Professional Documents
Culture Documents
If Source Impedance Is Complex, Then Maximum Power Transfer Occurs When The Load Impedance Is - The Source Impedance
Uploaded by
Siva ForeviewOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
If Source Impedance Is Complex, Then Maximum Power Transfer Occurs When The Load Impedance Is - The Source Impedance
Uploaded by
Siva ForeviewCopyright:
Available Formats
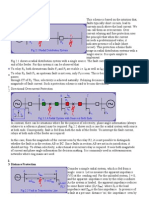
POWER SYSTEM PROTECTION
Unit 3 – Distance and Carrier Protection of Transmission Lines
MCQ
1. Reactance relay is normally used for protection against
a) Earth fault only
b) Phase fault only
c) Both earth and phase faults
d) None of the above
Ans: Earth fault only
2. Which of the following relay has inherent directional characteristics?
a) Mho
b) Reactance
c) Impedance
d) None of the above
Ans: Mho
3. The operating characteristics of the reactance relay in the complex impedance plane
is a
a) Circle with its origin at the centre of the R-X plane
b) Circle passing through the origin
c) Straight line passing through the origin
d) Straight line parallel to the X axis
Ans: Straight line parallel to the X axis
4. If source impedance is complex, then maximum power transfer occurs when the
load impedance is _______ the source impedance.
a) equal to
b) negative of
c) complex conjugate of
d) negative of complex conjugate of
Ans: Single bus-bar scheme
2 Marks
1. Define Distance relay.
A relay which measures impedance or a component of the impedance at the relay location
is known as a distance relay. It is used for the protection of a transmission line. As the impedance
of a line is proportional to the length of the line, a relay which measures impedance or its
component is called a distance relay.
2. Define Reactance relay and mho relay
Distance relay: A relay which measures reactance at the relay location is called a reactance
relay. It is a kind of a distance relay.
Mho Relay: This is a kind of a distance relay. It measures a particular component of the
Z
impedance, i.e.
cos(ϕ−θ)
where, ϕ is the power factor angle and θ is the design angle to shift MHO characteristic on the R-
X diagram. Its characteristic on the R-X diagram is a circle passing through the origin. It is a
directional relay. It is also known as an admittance or angle admittance relay.
3. What is mean by Power swing?
When a power system is operating in steady state, all the rotor or machine angles are
constant. Whenever there are sudden and large changes of power in the system, (say due to
outage of a major tie-line), the rotor angles undergo oscillations till the system reaches a new
stable state. This phenomenon is known as power swing.
4. Define reclosure.
Whenever a fault takes place, we can tentatively assume that a transient fault has
interrupted the supply. We then wait for a short while before switching on the circuit breaker.
This is known as reclosure. The reclosure can be carried out manually or automatically
Big Questions
1. Discuss in detail about the distance protection.
2. Explain the trip law for simple impedance relay, reactance relay and mho relay using
Universal Torque Equation.
3. Implement simple impedance relay using balanced beam structure and reactance relay,
mho relay using the induction cup structure.
4. Distinguish between Distance relays (Simple impedance relay, Reactance relay and mho
relay).
5. Discuss in detail about the Three-stepped Distance protection.
You might also like
- Distance RelaysDocument2 pagesDistance RelaysManuel Henríquez SantanaNo ratings yet
- Web - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1Document6 pagesWeb - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1sunitharajababuNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection - Part 08Document16 pagesPower System Protection - Part 08Rahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Distance Relay Interview Questions With AnswersDocument3 pagesDistance Relay Interview Questions With Answersprabakaran79No ratings yet
- Line ProtectionDocument91 pagesLine Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Power System Protection Lecture 2: Protection Paradigms - Apparatus ProtectionDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Power System Protection Lecture 2: Protection Paradigms - Apparatus Protectionsunny1725No ratings yet
- Transmission Lines Notes FMDocument12 pagesTransmission Lines Notes FMlamontfreemannNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document2 pagesAssignment 6Warda HanifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2-3Document170 pagesChapter 1-2-3Nitish Nageshwara RaoNo ratings yet
