Professional Documents
Culture Documents
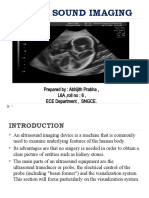
The Ultrasound Machine
Uploaded by
Sean AdamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Ultrasound Machine
Uploaded by
Sean AdamCopyright:
Available Formats
The Ultrasound Machine
Basic components of the machine and supplementary equipment:
Transducer Probe
The transducer probe is the main part of the ultrasound machine. The transducer probe
makes the sound waves and receives the echoes. It is, so to speak, the mouth and ears
of the ultrasound machine. The transducer probe generates and receives sound waves
using a principle called the piezoelectric (pressure electricity) effect, which was
discovered by Pierre and Jacques Curie in 1880. In the probe, there are one or more
quartz crystals called piezoelectric crystals. When an electric current is applied to these
crystals, they change shape rapidly. The rapid shape changes, or vibrations, of the
crystals produce sound waves that travel outward. Conversely, when sound or pressure
waves hit the crystals, they emit electrical currents. Therefore, the same crystals can be
used to send and receive sound waves. The probe also has a sound absorbing
substance to eliminate back reflections from the probe itself, and an acoustic lens to
help focus the emitted sound waves.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is the brain of the ultrasound machine. The CPU is basically a computer that
contains the microprocessor, memory, amplifiers and power supplies for the
microprocessor and transducer probe. The CPU sends electrical currents to the
transducer probe to emit sound waves, and also receives the electrical pulses from the
probes that were created from the returning echoes. The CPU does all of the
calculations involved in processing the data. Once the raw data are processed, the CPU
forms the image on the monitor. The CPU can also store the processed data and/or
image on disk.
Transducer Pulse Controls
The transducer pulse controls allow the operator, called the ultrasonographer, to set
and change the frequency and duration of the ultrasound pulses, as well as the scan
mode of the machine. The commands from the operator are translated into changing
electric currents that are applied to the piezoelectric crystals in the transducer probe.
Display
The display is a computer monitor that shows the processed data from the CPU.
Displays can be black-and-white or color, depending upon the model of the ultrasound
machine.
Keyboard/Cursor
Ultrasound machines have a keyboard and a cursor, such as a trackball, built in. These
devices allow the operator to add notes to and take measurements from the data.
Disk Storage
The processed data and/ or images can be stored on disk. The disks can be hard disks,
floppy disks, compact discs (CDs) or digital video discs (DVDs). Typically, a patient's
ultrasound scans are stored on a floppy disk and archived with the patient's medical
records.
Printers
Many ultrasound machines have thermal printers that can be used to capture a hard
copy of the image from the display.
You might also like
- USG (Ultrasound)Document30 pagesUSG (Ultrasound)DwiKrismaPratabaNo ratings yet
- How Ultrasound WorksDocument6 pagesHow Ultrasound WorksDoc AliNo ratings yet
- Group #1 UltrasoundDocument10 pagesGroup #1 UltrasoundAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture UltrasoundDocument51 pagesLecture UltrasoundVincent LyncottNo ratings yet
- Working of The UltrasoundDocument8 pagesWorking of The UltrasoundRagnar RagnarsonNo ratings yet
- What Is UltrasoundDocument5 pagesWhat Is UltrasoundEva VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Student Should Learn USGDocument17 pagesStudent Should Learn USGMM NabeelNo ratings yet
- UltrasoundDocument5 pagesUltrasoundHaseeb AliNo ratings yet
- UltrasoundDocument78 pagesUltrasoundAmeer MattaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Ultrasound Machine Echocardiograph Heart Lung Bypass Machine C-Arm Fluroscopy Machine PacemakerDocument16 pagesCardiac Ultrasound Machine Echocardiograph Heart Lung Bypass Machine C-Arm Fluroscopy Machine PacemakerRaghul BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Limitations of SightDocument11 pagesLimitations of SightLim Yung KienNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 35, Urgent Care Imaging and InterpretationFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 35, Urgent Care Imaging and InterpretationNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound ImagingDocument11 pagesUltrasound ImagingFikret Baz100% (1)
- Introduction To Ultrasonic TestingDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Ultrasonic TestingJayyid Ghaffar Ibnu MuharrijNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Ananya SharmaDocument26 pagesUltrasound Ananya Sharmapriyansh256No ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument8 pagesFinal ReportAkrit YadavNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorDocument4 pagesUltrasonic SensorcostpopNo ratings yet
