Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MATH 4000 - Lebesgue Integration Homework
Uploaded by
Tom LiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH 4000 - Lebesgue Integration Homework
Uploaded by
Tom LiCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH 4000 - LEBESGUE INTEGRATION - FALL 2020
Instructor: Jie Xiao ∼ Days: MWF ∼ Time: 10:00-10:50 ∼ Room: online
Assignment 2 (Riemann Integrals) - due by Oct 7, 2020
1. Let f be continuous on [a, b].
(i) If g is defined on [a, b] and equal to f at every Rpoint of [a, b]R bexcept for at most finitely
b
many points, show that g is integrable on [a, b] and a g(x) dx = a f (x) dx.
Rb
(ii) Prove that exists c ∈ (a, b) such that a f (x) dx = f (c)(b − a).
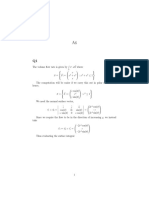
2. (i) Find the Fourier series of
x2 for x ∈ [−π, 0)
f (x) = f (x + 2π) = f (x).
with
π2 for x ∈ [0, π)
n−2 = π2 /6.
P∞
(ii) Deduce from (i) that n=1
3. Let f : [0, 1] → R be defined by
q−1 if x = pq−1 where p, 0 , q ∈ N have no common factors
f (x) =
0 if x is irrational, or x = 0, 1.
(i) Prove that f is continuous at every irrational point of [0, 1] and discontinuous where f (x) ,
0.
(ii) Prove that,
R 1 in spite of having infinitely many discontinuities, f is Riemann integrable on
[0, 1], and 0 f = 0.
(iii) Show that the composite function h = g ◦ f is not Riemann integrable whenever
1 as x ∈ (0, 1]
g(x) =
0 as x = 0.
4. Verify the following three facts:
(i) A \ B does not have measure zero if A ⊂ R does not have measure zero and B ⊂ A has
measure zero.
(ii) the Cantor n-ary set has measure zero.
(iii) If F is the Cantor ternary set and 1F : [0, 1] → R which takes 1 on F and 0 otherwise,
then 1F is Riemann integrable and its integral over [0, 1] is 0.
5. Let f : [0, 1] → R be such that
x2 sin x−2 for x , 0
f (x) =
0 for x = 0.
Prove that f is continuous and differentiable but f 0 is not Riemann integrable.
You might also like
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Ma403 hw5Document3 pagesMa403 hw5R KumarNo ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5monkeyng.bmedNo ratings yet
- 243 W 23 Ass 6Document1 page243 W 23 Ass 6谭朝予No ratings yet
- HW 1Document1 pageHW 1Vladimir EgorovNo ratings yet
- MATH20101 Jan 2016Document9 pagesMATH20101 Jan 2016Pawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Lebesgue Measure and Fourier Transforms QuestionsDocument6 pagesLebesgue Measure and Fourier Transforms QuestionsdanNo ratings yet
- Real 98sDocument2 pagesReal 98spusa123No ratings yet
- Analysis On Manifolds Assignment 1Document2 pagesAnalysis On Manifolds Assignment 1James AttenboroughNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Manifolds Assignment 1Document2 pagesAnalysis On Manifolds Assignment 1James AttenboroughNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet 4Document2 pagesExercise Sheet 4C ZoliansangiNo ratings yet
- Test 1 On Riemann IntegrationDocument1 pageTest 1 On Riemann IntegrationDushyant RathoreNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis Final Solutions ExplainedDocument10 pagesReal Analysis Final Solutions ExplainedBikash chutiaNo ratings yet
- May 2019 PaperDocument5 pagesMay 2019 PaperSomeoneNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Computational Mathematics Assignment MA1101 - Tutorial1Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Computational Mathematics Assignment MA1101 - Tutorial1Naresh SehdevNo ratings yet
- Work SheetDocument1 pageWork SheetPeter HuaNo ratings yet
