagesGoals and Scope of AstronomyIvejy QuiliopeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Jerry TaayDocument125 pagesEarth and Life Science - Jerry TaayJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- Ast 1Document1 pageAst 1anandphilipkurianNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument1 pageAstronomyHITNo ratings yet
- Thea Earth Sci L1Document2 pagesThea Earth Sci L1theaNo ratings yet
- Science: Laws of NatureDocument8 pagesScience: Laws of NaturemackoypogiNo ratings yet
- Indian Physics: Outline of Early History: Subhash Kak February 2, 2008Document36 pagesIndian Physics: Outline of Early History: Subhash Kak February 2, 2008danda1008716No ratings yet
- Diffrences Between Astronomy and AstrologyDocument9 pagesDiffrences Between Astronomy and AstrologyNegrila RaresNo ratings yet
- Jyoti ShaDocument71 pagesJyoti ShavarshneyrajeNo ratings yet
- U.P. NATSCI 1 ModuleDocument281 pagesU.P. NATSCI 1 ModuleNorman PascualNo ratings yet
- Spot Basic Space Science Booklet 2023 24 92336Document28 pagesSpot Basic Space Science Booklet 2023 24 92336shravanvk35No ratings yet
- Branches of ScienceDocument6 pagesBranches of SciencePeachy AbelidaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Q1 (Earth Sci)Document14 pagesReviewer Q1 (Earth Sci)Joash Charlotte VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience Revieweraxel angelus zerimar garinaNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument1 pageAstronomysaintjames2No ratings yet
- Main Branches of Earth ScienceDocument1 pageMain Branches of Earth ScienceDampil, Kriscia Nicole A.No ratings yet
- GEOS Exam 1 PreparationDocument6 pagesGEOS Exam 1 Preparationgeneabi012No ratings yet
- The Cosmogenesis of Dwelling Ancient Ecological PRDocument13 pagesThe Cosmogenesis of Dwelling Ancient Ecological PRKaran ChoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DefinitionDocument1 pagePhysical Science DefinitionGinle SatumcacalNo ratings yet
- SCI10 Activity1.2Document2 pagesSCI10 Activity1.2Feliza Mae BoquecosaNo ratings yet
- Science Promotion Orient Test Information Booklet: BasicDocument37 pagesScience Promotion Orient Test Information Booklet: BasicArchanaGupta80% (5)
- StudyIQ Complete Geography Handouts (ENG)Document370 pagesStudyIQ Complete Geography Handouts (ENG)Abinash katochNo ratings yet
- The Branches of ScienceDocument2 pagesThe Branches of ScienceLorraine Jem Izon BatallaNo ratings yet
- EL Lesson1Document36 pagesEL Lesson1Shiela BanicodNo ratings yet
- Integration by Reduction To Partial Fractions: Math 12 - Calculus 2Document19 pagesIntegration by Reduction To Partial Fractions: Math 12 - Calculus 2riza amoresNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1: Answer The Following Questions and Limit Your Answer To 1-5 Pages. 1. What Is Law?Document4 pagesAssignment No. 1: Answer The Following Questions and Limit Your Answer To 1-5 Pages. 1. What Is Law?riza amoresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Methods of Finding Estimators: Chapter 7 For BST 695: Special Topics in Statistical Theory. Kui Zhang, 2011Document30 pagesChapter 7 - Methods of Finding Estimators: Chapter 7 For BST 695: Special Topics in Statistical Theory. Kui Zhang, 2011riza amoresNo ratings yet
- Learning Activities #1 and 2Document6 pagesLearning Activities #1 and 2riza amoresNo ratings yet
- Inferences AND Preliminary Parts Research DefenseDocument11 pagesInferences AND Preliminary Parts Research Defenseriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Four Basic Operations On SetsDocument4 pagesFour Basic Operations On Setsriza amores100% (1)
- Guidelines IN Making THE Final Draft Rade EEK April: Research Project Inquiry Immersion AND InvestigationDocument3 pagesGuidelines IN Making THE Final Draft Rade EEK April: Research Project Inquiry Immersion AND Investigationriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politicsriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politicsriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Worksheet NoDocument8 pagesWorksheet Noriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Grade 12Document4 pagesScience, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Grade 12riza amores100% (1)
- Gen Physics 2Document10 pagesGen Physics 2riza amoresNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument1 pagePhysical and Chemical Properties of Matterriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Module in 2: General ChemistryDocument5 pagesModule in 2: General Chemistryriza amoresNo ratings yet