- Pass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewFrom EverandPass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Embedded System: Electronic StethoscopesDocument10 pagesEmbedded System: Electronic StethoscopesPranay Shinde100% (1)
- Ultrasound MachineDocument36 pagesUltrasound MachineYechale TafereNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Sensor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesUltrasonic Sensor - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediamuna222No ratings yet
- Haptic Feedback: Rationale and Source of Our Project IdeaDocument25 pagesHaptic Feedback: Rationale and Source of Our Project IdeasrujanNo ratings yet
- A Hearing Aid Is An Electroacoustic Body Worn Apparatus Which Typically Fits in or Behind The WearerDocument7 pagesA Hearing Aid Is An Electroacoustic Body Worn Apparatus Which Typically Fits in or Behind The WearerBryan WilsonNo ratings yet
- Ostate TesticlesDocument7 pagesOstate Testiclesgreathari1998No ratings yet
- D 50 483 491 PDFDocument9 pagesD 50 483 491 PDFlambanaveenNo ratings yet
- BHS INGGRIS UAS FixxDocument8 pagesBHS INGGRIS UAS FixxAldy N SNo ratings yet
- Scanning Systems, Ultrasonic, Cardiac Intravascular: Scope of This Product ComparisonDocument75 pagesScanning Systems, Ultrasonic, Cardiac Intravascular: Scope of This Product Comparisonkevin. mitnickNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing in Ultrasound Images: Kamaljeet KaurDocument6 pagesDigital Image Processing in Ultrasound Images: Kamaljeet KaurRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical InstrumentationDocument35 pagesBiomedical Instrumentationfaizfrasat123No ratings yet
- Design and Development of Microcontroller Based Ultrasonic Flaw DetectorDocument7 pagesDesign and Development of Microcontroller Based Ultrasonic Flaw DetectorBagusElokNo ratings yet
- Ragul Hospital Training Presentation FileDocument47 pagesRagul Hospital Training Presentation FileSandyNo ratings yet
- Ei 65 Unit 5Document31 pagesEi 65 Unit 5karthiha12No ratings yet
- Abhijithprabha 150622074444 Lva1 App6891Document27 pagesAbhijithprabha 150622074444 Lva1 App6891Abhijith PrabhaNo ratings yet
- A Novel Method of QRS Detection Using Adaptive Multilevel Thresholding With Statistical False Peak EliminationDocument10 pagesA Novel Method of QRS Detection Using Adaptive Multilevel Thresholding With Statistical False Peak EliminationIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound PhysicsDocument9 pagesUltrasound PhysicsawansurfNo ratings yet
- Usg Transducer - Basic Structure & FunctionDocument35 pagesUsg Transducer - Basic Structure & FunctionMadhu Mohan100% (1)
- Echocardiogram (Heart Ultrasound) : Name:Fatema Ilyas Organization:Tabba Heart Institute ROLL NO:16-02 Batch:ViiDocument28 pagesEchocardiogram (Heart Ultrasound) : Name:Fatema Ilyas Organization:Tabba Heart Institute ROLL NO:16-02 Batch:ViiFatema IlyasNo ratings yet
- Application of Ultra Sonic Wave in Medical Field: System Description See AlsoDocument19 pagesApplication of Ultra Sonic Wave in Medical Field: System Description See AlsoPrasad BuddyNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering Ktu Mod 4Document26 pagesBiomedical Engineering Ktu Mod 4Adheeb Shibu VattasserilNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument13 pagesBiology ProjectHome MarufNo ratings yet
- Arbitrary Function Generators in WavesDocument1 pageArbitrary Function Generators in Wavescal2_uniNo ratings yet
- EI 65 UNIT 5newDocument29 pagesEI 65 UNIT 5newAmol BhatkarNo ratings yet
- Smart Blind StickDocument15 pagesSmart Blind Stickunzilarauf39No ratings yet
- BEU 6233 Biomedical Sensor & Transducer-E: Name No - MatricsDocument10 pagesBEU 6233 Biomedical Sensor & Transducer-E: Name No - Matricsahmad faizNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document10 pagesLab 4ahmad faizNo ratings yet
- Basic Physics of B-ModeDocument12 pagesBasic Physics of B-ModeEd ShieldsNo ratings yet
- Principles and Instruments of Diagnostic UltrasoundDocument22 pagesPrinciples and Instruments of Diagnostic UltrasoundJames WangNo ratings yet
- Sound Amplification SystemDocument3 pagesSound Amplification Systemapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic DetectionDocument8 pagesUltrasonic DetectionSaravanan ViswakarmaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TransducerDocument9 pagesUltrasonic TransducerPrince PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorDocument4 pagesUltrasonic SensorgkarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Dept 5 Event a-hospital-Visit-At-GMERS-Gandhinagar15 Mar 2021 16-38-47Document10 pagesDept 5 Event a-hospital-Visit-At-GMERS-Gandhinagar15 Mar 2021 16-38-47Priyanka Anand PiroNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Physics and KnobologyDocument47 pagesIntroduction, Physics and KnobologyMihaela LoghinNo ratings yet
