Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula
Uploaded by
Farid ImranCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula
Uploaded by
Farid ImranCopyright:
Available Formats
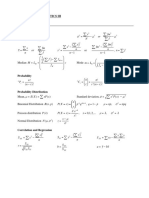
Numerical Methods Random Variables
Newton-Raphson n
f ( xn ) E( X )=∑ x i . P( X=x i )
x n+1 =x n − i=1 for X discrete
f '( x n ) ∞
Trapezoidal Rule
E(x)=∫−∞ x.f (x)dx for X continuous
Sum of the areas of trapeziums 2
Var ( X )=E[( X −μ) ]
h
¿ [ y 0 + y n +2( y 1 + y 2 +.. . .. .+ y n−1 ) ]
2
Data Description
Permutations and Combinations
Mean
n Median
n n!
Pr = ∑ xi c2 N
( n−r ) !
n
Cr =
n!
x= i=1
n
n
Q2 =L2 + (
f2 2
−∑ f 2 )
Mode
r ! ( n−r ) ! ∑ f i xi
x= i=1n d1
Probability
Conditional Probability
∑ fi
i=1
mod e=L+c
( d 1 + d2 )
P( A∩B ) Quartiles
P( A / B)= c1 N
P(B )
Hypothesis Testing
Q 1 =L1 + (
f1 4
−∑ f 1 )
X−μ c3 3
z test
z=
σ /√n
Q3 =L3 + (
f3 4
N−∑ f 3 )
ρ−π Sample Variance
z=
π ( 1−π )
√ n
X−μ
2
s=
∑ x2 − (∑ x )
n−1 n (n−1 )
2
t=
t test s/ √ n Sample Standard Deviation
2
(n−1 )s
2 χ2= 2
χ test
Special Probability Distribution
σ2
s=
√ ∑ x2 − (∑ x )
n−1 n(n−1)
2
n x n− x
Binomial
P( X= x)= C x p q
P( X= x )=
λ x e−λ
x!
s=
√ ∑ fx 2 − ( ∑ fx )
∑ f −1 (∑ f )(∑ f −1 )
Poisson
X−μ
z=
Normal σ
You might also like
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - FinalDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet - FinalkevinNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas Examen (1) 2Document1 pageFórmulas Examen (1) 2acatataacatataNo ratings yet
- Engineering Statistic FormulaeDocument5 pagesEngineering Statistic FormulaeYiXuanYeoNo ratings yet
- CCCJ Statistics Formula Sheet & TablesDocument11 pagesCCCJ Statistics Formula Sheet & TablesMÿ Ñämē Ïĥz TäñëkîãNo ratings yet
- Formulas Statistics II: ∫ = E (X) = ∫ = E (X) = ∫ ∫ Γ (p + 1) =Document1 pageFormulas Statistics II: ∫ = E (X) = ∫ = E (X) = ∫ ∫ Γ (p + 1) =pablo.sazhuangNo ratings yet
- List of Formulae and Normal TableDocument3 pagesList of Formulae and Normal Table梦魇spiritNo ratings yet
- Práctica Fourier SeriesDocument62 pagesPráctica Fourier SeriesMIGUEL ANGEL BARRERA TAMAYONo ratings yet
- La Place 5Document1 pageLa Place 5api-3821702No ratings yet
- Formula List and Statistical Tables Formula List and Statistical TablesDocument8 pagesFormula List and Statistical Tables Formula List and Statistical Tables赵博No ratings yet
- P182 List of EquationsDocument4 pagesP182 List of EquationsRomesor ApolNo ratings yet
- Discrete Distribution DetailsDocument2 pagesDiscrete Distribution DetailsKhalil RegaiegNo ratings yet
- Formula Engineering MathematicsDocument4 pagesFormula Engineering MathematicsAliff SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Spring 2013Document2 pagesTest 1 Spring 2013Ali BakhsasNo ratings yet
- Midterm Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMidterm Formula SheetShahd AlhamaydaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Mathematics FormulasDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Mathematics FormulasTra xeNo ratings yet
- List of FormulasDocument7 pagesList of Formulastimeijkhout92No ratings yet
- AP Statistics - Formulas and TablesDocument6 pagesAP Statistics - Formulas and TablesJinhui ZhengNo ratings yet
- Rumus Matematik KSSMDocument2 pagesRumus Matematik KSSMsaidah hamzah100% (4)
- Exam Formula SheetDocument5 pagesExam Formula SheetTusti JeebodhNo ratings yet
- Helpful Formulas PDFDocument1 pageHelpful Formulas PDFziyingkangNo ratings yet
- 2pc Cálculo Integral Fim 3Document7 pages2pc Cálculo Integral Fim 3Hafiz IqbalNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Hoja de FormulasDocument1 pageQuiz 2 Hoja de Formulaslsanc308No ratings yet
- σ p q ≤ n k x a n k p q np (1−p) : ĐÀO QUỐC THÁI - SE1508 - HE150059Document2 pagesσ p q ≤ n k x a n k p q np (1−p) : ĐÀO QUỐC THÁI - SE1508 - HE150059Quốc Thái ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Calc Practice PaperDocument1 pageCalc Practice PaperAaron OommenNo ratings yet
- Sol T2Document2 pagesSol T2Sohini RoyNo ratings yet
- Math 121A: Homework 7 SolutionsDocument9 pagesMath 121A: Homework 7 SolutionscfisicasterNo ratings yet
- 23 Power SeriesDocument15 pages23 Power Seriesk56jn7xzwxNo ratings yet
- Vidyalankar Vidyalankar Vidyalankar Vidyalankar: Applied Mathematics IIIDocument18 pagesVidyalankar Vidyalankar Vidyalankar Vidyalankar: Applied Mathematics IIIManoj NaikNo ratings yet
- Lec Generating FunctionDocument18 pagesLec Generating FunctionRaisa RashidNo ratings yet
- Characteristic functions identify distributionsDocument20 pagesCharacteristic functions identify distributionsJimmyNo ratings yet
- Ed 2Document8 pagesEd 2Fengfan RenNo ratings yet
- P (B !A) P (B) P (A!B) P (B) P (A!B) : 1 F (X) (X) DXDocument2 pagesP (B !A) P (B) P (A!B) P (B) P (A!B) : 1 F (X) (X) DXFrancisco Javier Colli PintoNo ratings yet
- Formula SPMDocument6 pagesFormula SPMSARIPAH BINTI TENGAH KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Integrals Formula GuideDocument1 pageGaussian Integrals Formula GuideKarinaNo ratings yet
- IIT BHU MA-201 Tutorial 10: Confidence Intervals and MLE EstimationDocument4 pagesIIT BHU MA-201 Tutorial 10: Confidence Intervals and MLE EstimationUjjwal BansalNo ratings yet
- Sistemas e Sinais (LEIC-Taguspark) 1 F Ormulas de EulerDocument3 pagesSistemas e Sinais (LEIC-Taguspark) 1 F Ormulas de Eulerrafael8080No ratings yet
- 120MP Statistics Formulae: (X X) (X X) (Y Y)Document2 pages120MP Statistics Formulae: (X X) (X X) (Y Y)LexNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesCheat SheetAsdNo ratings yet
- (Exercises and Problems) Convergence of Fourier SeriesDocument2 pages(Exercises and Problems) Convergence of Fourier SeriesJelo ArtozaNo ratings yet
- Stat 2500 Fomula Sheet For Final ExamDocument1 pageStat 2500 Fomula Sheet For Final Examamaka.iwu10No ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesFourier Transform Cheat Sheetalbert60467% (3)
- Gamma Distribution Parameter EstimationDocument3 pagesGamma Distribution Parameter EstimationRobinson Ortega MezaNo ratings yet
- Formulario OficialDocument3 pagesFormulario OficiallucasacunaespinozaNo ratings yet
- Cvit FT Derivation PDFDocument2 pagesCvit FT Derivation PDFkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Cvit FT Derivation PDFDocument2 pagesCvit FT Derivation PDFBlazeBlack54No ratings yet
- Mathematics: X NN X yDocument1 pageMathematics: X NN X yTomislav CarNo ratings yet
- DA (Sec. CD) Formula SheetDocument3 pagesDA (Sec. CD) Formula SheetGeetika JainNo ratings yet
- Formula Tov SPM 2022Document3 pagesFormula Tov SPM 2022SARIPAH BINTI TENGAH KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- S1 T01 Tabla DistribucionesDocument2 pagesS1 T01 Tabla DistribucionesPruebasNo ratings yet
- MA2002 Tutorial7Document3 pagesMA2002 Tutorial7yu hanyueNo ratings yet
- Solution QFT 1Document13 pagesSolution QFT 1Sara AvizNo ratings yet
- STAT 210B HWK #5 SOLUTIONSDocument5 pagesSTAT 210B HWK #5 SOLUTIONSDaniyal AsifNo ratings yet
- Materials SB: N) K X XDocument11 pagesMaterials SB: N) K X XNgô Hoàng Bích KhaNo ratings yet
- Membranska Teorija Rotacionih Ljuski Pri Rotaciono Simetričnom OpterećenjeDocument5 pagesMembranska Teorija Rotacionih Ljuski Pri Rotaciono Simetričnom OpterećenjeLazić MilošNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet 2009Document11 pagesFormula Sheet 2009Khim JuanNo ratings yet
- Riemann Zeta Functional Equation ChapterDocument14 pagesRiemann Zeta Functional Equation Chapterari wiliamNo ratings yet
- Fourier ConvergenceDocument8 pagesFourier Convergenceharshr3142No ratings yet
- Parcial Matematicas 505: 1. Ejercicio 1Document7 pagesParcial Matematicas 505: 1. Ejercicio 1JAIR ALBERTO ORTIZ AREVALONo ratings yet
- Harvard CS109A SyllabusDocument7 pagesHarvard CS109A Syllabuscshinsato18No ratings yet
- Doubtnut Today: 1 1. Introduction and DefinitionDocument13 pagesDoubtnut Today: 1 1. Introduction and Definitionziad abdelkadrNo ratings yet
