Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Agriculture - Farming in LEDC
Uploaded by
Ravi MothoorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Agriculture - Farming in LEDC
Uploaded by
Ravi MothoorCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Revision -
Agriculture - Farming in LEDC's
Most people in less economically developed countries are farmers and most of these are
subsistence farmers. Subsistence farming means producing crops and rearing animals for the use
of the farmer. Very little surplus produce is grown.
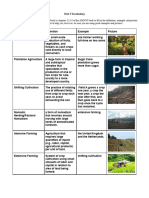
Extensive Shifting Cultivation Extensive Pastoral Nomadism
An area of land is cleared by cutting and burning In regions where grazing is poor, farmers herd
the vegetation. Crops are planted and harvested. animals over wide areas in search of pasture e.g.
When the land loses its fertility after about 5 sheep herding in North Africa.
years the area is abandoned and another area is
cleared and farmed e.g. shifting cultivation in the
Amazon Rainforest, Brazil
The Main Types
Intensive Arable Farming
The most common kind - Usually small patches
of land near to the village are farmed. Most of
the work is done by hand or using oxen - eg rice
farming in S.E. Asia
Case Study - Subsistence Rice Farming in the Ganges Valley
Physical Factors
A five month growing season with
temperatures over 21degrees centigrade
Monsoon rainfall over 2000mm
Flat land to allow the fields to flood
A dry period for harvesting
Rich alluvial soils to provide nutrients
A large labour force (intensive)
Human Factors Problems of Rice Growing
Rice gives high yields per hectare which Flooding - This provides water and fertile
helps to feed the large population. silt to grow the rice but sometimes
disaster strikes when the floods are so
Water buffaloes are used for work and
severe that they destroy the rice crop.
as a source of manure for the fields
Drought - In some years the monsoon
Rice seeds are stored from one year to
rains fail and the rice crop is ruined.
provide the next year's crop
Shortage of land and a growing
Rice growing is labour intensive so many
population - many patches of land are
people can be employed in the paddy
far too small to support the family. The
fields looking after the crops.
situation is made worse by the ever
increasing population. Food shortages
are a real problem.
Plantation Farming
Plantation farming involves the growing of one type of crop over a large area such as Bananas as
in Ecuador, Sugar Cane and coffee
It requires a lot of investment, usually from a wealthy company in an MEDC. Plantations are well
organised to get the highest possible yields.
Plantations have advantages and disadvantages for LEDC's
Advantages Disadvantages
Plantations can provide employment They can destroy large areas of natural
vegetation
They provide investments in modern
machinery and workers are trained Much of the profit from plantations goes
to MEDC's
They provide export earnings for LEDC's
Workers are low paid and usually
exploited
If world prices in the crop fail the
country gets very little income
Monoculture plantations are vulnerable
to pests diseases or climatic hazards can
wipe out a whole years crop.
