Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Basics Worksheet: Body Electrical Definitions and Rules Definitions
Uploaded by
Long HàOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Basics Worksheet: Body Electrical Definitions and Rules Definitions
Uploaded by
Long HàCopyright:
Available Formats
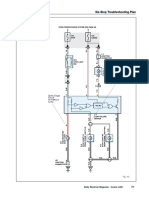
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
WORKSHEET 1-1
Electrical Basics Worksheet
Body Electrical Definitions and Rules
Definitions:
Electricity is the flow of electrical charges through simple materials and devices.
Automotive electrical systems use the flow of electrical charges to do work.
The pressure that pushes the electrical charges is called voltage. The unit of measure for electrical
pressure is Volts (V).
The amount of electrical charges flowing is called current. The unit of measure for current is Amps
(A). 1 Amp equals 6.28 x 1018 (6,280,000,000,000,000,000) electrons per second.
Resistance opposes current, converts the flow of electrical charges into work and causes voltage to
be used up. The unit of measure for resistance is Ohms (W).
Rules:
1. Current (A) can only flow when there is a complete path (circuit) between power and ground (or between a
higher voltage and a lower voltage). No complete path = an “open” circuit = 0 flow
2. The resistance of the load limits current in the circuit and converts current flow into work. In a perfect circuit
the only resistance would be the load.
3. Whenever current flows in a circuit, voltage drops (DV - D is the Greek letter Delta, which means change in,
so DV represents change in voltage or Voltage drop.) will happen. Voltage drops happens anywhere there is
resistance. The larger the resistance the larger the voltage drop.
4. Every circuit will use up all the source voltage (total DV will equal source voltage).
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 155
Current Path Tracing:
Current tracing is a technique that will be used throughout this course to analyze electrical circuits. Current
path tracing allows you to identify the critical components in the circuit, predict voltage levels at any point in the cir-
cuit and predict the locations of voltage drops (DV).
1. a. Using components from the 622 kit, build the following circuit:
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
b. Turn the switch on and make sure the lamp lights.
c. Turn the switch off.
Using the diagram below:
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
2. a. Use a pink (P for power) highlighter to trace from the voltage source to the open in the circuit.
b. Use a green (G for ground) highlighter to trace from ground to the open in the circuit.
No, the circuit is open
c. Does current flow in this circuit? ______________________________________________________
Rule#1 No complete circuit
d. Which body electrical rule helps answer this question? ____________________________________
Because the switch is open no current flows, but
e. Why did we change colors at the switch? _______________________________________________
voltage is present up to terminal 1 of the switch. Connection to ground is present at terminal
2 of the switch.
156 Lexus Technical Training
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
3 a. Draw the switch in the closed position and trace from the voltage source to terminal 1 of the #1187
lamp with a pink highlighter.
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
b. Trace from terminal 2 of the load to ground with a green highlighter.
c. Source V, 12V, +B
Pink represents a part of the circuit where the voltage level is ________________
d. Green represents a part of the circuit where the voltage is level isGround, 0V, -B
_____________
e. Yes, the circuit is complete.
Does current flow in this circuit? ________________________________________
f. The load uses up the voltage, causes DV
Why did we change colors at the load? __________________________________
Open Circuit Voltage, Voltage Drop and Available Voltage Tests
Open Circuit Voltage
4. a. Verify that the circuit built in step 1 is still assembled correctly;
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
b. Turn the switch on and verify that the lamp lights.
c. Turn the switch off.
5. a. Place the red lead of the voltmeter at terminal 1 of the #1500 switch and the black
lead on terminal 2 and record the reading.
Source Voltage, 12 volts, +B_(actual = 14.06V)
_______________________________________________________
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 157
6. a. Trace the current path for Step 5 on the diagram below:
Instructor Note: Because the circuit is open there is no current flow, so you really can't
trace a current path. What you are actually tracing is voltage present. Pink = 12V
present and green = ground present.
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
b. Why did the meter read battery voltage on Step 5?
HINT: A voltmeter reads the voltage difference between the red and the black test lead. Voltage at
the red (+) test lead minus voltage at the black (-) test lead equals the voltage reading displayed
on the meter
+ test lead has source voltage present, - lead has ground. 12V - 0V = 12V reading
c. Is this an open circuit voltage test or a voltage drop test? Open circuit voltage test.