- 3060 PROBLEM SET 9-1Document1 page3060 PROBLEM SET 9-1Person DuhNo ratings yet
- Business Report 14 May 2023 1Document8 pagesBusiness Report 14 May 2023 1Keerthi GaNo ratings yet
- Gulf PropDocument8 pagesGulf PropSagar GogiaNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument3 pagesAnovaammi890No ratings yet
- 4 Factors Affecting Procurement Performance PDFDocument15 pages4 Factors Affecting Procurement Performance PDFlynnthuNo ratings yet
- Skills and Design for Pitfall TrappingDocument5 pagesSkills and Design for Pitfall Trappingimma haznaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: Alumni Giving: Felicisimo, Jaurigue, Laset, Santos, TiuDocument34 pagesCase Analysis: Alumni Giving: Felicisimo, Jaurigue, Laset, Santos, TiuErika Anne JaurigueNo ratings yet
- Journal of Nutritional Disorders & TherapyDocument6 pagesJournal of Nutritional Disorders & TherapyTomas YeheisNo ratings yet
- Theorem 5.3.1.: 1 N 2 N I 2 IDocument18 pagesTheorem 5.3.1.: 1 N 2 N I 2 IBenNo ratings yet
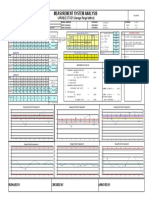
- Measurement System Analysis: VARIABLE STUDY (Average-Range Method)Document1 pageMeasurement System Analysis: VARIABLE STUDY (Average-Range Method)MahendraNo ratings yet
- Pipe Length Estimation SkillsDocument19 pagesPipe Length Estimation SkillsHalal BoiNo ratings yet
- Trellis Height Effect On The Production Characteristics of Raspberry PDFDocument6 pagesTrellis Height Effect On The Production Characteristics of Raspberry PDFSebastian GhermanNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression Techniques: 6 Practical ExercisesDocument3 pagesLinear Regression Techniques: 6 Practical ExercisesCapung flyNo ratings yet
- Understanding CEO Salaries and Firm PerformanceDocument6 pagesUnderstanding CEO Salaries and Firm PerformanceQuyên ThanhNo ratings yet
- Epbabi Iim RanchiDocument6 pagesEpbabi Iim RanchiDarshan MaldeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Ethical Values, Group Creativity, Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention: The Impact of Work Context On Work ResponseDocument20 pagesCorporate Ethical Values, Group Creativity, Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention: The Impact of Work Context On Work Responsezayan mustafaNo ratings yet
- Sme Covid-19 Seminar 2Document39 pagesSme Covid-19 Seminar 2api-581961377No ratings yet
- Testul Fisher ExactDocument33 pagesTestul Fisher ExactgeorgianapetrescuNo ratings yet
- Practical Approach for Evaluating Oil Analysis ResultsDocument12 pagesPractical Approach for Evaluating Oil Analysis ResultsINDRAJIT SAONo ratings yet
- PEER-R EV IEW ED Cleaning Validation: Factors Affecting Recovery Data and Material of Construction GroupingDocument6 pagesPEER-R EV IEW ED Cleaning Validation: Factors Affecting Recovery Data and Material of Construction GroupingkushalNo ratings yet
- Bias in Data CollectionDocument14 pagesBias in Data Collectionapi-204699162100% (1)
- This Chapter Presents The Review of Related Literature On The Students Profile and Their Computer SkillsDocument21 pagesThis Chapter Presents The Review of Related Literature On The Students Profile and Their Computer SkillsJim CerbitoNo ratings yet
- X-Bar Charts PDFDocument22 pagesX-Bar Charts PDFNitin SinghNo ratings yet
- Stats PTDocument15 pagesStats PT「 」No ratings yet
- Beyond Dichotomy - Conversations Between International Relations and Feminist TheoryDocument6 pagesBeyond Dichotomy - Conversations Between International Relations and Feminist TheoryMarinara MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Potential Critical Success Factors Common To Banking Sector Projects in GhanaDocument20 pagesPotential Critical Success Factors Common To Banking Sector Projects in GhanaDesmond WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Employee Satisfaction SurveyDocument40 pagesEmployee Satisfaction Surveypeellu100% (2)
- Customer Satisfaction at Kanhirode WeaversDocument77 pagesCustomer Satisfaction at Kanhirode WeaversPrabiNo ratings yet