You might also like
- Farm Crops - With Information on Soil Cultivation, Grain Crops, Forage Crops and PotatoesFrom EverandFarm Crops - With Information on Soil Cultivation, Grain Crops, Forage Crops and PotatoesNo ratings yet
- Ag AgDocument13 pagesAg AgJP MishraNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument20 pagesEconomicsfemtaciNo ratings yet
- Indian Agriculture - Subsistence, Monsoon-Dependent but Top ProducerDocument7 pagesIndian Agriculture - Subsistence, Monsoon-Dependent but Top ProducerAnonymous Rs28SnNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Vocab AssignmentDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Vocab AssignmentSydney BiondoNo ratings yet
- Unlock 2e L5 Listening and Speaking ScriptsDocument29 pagesUnlock 2e L5 Listening and Speaking ScriptsMeh HehNo ratings yet
- Michael Hard - 2024 Unit 5 VocabularyDocument15 pagesMichael Hard - 2024 Unit 5 VocabularywubdublesNo ratings yet
- Rice FarmingDocument29 pagesRice FarmingS.KAMBANNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument14 pagesGeographyPranav (GRADE IX)No ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument24 pagesAgricultureArchana KujurNo ratings yet
- Agriculture AssignmentDocument13 pagesAgriculture AssignmentRisa BeharryNo ratings yet
- Beushening A Traditional Method of Rice Crop Establishment in Eastern IndiaDocument4 pagesBeushening A Traditional Method of Rice Crop Establishment in Eastern Indiapriya9805No ratings yet
- Agricultural & Rural Transformation & Development: Developed By: Pup CSSD Department of EconomicsDocument4 pagesAgricultural & Rural Transformation & Development: Developed By: Pup CSSD Department of EconomicsMarcus MonocayNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Class 8Document67 pagesAgriculture Class 825 Aditya AhujaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Geog - L-4 AgricultureDocument3 pages8 - Geog - L-4 AgricultureAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: - What Do You Know About Agriculture?Document90 pagesAgriculture: - What Do You Know About Agriculture?Celise GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Rainfed Agriculture-Introduction, Definition and Importance: Lecture No. 1Document9 pagesRainfed Agriculture-Introduction, Definition and Importance: Lecture No. 1Pankhuri SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Natural CalamitiesDocument29 pagesNatural CalamitiesPreeti KumariNo ratings yet
- Monsoon Irrigated Agriculture: Topic 2: Primary Economic Activities Topic 2: Primary Economic ActivitiesDocument3 pagesMonsoon Irrigated Agriculture: Topic 2: Primary Economic Activities Topic 2: Primary Economic ActivitiesMichelle Gutierrez GuerreroNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF-converted-STUDY MAT - AGRICULTUREDocument31 pagesSodaPDF-converted-STUDY MAT - AGRICULTUREMayank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- (3.2) ig geo food production savemyexams pdfDocument15 pages(3.2) ig geo food production savemyexams pdfwaihon.pang2011No ratings yet
- Agricultural Production Regions and Farming Practices: Subsistence AgricultureDocument4 pagesAgricultural Production Regions and Farming Practices: Subsistence AgricultureIdan LevyNo ratings yet
- Agriculture and Land ReformDocument43 pagesAgriculture and Land Reformjames jumaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics Features of Tropical Agriculture and How They Affect ProductionDocument2 pagesCharacteristics Features of Tropical Agriculture and How They Affect Productionigbinosadaniel35No ratings yet
- Agr-322 Notes 2020Document86 pagesAgr-322 Notes 2020Nisarga T DaryaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Class-8Document67 pagesAgriculture Class-8Sahej100% (2)
- Characteristics of AgricultureDocument16 pagesCharacteristics of AgricultureDhillon Taranjit0% (1)
- Agri Development Facts PDFDocument12 pagesAgri Development Facts PDFMerryl Joyce Basco YabaNo ratings yet
- Types of FarmingDocument9 pagesTypes of FarmingShaurya SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 (Agriculture)Document156 pagesTopic 6 (Agriculture)Rana Ahmad BilalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AgricultureDocument4 pagesChapter 4 AgricultureAkshant MukeshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Agriculture in INDIADocument48 pagesIntroduction To Agriculture in INDIAArvind Kumar GNo ratings yet