_____________________
HINT: See the Technician Handbook, page 8.
Instructor Note: Voltage present confirms continuity only, not the quality of the circuit.
See Step 18 for an example.
Voltage Drop (DV)
7. a. Turn the switch on and verify that the lamp is illuminated.
b. Place the red test lead on terminal 1 of the #1500 switch and the black test lead on
terminal 2 and record the reading.
Very low volts, should be less than .1Volts (Actual = .002V)
_________________________________________________________________
8. a. Trace the current path for Step 7 on the diagram below:
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
b. Why was the voltage reading on Step 7 very low ? 12V - 12V = 0V
_________________________
c. Is this test an open circuit voltage test or a voltage drop (DV) test? voltage drop
_____________
Instructor Note: If the entire circuit is not traced (see Step 6a trace) the circuit is open
and any voltage tests will be open circuit voltage. DV tests require a complete circuit
with current flowing.
d. When testing DV on a non load (conductor, control device, circuit protection device etc.) what
does a low voltage reading confirm?
Good component and connections.
_____________________________
158 Lexus Technical Training
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
9. a. Verify that the circuit built in step 1 is still assembled correctly;
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
b. Turn the switch on and verify that the lamp lights.
c. Remove the lamp from the socket.
10. Measure and record the open circuit voltage between terminals 1 and 2 of the empty lamp socket.
Battery voltage, source voltage, 12 Volts, +B voltage (Actual = 14.0V)
____________________________________________________________________
11. Install the lamp. Measure and record the voltage drop between terminals 1 and 2 of the #1187 lamp.
Battery voltage, source voltage, 12 Volts, +B voltage (Actual = 13.88V)
____________________________________________________________________
12. What is the key difference between an open circuit voltage test across an open (step 10) and a voltage drop
(DV) test across an operating load (step 11)?
HINT: It is not the meter reading. It was the same for both Steps 10 and 11.
The lamp is lit. Step 10 is open circuit, Step 11 is voltage drop DV
_____________________________________________________________________
13. What does a battery voltage drop across an operating load indicate?
Entire circuit is performing correctly. Load receiving and using correct voltage. The only way to
___________________________________________________________________________________
get a battery voltage drop across an operating load is to have a good circuit. To quote Allen
___________________________________________________________________________________
Woodrum, "If you see a battery voltage reading across a load and the load is not working, the
___________________________________________________________________________________
problem is between the test leads." A battery voltage DV reading across an operating load
___________________________________________________________________________________
confirms everything about the circuit. A battery voltage open circuit reading across a load
___________________________________________________________________________________
indicates an open load.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 159
Available Voltage and Voltage Drop (DV)
14. a. Measure and record Available Voltage(with the switch closed) at the points listed:
Hint: Red (+) test lead to the test point, Black (-) test lead to ground.
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
Source voltage, +B, 12 volts (Actual = 13.9V)
1. Source Voltage ___________________________________________
Source voltage, +B, 12 volts (Actual = 13.9V)
2. Terminal 1 of the #1210 fuse ___________________________________________
3. Terminal 2 of the #1210 fuse
Source voltage, +B, 12 volts (Actual = 13.88V)
___________________________________________
4. Terminal 1 of the #1500 switch
Source voltage, +B, 12 volts (Actual = 13.87V)
___________________________________________
Source voltage, +B, 12 volts (Actual = 13.87V)
5. Terminal 2 of the #1500 switch ___________________________________________
Source voltage, +B, 12 volts (Actual = 13.87V)
6. Terminal 1 of the #1187 lamp ___________________________________________
Ground, low voltage, .1V or less (Actual = .002V)
7. Terminal 2 of the #1187 lamp ___________________________________________
b. What does reading 6 (terminal 1 of the #1187 lamp) indicate?
Good connections and power supply from source to lamp
_____________________________________________________
c. What does reading 7 (terminal 2 of the #1187 lamp) indicate?
