Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanics 4
Uploaded by
yogeshkumar3089_82500 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesOriginal Title
mechanics4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesMechanics 4
Uploaded by
yogeshkumar3089_8250Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Solution:
Given Data:
*The vertical force at joint A is: PA 80 N
*The vertical force at joint D is: PD 60 N
*The vertical force at joint E is: PE 20 N
*The vertical force at point G is: PG 40 N
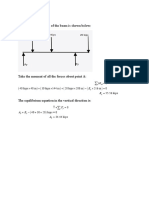
The free body diagram of the linkage is shown below:
The deflection at point C in upward direction is twice the deflection at point A:
C 2 A
The deflection at point A in downward direction is same as the deflection at
point D:
A D
The deflection at point E in downward direction is half of the deflection at point
A and deflection of point D:
1 1
E A D
2 2
The deflection at point G in upward direction is:
1
G E A
2
The value of the angle of deflection in counter clockwise direction can be
calculated as:
A
0.3 m
The magnitude of the vertical force P at point C can be calculated by the
application of the virtual work method:
The total work done over the linkage is:
W 80 A P C M 60 D 20 E 40 G
For the equilibrium:
80 A P C M 60 D 20 E 40 G 0
20 40
80 A 2 P A M A 60 A A A 0
0.3 m 2 2
M
80 2 P 60 10 20 0
0.3
M
130 2 P 0
0.3
For external moment M 0 :
130 2 P 0
P 65 N
Thus, the magnitude of the vertical force at point C in downward direction is 65 N.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Bartleby MaterialDocument13 pagesBartleby Materialyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Solution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 CDocument83 pagesSolution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 Cyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Correct Option Is (C) .: SolutionDocument271 pagesCorrect Option Is (C) .: Solutionyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Solution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 CDocument30 pagesSolution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 Cyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Solution: The Free Body Diagram Is Shown Below:: M P R Q W R Q W R Q WDocument16 pagesSolution: The Free Body Diagram Is Shown Below:: M P R Q W R Q W R Q Wyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Bartleby MaterialDocument13 pagesBartleby Materialyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- 10 MM 8 MMDocument25 pages10 MM 8 MMyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Thus, The Velocity of The Exhaust Gas Is: MethaneDocument19 pagesThus, The Velocity of The Exhaust Gas Is: Methaneyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- 350 Mpa 103 Gpa : PlasticDocument14 pages350 Mpa 103 Gpa : Plasticyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Solution: The Free Body Diagram of The Beam Is Shown BelowDocument42 pagesSolution: The Free Body Diagram of The Beam Is Shown Belowyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- 100 N/M 100 N/MDocument22 pages100 N/M 100 N/Myogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Bartleby 2Document21 pagesBartleby 2yogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Solution: Given Data: The Torque at C Is: The Torque at B IsDocument17 pagesSolution: Given Data: The Torque at C Is: The Torque at B Isyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- The Mass Flow Rate of Hot Water Can Be Calculated AsDocument3 pagesThe Mass Flow Rate of Hot Water Can Be Calculated Asyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- BartlebyfluidDocument3 pagesBartlebyfluidyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Thus, The Horizontal Reaction Force at B IsDocument2 pagesThus, The Horizontal Reaction Force at B Isyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet