Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Information Technology Infrastructure
Uploaded by
coursework0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
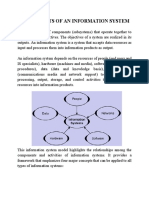
59 views1 pageAn information technology infrastructure consists of various hardware, software, network, and data components that form the foundation of an IT service in an organization. These components include data that is input and processed; hardware like computers, storage, and networking equipment; software applications and operating systems; communication networks for transmitting electronic data; IT professionals and users; and procedures for processing data and maintaining system security and functionality.
Original Description:
Original Title
Information technology infrastructure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn information technology infrastructure consists of various hardware, software, network, and data components that form the foundation of an IT service in an organization. These components include data that is input and processed; hardware like computers, storage, and networking equipment; software applications and operating systems; communication networks for transmitting electronic data; IT professionals and users; and procedures for processing data and maintaining system security and functionality.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views1 pageInformation Technology Infrastructure
Uploaded by
courseworkAn information technology infrastructure consists of various hardware, software, network, and data components that form the foundation of an IT service in an organization. These components include data that is input and processed; hardware like computers, storage, and networking equipment; software applications and operating systems; communication networks for transmitting electronic data; IT professionals and users; and procedures for processing data and maintaining system security and functionality.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Information technology infrastructure is defined broadly as a set of information technology (IT)
components that are the foundation of an IT service; typically physical components (computer and
networking hardware and facilities, but also various software and network components. In an
organization, information systems consist of the following components.
1. Data - Input that the system takes to produce information
2. Hardware - The building as information system may own multiple computers in the form of
sensors and other wearable devices. Together with the peripheral equipment—such as magnetic
or solid-state storage disks, input-output devices, and telecommunications gear—these
constitute the hardware of information systems.
3. Software - Sets of instructions that tell the computer how to input, process, output and store
data. Examples include general-purpose application suites with their spreadsheet and word-
processing programs or accounting software.
4. Communication networks - Hardware and software specializing in transmission and reception of
electronic data like Windows server operating systems. Connections can be through wires, such
as Ethernet cables or fibre optics, or wireless, such as through Wi-Fi.
5. People - IS professionals and users who design, construct, operate and maintain IS. From the
front-line user support staff, to systems analysts, to developers, all the way up to the chief
information officer (CIO), the people involved with information systems are an essential
element.
6. Procedures - Rules to process data, e.g. priorities in running different applications, security
measures, routines for malfunctioning IS, etc.
You might also like
- Computer Knowledge Guide For All Competitive ExamsFrom EverandComputer Knowledge Guide For All Competitive ExamsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- PCA20S01L - IT Infrastructure ManagementDocument25 pagesPCA20S01L - IT Infrastructure ManagementMOHAMED FIRNAS (RA1931005020191)No ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage - Resource Based View (Cirque Du Soleil)Document2 pagesCompetitive Advantage - Resource Based View (Cirque Du Soleil)courseworkNo ratings yet
- Definition - What Does IT Infrastructure Mean?Document2 pagesDefinition - What Does IT Infrastructure Mean?Novryzal prihatnaNo ratings yet
- MIS Unit-4Document19 pagesMIS Unit-4Kunal KambleNo ratings yet
- Accountants Role On ITDocument36 pagesAccountants Role On ITJayvee FelipeNo ratings yet
- Build NetworkDocument2 pagesBuild Networkfikru tesefayeNo ratings yet
- Unit1 PDFDocument49 pagesUnit1 PDFSandeep PotnuruNo ratings yet
- Information System in Our LifeDocument3 pagesInformation System in Our LifeMaleeha SabirNo ratings yet
- 03.CA (CL) - IT - (Module-2) - (3) Information Technology-HardwareDocument18 pages03.CA (CL) - IT - (Module-2) - (3) Information Technology-Hardwareilias khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1/1Document8 pagesChapter - 1/1Eleni MulualemNo ratings yet
- Lecture by Saad S. Naif: University of DuhokDocument9 pagesLecture by Saad S. Naif: University of DuhokaafrasyawNo ratings yet
- Digital Literacy Notes Level 6Document49 pagesDigital Literacy Notes Level 6themagero999No ratings yet
- Components of Information System: 1. Computer HardwareDocument2 pagesComponents of Information System: 1. Computer HardwareIntan KomaladewiNo ratings yet
- Example: Raw Materials, Energy, Data, and Human Effort Must Be Secured andDocument2 pagesExample: Raw Materials, Energy, Data, and Human Effort Must Be Secured andAiko TsukamotoNo ratings yet
- Auditing in A Cis Environment-Part 1Document17 pagesAuditing in A Cis Environment-Part 1Aira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Week 01Document19 pagesWeek 01ak2511803No ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER TopivDocument7 pagesINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER TopivSteven SalehNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lesson 4 CSSDocument5 pagesWeek 4 Lesson 4 CSSShe SheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document10 pagesChapter 01iKqliNo ratings yet