Good ground connection
______________________________________________________
15. a. Measure and record the Voltage drop across the components listed:
HINT: Red (+) test lead to terminal 1 of the component and the Black (-) test lead to terminal 2 of the
component.
Very low voltage, .1 volt or less(Actual = .019V)
#1210 fuse ________________________________________
#1500 switch Very low voltage, .1 volt or less (Actual = .002V)
________________________________________
#1187 lamp +B, source voltage, 12 volts (Actual = 13.86V)
________________________________________
b. What is indicated by a low Voltage Drop at the #1210 fuse and the #1500 switch and a high Voltage drop at
the #1187 lamp?Good components at the fuse and the switch shown by very low voltage
_____________________________________________________________
drops. Good lamp and power supply shown by +B DV across the lamp.
_________________________________________________________________________________
c. Do both types of tests (Step 14 Available Voltage & Step 15 DV) give you the same information?
Yes. Step 14 requires subtraction to calculate DV measured in Step 15.
_________________________________________________________________________________
160 Lexus Technical Training
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
16. a. Add a #1152 lamp to the circuit as indicated below:
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1152 1500 1187
b. Turn the switch on and make sure both lamps light.
c. The #1152 lamp will simulate unwanted resistance between the fuse and the switch in an otherwise
normal lamp circuit. In a normal circuit this unwanted resistance would not be visible (so pretend that you
can’t see the #1152 lamp). The next few steps will use Available Voltage and Voltage Drop tests to locate
the unwanted resistance.
17 a. The customer concern is a dim lamp in this circuit. Can you verify the condition?
yes, the 1187 lamp is dim and since I can't see the invisible 1152 I don't know why.
______________________________________________________________________________
b. Trace the current path for a normal circuit using the diagram below. When using current path tracing as a
diagnostic method you always trace the circuit as it appears in the EWD. The purpose of current path
tracing is to learn how a normal circuit works. Then you use your circuit knowledge to find out where the
problem circuit is different.
c. Use this trace to predict normal voltage levels for this circuit in the steps below.
invisible
1152
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 161
18. a. Based on your current path trace from Step 17b predict the voltage at terminal 1 of the #1187 lamp.
+B, Source voltage, 12 volts
_________________________________________________________________
b. Remove the #1187 lamp. Measure and record the Open Circuit Voltage at Terminal 1 of the empty
socket.
+B, Source voltage, 12 volts (Actual = 13.97V)
__________________________________________________________________
Continuity only. An open circuit voltage test will NOT
c. What does this reading indicate? _____________________________________________________
show high resistance problems in circuits. Meter impedance is too high to load the circuit
__________________________________________________________________________________
so no DV happens at invisible 1152.
__________________________________________________________________________________
d. Install the lamp.
19. a. Based on the trace from step 17b, predict the Voltage Drop (DV) across the #1187 lamp.
+B, source voltage
___________________________________________________________________
12V, +B , source voltage (Actual = 13.97V)
b. Measure and record source voltage. _____________________________________
Approx 3.0V (Actual = 3.24V).
c. Measure and record DV across #1187 lamp. _______________________________
Note: Leave the meter leads connected to the circuit after taking this reading.
High resistance in the circuit. A good circuit
d. What does this reading indicate? ________________________________________
would show approximately source voltage DV across the only load in the circuit.
_____________________________________________________________________
20. a. Based on the current path trace from Step 17b, predict the Available Voltage (for a normal circuit) at
terminal 1 of the #1187 lamp.
Based on the normal circuit trace, there should be 12V, +B, source voltage available.
_____________________________________________________________________
b. Move the Black (-) test lead to ground, measure and record Available Voltage at terminal 1 of
the #1187 lamp.
Approximately 3.0 Volts (Actual = 3.24V), same reading as Step 19c.
_____________________________________________________________________
Instructor Note: As a generic test procedure the following method is very effective.
Step 1 - Trace current path and predict the DV of the load. Step 2 - Voltage drop the
load. Full source V with an operating load indicates a good, normal circuit. Full source
V with no load operation indicates an open load. Less than full source DV indicates
high resistance in the circuit. 0V indicates an open. Step 3 - Move the negative test
lead to ground to find out if the problem is in the power supply side of the circuit.
