Professional Documents
Culture Documents
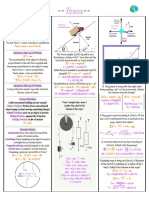
Two-Dimensional Motion : V Initial Velocity V Final Velocity X Change in Position A Acceleration Time
Uploaded by
Rose Bud Eaint Thiri KhineOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Two-Dimensional Motion : V Initial Velocity V Final Velocity X Change in Position A Acceleration Time
Uploaded by
Rose Bud Eaint Thiri KhineCopyright:
Available Formats
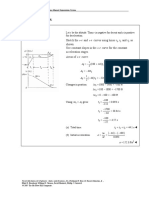
-- Two-Dimensional Motion--
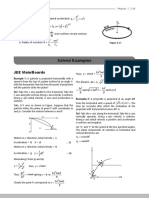
Scalar: quantity composed of only magnitude Vi = initial velocity No Vi : ∆x = Vf t - 12 a t2
(distance, volume, speed, mass, energy, power) Vf = final velocity No Vf : ∆ x = Vi t + 12 a t2
∆x = change in position No ∆x : Vf = Vi + a t
Vector: quantity composed of both magnitude V 1+ V f
a = a cceleration No a : ∆ x = ( 2 )t
and direction (scalar with direction; displacement,
t = time No t : Vf2 = Vi2 + 2a∆x
velocity, acceleration, force, weight)
Ball travelling 500m/s =
Ball travelling 885 m/s Ball travelling 385 m/s
Vy −1
θ1 = tan−1 ( V x ) θ2 = tan ( VV yx )
√V
2
Vr = a +Vb2
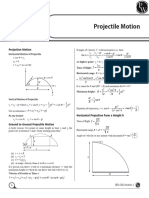
Relative Velocity ☆ there is no air resistance in an ideal Horizontal Projectile:
world
☆ horizontal & vertical components act
separately of each other
Ref. F-15 XF-85 Burj K
Frames (km/h) (km/h) (km/h)
☆ gravity is the only force pushing the object
F-15 0 4830+1060 4830 downwards (Vy initial is 0, a=-g, y=h)
= 5890
☆ V0 is x comp. of velocity (stays the same)
XF-8 1060+4830 0 1060 ☆ initial velocity doesn’t determine time in
= 5890 air, but height does, which also affects ∆x
5 Find resultant vector:
√ √
2h 2h
☆t= ☆ ∆x = v i
Burj K 4830 1060 0 Vx = 30cos68°-
20cos20° = -7.56 g g
Vy = 30sin68°+ 20sin20° = 34.66
Angular Projectile
☆ no horizontal acceleration
☆ Vx = vcosθ ☆ Vy = vsinθ - gt
∆x = ? Max height? ☆ inc θ inc time, dec horizontal speed &
☆Vx = 50cos32° ☆ Vy = 50sin32° distance
√
2(10)
☆t= = 1.43 ☆ 0 = 26.5 - gt; t = 2.7
9.8 ☆ greatest horizontal ∆x is at 45°
∆x = v i t = (8)(1.43) = 11.43 ☆ ∆y = (26.5)(2.7) = 71.66 m
You might also like
- 3.motion in A PlaneExercise PDFDocument47 pages3.motion in A PlaneExercise PDFsonuvuce100% (1)
- Physics | Radial Acceleration and Angular AccelerationDocument47 pagesPhysics | Radial Acceleration and Angular AccelerationsonuvuceNo ratings yet
- Equation Sheet-1 PDFDocument4 pagesEquation Sheet-1 PDFBruna GentilNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument4 pagesFormulae SheetOMARNo ratings yet
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Document4 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- 65cc56b8e7b7e10018a106bf - ## - Projectile Motion Short Notes JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2.0 2024Document2 pages65cc56b8e7b7e10018a106bf - ## - Projectile Motion Short Notes JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2.0 2024Krishanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- PHYS211 Sp22 Formula SheetsDocument4 pagesPHYS211 Sp22 Formula SheetsSiddharth ShahNo ratings yet
- 2017Document8 pages2017CP BORCHERDSNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear motion and projectile motion equationsDocument5 pagesRectilinear motion and projectile motion equationssatyamNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 EquationsDocument3 pagesPhysics 71 EquationsElah PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument23 pagesCircular MotionIshanshu BajpaiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS FORMULAS: 71 Equations for Kinematics, Forces, Energy, Momentum, and MoreDocument3 pagesPHYSICS FORMULAS: 71 Equations for Kinematics, Forces, Energy, Momentum, and MoreJames Patrick TorresNo ratings yet