- Distance Protection of Series Compensated Transmission LineDocument9 pagesDistance Protection of Series Compensated Transmission Lineyand_carlosNo ratings yet
- PBC Slide 2Document53 pagesPBC Slide 2Arnold SNo ratings yet
- 7 e Applied EMCh 2Document82 pages7 e Applied EMCh 2Dr. Mohammad ZunoubiNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument60 pagesTransmission LinesChenette Ahorro FerrerNo ratings yet
- Review Atc IVDocument13 pagesReview Atc IVArsenio MalapitNo ratings yet
- Distance RelaysDocument2 pagesDistance Relaysuadikema01No ratings yet
- LINEREV ProtectionDocument92 pagesLINEREV Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (2)
- Applied EM7 e CH 02Document81 pagesApplied EM7 e CH 02محمد عبد الوهابNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument5 pagesTransmission LinesEchizen KinichiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 BASIC-LINE-PROTECTIONDocument46 pagesLecture 9 BASIC-LINE-PROTECTIONmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Ant Part 1Document17 pagesAnt Part 1alaayousefmmNo ratings yet
- EE466 C5 Distance Protection of Transmission Lines PDFDocument7 pagesEE466 C5 Distance Protection of Transmission Lines PDFSaisreeNo ratings yet
- EE466 C5 Distance Protection of Transmission Lines PDFDocument7 pagesEE466 C5 Distance Protection of Transmission Lines PDFSaisreeNo ratings yet
- EE466 - C5 Distance Protection of Transmission Lines PDFDocument7 pagesEE466 - C5 Distance Protection of Transmission Lines PDFjameelahmadNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines Introduction and Lab 1Document36 pagesTransmission Lines Introduction and Lab 1Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Antennas and Propagation (5) : Asst. Lect. Adham R. AzeezDocument30 pagesAntennas and Propagation (5) : Asst. Lect. Adham R. Azeezجعفر رحيم جبرNo ratings yet
- PSP (EX-701) 50 Questions Bank With SolutionDocument35 pagesPSP (EX-701) 50 Questions Bank With SolutionVarun YadavNo ratings yet
- Ece 3323 Experiment 1Document11 pagesEce 3323 Experiment 1TANQUERO_WW20% (1)
- PE452 - Lect13 - Distance Protection of Transmission LinesDocument44 pagesPE452 - Lect13 - Distance Protection of Transmission LinesZallan KhanNo ratings yet
- Distance ProtectionDocument23 pagesDistance Protectionhadrien100% (2)
- ALTAE 2009 Velasquez Kraetge ENUDocument6 pagesALTAE 2009 Velasquez Kraetge ENUInsan AzizNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 PSP 24march21Document10 pagesLecture 2 PSP 24march21rao asadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 BASIC-LINE-PROTECTIONDocument46 pagesLecture 9 BASIC-LINE-PROTECTIONTEMIDAYONo ratings yet
- Ce Unit IiDocument5 pagesCe Unit Iibalusasi_skgNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument109 pagesTransmission LinesJoshua RefeNo ratings yet
- Aim of ExperimentDocument23 pagesAim of ExperimentPANKAj Kr. [IIT KGP]No ratings yet
- Mho Distance RelayDocument9 pagesMho Distance RelayjeyavanianbudanNo ratings yet
- TLWG 2marksDocument10 pagesTLWG 2marksElakya PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Development of Distance Relay in Matlab: Jayant Lamture, A. P. VaidyaDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Distance Relay in Matlab: Jayant Lamture, A. P. VaidyahasanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Q and A SupplementaryDocument25 pagesTutorial Q and A SupplementaryKhadar A. FarahNo ratings yet
- CE CAT 1 Answer KeyDocument7 pagesCE CAT 1 Answer KeyVanitha DNo ratings yet
- Protection of Transmission Lines (Distance Protection)Document35 pagesProtection of Transmission Lines (Distance Protection)abdul basitNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Lect3Document7 pagesChap1 Lect3Ibraheem MahmoodNo ratings yet
- 5 Application of Complex Number in Marine Engineering FieldDocument19 pages5 Application of Complex Number in Marine Engineering Fieldainul sufiahNo ratings yet
- Principio de ProteccionesDocument5 pagesPrincipio de ProteccionesBrenda Naranjo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Antennas Theory DesignDocument11 pagesAntennas Theory DesignotienostevineNo ratings yet
- Application of Zone 3 Distance Relays On Transmission LinesDocument6 pagesApplication of Zone 3 Distance Relays On Transmission LinesLog in 2007No ratings yet
- Three Zones Adaptive Characteristic of The Mho Distance Relay by KU MethodDocument5 pagesThree Zones Adaptive Characteristic of The Mho Distance Relay by KU MethodSenthamizhan PanneerNo ratings yet