Less than source V indicates high resistance in the supply side of the circuit. 0V indi-
cates an open. If Step 3 shows source V go to Step 4. Step 4 - Move the positive
test lead to the ground side of the load. Anything over 0.1V indicates a problem in the
ground side of the circuit.
c. What does this reading indicate? High resistance in the power supply side of the
________________________________________
circuit causes the #1187 lamp to be dim.
_____________________________________________________________________
162 Lexus Technical Training
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
21. a. Based on the current path trace from Step 17b, predict the available voltage (for a normal circuit) at
the following points.
Source voltage, +B, 12 Volts
Terminal 2 of the #1500 switch. ________________________________
Source voltage, +B, 12 Volts
Terminal 1 of the #1500 switch. ________________________________
Source voltage, +B, 12 Volts
Terminal 2 of the #1210 fuse. _________________________________
Source voltage, +B, 12 Volts
Terminal 1 of the #1210 fuse. __________________________________
b. Measure and record Available Voltage at these points.
Approximately 3 Volts (Actual = 3.25V)
Terminal 2 of the #1500 switch. ________________________________
Approximately 3 Volts (Actual = 3.25V)
Terminal 1 of the #1500 switch. ________________________________
Source voltage, +B, 12 Volts
Terminal 2 of the #1210 fuse. _________________________________
Source voltage, +B, 12 Volts
Terminal 1 of the #1210 fuse. __________________________________
Voltage is lost between the fuse and the
c. What do these readings indicate? ___________________________________
switch. High resistance located between the fuse and the switch.
_________________________________________________________________
22. a. Based on the trace from Step 17b, predict DV from terminal 2 of the #1210 fuse to terminal 1 of
the #1500 switch.
Should be very low, probably less than .01V, definitely less than .1V.
_____________________________________________________________________
b. Measure the DV from terminal 2 of the #1210 fuse to terminal 1 of the #1500 switch.
Approximately 10 Volts. (Actual = 10.66V)
____________________________________________________________________
High resistance between the the fuse and
c. What does this reading indicate? ________________________________________
the switch.
_____________________________________________________________________
d. Do both types of tests (Step 21b Available Voltage and Step 22b DV) give you the same
information?
Yes. Step 21b Available Voltage requires subtraction to determine the amount of voltage
________________________________________________________________________________
drop, while Step 22b DV shows the voltage drop directly.
________________________________________________________________________________
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 163
Series Circuits
Hint: See the Series Circuit rules on pages 6 and 7 of this handbook.
23. a. Using components from the L622 kit, build the following circuit:
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187
b. Close the switch and make sure the lamp lights.
c. Trace the current path for this circuit.
d. Measure and record voltage readings at the following points:
Source voltage »13.9 V
____________
DV between terminals 1 and 2 of the #1500 switch ».001 V
____________
DV between terminals 1 and 2 of the #1187 lamp
»13.9 V
____________
e. Do the meter readings match your current path trace predictions? YES
___________
If there is only one load in the circuit, all the voltage is used up
in that load.
24. a. Add a #1152 bulb to the circuit as shown below:
b. Close the switch and verify that both lamps light, then turn the lamps off.
c. Disconnect the lamps from the circuit, then measure and record the resistance of each lamp.
»6 W
#1187 __________________
»12 W
#1152 __________________
164 Lexus Technical Training
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
d. Why is it necessary to disconnect the components before measuring resistance?
Components must be isolated from circuit for accurate ohmeter readings
___________________________________________________________________
e. Connect the lamps to the circuit and close the switch.
The 1152 is much brighter than the 1187
f. Which lamp is brighter? ______________________________________________
g. Measure and record the DV of each lamp:
» 3.2V
#1187 _________________
» 10.7V
#1152 _________________
h. Trace the current path for this circuit.
i. What is the voltage between the lamps (the part of the circuit traced in blue)?
» 10.7V
_____________________________________________________________________
If there are multiple loads in the circuit, voltage is divided ac-
cording to the resistance of the loads. The load with the most
resistance will use the most voltage, the load with the least re-
sistance will use the least voltage. The voltage used is directly
proportional to the resistance.