- GEN PHYSICS 2 WEEK 5 Magnetic Force On A Current Carrying WireDocument5 pagesGEN PHYSICS 2 WEEK 5 Magnetic Force On A Current Carrying Wireriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: What Is The Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions?Document7 pagesThermochemistry: What Is The Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions?riza amoresNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (G 12) W 3 M 23-27, 2020Document2 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics (G 12) W 3 M 23-27, 2020riza amores100% (1)
- Module in RP Week1Document4 pagesModule in RP Week1riza amoresNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Grade 12 General Physics 2Document5 pagesScience, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Grade 12 General Physics 2riza amoresNo ratings yet
- Module Cpar 70s To ComtemporaryDocument4 pagesModule Cpar 70s To Comtemporaryriza amores100% (1)
- Classification of MatterDocument1 pageClassification of Matterriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Engineering Structures: Eduardo Cavaco, Ilton Pacheco, José CamaraDocument14 pagesEngineering Structures: Eduardo Cavaco, Ilton Pacheco, José CamaraElber Cuya PillacaNo ratings yet
- Scientific Heresies and Their - Sungenis, Robert A. - 6913Document574 pagesScientific Heresies and Their - Sungenis, Robert A. - 6913Araceli100% (2)
- Photoelectric Effect Lab ReportDocument5 pagesPhotoelectric Effect Lab Reportsans_serif100% (2)
- Problemas Resueltos Del Reichl - TMPDocument141 pagesProblemas Resueltos Del Reichl - TMPLuis Alberto Aliaga VásquezNo ratings yet
- Will My Polymers MixDocument85 pagesWill My Polymers MixpolypolyyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Passive DevicesDocument72 pagesChapter 7 Passive DevicessvijiNo ratings yet
- Exe Melting and BoilingDocument3 pagesExe Melting and BoilingKuan LoongNo ratings yet
- CFD Simulation of Human Coughs and Sneezes: A Study in Droplet Dispersion, Heat, and Mass TransferDocument11 pagesCFD Simulation of Human Coughs and Sneezes: A Study in Droplet Dispersion, Heat, and Mass TransferNishant VermaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Design Manual (Moss) 205Document1 pagePressure Vessel Design Manual (Moss) 205anu radha100% (1)
- Lab 05 PDFDocument7 pagesLab 05 PDFAbdul Rehman AfzalNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Hariyana Vidya Mandir Salt Lake, KolkataDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Hariyana Vidya Mandir Salt Lake, KolkataIndrani BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Encapsulados Ensayos E2 C2 F1Document4 pagesEncapsulados Ensayos E2 C2 F1fgdfgdfNo ratings yet
- Presentation On LaserDocument19 pagesPresentation On LaserBhargavNo ratings yet
- Tutorial SheetDocument4 pagesTutorial SheetjaiNo ratings yet
- 0625 w01 Ms 2Document6 pages0625 w01 Ms 2Anonymous Y2uv3vNo ratings yet
- A Representative Volume Element Simulation of A Thermo Plastic ElastomerDocument34 pagesA Representative Volume Element Simulation of A Thermo Plastic Elastomervivashwanth paiNo ratings yet
- UlabyISMCh03Document58 pagesUlabyISMCh03taulanberishaNo ratings yet
- Electricity PP TDocument18 pagesElectricity PP Tahmer100% (3)
- Rutherford's Alpha-Particle Scattering ExperimentDocument10 pagesRutherford's Alpha-Particle Scattering ExperimentAhmad HussainNo ratings yet
- Identifying Matter: Physical PropertiesDocument1 pageIdentifying Matter: Physical PropertiesbecaNo ratings yet
- Using Labview To Measure Temperature With A ThermistorDocument18 pagesUsing Labview To Measure Temperature With A ThermistorjdaudpotoNo ratings yet
- Quantum ConfinementDocument60 pagesQuantum ConfinementSaeed AzarNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Part 1Document8 pagesMagnetism Part 1AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Rheology in Paper and Paperboard Coating: Pekka KomulainenDocument102 pagesRheology in Paper and Paperboard Coating: Pekka KomulainenjjccmmaaNo ratings yet
- Design of Elastomeric Bearing System and AnalysisDocument11 pagesDesign of Elastomeric Bearing System and Analysisabdelrahman emadNo ratings yet
- Golden Ratio Geometry and The Fine-Structure Constant2Document8 pagesGolden Ratio Geometry and The Fine-Structure Constant2Michael A. SherbonNo ratings yet
- Impacts of HVDC Lines On The Economics of HVDC ProjectsDocument149 pagesImpacts of HVDC Lines On The Economics of HVDC ProjectsArturo Isidro Conde Pérez0% (1)
- Instructor Dean For Academic AffairsDocument9 pagesInstructor Dean For Academic Affairsjhen bautistaNo ratings yet
- Composite MaterialsDocument2 pagesComposite MaterialsmaheshNo ratings yet
- Seismic Assessment of Hollow Core Concrete Bridge Piers: Research OnlineDocument11 pagesSeismic Assessment of Hollow Core Concrete Bridge Piers: Research Onlineshravan38No ratings yet