- Analysis Epi Sheet3Document2 pagesAnalysis Epi Sheet3Tom BombardeNo ratings yet
- MATH 104 SOLUTIONSDocument5 pagesMATH 104 SOLUTIONSRizky AdhaNo ratings yet
- AnalysisPrelimJanuary2023 PDFDocument2 pagesAnalysisPrelimJanuary2023 PDFrcherry calaorNo ratings yet
- 2004-01-analysis-t1Document2 pages2004-01-analysis-t1Sachin BarthwalNo ratings yet
- Xercise: Advanced Subjective QuestionsDocument2 pagesXercise: Advanced Subjective QuestionsAnmol KumarNo ratings yet
- Unm Exam 202108 Real QualDocument2 pagesUnm Exam 202108 Real Qualsahan gunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Applications of Lagrange's theorem in integrationDocument12 pagesApplications of Lagrange's theorem in integrationhungkgNo ratings yet
- Homework 6Document3 pagesHomework 6Luis EduardoNo ratings yet
- (Odd) End Semester Examination: November, 2019Document4 pages(Odd) End Semester Examination: November, 2019Sanjoy BrahmaNo ratings yet
- MA101 Integration SummaryDocument5 pagesMA101 Integration Summaryleandro1281No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 1Ayush Kumar100% (1)
- Tutorial Sheet 4 & 5Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 4 & 5Avinash Kumar Jha 4-Year B.Tech. Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- 5a - The Riemann IntegralDocument3 pages5a - The Riemann IntegralBhaskar KarolNo ratings yet
- 243 W 23 Ass 3Document1 page243 W 23 Ass 3谭朝予No ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument8 pagesExercisekian13No ratings yet
- Analysis Prelim August 2022Document2 pagesAnalysis Prelim August 2022rcherry calaorNo ratings yet
- smat_back_paperDocument2 pagessmat_back_paperjioevatestingNo ratings yet
- Analysis II Sheet 1Document1 pageAnalysis II Sheet 1TURKHUNTER 571No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Manish AtriNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Qualifying Exam, Real Analysis Fall 2009,: J J 1 N 1 N N 1 NDocument2 pagesPh.D. Qualifying Exam, Real Analysis Fall 2009,: J J 1 N 1 N N 1 NpaimoNo ratings yet
- Ma403 hw4Document2 pagesMa403 hw4R KumarNo ratings yet
- 243 W 23 Ass 5Document1 page243 W 23 Ass 5谭朝予No ratings yet
- Analysis 1 Examples 2Document2 pagesAnalysis 1 Examples 2HasufinNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers and Sequences AssignmentDocument7 pagesReal Numbers and Sequences AssignmentSURYANSH KUMAR 18110168No ratings yet
- CALCULUS PROBLEM SHEETDocument2 pagesCALCULUS PROBLEM SHEETs rkNo ratings yet
- MA101, Real Analysis Riemann IntegrationDocument1 pageMA101, Real Analysis Riemann IntegrationShivam ShekharNo ratings yet
- MA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiability: Exercise Set 1Document1 pageMA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiability: Exercise Set 1AdityaNo ratings yet
- Real (End1)Document1 pageReal (End1)akashNo ratings yet
- Mat202 Tutorials Sheets IDocument7 pagesMat202 Tutorials Sheets ITaffohouo Nwaffeu Yves ValdezNo ratings yet
- MA 105: Calculus (Autumn 2019) Additional Problems For Tutorial 5Document1 pageMA 105: Calculus (Autumn 2019) Additional Problems For Tutorial 5gyandevNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Tripos Part IA 2021Document35 pagesMathematical Tripos Part IA 2021ndndbshxNo ratings yet
- Ass2019 Maths1 Single Variable PDFDocument2 pagesAss2019 Maths1 Single Variable PDFAnantaRajNo ratings yet
- Assignment I: (To Be Submitted in Tutorial Class by September 13, 2019)Document2 pagesAssignment I: (To Be Submitted in Tutorial Class by September 13, 2019)AnantaRajNo ratings yet