- Intro To Beam InstrumentationDocument38 pagesIntro To Beam InstrumentationDen BavisNo ratings yet
- Step 4Document6 pagesStep 4Oscar VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Actuators and Motion Control DevicesDocument84 pagesChapter 4. Actuators and Motion Control Devicesjohanna shaanyenengeNo ratings yet
- Mini FM Transmitter PDFDocument16 pagesMini FM Transmitter PDFAreeba NasirNo ratings yet
- T V Antenna - PPT (By A K)Document117 pagesT V Antenna - PPT (By A K)Dharamveer KumarNo ratings yet
- Antena - L4 - Input Impedance of Antenna2023Document9 pagesAntena - L4 - Input Impedance of Antenna2023مؤمل عبدالهاديNo ratings yet
- İnstruction To System ProtectionDocument91 pagesİnstruction To System ProtectionSuat KaracanNo ratings yet
- C1-1 PH ckts-S1Document38 pagesC1-1 PH ckts-S1mhmd.akzrNo ratings yet
- EC1311 Communication EngineeringDocument23 pagesEC1311 Communication EngineeringVidya NeemuNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- An Industrial Training Report On Autocad DesigningDocument39 pagesAn Industrial Training Report On Autocad DesigningSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- A Training Report On Bascs of PythonDocument53 pagesA Training Report On Bascs of PythonSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- KVASIR: A Multi-Class Image Dataset For Computer Aided Gastrointestinal Disease DetectionDocument7 pagesKVASIR: A Multi-Class Image Dataset For Computer Aided Gastrointestinal Disease DetectionSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- 13 Level Nagar2017Document5 pages13 Level Nagar2017Siva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Ramy ReddyDocument9 pagesRamy ReddySiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- An Optimized Dynamic Fair Resource Allocation Technique in A FemtocellDocument11 pagesAn Optimized Dynamic Fair Resource Allocation Technique in A FemtocellSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Speech Intention Classification With Multimodal Deep LearningDocument13 pagesSpeech Intention Classification With Multimodal Deep LearningSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Both Turkish Journal TemplateDocument9 pagesBoth Turkish Journal TemplateSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Electronics: An Algorithm For Natural Images Text Recognition Using Four Direction FeaturesDocument13 pagesElectronics: An Algorithm For Natural Images Text Recognition Using Four Direction FeaturesSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Development of Power Electronic Distribution Transformer Based On Anfis ControllerDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Power Electronic Distribution Transformer Based On Anfis ControllerSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- A Novel Method of Designing Multifunctional Electrical VehicleDocument27 pagesA Novel Method of Designing Multifunctional Electrical VehicleSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Reserch Paper ReviewDocument6 pagesChecklist For Reserch Paper ReviewSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Columns Fire Loading ExampleDocument10 pagesColumns Fire Loading ExampleSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Automated Wild-Animal Intrusion Detection and Repellent System Using Artificial Intelligence of ThingsDocument6 pagesAutomated Wild-Animal Intrusion Detection and Repellent System Using Artificial Intelligence of ThingsSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Chandra SekharDocument16 pagesChandra SekharSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- NPTI (PSTI) 5 Days ATAL Sponsored FDP On EV & Charging InfraDocument2 pagesNPTI (PSTI) 5 Days ATAL Sponsored FDP On EV & Charging InfraSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Powered Dual Battery Charging in Electric VehicleDocument6 pagesRenewable Energy Powered Dual Battery Charging in Electric VehicleSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Electric PropulsionDocument6 pagesElectric PropulsionSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- A Family of Ćuk-, Zeta-, and SEPIC-based SoftSwitching DC-DC ConvertersDocument16 pagesA Family of Ćuk-, Zeta-, and SEPIC-based SoftSwitching DC-DC ConvertersSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Based Hybrid Energy Sources Electric Vehicle With Bi-Directional Non Isolated DC-DC ConverterDocument5 pagesInduction Motor Based Hybrid Energy Sources Electric Vehicle With Bi-Directional Non Isolated DC-DC ConverterSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Binhayeeding2020 - 1Document12 pagesBinhayeeding2020 - 