25. Using the circuit built for Step 24, measure and record the current (A) at the following points:
» 92 mA
Between terminal 2 of the #1500 switch and terminal 1 of the #1187 lamp. ________
» 92 mA
Between terminal 2 of the #1187 lamp and terminal 1 of the #1152 lamp. __________
» 92 mA
Between terminal 2 of the #1152 lamp and ground. ___________
Amperage is the same throughout the circuit. This means that
an ammeter can be connected anywhere in the circuit and
measure the Amperage.
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 165
26. a. Using components from the L622 kit, build the circuit shown below:
b. Close the switch and verify that all three lamps light.
c. Trace the current path for this circuit.
d. Measure and record the following readings:
Current (A) » 81 mA
______________
DV across the first #1187 lamp » 2.6 V
______________
DV across the #1152 lamp » 8.7 V
______________
DV across the second #1187 lamp » 2.6 V
______________
e. Compare the current (A) for this circuit with the reading from Step 25.
Total resistance is the sum of all the resistance in the circuit.
Adding a resistance in series will increase total circuit resis-
tance and decrease current (A).
Parallel Circuits
Hint: See the parallel circuit rules on page 7 of the Technician Handbook
27. a. Using components from the L622 kit, build the circuit shown below:
1 2
1187 #1
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187 #2
b. Trace the current path for this circuit.
166 Lexus Technical Training
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
c. Measure and record the Available Voltage at terminal 1 of each #1187 lamp:
» 13.8 V
1187 #1 __________________
» 13.8 V
1187 #2 __________________
The voltage applied to each branch is the same.
28. Using the circuit built for Step 27, measure and record the current between the following points:
» 440 mA
Terminal 2 of the #1210 fuse and terminal 1 of the #1500 switch. _________________
» 220 mA
Terminal 2 of the #1500 switch and terminal 1 of 1187 #1. ______________________
» 220 mA
Terminal 2 of the #1500 switch and terminal 1 of 1187 #2. ______________________
29. a. Using components from the L622 kit, build the circuit shown below:
1 2
1187 #1
+ 1 2 1 2 1 2
–
1210 1500 1187 #2
1 2
1152
b. Trace the current path for this circuit.
c. Disconnect the lamps from the circuit and measure and record their resistances:
»6W
1187 #1 _______________________
»6W
1187 #2 _______________________
» 12 W
1152 ________________________
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 167
d. Why is it necessary to disconnect the lamps to measure their resistance?
» To isolate each lamp from parallel connections in the circuit
__________________________________________________________________
e. Install the lamps and close the switch. Verify that all 3 lamps light.
f. Measure and record the current between the following points:
Terminal 2 of the #1210 fuse and terminal 1 of the #1500 switch. » 540 mA
__________
Terminal 2 of the #1500 switch and terminal 1 of 1187 #1. » 220 mA
__________
Terminal 2 of the #1500 switch and terminal 1 of 1187 #2. » 220 mA
__________
» 100 mA
Terminal 2 of the #1500 switch and terminal 1 of the #1152 lamp. __________
The current in a branch is determined by the branch’s
resistance. The branch with the least resistance will have
the most current.
31. a. Compare total current for Step 28 and Step 29:
» 440 mA
Total current for Step 28. ______________________
» 540 mA
Total current for Step 29 ______________________
Total resistance decreases as branches are added. Adding a
branch lowers total resistance and increases current.
The total circuit resistance is always lower than the lowest
branch resistance.
168 Lexus Technical Training
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
Series-Parallel Circuits
32. a. Using components from the L622 kit, build the following circuit:
Note: This circuit is a simulation of the horn circuit for the 1998 ES 300. Lamps are substituted for
horns, otherwise the circuit is functionally identical.
b. Which meter function would help to identify the terminals of the relay?
Ohmeter, the coil will show » 70w and all other terminals infinite resistance
_________________________________________________________________ (OL)
c. Turn the switch on and off and verify that the lamps light.
33. a. Using the diagram below, trace the current path for this circuit when the lamps are off.
b. Predict the voltage at terminal 1 of the #1500 switch when the lamps are off.