- JEE Physics Kinematics Crash CourseDocument15 pagesJEE Physics Kinematics Crash CourseChetan SainiNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Equations in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesProjectile Motion Equations in 40 Charactersresty12No ratings yet
- Chapter. 2-Curvilinear Motion of Particles PDFDocument45 pagesChapter. 2-Curvilinear Motion of Particles PDFEng-Al Raie SaadNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula: Topic Phase-1Document13 pagesPhysics Formula: Topic Phase-1testerNo ratings yet
- Physics Handout: Classical MechanicsDocument2 pagesPhysics Handout: Classical MechanicsAlexis GarciaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C Mechanics Review Lecture Notes - AllDocument29 pagesAP Physics C Mechanics Review Lecture Notes - AllAnanda WiselyNo ratings yet
- Equations SummaryDocument4 pagesEquations SummaryBianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: R X I+y J+ Z KDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet: R X I+y J+ Z KHassan FadenNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Under Constant Acceleration: Average & Instantaneous Velocity and AccelerationDocument4 pagesKinematics Under Constant Acceleration: Average & Instantaneous Velocity and AccelerationHayden KNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics Lecture 2 VectorsDocument14 pagesClassical Mechanics Lecture 2 VectorsDiego ForeroNo ratings yet
- CIVL3612/9612 Fluid Mechanics: Equation SheetDocument3 pagesCIVL3612/9612 Fluid Mechanics: Equation Sheetvincent vivekNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Equations and Free Body DiagramsDocument7 pagesKinematic Equations and Free Body DiagramsJohn McEnroeNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes (G - !!) (CH 1+2)Document16 pagesPhysics Notes (G - !!) (CH 1+2)Khin Khin ThanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 CreightonDocument49 pagesLecture 4 CreightonKamran QadirNo ratings yet
- Exam3 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesExam3 Formula SheetMario GlezNo ratings yet
- AY2010 CE2134 Hydraulics P05 Linear & Moment of MomentumDocument14 pagesAY2010 CE2134 Hydraulics P05 Linear & Moment of MomentumEmily ShumNo ratings yet
- 4BCh07 (Basic Properties of Circles 2)Document25 pages4BCh07 (Basic Properties of Circles 2)api-3826695100% (1)
- 03 - Motion in A Straight Line Super NotesDocument3 pages03 - Motion in A Straight Line Super Notesprakashsinghsatya448No ratings yet
- General Physics Summary of FormulasDocument8 pagesGeneral Physics Summary of FormulasJemimah FVNo ratings yet
- Opgaver Fra Meriam: Kræfter-VektorerDocument4 pagesOpgaver Fra Meriam: Kræfter-VektorerErik PoulsenNo ratings yet
- phy201_lect8Document25 pagesphy201_lect8meidinania0No ratings yet
- Carnot CycleDocument10 pagesCarnot CycleSande NasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Motion in A Plane: Physics Grade 11Document14 pagesChapter - 1 Motion in A Plane: Physics Grade 11Catherine Yati OoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesEngineering Fluid Mechanics Formula SheetIñigoNo ratings yet
- Manipulator Dynamics: Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology DepartmentDocument44 pagesManipulator Dynamics: Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology DepartmentWajdi SadiqNo ratings yet
- Fluid mechanics equations and conceptsDocument20 pagesFluid mechanics equations and conceptsRosaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument29 pagesFluid MechanicsTemesgen DemessieNo ratings yet