1Siva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Building The Internet of ThingsDocument55 pagesBuilding The Internet of ThingsSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Base 1Document10 pagesBase 1Siva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- NEW Final Report 3rd Sem DFIGDocument61 pagesNEW Final Report 3rd Sem DFIGSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Spam Detection & Classification FinalDocument38 pagesSpam Detection & Classification FinalSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Maximum Power Tracking Based Open Circuit Voltage Method For PV SystemDocument12 pagesMaximum Power Tracking Based Open Circuit Voltage Method For PV SystemSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Crescent KarthikDocument58 pagesCrescent KarthikSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Bridgeless Step-Up Ac/Dc Converter by Using Fuzzy Logic ControllerDocument3 pagesDesign and Implementation of Bridgeless Step-Up Ac/Dc Converter by Using Fuzzy Logic ControllerSiva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Electrical Layout - Ground Floor Plan: Sheet No. InstructionsDocument1 pageElectrical Layout - Ground Floor Plan: Sheet No. InstructionsAbhishek AjayNo ratings yet
- Battery Desulfator DA PIMP 2Document6 pagesBattery Desulfator DA PIMP 2lljpepeNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes Bard WADocument14 pagesManual de Partes Bard WAFausto CompeanNo ratings yet
- Novel Thermal Analysis Tool For Altium by Bernd SchroederDocument24 pagesNovel Thermal Analysis Tool For Altium by Bernd SchroederyarigijonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines IIDocument8 pagesElectrical Machines IImadhueeNo ratings yet
- Standard Enclosure Testing (IEC62208) : IP Rating For Enclosures IEC 60529Document2 pagesStandard Enclosure Testing (IEC62208) : IP Rating For Enclosures IEC 60529fajar agungNo ratings yet
- Physics by Sanjay Kumar Sharma: Edu Assignment Tutors Point, 8505062067Document2 pagesPhysics by Sanjay Kumar Sharma: Edu Assignment Tutors Point, 8505062067sanjay sharma100% (1)
- 2SD10617Document12 pages2SD10617info5280No ratings yet
- Alternating Current DPPsDocument2 pagesAlternating Current DPPsMayur BelsareNo ratings yet
- Lec29 - 32 - FET Application PDFDocument86 pagesLec29 - 32 - FET Application PDFRichard ParkerNo ratings yet
- IEC Asea Siemens Sprecher MeidenDocument9 pagesIEC Asea Siemens Sprecher MeidenEspidan68No ratings yet
- Premold JointDocument6 pagesPremold JointbenwkgNo ratings yet
- Elechome QuestionsDocument22 pagesElechome QuestionsasifshahanaNo ratings yet
- IIR Filter Design With MATLABDocument13 pagesIIR Filter Design With MATLABseemabNo ratings yet
- Antenna Power DividerDocument2 pagesAntenna Power DividerStephen Dunifer100% (2)
- Canon CXDI-60 X-Ray - Service ManualDocument186 pagesCanon CXDI-60 X-Ray - Service ManualGuranda IonNo ratings yet
- Thyristors, Triacs, DiacsDocument5 pagesThyristors, Triacs, DiacsAnonymous n50GmJNo ratings yet
- SJSU EE288 Lecture22 OPAMP For ADCDocument40 pagesSJSU EE288 Lecture22 OPAMP For ADCTING LEE100% (1)
- Electrostatic 1 (Mcq. For Board)Document9 pagesElectrostatic 1 (Mcq. For Board)Sheetal meenaNo ratings yet
- Clearing of Electrical PlansDocument3 pagesClearing of Electrical PlansPatty GorospeNo ratings yet
- Partial DischargeDocument6 pagesPartial Dischargebrockwell4960% (1)
- Small Signal MOSFET Bare Die 2N7000: Features: Die Dimensions in M (Mils)Document4 pagesSmall Signal MOSFET Bare Die 2N7000: Features: Die Dimensions in M (Mils)Saints RowNo ratings yet
- Full Length Test - 60 Qs (60 Mins)Document6 pagesFull Length Test - 60 Qs (60 Mins)Junaid MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Please Note That Cypress Is An Infineon Technologies CompanyDocument37 pagesPlease Note That Cypress Is An Infineon Technologies CompanyWaldo Perez SolisNo ratings yet
- GSCC014 LV - Concentric Cables Rev 0Document54 pagesGSCC014 LV - Concentric Cables Rev 0zambito2012No ratings yet
- PACOM 8003 Intelligent Controller DatasheetDocument4 pagesPACOM 8003 Intelligent Controller DatasheetThe FaderS100% (1)
- Toshiba Small Form Factor Disk Drive White PaperDocument3 pagesToshiba Small Form Factor Disk Drive White Papernjk19No ratings yet
- Overview of NTPC PDFDocument40 pagesOverview of NTPC PDFRahul KediaNo ratings yet
- Technical Issues On Distributed Generation (DG) Connection and GuidelinesDocument4 pagesTechnical Issues On Distributed Generation (DG) Connection and GuidelinesKristiano RonaldoNo ratings yet
- RBFBBEDocument66 pagesRBFBBELauro RdzNo ratings yet