Professional Documents
Culture Documents
References: Chapter 3 - Sec - Ons 3-6, 3-7, 3-8
Uploaded by
nickOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
References: Chapter 3 - Sec - Ons 3-6, 3-7, 3-8
Uploaded by
nickCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Review
Chapter 1: References: Chapter 3 - Sec ons 3-6, 3-7, 3-8 • Conversion between phasor-domain and me-
• Circuit Representa ons and Nota ons Chapter 4: Opera onal Ampli ers domain quan es
• Electric Charge • Op-Amp Characteris cs • Determining an ac voltage/current in phasor-
• Electric Current • Ideal Op-Amp Model domain and conver ng back to me-domain
• Voltage • Op-Amp Applica ons: • The Lead/lag concept
• Power and Passive Sign Conven on - Noninver ng ampli er circuit References: Chapter 7 - Sec ons 7-1, 7-2, 7-3, 7-4,
• Circuit Elements and Nota ons - Inver ng ampli er circuit 7-5, 7-6, 7-9 (excluding Wye-Delta transforma on
Refs: Sec ons 1-3, 1-4, 1-5, 1-6; solved examples, - Inver ng Summing Ampli er circuit of impedances in Sec on 7-5);
HW problems, and class lectures - Di erence Ampli er
- Voltage follower/Bu er Chapter 8: AC Power
Chapter 2: References: • Periodic Waveforms
• Ohm’s Law & Passive Sign Conven on, Sec ons 4-1, 4-2, 4-3, 4-4, 4-5, 4-6, 4-7; • Average Power, Complex Power, Reac ve
Resistance, Conductance, i-v characteris cs of Power, Apparent Power
ideal resistor, series/parallel connec ons of Chapter 5: Analysis of RLC circuits under dc • The Power Factor
elements condi ons • Power Factor Compensa on (only in nal
• Kirchho ’s Laws (KCL, KVL) • Determining currents through capacitors and exam)
• Circuit Analysis using KCL and KVL inductors • Maximum Power Transfer
• Solving linear system equa ons using Cramer’s • Determining voltages across capacitors and References: Chapter 8 - Sec ons 8-1, 8-2, 8-3, 8-4,
Rule inductors 8-5
• Equivalent Circuits and source transforma on • Determining power transferred in/out for
*(conver ng voltage-source/resistor into capacitors and inductors Chapter 11: Magne cally Coupled Circuits
*current-source/resistor circuit and vice-versa) • Determining amount of energy stored in • Magne c Coupling, Dot Conven on
• Combining resistors in series and resistors in capacitors and inductors • Analyzing magne cally couples circuits
parallel References: Chapter 5 - Sec ons 5-2, 5-3 • Input Impedance of magne cally couples
• Wye–Delta (Y–Δ) Transforma on circuits
• The Wheatstone Bridge & Wheatstone Chapter 7 Analysis of RLC circuits under ac • Coupling Coe cient
Sensor condi ons • T and Pi Equivalent Circuits
Refs: Sec ons 2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-4, 2-5; • U n d e rsta n d i n g s i n u s o i d a l wavefo r m s • Transformers and Ideal Transformers
parameters and lead/lag concept • Thevenin Equivalent of Ideal Transformers
Chapter 3: • Understanding complex variables/numbers • Autotransformers
• Linear Circuits & Ohm’s Law and conversion between rectangular and polar References: Chapter 11 - Sec ons 1, 2, 4;
• Node-voltage Analysis (including supernode coordinates
concept) • Conver ng from me-domain form to
• Mesh-Current Analysis (including supermesh frequency-domain form (i.e., phasor-domain
concept) counterpart) and vice-versa
• Source superposi on • Finding impedance of capacitor, inductor,
References: Chapter 3 Sec ons 3-1, 3-2, 3-3, 3-5; resistor, or a combina on
solved examples, HW problems, and class lecture • Finding equivalent impedance in a given ac
circuit
Chapter 3: Analysis Techniques • Analyzing ac RLC circuits using phasor analysis
• Thevenin Equivalent Circuits technique: KVL, KCL, Node-voltage Analysis,
• Norton Equivalent Circuits Mesh-Current Analysis, Source superposi on,
• Maximum Power Transfer Thevenin Equivalent, Norton Equivalent, …etc.
