Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Principles of Speech Writing
Uploaded by
Christine FerrerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Principles of Speech Writing
Uploaded by
Christine FerrerCopyright:
Available Formats
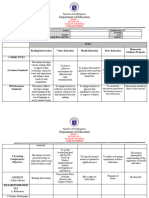
PRINCIPLES OF SPEECH WRITING 5.
Cite sources
6. Headstart with good note taking
This refers to the different steps that need to be undertaken by
the speaker in order to deliver a well-prepared speech. Outlining and organizing your speech
1. Choosing a topic Purpose
2. Analyzing your audience a. General purpose: inform, entertain,
3. Sourcing information inspire, persuade
4. Outlining and organizing your speech b. Specific purpose: main idea
c. Key points to discuss
Choosing a topic Introduction
A. Timely: is it sensible as of the moment? a. Preview/attention getter
a. Are there aspects of the issue that will be b. Directs the audience towards the
useful to your audience? purpose
b. Does the topic arouse questions that is Introduction techniques
wanting to be answered? a. Ask rhetorical question
c. Does the topic leave an impression that b. Cite a biblical passage
would automatically engage the audience ? c. Use a quote
B. Relatable: will my audience have even a little d. Sing lines/ recite a poem
background info. About my topic? e. Tell an anecdote
a. How much info. Should be provided in the f. Use a startling statement
speech? g. Use a narrative
b. How knowledgeable am i of the chosen Writing the body of a speech
topic? a. Contains the main points
C. Interesting: is it appealing from my perspective? b. Expounds the main points with
a. Will i be motivated enough to develop a examples, evidence, arguments, or
speech out of the chosen topic? illustrations
a. Recall key points previewed in
Analyzing your audience: the more information you are able introduction.
to gather from your target audience and elements related to b. Provide details to discuss each
them, the more you would easily be able to adapt to their key point.
needs. c. Use transitions.
A. Demographic analysis: general profile of your Writing the conclusion
audience a. Recaps important points
i. Age b. A clincher/leaves something to think of
ii. Gender a. Summarize key points.
iii. Culture b. Provide insights on the
iv. Religion implication of your speech.
v. Group membership c. End with a thought provoking
vi. Education occupation statement.
B. Psychographic analysis: perceptions of your audience
i. Values
ii. Opinions
iii. Attitudes
iv. Beliefs
v. Pre-existing notions (topic and you)
vi. Interest & needs
C. Situational analysis: environment and setting
i. Physical setting
ii. Size
iii. Occasion
iv. Voluntary: audience attending
based on their will to listen
v. Captive: audience who are required
to attend
Sourcing information
1. Seek reliable references
2. Provide supporting information
3. Extract important points
4. Ethical information must be sought
You might also like
- 2022 AMC Paper MP OMRDocument12 pages2022 AMC Paper MP OMRshilpa_aryan100% (1)
- Melc DLL Eng 8 Week 2 Q1 DoneDocument11 pagesMelc DLL Eng 8 Week 2 Q1 DoneRitchell Salamaña Dohina100% (1)
- TUDelft Clay Suction PDFDocument8 pagesTUDelft Clay Suction PDFDing LiuNo ratings yet
- DLL Catch Up Friday Grade 4 Jan 19Document7 pagesDLL Catch Up Friday Grade 4 Jan 19reyannmolinacruz21100% (30)
- Handbook Valve Technology 03.04.2020Document132 pagesHandbook Valve Technology 03.04.2020Ramazan YaşarNo ratings yet
- Types of Speech..Document42 pagesTypes of Speech..Gil foroble67% (3)
