Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IX Chemistry Chemical Changes and Reactions D 2 P2
Uploaded by
Dilson Babu Don0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesA catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed. It works by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. Catalysts can accelerate (positive catalyst) or decelerate (negative catalyst) reactions. Examples given are manganese dioxide catalyzing the decomposition of potassium chlorate and platinum catalyzing the reaction of ammonia and oxygen to produce nitric oxide. Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living things. Promoters are substances that improve the efficiency of catalysts. Characteristics used to identify chemical reactions include the evolution of gases, changes in color, formation of precipitates, and changes in state.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed. It works by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. Catalysts can accelerate (positive catalyst) or decelerate (negative catalyst) reactions. Examples given are manganese dioxide catalyzing the decomposition of potassium chlorate and platinum catalyzing the reaction of ammonia and oxygen to produce nitric oxide. Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living things. Promoters are substances that improve the efficiency of catalysts. Characteristics used to identify chemical reactions include the evolution of gases, changes in color, formation of precipitates, and changes in state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesIX Chemistry Chemical Changes and Reactions D 2 P2
Uploaded by
Dilson Babu DonA catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed. It works by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. Catalysts can accelerate (positive catalyst) or decelerate (negative catalyst) reactions. Examples given are manganese dioxide catalyzing the decomposition of potassium chlorate and platinum catalyzing the reaction of ammonia and oxygen to produce nitric oxide. Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living things. Promoters are substances that improve the efficiency of catalysts. Characteristics used to identify chemical reactions include the evolution of gases, changes in color, formation of precipitates, and changes in state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
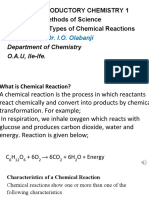
CATALYST
A catalyst is a substance that is used in some reactions either to increase or
decrease the rate of reaction. The substance acting as catalyst does not take part
in the reaction,
1. A catalyst is a chemical substance that can either accelerate or decelerate a
chemical reaction without itself undergoing any change.
2. A positive catalyst accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction.
Example:
i) Potassium chlorate decomposes only when heated up to 7000c, but
when added with MANGANESE DIOXIDE, it decomposes at 3000c
and evolves oxygen gas.
2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
ii) Ammonia on reacting with oxygen, produces Nitric oxide and water in
the presence of catalyst PLATINUM. It is an important chemical
reaction used in in the manufacture of nitric acid in industries.
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
iii) Hydrogen peroxide decomposes fast in the presence of catalyst
MANGANESE DIOXIDE.
2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
In the above given reactions Manganese dioxide and platinum act as
positive catalyst.
2. Enzymes present in our body also act as positive catalyst. They are
proteins and act as positive catalysts in the biochemical reactions.
During digestion they break the complex substances present in the
food and form simpler substances in two or three hours ,otherwise it
will take months to get digest the food.
3. The negative catalysts slow down the rate of chemical reactions.
Examples
i) Phosphoric acid slows down the rate of decomposition of hydrogen
peroxide.
ii) Alcohol acts as a negative catalyst and reduces the rate of oxidation of
Chloroform.
4. Some reactions take place by the absorption of Sound energy.
Example
Acetylene breaks up by absorbing sound energy and decomposes into Carbon and
Hydrogen.
C2H2 → 2C + H2
PROMOTERS:
The substances that improve the efficiency of catalysts and influence the rate of
chemical reactions are called promoters.
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3.
Example
During the industrial manufacture of Ammonia by Haber process, iron acts as
catalyst and molybdenum or aluminium oxide acts as promoter.
A promoter cannot increase the rate of chemical reaction in the absence of a
catalyst.
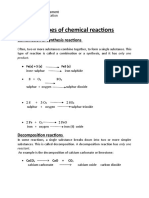
CHARECTERISTICS OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS:
Chemical reactions can be characterized by observing the type of changes they
have undergone.
1. Evolution of a gas as one of the product.
Example:
i. Zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid and liberates hydrogen gas, with
effervescence.
Zn +H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
ii. Calcium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid and gives Carbon
dioxide.
CaCO3 + 2 HCl → CaCl2 + H2O+ CO2
EFFERVESCENCE
The quick evolution of a gas seen as bubbles through a solution during a chemical
reaction is called effervescence.