- RM19 Hydraulics4 Part1Document1 pageRM19 Hydraulics4 Part1Alexander P. BelkaNo ratings yet
- FormulasheetDocument3 pagesFormulasheetAnnypaola MartinezNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Flow EquationsDocument28 pagesFluid-Flow EquationsHassan AliNo ratings yet
- 1-D MotionDocument1 page1-D Motionseries recapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Kinematics of Particles: Constrained MotionDocument3 pagesChapter 2: Kinematics of Particles: Constrained MotionRicardo TapiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 68Document1 pageChapter 11, Solution 68LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- SINGLE PHASE HALF WAVE CONTROLLED RECTIFIERDocument7 pagesSINGLE PHASE HALF WAVE CONTROLLED RECTIFIERkhyati patelNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Quick NotesDocument4 pagesProjectile Motion Quick NotesJoseph CruzNo ratings yet
- Monofásico Voltaje: T Tiempo Que Transcurre Un Ciclo F W W V V V 2 V V V 0.707 (V) V 0.637 (V)Document2 pagesMonofásico Voltaje: T Tiempo Que Transcurre Un Ciclo F W W V V V 2 V V V 0.707 (V) V 0.637 (V)Johnny Castro DiazNo ratings yet
- Circuitos Electricos Ii: Universidad Nacional Pedro Ruiz Gallo Facultad de Ingenieria Mecanica Y ElectricaDocument28 pagesCircuitos Electricos Ii: Universidad Nacional Pedro Ruiz Gallo Facultad de Ingenieria Mecanica Y ElectricaPercy Aranda CeraNo ratings yet
- 7. Circular MotionDocument3 pages7. Circular Motiongokulkrishna2k7No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet for LSU Physics 2101Document1 pageFormula Sheet for LSU Physics 2101Scott BurkeNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument14 pagesFormula SheetQER TUGNo ratings yet
- Solution Paper - 02: 199 200 Cos 2 Cos CosDocument7 pagesSolution Paper - 02: 199 200 Cos 2 Cos CosLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Particles: - IntroductionDocument38 pagesKinematics of Particles: - IntroductionTan Yu TeikNo ratings yet
- Recap On G - 11 Withteacher' SguideDocument5 pagesRecap On G - 11 Withteacher' SguideKhin Khin ThanNo ratings yet
- StructuresDocument22 pagesStructuresNandan HegdeNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM FORMULAS - PHYS 111Document1 pageFINAL EXAM FORMULAS - PHYS 111Venkataramanan SureshNo ratings yet
- 3.motion in A PlaneExerciseDocument47 pages3.motion in A PlaneExerciseGomes RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
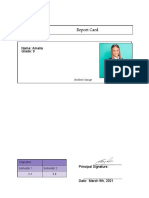
- Report Card: Name: Amelia Grade: 9Document2 pagesReport Card: Name: Amelia Grade: 9Rose Bud Eaint Thiri KhineNo ratings yet
- 41 F 669Document1 page41 F 669MCapitolinaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 - Formula SheetDocument2 pagesAP Physics 1 - Formula SheetRunze LiNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Course and Exam DescriptionDocument246 pagesAP Physics 1 Course and Exam Descriptionshivank kapurNo ratings yet
- EnergyandworkDocument1 pageEnergyandworkRose Bud Eaint Thiri KhineNo ratings yet
- 41 F 669Document1 page41 F 669MCapitolinaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Cardiology Curriculum (Amendments 2016)Document179 pages2010 Cardiology Curriculum (Amendments 2016)RevoNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument1 pageMomentumRose Bud Eaint Thiri KhineNo ratings yet
- APP1 Official Student Workbook Answers (Teacher Edition) 2019Document378 pagesAPP1 Official Student Workbook Answers (Teacher Edition) 2019Your Daddy82% (45)
- Construction code pressure vesselsDocument24 pagesConstruction code pressure vesselshugo.dutillet6002100% (1)