- 2011-08-analysis-t1Document2 pages2011-08-analysis-t1Sachin BarthwalNo ratings yet
- Convex Functions and OptimizationDocument20 pagesConvex Functions and OptimizationhoalongkiemNo ratings yet
- Further Questions For EnthusiastsDocument2 pagesFurther Questions For EnthusiastsB KNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Tripos Part IA 2017Document34 pagesMathematical Tripos Part IA 2017mile1966No ratings yet
- Real Analysis - EndsemDocument13 pagesReal Analysis - EndsemHari Madhavan Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2020Document2 pagesAssignment 1 2020BISWARUP MANDALNo ratings yet
- Mathematics IV SEMDocument3 pagesMathematics IV SEMram_somalaNo ratings yet
- Integration Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIntegration Cheat SheetgwagsiglenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2JOHNNo ratings yet
- 3098 Mathcc5 L 3Document4 pages3098 Mathcc5 L 3neetmonthsNo ratings yet
- IELTSSupportTools 1 28 18Document1 pageIELTSSupportTools 1 28 18Tom LiNo ratings yet
- Complete IELTS Reading Answer SheetDocument1 pageComplete IELTS Reading Answer SheetTom LiNo ratings yet
- IELTSSupportTools 1 28 15Document1 pageIELTSSupportTools 1 28 15Tom LiNo ratings yet
- The Test That Opens Doors Around The WorldDocument1 pageThe Test That Opens Doors Around The WorldTom LiNo ratings yet
- IELTSSupportTools 1 28 14Document1 pageIELTSSupportTools 1 28 14Tom LiNo ratings yet
- Helping You Get Ready For Test DayDocument1 pageHelping You Get Ready For Test DayTom LiNo ratings yet
- Understanding IELTS Academic and IELTS General TrainingDocument1 pageUnderstanding IELTS Academic and IELTS General TrainingTom LiNo ratings yet
- IELTSSupportTools 1 28 16Document1 pageIELTSSupportTools 1 28 16Tom LiNo ratings yet
- Cheat 8Document1 pageCheat 8Tom LiNo ratings yet
- Accessible and Convenient: The IELTS Band Score ScaleDocument1 pageAccessible and Convenient: The IELTS Band Score ScaleTom LiNo ratings yet
- Cheat 7Document1 pageCheat 7Tom LiNo ratings yet
- 1ielts Support Tools 2018Document28 pages1ielts Support Tools 2018Bacem FarhatNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Computer Science Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTheoretical Computer Science Cheat SheetTom LiNo ratings yet
- IELTS Choice: Paper or ComputerDocument1 pageIELTS Choice: Paper or ComputerTom LiNo ratings yet
- Cheat 4Document1 pageCheat 4Tom LiNo ratings yet
- Cheat 10Document1 pageCheat 10Tom LiNo ratings yet
- Cheat 5Document1 pageCheat 5Tom LiNo ratings yet
- 4000assignment2020 1Document1 page4000assignment2020 1Tom LiNo ratings yet
- Cheat 1Document1 pageCheat 1Tom LiNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Computer Science Cheat Sheet IdentitiesDocument1 pageTheoretical Computer Science Cheat Sheet IdentitiesTom LiNo ratings yet
- IELTS Refund RequestDocument2 pagesIELTS Refund RequestTom LiNo ratings yet
- 4000assignment2020 1Document1 page4000assignment2020 1Tom LiNo ratings yet
- 1ielts Support Tools 2018Document28 pages1ielts Support Tools 2018Bacem FarhatNo ratings yet
- 4000assignment2020 1Document1 page4000assignment2020 1Tom LiNo ratings yet
- 1ielts Support Tools 2018Document28 pages1ielts Support Tools 2018Bacem FarhatNo ratings yet
- National University: Syllabus Department of MathematicsDocument9 pagesNational University: Syllabus Department of MathematicsbdriponNo ratings yet
- TT2223 Week 12a Z-TransformDocument39 pagesTT2223 Week 12a Z-TransformAjiMaulanaNo ratings yet
- Exam Question Complex AnalysisDocument3 pagesExam Question Complex AnalysisJaZz SFNo ratings yet