- Commercial Farming AdvantagesDocument5 pagesCommercial Farming AdvantagesRAZE GAMER ZINDABADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AGRICULTUREDocument17 pagesIntroduction To AGRICULTUREVan SweetingNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document47 pagesModule 2Lyka CantosNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of PortableDocument7 pagesDesign and Fabrication of PortableWILLIAM CAMILO ESPINOSA ROJASNo ratings yet
- AGR 302 Before MidDocument48 pagesAGR 302 Before Midsuriya kishoreNo ratings yet
- Skjxc2 JDDocument16 pagesSkjxc2 JDscribduser0811972No ratings yet
- Push Pull Climate-SmartDocument8 pagesPush Pull Climate-SmartkerateaNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument36 pagesAgricultureKordell McShineNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: I. Answer The Following QuestionsDocument3 pagesAgriculture: I. Answer The Following QuestionsTulshiram NerkarNo ratings yet
- Farming Today Issue 4Document25 pagesFarming Today Issue 4Peter MukunzaNo ratings yet
- Ac&ri, Vvnr-Agr 302 Theory Notes Upto Mid Semester 2019Document47 pagesAc&ri, Vvnr-Agr 302 Theory Notes Upto Mid Semester 2019Shubham BhadeNo ratings yet
- Hess 404Document10 pagesHess 404Kezia NatashaNo ratings yet
- Agricultural challenges and opportunities in IndiaDocument3 pagesAgricultural challenges and opportunities in IndiaSayani AbrahamNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument27 pagesAgriculturetumati venkata vinayNo ratings yet
- Major CropsDocument30 pagesMajor CropsSahil MathurNo ratings yet
- VdhsihvdskbskjfvbkjvdjDocument10 pagesVdhsihvdskbskjfvbkjvdjiowvhvovewioNo ratings yet
- Agriculture in India - Land Use, EtcDocument2 pagesAgriculture in India - Land Use, EtcK KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 AgricultureDocument4 pagesLecture 04 Agriculturemohamedlaissani209No ratings yet
- Topic 6 (Agriculture) - 01Document155 pagesTopic 6 (Agriculture) - 01usmanrandhawa67889No ratings yet
- MajorCrops PDFDocument30 pagesMajorCrops PDFPadminiNarayanNo ratings yet
- CAG 2013 TANAMAN BIJIRIN DAN BIJIAN KULIAH 3 SEM 2 2012/2013Document18 pagesCAG 2013 TANAMAN BIJIRIN DAN BIJIAN KULIAH 3 SEM 2 2012/2013Zulhelmi MustafaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture PDFDocument6 pagesAgriculture PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- The Story of Village Palampur - Notes09Document7 pagesThe Story of Village Palampur - Notes09Vedant TiwareNo ratings yet
- Biggest Problems Faced by Farmers in IndiaDocument6 pagesBiggest Problems Faced by Farmers in IndiaIlayaraja BarnabasNo ratings yet
- Farming Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Document8 pagesFarming Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Georgina HolmesNo ratings yet
- Mushrooms Get Popular: Conserving Soil Increases YieldsDocument8 pagesMushrooms Get Popular: Conserving Soil Increases YieldsMwape Martin WakamaiNo ratings yet
- Hess404 MergedDocument14 pagesHess404 Mergedmendivelsosteven197No ratings yet
- Agriculture and MonsoonDocument23 pagesAgriculture and MonsoonKanavdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Convection Currents: What Is A Current?Document8 pagesConvection Currents: What Is A Current?Ravi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Distribution of EarthquakesDocument9 pagesDistribution of EarthquakesRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Destructive, Constructive and Conservative Plate MarginsDocument11 pagesDestructive, Constructive and Conservative Plate MarginsRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Destructive, Constructive and Conservative Plate MarginsDocument11 pagesDestructive, Constructive and Conservative Plate MarginsRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Distribution of VolcanoesDocument9 pagesDistribution of VolcanoesRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- The Challenge of UrbanisationDocument53 pagesThe Challenge of UrbanisationRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Agriculture - Farming in LEDCDocument2 pagesAgriculture - Farming in LEDCRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Destructive Waves V/s Constructive Waves Constructive (Or Depositional) Waves. 1. Destructive Waves Have A Number of Important CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesDestructive Waves V/s Constructive Waves Constructive (Or Depositional) Waves. 1. Destructive Waves Have A Number of Important CharacteristicsRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Convection Currents: What Is A Current?Document8 pagesConvection Currents: What Is A Current?Ravi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument9 pagesCarbon CycleRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY MARK SCHEMEDocument8 pagesGEOGRAPHY MARK SCHEMERavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY MARK SCHEMEDocument8 pagesGEOGRAPHY MARK SCHEMERavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Physical Landscapes in The UKDocument12 pagesPhysical Landscapes in The UKAndreea ŞerbanoiuNo ratings yet