2. Change in colour:
Some chemical reactions can be characterized by observing the change in colour
of the reactants.
Examples
i. Add a few pieces of iron in a solution of blue coloured copper sulphate
solution and observe. The blue coloured solution. Fades and finally
turns into light green due to the formation of the product ferrous
sulphate and reddish brown coloured particles settle down.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
ii. When copper turnings are added to Conc. Sulphuric acid, it forms a
blue coloured solution of Copper sulphate with evolution of a gas that
has the smell of burning sulphur.
Cu + H2SO4 (conc.) → CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O.
3. Formation of Precipitates
In certain chemical reactions an insoluble solid substance having a definite
colour is formed which are known as precipitates. Such reactions can be
characterized from the precipitate formed.
Example:
i. When silver nitrate solution and Sodium chloride solutions are added
together, a white precipitate of Silver chloride is firmed.
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
ii. When ferrous sulphate solution is added with Sodium hydroxide solution a
dirty green precipitate of Ferrous hydroxide is formed.
FeSO4 + 2NaOH → Fe (OH) 2 + Na2SO4.
3. Change of state:
In some reactions the reactants and the products formed may be in different
states.
Example
i. Ammonia and Hydrogen chloride are gases, when they react together form as
solid product Ammonium chloride.
NH3+ HCl → NH4Cl
2. Carbon and sulphur are solids, on heating together they form a liquid Carbon
sulphide.
C + 2S → CS2.
You might also like
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookFrom EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Notesashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988003Document9 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988003abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- X Ch.1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Key ConsentsDocument13 pagesX Ch.1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Key ConsentsheroNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations2Document28 pagesChemical Equations2Saleem BashaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationDocument15 pagesChemical Reaction and Equationsanjayjoshi.jnvNo ratings yet
- Lec Chemical ReactionDocument6 pagesLec Chemical ReactionSaroj SahNo ratings yet
- 1110 ChemistryDocument6 pages1110 ChemistryPatrickNo ratings yet
- Science Revision STUDY MATERIALDocument94 pagesScience Revision STUDY MATERIALYoNo ratings yet
- LAB ACT 5 Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument12 pagesLAB ACT 5 Types of Chemical ReactionsJerome MosadaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Chemical Equation NotesDocument7 pagesCh1 - Chemical Equation Notesਕੇਸ਼ਵ ਗੁਰਜਰNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Chemical Reaction ReviewerDocument4 pagesLESSON 2 Chemical Reaction Reviewerjohnromar VilasNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985607Document16 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985607abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Notes - Chemical Rections and EquationsDocument7 pagesNotes - Chemical Rections and EquationsLizannNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Ch:1 - Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument6 pagesIntroduction: Ch:1 - Chemical Reactions and EquationsJitendra PatelNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions - Introduction and ExamplesDocument5 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions - Introduction and ExamplesK.S.Yogeswar 7-CNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and Its EquationDocument125 pagesChemical Reaction and Its EquationSumanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations: ZN Grey Hsodil Znso H GasDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations: ZN Grey Hsodil Znso H GasBhavik ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions & Chemical Equations (1-39)Document39 pagesChemical Reactions & Chemical Equations (1-39)Anisha PanditNo ratings yet
- Kvs Ro, Jaipur: Class:-XDocument24 pagesKvs Ro, Jaipur: Class:-XVedant DuaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Integrated Science Summary and Exercise Chemistry 4 Chemical ReactionDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Integrated Science Summary and Exercise Chemistry 4 Chemical Reactionnana widyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions - Notes & Q - ADocument21 pagesChemical Reactions - Notes & Q - AYOGESHNo ratings yet