- Calculus Signature Assignment 1 The Mean Value Theorem 1Document2 pagesCalculus Signature Assignment 1 The Mean Value Theorem 1api-331199595No ratings yet
- Power Series & Taylor SeriesDocument59 pagesPower Series & Taylor SeriesNguyễnXuânNo ratings yet
- Nsu Computer ScienceDocument24 pagesNsu Computer ScienceMir SahibNo ratings yet
- 20MA210 Syllabus & Other DetailsDocument3 pages20MA210 Syllabus & Other DetailsAbhijith iyerNo ratings yet
- AMATH 231 Calculus IV Solutions A6Document5 pagesAMATH 231 Calculus IV Solutions A6Forsen ShungiteNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics DR A B Mathur, V P Jaggi VolumeDocument1,122 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics DR A B Mathur, V P Jaggi Volumepaakhipriya10No ratings yet
- Calculus Topic 5Document11 pagesCalculus Topic 5Ceejay IgnacioNo ratings yet
- "Differential Equations and Its Applications": Jignsa Student Study Project inDocument18 pages"Differential Equations and Its Applications": Jignsa Student Study Project inmishrachiranjeev06No ratings yet
- Unit Iii Partial Differential Equations: Z X A y BDocument30 pagesUnit Iii Partial Differential Equations: Z X A y BCSETUBENo ratings yet
- Z TransformsDocument25 pagesZ TransformsSujesh ShettyNo ratings yet
- Delta Notes PDFDocument7 pagesDelta Notes PDFfatikNo ratings yet
- A Little Bit of CalculusDocument211 pagesA Little Bit of CalculusThirumal VenkatNo ratings yet
- MIT6 003F11 Lec06 PDFDocument38 pagesMIT6 003F11 Lec06 PDFIlhariri Muhammad IrlisNo ratings yet
- Mat - TurunanDocument19 pagesMat - TurunanJesslyn IvaniaNo ratings yet
- 27 Introduction To Laplace TransformsDocument21 pages27 Introduction To Laplace TransformsSadek AhmedNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 CE2C - Definition and Classifications of Differential Equations-1Document4 pagesMODULE 1 CE2C - Definition and Classifications of Differential Equations-1alfred nuludNo ratings yet
- I. A Maron-Problems in Calculus of One Variable-Mir Publishers, Moscow (1973)Document453 pagesI. A Maron-Problems in Calculus of One Variable-Mir Publishers, Moscow (1973)Dilip Bhati100% (1)
- Numerical RecipesDocument8 pagesNumerical RecipesNicolasNo ratings yet
- Assignmnet # 03: A. Implicit DerivativesDocument4 pagesAssignmnet # 03: A. Implicit DerivativesAbraham Mallari MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Habits of Mind Article 1Document8 pagesHabits of Mind Article 1api-296658056No ratings yet
- Assignment: 1: Regional Centre: Dhaka (DRC)Document14 pagesAssignment: 1: Regional Centre: Dhaka (DRC)TaohidNo ratings yet
- ECON 500 - Problem Set 0Document3 pagesECON 500 - Problem Set 0Harrison NgNo ratings yet
- ODE Cheat Sheet: Nonhomogeneous Problems Series SolutionsDocument2 pagesODE Cheat Sheet: Nonhomogeneous Problems Series SolutionsHannah Aquino NiroNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods 1 Course OverviewDocument5 pagesMathematical Methods 1 Course OverviewUsman Samuel BabalolaNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-9. DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSDocument4 pagesHsslive-9. DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSTeam Electrical inspectorNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Grade 11 Curriculum Map 2022 2023Document6 pagesAP Calculus AB Grade 11 Curriculum Map 2022 2023Nino TedoradzeNo ratings yet
- Ide SyllabusDocument28 pagesIde Syllabusswapnil155No ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)