- Module 1 Communication Skills Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesModule 1 Communication Skills Multiple ChoiceMariel Corbin100% (1)
- Syringe Infusion Pump S300: Technical SpecificationDocument1 pageSyringe Infusion Pump S300: Technical SpecificationJonathan Flores Gutang100% (1)
- Theoretical Foundation in Nursing: LESSON 8Document4 pagesTheoretical Foundation in Nursing: LESSON 8Gabriel SorianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Study GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 13 Study Guideapi-450369672No ratings yet
- 1st Monthly in ENGLISH10Document3 pages1st Monthly in ENGLISH10Juvelyn AbuganNo ratings yet
- Academic Essay Target Readers and PurposesDocument3 pagesAcademic Essay Target Readers and PurposesRomnickCelestinoNo ratings yet
- Speech and Oral Communication QuizDocument1 pageSpeech and Oral Communication QuizEdrea MarielNo ratings yet
- 1st QUARTERLY EXAM in ENGLISH10Document4 pages1st QUARTERLY EXAM in ENGLISH10Juvelyn AbuganNo ratings yet
- GE COURSES PRE TEST March 16 2022Document28 pagesGE COURSES PRE TEST March 16 2022Dara Lazada100% (1)
- Week 8 Oral CommunicationDocument16 pagesWeek 8 Oral CommunicationApril jane EstacioNo ratings yet
- Quiz # 2 PurposiveDocument1 pageQuiz # 2 PurposivelitamarieNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Question 1 (B)Document2 pagesBusiness Communication Question 1 (B)Md Tareq100% (3)
- Melc DLL Eng 10 Week 5 Q4 DoneDocument9 pagesMelc DLL Eng 10 Week 5 Q4 Doneje-ann montejoNo ratings yet
- Melc DLL Eng 10 Week 1 Final Q3 DoneDocument10 pagesMelc DLL Eng 10 Week 1 Final Q3 DoneChrisneliane BarilNo ratings yet
- Principles of Effective Speech WritingDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Effective Speech WritingCleofe SobiacoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Instructions-2022Document4 pagesMidterm Instructions-2022Shehzad QureshiNo ratings yet
- EAPP 2nd Quarter ExamDocument5 pagesEAPP 2nd Quarter ExamPearl Angelah LazarenoNo ratings yet
- Organizational Plans for Business CommunicationDocument1 pageOrganizational Plans for Business Communicationunsa soomro100% (1)
- Oct 03 (Modal Verb)Document3 pagesOct 03 (Modal Verb)Aiella Jerizel EscobarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3-5 EnglishDocument13 pagesLesson Plan 3-5 EnglishDon James VillaroNo ratings yet
- DLP-Q3W5-LEGGIE-M (Quiz-2)Document3 pagesDLP-Q3W5-LEGGIE-M (Quiz-2)Mark Leggie Feliciano RontaleNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Las Week 1Document4 pages1st Quarter Las Week 1krishamaecapeNo ratings yet
- Informative Writing Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesInformative Writing Lesson Planarvin jay sacilNo ratings yet
- Oct 05-06 (Modal Verb)Document4 pagesOct 05-06 (Modal Verb)Aiella Jerizel EscobarNo ratings yet
- How To Use This Module?: and Secondary SourcesDocument10 pagesHow To Use This Module?: and Secondary SourcesEdwin reyesNo ratings yet
- Oct 04-05 (Modal Verb)Document4 pagesOct 04-05 (Modal Verb)Aiella Jerizel EscobarNo ratings yet
- Task 4 - Prepared SpeechDocument2 pagesTask 4 - Prepared Speechmoodleyclaryce345No ratings yet
- English8_Quarter4_Module2Document22 pagesEnglish8_Quarter4_Module2carenestrada95No ratings yet
- Report in Speech and Oral Communication Chapter VII - Preparing A SpeechDocument2 pagesReport in Speech and Oral Communication Chapter VII - Preparing A SpeechMisael CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Public SpeakingDocument43 pagesReviewer Public SpeakingMark Zed Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- READING AND WRITING EXAM-January FINALDocument2 pagesREADING AND WRITING EXAM-January FINALSheryl SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Escalante Co2 DLPDocument3 pagesEscalante Co2 DLPRea Ann ManaloNo ratings yet