ff
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ff
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ffi
ti
ti
fi
ti
fi
ti
ti
ti
ti
fi
ti
ti
ff
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
fi
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
fi
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
ti
fi
ti
ti
ti
ti
You might also like
- Features Description Cutout Details Ordering Information: Trip Circuit Supervision RelayDocument4 pagesFeatures Description Cutout Details Ordering Information: Trip Circuit Supervision RelayDeepak WaikarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Construction Kit DC Virtual Lab HTML Guide - enDocument3 pagesCircuit Construction Kit DC Virtual Lab HTML Guide - enDannisa aaNo ratings yet
- SF6 Insulated Instrument Transformers For Outdoor Installation From 362 KV To 550 KVDocument4 pagesSF6 Insulated Instrument Transformers For Outdoor Installation From 362 KV To 550 KVAleksa KneževićNo ratings yet
- IMS Lab Report 1Document4 pagesIMS Lab Report 1Waleed TariqNo ratings yet
- Jambaran Tiung Biru Project: Electrical Power and Control Cable Schedule - Substation No. 1Document2 pagesJambaran Tiung Biru Project: Electrical Power and Control Cable Schedule - Substation No. 1Alif AnsharNo ratings yet
- Creating A Reactive Energy Pulse Output Based On The ADE7753Document12 pagesCreating A Reactive Energy Pulse Output Based On The ADE7753api-3744762No ratings yet
- EXFO Reference-Poster Raman V1 enDocument3 pagesEXFO Reference-Poster Raman V1 enBoy Tai HinNo ratings yet
- 24-Port 100/1000BASE-X SFP With 4-Port 10G SFP+ L2/L4 Managed Metro Ethernet SwitchDocument8 pages24-Port 100/1000BASE-X SFP With 4-Port 10G SFP+ L2/L4 Managed Metro Ethernet SwitchhauNo ratings yet
- In-Lab Work: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 2262 - Electric CircuitsDocument4 pagesIn-Lab Work: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 2262 - Electric CircuitsThiago Araújo de AssisNo ratings yet
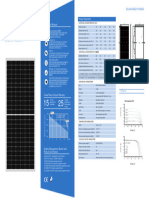
- Solar Panel 550W Technical SpecificationsDocument1 pageSolar Panel 550W Technical SpecificationsRohit MEPNo ratings yet
- Page 1 - Location and Site PlanDocument1 pagePage 1 - Location and Site PlanElynor Acio MercadoNo ratings yet
- KV-5500/5000/3000 KV-DR1: Programmable ControllerDocument2 pagesKV-5500/5000/3000 KV-DR1: Programmable ControllerCatngoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8: Voltage Regulation: ECE 5984: Power Distribution System AnalysisDocument34 pagesLecture 8: Voltage Regulation: ECE 5984: Power Distribution System Analysisante mitarNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi ElectrikDocument38 pagesMitsubishi ElectrikTemirlanNo ratings yet
- ABB - AF - Contactor - 4poleDocument6 pagesABB - AF - Contactor - 4poleAhmad HamdanNo ratings yet
- Sunlight RES SOPzS PDFDocument4 pagesSunlight RES SOPzS PDFAnonymous AnonyNo ratings yet
- RF and EMC Formulas and Charts: Conversions for 50Ω Environment Antenna Equations www.arworld.usDocument1 pageRF and EMC Formulas and Charts: Conversions for 50Ω Environment Antenna Equations www.arworld.usamirNo ratings yet
- AKRE 4lista ANG Koregirano 1Document2 pagesAKRE 4lista ANG Koregirano 1JovanNo ratings yet
- Current Electrical: Flow Electrons ATDocument2 pagesCurrent Electrical: Flow Electrons ATFajar MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Rotary Encoder E40S-H-HB Series Intruction ManualDocument1 pageRotary Encoder E40S-H-HB Series Intruction ManualArie Cahyo UtomoNo ratings yet
- Eplob Eplob/A Epmob Epmob/A: PhotocellsDocument2 pagesEplob Eplob/A Epmob Epmob/A: PhotocellsSupuran RichardoNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetRobertoNo ratings yet
- Installation & Owner'S Manual: EnglishDocument8 pagesInstallation & Owner'S Manual: EnglishAdilen A. NadlorNo ratings yet
- CX3G PLC User Manual V22.11Document2 pagesCX3G PLC User Manual V22.11Lalo MendezNo ratings yet