- Hydrogen: Books RefDocument15 pagesHydrogen: Books Refmohtasim hasanNo ratings yet
- 3D Analysis of Failure Modes in The Charpy Impact TestDocument21 pages3D Analysis of Failure Modes in The Charpy Impact TestEdna Odette Melo UscangaNo ratings yet
- 3D Holographic Techonology PPT - 1Document17 pages3D Holographic Techonology PPT - 1rajesh mangena100% (1)
- NX Nastran Basic Fs W6Document7 pagesNX Nastran Basic Fs W6Praveen ThankachanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Power and EfficiencyDocument4 pagesCalculating Power and EfficiencyAdam ChiangNo ratings yet
- Flutter Analysis of A Low Aspect Ratio Swept-Back Trapezoidal Wing at Low Subsonic FlowDocument6 pagesFlutter Analysis of A Low Aspect Ratio Swept-Back Trapezoidal Wing at Low Subsonic FlowAli BaigNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of Brass and PLADocument10 pagesThermal Conductivity of Brass and PLAJonathan WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Izn Two Stage CompressorDocument2 pagesIzn Two Stage CompressorLhexter Mhervin CoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Joists Beams and GirdersDocument23 pagesAnalysis of Joists Beams and GirdersMonica Ann Louise IntongNo ratings yet
- Support 3Document15 pagesSupport 3Shreyas AlagundiNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY and PHDocument7 pagesELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY and PHGobe JamNo ratings yet
- CH 19-Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument31 pagesCH 19-Chemical ThermodynamicsAdiPutraSaragihTurnipNo ratings yet
- Midterm Physics Exam GuideDocument4 pagesMidterm Physics Exam GuideWilfredNo ratings yet
- Elder 1967Document22 pagesElder 1967ALEJANDRO GANCEDO TORALNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal CompressorsDocument52 pagesCentrifugal CompressorsFadoooll75% (4)
- Electrowinning and Electrorefining of Copper (Murdoch University)Document76 pagesElectrowinning and Electrorefining of Copper (Murdoch University)Victor100% (8)
- CE 414, CE4B, August 2022Document25 pagesCE 414, CE4B, August 2022Roque III JaguioNo ratings yet
- 317114162-EDDY-CURRENT-AND-APPLICATIONS-PROJECT Class 12 Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument9 pages317114162-EDDY-CURRENT-AND-APPLICATIONS-PROJECT Class 12 Physics Investigatory Projectpseudo network67% (9)
- RC Column 1Document3 pagesRC Column 1Nurul SyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Ms 2508Document16 pagesMs 2508Youcef FermiNo ratings yet
- Protein FoldingDocument9 pagesProtein FoldingAyush ZalaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Towers Improve HVAC EfficiencyDocument18 pagesCooling Towers Improve HVAC EfficiencyHarjo Wiyono100% (1)
- Plane Failure Analysis Wedge Failure Analysis Toppling Failure AnalysisDocument30 pagesPlane Failure Analysis Wedge Failure Analysis Toppling Failure AnalysisSEDIMNo ratings yet
- ASMEDocument27 pagesASMERoy DreinaNo ratings yet
- SKF Composite Plain Bearings - 11004 EN - TCM - 12-107917 PDFDocument60 pagesSKF Composite Plain Bearings - 11004 EN - TCM - 12-107917 PDFAnonymous 1qAH6CKCNo ratings yet
- Avogadro's Law and Ideal Gas CalculationsDocument1 pageAvogadro's Law and Ideal Gas Calculationsmel vinNo ratings yet
- 973-SF Analyzer: Laboratory Precision - Field ReadyDocument4 pages973-SF Analyzer: Laboratory Precision - Field ReadymersiumNo ratings yet
- IJME Volume3 Issue3 Pages13-19Document8 pagesIJME Volume3 Issue3 Pages13-19Alex NoNo ratings yet
- CORM 2011 Calculation of CCT and Duv and Practical Conversion FormulaeDocument28 pagesCORM 2011 Calculation of CCT and Duv and Practical Conversion FormulaeAnonymous D0fu6XjKLNo ratings yet