- Computer Reviewer Chap 1 5Document4 pagesComputer Reviewer Chap 1 5Sunny MaeNo ratings yet
- E223 Lesson 1 (IS Slide)Document62 pagesE223 Lesson 1 (IS Slide)eeshien1No ratings yet
- Interrelated Components With A Clearly Defined Boundary, Working Together To Achieve A Common Set of ObjectivesDocument19 pagesInterrelated Components With A Clearly Defined Boundary, Working Together To Achieve A Common Set of ObjectivesNarender KumarNo ratings yet
- Is ResourcesDocument3 pagesIs ResourcesJean AumaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Comoponents of Information SystemDocument9 pagesUnit - 2: Comoponents of Information SystemAmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Using Technology To Manage InformationDocument14 pagesUsing Technology To Manage Informationmonel_24671No ratings yet
- IT Infrastracture Slides.Document6 pagesIT Infrastracture Slides.Tinotenda Reginald ChabvongaNo ratings yet
- WK 7 Introduction To IctDocument7 pagesWK 7 Introduction To IctMARY LORD GERALDINE VELASCONo ratings yet
- A120215909 - 12438 - 27 - 2020 - Lect 1-2Document15 pagesA120215909 - 12438 - 27 - 2020 - Lect 1-2Mahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Session 11 Information TechnologyDocument39 pagesSession 11 Information TechnologyHamond OliverNo ratings yet
- Annex B: (Informative)Document10 pagesAnnex B: (Informative)Sky DennNo ratings yet
- Iot IAT-2Document2 pagesIot IAT-2Sujamoni 824No ratings yet
- Data and InformationDocument15 pagesData and InformationFatima Alh BakuraNo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Lecture: FIVE Chapter: THREEDocument11 pagesInformation Systems: Lecture: FIVE Chapter: THREEMd. Saiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Doc3 v.2Document3 pagesDoc3 v.2John Lorence FalogmeNo ratings yet
- Digital Literacy NotesDocument48 pagesDigital Literacy NotesKIBETT KEMEINo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Introduction To ITDocument35 pagesChap 1 Introduction To ITainamikhail954No ratings yet
- Information Technology Essentials: Prepared By: Arlene N. BaratangDocument31 pagesInformation Technology Essentials: Prepared By: Arlene N. BaratangKris Anne Delos Santos100% (1)
- L-6th Sem (Eng Revised 24) Cyber Crime Law-1-8Document8 pagesL-6th Sem (Eng Revised 24) Cyber Crime Law-1-8satyaNo ratings yet
- L-6th Sem (Eng Revised 24) Cyber Crime LawDocument56 pagesL-6th Sem (Eng Revised 24) Cyber Crime LawsatyaNo ratings yet
- L1-OVERVIEW OF COMPUTERS 165 177 Computer ScienceDocument16 pagesL1-OVERVIEW OF COMPUTERS 165 177 Computer ScienceBetty Njeri MbuguaNo ratings yet
- Networking PDFDocument35 pagesNetworking PDFYasir ArfatNo ratings yet
- Module 5 IT InfrastructureDocument9 pagesModule 5 IT Infrastructureuzair ansariNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure & ComponentsDocument18 pagesIT Infrastructure & Componentsrohaibzameer001No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document6 pagesUnit 1Mohamed RiyazNo ratings yet
- 01 ITFRST 21032023 121033amDocument12 pages01 ITFRST 21032023 121033amAMIRNo ratings yet
- It 1Document11 pagesIt 1Anurenj K.hNo ratings yet
- Components in Internet of ThingsDocument3 pagesComponents in Internet of ThingsAmmu SudaNo ratings yet
- ItimDocument12 pagesItimLalita TiwariNo ratings yet
- IT ManagementDocument30 pagesIT ManagementJordan StarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basics of Computer ScienceDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Basics of Computer ScienceMengistu TekollaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Ict: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. v. VIDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Ict: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. v. VIArnold NdukuyuNo ratings yet
- It Infrastructure Management An IntroductionDocument7 pagesIt Infrastructure Management An IntroductionsghoongNo ratings yet
- 5 Components of Information SystemsDocument2 pages5 Components of Information SystemsDave ChapelleNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument22 pagesIntroductionAbdulsalam Taiwo DhikrullahNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Introduction To Telecommunication: SPM1012: Telecommunication and NetworkingDocument22 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To Telecommunication: SPM1012: Telecommunication and Networkingkhalfan athmanNo ratings yet
- What Is Information TechnologyDocument5 pagesWhat Is Information TechnologyVanessa Siano TangonanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer ApplicationDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Computer ApplicationCaleb OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document16 pagesCH 2Dessu AshagrieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information SystemDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Information Systemhadia jawadNo ratings yet
- Components of An Information SystemDocument9 pagesComponents of An Information SystemKhoa Anh BùiNo ratings yet
- Report On M.I Cement Factory Limited.Document2 pagesReport On M.I Cement Factory Limited.courseworkNo ratings yet
- Competitive Landscape of Ticketing IndustryDocument1 pageCompetitive Landscape of Ticketing IndustrycourseworkNo ratings yet
- Analysis Model - X FactorDocument1 pageAnalysis Model - X FactorcourseworkNo ratings yet
- Skills Acquired During InternshipDocument1 pageSkills Acquired During InternshipcourseworkNo ratings yet
- Sew WhatDocument1 pageSew WhatcourseworkNo ratings yet
- Lysis Buffer CompositionDocument1 pageLysis Buffer CompositioncourseworkNo ratings yet
- Competition Analysis of Cirque Du SoleilDocument1 pageCompetition Analysis of Cirque Du SoleilcourseworkNo ratings yet
- DNA QuantificationDocument2 pagesDNA QuantificationcourseworkNo ratings yet
- Interna L Analysis: Distinctive CompetenceDocument2 pagesInterna L Analysis: Distinctive CompetencecourseworkNo ratings yet