- English8 Quarter4 Module2Document22 pagesEnglish8 Quarter4 Module2Niah NiahNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm NAT ReviewDocument3 pagesOral Comm NAT ReviewAna CrishnaNo ratings yet
- 3nd Quarter RecitationDocument7 pages3nd Quarter Recitationchloesevillano277No ratings yet
- READING AND WRITING EXAM-JanuaryDocument3 pagesREADING AND WRITING EXAM-JanuarySheryl SalvadorNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesQuestionnaireSionny GandicelaNo ratings yet
- Eng Lesson Plan3Document3 pagesEng Lesson Plan3Loreza DelatorNo ratings yet
- Compre RWDocument5 pagesCompre RWKaycee ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestDocument3 pagesDiagnostic TestKim BandolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ResearchDocument1 pageLesson Plan in ResearchMeylene Balverde IbarraNo ratings yet
- Exam Oral ComDocument5 pagesExam Oral ComJennifer T. DiganNo ratings yet
- Steps To Research PaperDocument7 pagesSteps To Research PaperJoaquin AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Presentation Extemporaneous Speech 20231204 090901 0000Document11 pagesGroup 4 Presentation Extemporaneous Speech 20231204 090901 0000Loraine SenilloNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm Module For Blended Learning Oct 30 To Nov 3Document3 pagesOral Comm Module For Blended Learning Oct 30 To Nov 3ljcosm3No ratings yet
- English 74 TH Module 8Document12 pagesEnglish 74 TH Module 8Hellen DeaNo ratings yet
- LP Feb 07 ThursdayDocument2 pagesLP Feb 07 ThursdayClarisse Joyce GenerNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 3A Chapt 7 OutlineDocument5 pagesENGLISH 3A Chapt 7 OutlineRonweL OcsonaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Plan-G10-SedenoDocument4 pagesLesson-Plan-G10-SedenoJelly SedeñoNo ratings yet
- Q1 - M5 Ans (Eapp)Document5 pagesQ1 - M5 Ans (Eapp)JD MartinNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Profesional PPG Bahasa InggrisDocument18 pagesModul 1 Profesional PPG Bahasa InggrisSiti NurzulianaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Prof Ed - Question Without AnswerDocument11 pagesPart 1 Prof Ed - Question Without AnswerFaye SuarezNo ratings yet
- 8 TQ Quarter4Document2 pages8 TQ Quarter4Kathlene DimasuhidNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Descriptive Text TechniquesDocument20 pagesAnalyzing Descriptive Text TechniquesinamowtoNo ratings yet
- Gregson Eloho 8/5/19 COMM 173 Tue/Thurs 6:00pmDocument2 pagesGregson Eloho 8/5/19 COMM 173 Tue/Thurs 6:00pmben daigleNo ratings yet
- OUTLINING 2Document3 pagesOUTLINING 2Tane MBNo ratings yet
- dLp PR2 - 5Document6 pagesdLp PR2 - 5michelle.mijarezNo ratings yet
- Co1 DLP Desaville, JMDocument5 pagesCo1 DLP Desaville, JMJesh Manansala-DesavilleNo ratings yet
- Composing An Argumentative EssayDocument33 pagesComposing An Argumentative EssayEurie TiexieraNo ratings yet
- Physci 7 - Atoms, Electron Distribution, Valence, LedsDocument44 pagesPhysci 7 - Atoms, Electron Distribution, Valence, LedsChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- Physci 8 - Chemical BondingDocument57 pagesPhysci 8 - Chemical BondingChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Lewis Structure Formal Charges Molecular GeometryDocument29 pagesChemical Bonding Lewis Structure Formal Charges Molecular GeometryChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- MIL Prelim ReviewerDocument6 pagesMIL Prelim ReviewerChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- S11PD Prelims ReviewerDocument23 pagesS11PD Prelims ReviewerChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- Cpar Finals Reviewer MediumDocument3 pagesCpar Finals Reviewer MediumChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- Classification of Art Drawing - First Step in Producing 2D ArtworksDocument5 pagesClassification of Art Drawing - First Step in Producing 2D ArtworksChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- © Johnelle CobarrubiasDocument4 pages© Johnelle CobarrubiasChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- S11SP Finals Reviewers - Statistics Tests & CorrelationDocument2 pagesS11SP Finals Reviewers - Statistics Tests & CorrelationOsdfjosadfNo ratings yet
- Anlage C DQC III-18 La DQC IV-18 LaDocument5 pagesAnlage C DQC III-18 La DQC IV-18 LaPEDRONo ratings yet
- Castro DW 32Document3 pagesCastro DW 32Jeetu GosaiNo ratings yet
- BU - Assignment 2 PDFDocument2 pagesBU - Assignment 2 PDFMaliha FarzanaNo ratings yet
- 8.4.3 Alien Genetics LabDocument2 pages8.4.3 Alien Genetics LabCharles KnightNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Et Al. - 2015 - Screening The Optimal Ratio of Symbiosis Between Isolated Yeast and Acetic Acid Bacteria Strain From Traditional-AnnotatedDocument25 pagesNguyen Et Al. - 2015 - Screening The Optimal Ratio of Symbiosis Between Isolated Yeast and Acetic Acid Bacteria Strain From Traditional-AnnotatedKim NgânNo ratings yet
- Prof. Hanumant Pawar: GeomorphologyDocument15 pagesProf. Hanumant Pawar: GeomorphologySHAIK CHAND PASHANo ratings yet
- Uncertainty in Measurements - Lab ReportDocument4 pagesUncertainty in Measurements - Lab ReportStaniaNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10 CH-1 ECO DEVELOPMENT Question AnswersDocument8 pagesCLASS 10 CH-1 ECO DEVELOPMENT Question AnswersDoonites DelhiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Quiz (01-16-21)Document3 pagesConsumer Behavior Quiz (01-16-21)litNo ratings yet
- Superheterodyne ReceiverDocument22 pagesSuperheterodyne ReceiverdeepanilsaxenaNo ratings yet
- Manual Completo Sinovo SD600Document221 pagesManual Completo Sinovo SD600Felipe de PaulaNo ratings yet
- Redmi 9 Power Blazing Blue, 64 GB: Adilaxmi E-Commerce Private LimitedDocument1 pageRedmi 9 Power Blazing Blue, 64 GB: Adilaxmi E-Commerce Private Limitedask meNo ratings yet
- LCD LG (M17,1917S-BNN E)Document34 pagesLCD LG (M17,1917S-BNN E)Ion IonutNo ratings yet
- SP-1127 - Layout of Plant Equipment and FacilitiesDocument11 pagesSP-1127 - Layout of Plant Equipment and FacilitiesParag Lalit SoniNo ratings yet
- DE Monthly Assessment - IDocument5 pagesDE Monthly Assessment - IJay KakadiyaNo ratings yet
- Unleashing Learner PowerDocument188 pagesUnleashing Learner PowerEka MeilinaNo ratings yet
- Crown Platform Crown Battery Operated Pallet TruckDocument7 pagesCrown Platform Crown Battery Operated Pallet Truckgaurav champawatNo ratings yet
- P90X2 Les Mills PUMP HybridDocument7 pagesP90X2 Les Mills PUMP HybridRamonBeltranNo ratings yet
- Ai, Iot, Big Data & BlockchainDocument19 pagesAi, Iot, Big Data & BlockchainClick GroupNo ratings yet
- OM Sample QPDocument8 pagesOM Sample QPChandra ShekarNo ratings yet
- hts336555 Philips Manual PDFDocument35 pageshts336555 Philips Manual PDFSalomão SouzaNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument3 pagesSummaryОля ВласійчукNo ratings yet
- Alumni Speaks... : Axay GandhiDocument4 pagesAlumni Speaks... : Axay GandhiSajal MorchhaleNo ratings yet
- M-I LLC - Pac All Grades SDSDocument3 pagesM-I LLC - Pac All Grades SDSimamNo ratings yet