- Destructive Waves V/s Constructive Waves Constructive (Or Depositional) Waves. 1. Destructive Waves Have A Number of Important CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesDestructive Waves V/s Constructive Waves Constructive (Or Depositional) Waves. 1. Destructive Waves Have A Number of Important CharacteristicsRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- AIDS in AfricaDocument6 pagesAIDS in AfricaRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument9 pagesCarbon CycleRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- AIDS in AfricaDocument6 pagesAIDS in AfricaRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- 3 - Waterfalls & V Shaped Valleys Home StudyDocument17 pages3 - Waterfalls & V Shaped Valleys Home StudyRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- 3 - Waterfalls & V Shaped Valleys Home StudyDocument17 pages3 - Waterfalls & V Shaped Valleys Home StudyRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- 2 - Long Profile and Processes Home StudyDocument18 pages2 - Long Profile and Processes Home StudyRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Physical Landscapes in The UKDocument12 pagesPhysical Landscapes in The UKAndreea ŞerbanoiuNo ratings yet
- Global Interdependence - Key Terms and Trade FlowsDocument110 pagesGlobal Interdependence - Key Terms and Trade FlowsRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- 2 - Long Profile and Processes Home StudyDocument18 pages2 - Long Profile and Processes Home StudyRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Coastal Environment: Topic 2 A-Level Physical GeographyDocument203 pagesCoastal Environment: Topic 2 A-Level Physical Geographywisdom zhakataNo ratings yet
- Location, Production and Change: Topic 1 A-Level Human GeographyDocument210 pagesLocation, Production and Change: Topic 1 A-Level Human GeographyRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Coastal Environment: Topic 2 A-Level Physical GeographyDocument203 pagesCoastal Environment: Topic 2 A-Level Physical Geographywisdom zhakataNo ratings yet
- Global Interdependence - Key Terms and Trade FlowsDocument110 pagesGlobal Interdependence - Key Terms and Trade FlowsRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Migration Types and CausesDocument67 pagesMigration Types and CausesRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Population 140510034528 Phpapp01Document15 pagesPopulation 140510034528 Phpapp01Ravi MothoorNo ratings yet
- PQRSTDocument3 pagesPQRSTcandrarialNo ratings yet
- Technology and Home Economics (Cookery) : Generate A Business Idea That Relates With Career Choice in CookeryDocument21 pagesTechnology and Home Economics (Cookery) : Generate A Business Idea That Relates With Career Choice in Cookerykenneth sison100% (7)
- Developing EthicsDocument24 pagesDeveloping EthicsChintoo KalyanadurgamNo ratings yet
- Self Tower InstallDocument88 pagesSelf Tower InstallBoris BravoNo ratings yet
- Kevin VollrathDocument2 pagesKevin VollrathMargaret ElwellNo ratings yet
- Section A Module 1 - Gathering and Processing Information 1. Read The Following Extract Carefully and Then Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesSection A Module 1 - Gathering and Processing Information 1. Read The Following Extract Carefully and Then Answer The Questions That FollowSelena Reid0% (1)
- 8 SIM336 Evaluating StrategyDocument30 pages8 SIM336 Evaluating StrategyigotoschoolbybusNo ratings yet
- Nurse CPD Requirements for Resuscitation Council CoursesDocument2 pagesNurse CPD Requirements for Resuscitation Council CoursesEdy Syahputra HarahapNo ratings yet
- Dahms, Monrad & Dalsgaard (2017)Document25 pagesDahms, Monrad & Dalsgaard (2017)irma floresNo ratings yet
- Lectura - Magazine Leica Reporter #86Document76 pagesLectura - Magazine Leica Reporter #86Oier Juez UriagerekaNo ratings yet
- General Essentials QA/QC Plan Sample: Good For Smaller Projects and Bid QualificationsDocument8 pagesGeneral Essentials QA/QC Plan Sample: Good For Smaller Projects and Bid QualificationsBaher ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Curr & Modules BMWDocument62 pagesOutcome Based Curr & Modules BMWEahbm KaduNo ratings yet
- Universal Standards for Accessible Fitness EquipmentDocument101 pagesUniversal Standards for Accessible Fitness EquipmentMehdi Bostan ShirinNo ratings yet