- Sound and Vibration Tutorial enDocument4 pagesSound and Vibration Tutorial envvasileNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of UltrasoundDocument44 pagesQuality Control of Ultrasoundمحمد عوض الكريم عبدالله محمدNo ratings yet
- Medical Auscultation Heart Sounds Intestines Arteries Veins Sphygmomanometer Blood PressureDocument3 pagesMedical Auscultation Heart Sounds Intestines Arteries Veins Sphygmomanometer Blood Pressure李炫苇No ratings yet
- Vibration Measurement System With Accelerometer Sensor Based On ARM PDFDocument5 pagesVibration Measurement System With Accelerometer Sensor Based On ARM PDFAndreasNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Ultrasonic and Infrared SensorsDocument27 pagesUNIT 6 Ultrasonic and Infrared SensorsDương Bá LinhNo ratings yet
- NIT Ltrasonic Ransducers: Unit ObjectiveDocument12 pagesNIT Ltrasonic Ransducers: Unit ObjectiveClaudia Ioana100% (2)
- BRAIN PORT (A Neural Network Visual Device) 1Document30 pagesBRAIN PORT (A Neural Network Visual Device) 1Priya Mandal0% (1)
- User Manual: Apple Carplay Android AutoDocument22 pagesUser Manual: Apple Carplay Android AutoAdrio BianchiNo ratings yet
- Cisco Room Bar ProDocument28 pagesCisco Room Bar ProJeanAndradeNo ratings yet
- 5 TH Computer 1 ST TermDocument20 pages5 TH Computer 1 ST TermDanial MurtazaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Canon Entrepreneur BiographyDocument14 pages1.0 Canon Entrepreneur Biographyima87_daisyNo ratings yet
- Best Buy Usa PDFDocument1 pageBest Buy Usa PDFBettina BergnerNo ratings yet
- Mercury Brochure XchangeDocument11 pagesMercury Brochure XchangeRuweida OsmanNo ratings yet
- Philips LCD TV 37pfl9604h 37pfl9604h 12 Manual de UsuarioDocument3 pagesPhilips LCD TV 37pfl9604h 37pfl9604h 12 Manual de UsuarioRonald Frenzel GilNo ratings yet
- Viva Android SettingDocument6 pagesViva Android SettingFawaz AlsaifNo ratings yet
- TLE-TE 10 - Q1 - W5 - Mod5 - ICT CSS WorksheetDocument2 pagesTLE-TE 10 - Q1 - W5 - Mod5 - ICT CSS WorksheetJohn King johnking.monderinNo ratings yet
- The Most Essential Phone Etiquette Rules To RememberDocument4 pagesThe Most Essential Phone Etiquette Rules To Rememberpraks758No ratings yet
- RAB ASUS LaptopDocument8 pagesRAB ASUS LaptopAsep BambangNo ratings yet
- Cellphone KillerDocument2 pagesCellphone Killerapi-266264117No ratings yet
- How A Power Bank Works1Document9 pagesHow A Power Bank Works1Dwisri Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- DS-MH6171I 2MP Network Portable IR Speed Dome: Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesDS-MH6171I 2MP Network Portable IR Speed Dome: Key FeaturesDaniellaExilisReyesNo ratings yet
- Numeric LCD Display 3.5 Digits: Datasheet 16-Sep-10 3611Document3 pagesNumeric LCD Display 3.5 Digits: Datasheet 16-Sep-10 3611Angappa MegatechNo ratings yet
- FINA1035 Strategic Financial Management - Exam Case Study Aug 12Document49 pagesFINA1035 Strategic Financial Management - Exam Case Study Aug 12Kartik Jain100% (1)
- English Quarter 2-Module 6 Week 6Document29 pagesEnglish Quarter 2-Module 6 Week 6Teacher CelineNo ratings yet
- AK7521S6WOS AKAI 75in webOS IM v5Document52 pagesAK7521S6WOS AKAI 75in webOS IM v5rohan aroraNo ratings yet
- ImaxeonSalient DUALDocument4 pagesImaxeonSalient DUALRSUD Kepulauan MerantiNo ratings yet
- Poly Studio P5 Series Kits BrochureDocument2 pagesPoly Studio P5 Series Kits BrochureSchool PracticeNo ratings yet
- Consumer Ease - All in One Sheet 05-Jan-2021.Document48 pagesConsumer Ease - All in One Sheet 05-Jan-2021.Aarish KhanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Ford Ranger Quick Reference GuideDocument10 pages2019 Ford Ranger Quick Reference GuideCharles MutetwaNo ratings yet
- Business Devices - Smartphones: Application FormDocument8 pagesBusiness Devices - Smartphones: Application FormKrishna PrasathNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Logic Gate in PLC Using Ladder Programming LanguageDocument29 pagesImplementation of Logic Gate in PLC Using Ladder Programming LanguageAvinash RajNo ratings yet
- DIT103 Information Technology Hardware and Software HIND104 Computer EnvironmentsDocument53 pagesDIT103 Information Technology Hardware and Software HIND104 Computer EnvironmentsMustafa Babiker HamadNo ratings yet
- ThinkCentre M720 Tiny SpecDocument9 pagesThinkCentre M720 Tiny SpecPaulo BurneoNo ratings yet
- Samsung Ue32d5500 PDFDocument20 pagesSamsung Ue32d5500 PDFArmoured SmilerNo ratings yet
- Module IV: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 4.1 To Understand Bluetooth TechnologyDocument13 pagesModule IV: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 4.1 To Understand Bluetooth TechnologyAbhirami SNo ratings yet
- Mobile Usability 2nd EditionDocument307 pagesMobile Usability 2nd EditionSam DiazNo ratings yet
- 802.15.4 ZigbeeDocument33 pages802.15.4 ZigbeeAshutosh Gupta0% (1)