- CH 10 RedoxDocument33 pagesCH 10 RedoxTami MNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 1 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 1 2017 PDFKaran Pratap88% (8)
- H +CL 2Hcl 3bacl +al (So) 2alcl +3baso 2Na+2H O 2Naoh+H: QuestionsDocument98 pagesH +CL 2Hcl 3bacl +al (So) 2alcl +3baso 2Na+2H O 2Naoh+H: Questionsakky81No ratings yet
- VSA Type QuestionsDocument7 pagesVSA Type QuestionsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationsDocument8 pagesChemical Reaction and Equationsdsarika61No ratings yet
- M7 Analysis of Data1 by Group 10Document3 pagesM7 Analysis of Data1 by Group 10DaenizeeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Stoichiometry IVDocument71 pagesChemical Reactions Stoichiometry IVManuel Alejandro Soto CorreaNo ratings yet
- Type of Chemical Reaction: Prepared By-Abhay Bohra Guided by - Aakansha LalDocument8 pagesType of Chemical Reaction: Prepared By-Abhay Bohra Guided by - Aakansha LalVishal NandwanaNo ratings yet
- Chemicalreactionandequations Notes&PracticequestionsDocument8 pagesChemicalreactionandequations Notes&PracticequestionsVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Chm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument34 pagesChm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsOluwabusolami Akinola100% (1)
- All Reactions - PadhleDocument18 pagesAll Reactions - Padhlerakshitham603No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledAarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesRodel AzaresNo ratings yet
- 1 - NOTES Reactions and Stoichiometry PreAP ReviewDocument5 pages1 - NOTES Reactions and Stoichiometry PreAP ReviewspamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations-1Document22 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations-1krithicktcrNo ratings yet
- Aakash Institute: NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument8 pagesAakash Institute: NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsSuneethaNo ratings yet
- CatalysisDocument32 pagesCatalysismanvi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Selina-Sol-Concise-Chem-Class-10-Ch-8 JGHHJKDocument6 pagesSelina-Sol-Concise-Chem-Class-10-Ch-8 JGHHJKPROGRAMMING HUBNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction & EquationDocument8 pagesChemical Reaction & EquationMerakiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Ch. 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes 2020-2021Document4 pagesClass 10 Ch. 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes 2020-2021ramya anil nairNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988010Document4 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988010abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and Equations (Class X) : Characteristics of Chemical ReactionsDocument8 pagesChemical Reaction and Equations (Class X) : Characteristics of Chemical ReactionsAngelic ShineNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument19 pagesChemical Reactionsimraan smNo ratings yet
- S - 10 - HO 1.2 - Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument3 pagesS - 10 - HO 1.2 - Chemical Reactions and EquationsSaatvik RanjanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument8 pagesNCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equationssamiksha choudharyNo ratings yet
- 10th Science Byjus SolutionsDocument159 pages10th Science Byjus SolutionsChinmay B PNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Quarter 4: Module 2 Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesChemistry 1: Quarter 4: Module 2 Types of Chemical ReactionsRain AlmsNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination or Synthesis ReactionsDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination or Synthesis ReactionselizabethNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument27 pagesChem NotesRaya DhanushNo ratings yet
- Advanced Material Chemistry Term 1Document74 pagesAdvanced Material Chemistry Term 1Shruti SinghNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Chapter - 1Document8 pagesNcert Solution Chapter - 1joydeep17590No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 File 1 PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 1 File 1 PDFAadi ProNo ratings yet
- 1455780078science 10 - T 1 - (CH 1)Document29 pages1455780078science 10 - T 1 - (CH 1)vv1234567No ratings yet
- ChemChapter7 RojasDocument6 pagesChemChapter7 RojasTn F'dzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CH 1 & 2Document17 pagesChemistry CH 1 & 2Mallesh RaoNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) Chemical ReactionsDocument32 pages(CHEM) Chemical Reactionssodiumboyupinthishoe100% (2)