- Installation - Kwh-3 Energy Meter: Reset To InstallDocument2 pagesInstallation - Kwh-3 Energy Meter: Reset To InstalldeetaufikNo ratings yet
- EVLunic AC-Wallbox Selection Table Rev2 ABBDocument1 pageEVLunic AC-Wallbox Selection Table Rev2 ABBManuel Alejandro Erices BravoNo ratings yet
- Development of A 500-kV DC XLPE Cable SystemDocument6 pagesDevelopment of A 500-kV DC XLPE Cable SystemalchernNo ratings yet
- Rockford Fosgate Prime r150x2 Manual de PropietarioDocument17 pagesRockford Fosgate Prime r150x2 Manual de PropietarioFernando FloresNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instruccion 5kvaDocument1 pageManual de Instruccion 5kvaJuanca PiaNo ratings yet
- Samsung Mm-E320 SCHDocument8 pagesSamsung Mm-E320 SCHCarlos EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Hoppecke Sun Power VR M BrochureDocument2 pagesHoppecke Sun Power VR M Brochurediego santiago paucarNo ratings yet
- Upscaling Slides May 2012Document41 pagesUpscaling Slides May 2012chrisofoma100% (1)
- Models Available Psp1 Plug-In Special Purpose Supervisory SwitchDocument2 pagesModels Available Psp1 Plug-In Special Purpose Supervisory SwitchArgile-assholeNo ratings yet
- Cat 312c Diagr Elec PDFDocument4 pagesCat 312c Diagr Elec PDFDaniel GalvisNo ratings yet
- Cat 312c Diagr ElecDocument4 pagesCat 312c Diagr ElecDaniel Galvis75% (12)
- Mulimbayan Residence - EE (For Construction)Document4 pagesMulimbayan Residence - EE (For Construction)Jhanchris CortezNo ratings yet
- IN Pulse Oximeter 7090Document2 pagesIN Pulse Oximeter 7090klamaryNo ratings yet
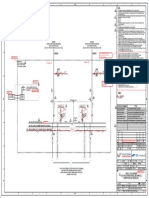
- 2 DRP001-OUF-490010-E-SLD-004-001-R1-signed-signed - Signed-Signed PDFDocument1 page2 DRP001-OUF-490010-E-SLD-004-001-R1-signed-signed - Signed-Signed PDFShivaNo ratings yet
- Digital HV 5KV Insulation Tester HTC 6250INDocument1 pageDigital HV 5KV Insulation Tester HTC 6250INindustrialindiaNo ratings yet
- 02.optical Network TestingDocument1 page02.optical Network Testingphuongnt1710No ratings yet
- QEP Range: Which Model Will You Choose?Document2 pagesQEP Range: Which Model Will You Choose?Ahmad El KhatibNo ratings yet
- SPR3 en Tcd210147ad 20220704 Inst WDocument2 pagesSPR3 en Tcd210147ad 20220704 Inst WManel CoelloNo ratings yet
- HR106X brochure-EN-20211021Document2 pagesHR106X brochure-EN-20211021ufology123No ratings yet
- SP0793-E951.00-G30-1252 - Rev A - VSD - Block Diagram - ABB - 2021-01-20Document2 pagesSP0793-E951.00-G30-1252 - Rev A - VSD - Block Diagram - ABB - 2021-01-2018-01-0096No ratings yet
- Epmab Epmab/A: PhotocellsDocument2 pagesEpmab Epmab/A: PhotocellsSupuran RichardoNo ratings yet
- ABBManobra A LineMidi2008Document82 pagesABBManobra A LineMidi2008Claudia MartinsNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Loads: Notes and SpecificationsDocument1 pageSchedule of Loads: Notes and SpecificationsAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Tan-Delta and Capacitance Test Set For HT Generator/Motor TestingDocument3 pagesTan-Delta and Capacitance Test Set For HT Generator/Motor Testingmustafa180567% (3)
- QB400Document2 pagesQB400Éverton KafskiNo ratings yet
- Fusion PosterDocument1 pageFusion PosterGreg SonnenfeldNo ratings yet
- Plakat Transient Immunity TestingDocument1 pagePlakat Transient Immunity TestingSKN PiorunNo ratings yet
- FireNET Plus Wiring DiagramDocument1 pageFireNET Plus Wiring DiagramYusuf HungundNo ratings yet
- Power Supply 1/4 Schematic Diagram: Caution ! Caution !: ATTENTION: Utiliser Un Fusible de Rechange de MDocument6 pagesPower Supply 1/4 Schematic Diagram: Caution ! Caution !: ATTENTION: Utiliser Un Fusible de Rechange de MErick MoraNo ratings yet
- ETAP-Harmonics Study ReportDocument70 pagesETAP-Harmonics Study ReportBilal Ashraf100% (2)
- Talyvel SchematicDocument1 pageTalyvel SchematicChuck NorrisNo ratings yet
- Ayl 950GDocument4 pagesAyl 950Ghamza MoussaidNo ratings yet
- High Temperature Infrared Thermometer IRX68 IRX69Document1 pageHigh Temperature Infrared Thermometer IRX68 IRX69industrialindiaNo ratings yet