- Pestel AnalysisDocument6 pagesPestel AnalysisHarshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Dave - Kissoondoyal - ProfileDocument10 pagesDave - Kissoondoyal - ProfiledkissoondoyalNo ratings yet
- Bill of The Magna Carta of PatientDocument13 pagesBill of The Magna Carta of PatientjuhlynNo ratings yet
- Accenture《industry blueprint》Document16 pagesAccenture《industry blueprint》jerrywoo0% (1)
- People v. Tengson (Manalastas)Document2 pagesPeople v. Tengson (Manalastas)Arnel Manalastas100% (1)
- Study in Germany for Free - Guide to Bachelor's ProgramsDocument9 pagesStudy in Germany for Free - Guide to Bachelor's ProgramsJuvbayer omayerNo ratings yet
- Diamond ModelDocument15 pagesDiamond Modelcherry d.bandolaNo ratings yet
- Moot Court Memorial (Aadil)Document14 pagesMoot Court Memorial (Aadil)Touseef Hamid83% (6)
- Agricultural Systems: Augustine Perrin, Magali San Cristobal, Rebecka Milestad, Guillaume Martin TDocument10 pagesAgricultural Systems: Augustine Perrin, Magali San Cristobal, Rebecka Milestad, Guillaume Martin TMurilo Sabater da Silva GuerraNo ratings yet
- Analyzing political will and traffic management in the PhilippinesDocument11 pagesAnalyzing political will and traffic management in the PhilippinesKell LynoNo ratings yet
- Module 9 AssignmentDocument5 pagesModule 9 AssignmentAngela BarrettNo ratings yet
- GAIL CSR Project Boosts Girls Education in UttarakhandDocument34 pagesGAIL CSR Project Boosts Girls Education in UttarakhandKarthik RNo ratings yet
- Ibn Khaldun Critique PDFDocument25 pagesIbn Khaldun Critique PDFuser12345678901No ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory (Victor Vroom's)Document8 pagesExpectancy Theory (Victor Vroom's)Pavan Kumar IrrinkiNo ratings yet
- GPWS (TAS) Explained: How the Ground Proximity Warning System WorksDocument40 pagesGPWS (TAS) Explained: How the Ground Proximity Warning System WorksPrerak Kumar Sharma100% (1)
- NWABSD Lesson PlansDocument5 pagesNWABSD Lesson Plansapi-379699844No ratings yet
- CMMS - A Timesaving Implementation Process-Edit - Daryl MatherDocument95 pagesCMMS - A Timesaving Implementation Process-Edit - Daryl MatherMisael Acosta cortes100% (1)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignFrom EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Green Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsFrom EverandGreen Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsNo ratings yet
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (137)
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsFrom EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNo ratings yet
- Flow-Induced Vibrations: Classifications and Lessons from Practical ExperiencesFrom EverandFlow-Induced Vibrations: Classifications and Lessons from Practical ExperiencesTomomichi NakamuraRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsFrom EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Engineering for Kids: Building and Construction Fun | Children's Engineering BooksFrom EverandEngineering for Kids: Building and Construction Fun | Children's Engineering BooksRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresFrom EverandAdvanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Transmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualFrom EverandTransmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Building Support Structures, 2nd Ed., Analysis and Design with SAP2000 SoftwareFrom EverandBuilding Support Structures, 2nd Ed., Analysis and Design with SAP2000 SoftwareRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Piezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation EngineeringFrom EverandPiezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Built: The Hidden Stories Behind Our StructuresFrom EverandBuilt: The Hidden Stories Behind Our StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (27)
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Marine Structural Design CalculationsFrom EverandMarine Structural Design CalculationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Natural Ventilation of Buildings: Theory, Measurement and DesignFrom EverandNatural Ventilation of Buildings: Theory, Measurement and DesignNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Planning and Construction Field ManualFrom EverandPipeline Planning and Construction Field ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Climate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingFrom EverandClimate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Soil Anchor PlatesFrom EverandDesign and Construction of Soil Anchor PlatesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)