- Lab - Investigating Chemical ReactionsDocument14 pagesLab - Investigating Chemical ReactionsYusuf RaheemNo ratings yet
- Changes and ReactionsDocument4 pagesChanges and ReactionsMayukh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Ix Biology Notes (08!07!2021)Document3 pagesIx Biology Notes (08!07!2021)Dilson Babu DonNo ratings yet
- Ix Mathematics Unit 2 Maths - CH 2 - Class NotesDocument4 pagesIx Mathematics Unit 2 Maths - CH 2 - Class NotesDilson Babu DonNo ratings yet
- IX Geography Chapter 3 Rotation and RevolutionDocument11 pagesIX Geography Chapter 3 Rotation and RevolutionDilson Babu DonNo ratings yet
- IX Physics Reflection of Light Day-9 NotesDocument3 pagesIX Physics Reflection of Light Day-9 NotesDilson Babu DonNo ratings yet
- MercaptansDocument8 pagesMercaptansAnand ChristyNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Energy and ChemistryDocument4 pagesActivity 3 - Energy and ChemistryTikie TokieNo ratings yet
- Final Hydrogen-Peroxide ReportDocument9 pagesFinal Hydrogen-Peroxide ReportAshley PeridaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 2Document5 pagesEnzymes 2Ema Arroyo LopezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 BIO121Document12 pagesExperiment 4 BIO121Pui Ling ChanNo ratings yet
- Elephants ToothpasteDocument3 pagesElephants Toothpasteapi-528729236No ratings yet
- Brochure LF Lubicants and Fuels Global enDocument5 pagesBrochure LF Lubicants and Fuels Global enJulian SerranoNo ratings yet
- ICT Mumbai-Marathwada Campus, Jalna Chemical Reaction Engineering Batch: 2019-20 10-Feb-2022 Test 1 Marks: 22 Time: 2 H Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesICT Mumbai-Marathwada Campus, Jalna Chemical Reaction Engineering Batch: 2019-20 10-Feb-2022 Test 1 Marks: 22 Time: 2 H Page 1 of 2soham kawaleNo ratings yet
- Silver MetalDocument5 pagesSilver MetalSholekhah ArviyantiNo ratings yet
- H2O2 DecompositionDocument14 pagesH2O2 Decompositionpulcherimus1No ratings yet
- Chemical Incompatibility Part2Document11 pagesChemical Incompatibility Part2Dina KhalidNo ratings yet
- Vitamina C PDFDocument46 pagesVitamina C PDFStefano D'AlessandroNo ratings yet
- CHM12 Experiment 5 KineticsDocument15 pagesCHM12 Experiment 5 Kineticsshaam030% (2)
- Mole Concept NewDocument10 pagesMole Concept Newsrinivas2111No ratings yet
- Pahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryDocument285 pagesPahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryJeyShida100% (1)
- Ácido Paracético en PreparadosDocument3 pagesÁcido Paracético en PreparadosAdrián GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Safe Suitable Ingredients - FSIS Directive 7120.1 Revision 7Document48 pagesSafe Suitable Ingredients - FSIS Directive 7120.1 Revision 7Laura Michelle RossNo ratings yet
- Sulfate Removal From Waste Chemicals by Precipitation PDFDocument8 pagesSulfate Removal From Waste Chemicals by Precipitation PDFmarcoNo ratings yet
- BIDIOX TecnologyH2O Heimo (English) 06.17Document41 pagesBIDIOX TecnologyH2O Heimo (English) 06.17Daniel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Ozone Pharmaceutical Water SystemsDocument4 pagesDissolved Ozone Pharmaceutical Water Systemsraju155940550% (2)
- Wool 482 582 12 T 15Document22 pagesWool 482 582 12 T 15KathirrveluSubramainanNo ratings yet
- Safety and Handling: Technical Data SheetDocument15 pagesSafety and Handling: Technical Data SheetRonak MotaNo ratings yet
- IOC - IRP - Home Test-3 (Without Answer) - SendDocument20 pagesIOC - IRP - Home Test-3 (Without Answer) - SendNicholas BourbakiNo ratings yet
- Zigmond MJ, Burke RE - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument14 pagesZigmond MJ, Burke RE - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Diseaseursula_ursula100% (1)
- Enhanced Visual Wireless ElectrochemiluminescenceDocument8 pagesEnhanced Visual Wireless ElectrochemiluminescenceXuân Vũ Quốc Huy HồNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Polymer ChemistryDocument48 pagesFundamentals of Polymer ChemistryRUSTSHIELD Indonesia100% (1)
- 1340-02 Assessment Report PDFDocument99 pages1340-02 Assessment Report PDFSergio RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Corrosion Potentials of Aluminum Alloys: Standard Test Method ForDocument4 pagesMeasurement of Corrosion Potentials of Aluminum Alloys: Standard Test Method ForNav Talukdar100% (1)
- Seperation Techniques PDFDocument232 pagesSeperation Techniques PDFAmitranjan KarNo ratings yet