- CityRover Workshop ManualDocument645 pagesCityRover Workshop ManualTheCityRover100% (17)
- Smart Glasses Augmented Reality: April 2021Document5 pagesSmart Glasses Augmented Reality: April 2021علي السجاد خضير عباس اللاميNo ratings yet
- Electronics: A Review On Small Power Rating PV Inverter Topologies and Smart PV InvertersDocument26 pagesElectronics: A Review On Small Power Rating PV Inverter Topologies and Smart PV InvertersPadmavathi RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 InstrumentDocument24 pagesChapter 4 InstrumentHopedejene DejeneNo ratings yet
- 973B - Hi - Tech Smart Key - Handbook - 01 - 08 - 09 PDFDocument64 pages973B - Hi - Tech Smart Key - Handbook - 01 - 08 - 09 PDFNguyễn Chánh Sĩ100% (6)
- Nabl 500 PDFDocument124 pagesNabl 500 PDFFundary ShopNo ratings yet
- Nokia 808 Pureview: Service Manual Level 1&2Document20 pagesNokia 808 Pureview: Service Manual Level 1&2Damar Yoga KusumaNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: HSU-12HQA03/R2 (DB)Document16 pagesOperation Manual: HSU-12HQA03/R2 (DB)AwaisNo ratings yet
- F2490Document8 pagesF2490John Amortegui100% (2)
- Fpga WorkshopDocument4 pagesFpga WorkshopPardha Saradhi DamarlaNo ratings yet
- EOM017Document140 pagesEOM017the dovanNo ratings yet
- 2300 - Series Vibration Monitors Keyphasors Datasheet - With Hookup 105M0340Document24 pages2300 - Series Vibration Monitors Keyphasors Datasheet - With Hookup 105M0340soumya voraNo ratings yet
- Standard Questioner For Radar Navigation, Radar Plotting and Use of ArpaDocument5 pagesStandard Questioner For Radar Navigation, Radar Plotting and Use of ArpaAbdo KhamisNo ratings yet
- Current Gain Enhancement at High-Temperature Operation of Triple-Quantum-Well Heterojunction Bipolar Light-Emitting Transistor For Smart Thermal Sensor ApplicationDocument8 pagesCurrent Gain Enhancement at High-Temperature Operation of Triple-Quantum-Well Heterojunction Bipolar Light-Emitting Transistor For Smart Thermal Sensor Applicationsam rokNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms and Mechanical DevicesDocument10 pagesMechanisms and Mechanical Devicesoana_avram50% (4)
- Cannon Connector Ms - E-RDocument24 pagesCannon Connector Ms - E-RsunhuynhNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3: Universiti Teknik Malaysia MelakaDocument2 pagesTutorial 3: Universiti Teknik Malaysia MelakaSYAFIQAH ISMAIL0% (2)
- Mars5 Operation ManualDocument99 pagesMars5 Operation Manualmj alvarezNo ratings yet
- Isotech Industrial SolutionsDocument23 pagesIsotech Industrial SolutionsHernán ZapataNo ratings yet
- VHF Transmit-Receive Antenna / VHF Sende-Empfangs-Antenne: Sta IsfDocument1 pageVHF Transmit-Receive Antenna / VHF Sende-Empfangs-Antenne: Sta Isfson nguyenNo ratings yet
- System/Battery Type Emerson Narada 12NDT100A Narada 12NDT180 Vision CT12 180XDocument2 pagesSystem/Battery Type Emerson Narada 12NDT100A Narada 12NDT180 Vision CT12 180XBysNo ratings yet
- 200A, 15 KV Class Loadbreak Rotatable Feed Thru Insert: 15-LFTI200Document3 pages200A, 15 KV Class Loadbreak Rotatable Feed Thru Insert: 15-LFTI200Diego AlvesNo ratings yet
- ARNU42GTMC4Document2 pagesARNU42GTMC4jaimegutierrezlinganNo ratings yet
- Neo Classica 13SPDocument1 pageNeo Classica 13SPjuliando indamedNo ratings yet
- RS PRO Digital Multimeters - IDM8351 Bench Digital MultimeterDocument4 pagesRS PRO Digital Multimeters - IDM8351 Bench Digital Multimeterjuan manuelNo ratings yet
- cgs75 VcsDocument5 pagescgs75 VcsMustafa Umut SaracNo ratings yet
- 13.-JMG M-PRO-S Fintec 1080 ConeDocument30 pages13.-JMG M-PRO-S Fintec 1080 ConeJose Luis Atao SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Digital HD Video Camera RecorderDocument69 pagesService Manual: Digital HD Video Camera RecorderDanNo ratings yet
- GIS Installation PDFDocument143 pagesGIS Installation PDFHicham Boutouche100% (2)
- Geiger-Muller Tube (GM Tube)Document12 pagesGeiger-Muller Tube (GM Tube)bdb6wxhyxfNo ratings yet