Battery voltage, +B, source voltage (Actual » 13.9 V)
_________________________________________________________________
c. Measure and record the voltage at terminal 1 of the #1500 switch when the lamps are off.
Battery voltage, +B, source voltage (Actual » 13.9 V)
___________________________________________________________________
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 169
34. a. Using the diagram below, trace the current path for this circuit when the lamps are on.
b. Predict the voltage at terminal 1 of the #1500 switch when the lamps are on.
Ground, very low voltage, less than .1V
________________________________________________________________
c. Measure and record the voltage at terminal 1 of the #1500 switch when the lamps are on.
Ground, very low voltage, less than .1V (actual » .002V)
_________________________________________________________________
170 Lexus Technical Training
SIX-STEP TROUBLESHOOTING PLAN
35. Using the 1998 ES300 horn circuit diagrams provided below:
a. Trace the current path with the horns off.
b. Trace the current path with the horns on.
a. Horns off b. Horns on
10A 10A
HORN HORN
1 5 1 5
HORN HORN
RELAY RELAY
2 3 2 3
10 2K 1 2F 10 2K 1 2F
G-B
G-B
J2 A J2 A
G-W
G-W
JUNCTION JUNCTION
CONNECTOR CONNECTOR
A A
G-B
G-B
G-W G-W
6 1 1 6 1 1
H7 H8 H7 H8
C12 HORN HORN C12 HORN HORN
HORN SW LH RH HORN SW LH RH
[COMB. SW] [COMB. SW]
36. Refer to the current path traces from Step 35 to answer the following questions:
a. Why is there battery voltage at connector C12, terminal 6 of the switch when the horns are off?
There is no connection to ground through the switch, so no DV happens at
_____________________________________________________________________
the relay coil.
_____________________________________________________________________
b. What does a battery voltage reading at connector C12, terminal 6, horns off, tell you about
the circuit?
There is no continuity between the fuse and connector C12, terminal 6. No
_____________________________________________________________________
information on circuit quality, but continuity exists.
_____________________________________________________________________
c. Where would your next test point be if you did not measure battery voltage at connector C12,
terminal 6, with the horns off?
Multiple acceptable answers. Junction connector 2, Connector 2K,
_____________________________________________________________________
pin 10 etc.
_____________________________________________________________________
Body Electrical Diagnosis - Course L652 171
d. Why is there low voltage at connector C12, terminal 6, when the horns are on?
Grounding the control side of the horn relay causes to flow. The coil in
_____________________________________________________________________
the relay uses up the voltage.
_____________________________________________________________________
e. If both horns were inoperative, where would you test first?
Multible acceptable answers. Most likely are the fuse or the relay.
_____________________________________________________________________
f. If only one horn was inoperative, would you test the relay or the switch?
No. One operating horn confirms the relay and the switch. The problem would
_____________________________________________________________________
have to be in the branch with the inoperative horn.
_____________________________________________________________________
Problems in the series portion of a series-parallel circuit affect
the entire circuit. Problems in a parallel branch of a series par-
allel circuit affect only the branch where the problem is.
172 Lexus Technical Training
You might also like
- Diodes Clipping and Clamping Circuits ExperimentDocument15 pagesDiodes Clipping and Clamping Circuits ExperimentAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 2 (Final)Document11 pagesExperiment # 2 (Final)John Mickelson FaustinoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Wave Shaping CircuitsDocument9 pagesExperiment 2 Wave Shaping CircuitsMaria Abia Lapena50% (2)
- A. DC Operation I. ObjectiveDocument9 pagesA. DC Operation I. ObjectivedummyNo ratings yet
- ALMOST HALF DONE Experiment 5 Clamping and ClippingDocument16 pagesALMOST HALF DONE Experiment 5 Clamping and ClippingAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No1Document20 pagesExperiment No1Deepanshu Gupta100% (2)
- Applied Electronics Lab 2Document9 pagesApplied Electronics Lab 2Rickel RoweNo ratings yet
- Exp._1_ManualDocument4 pagesExp._1_Manualf20212001No ratings yet
- Quaid-E-Awam University of Engg., Sci. & Tech., Nawabshah Department of Telecommunication Engineering Amplifiers & OscillatorsDocument5 pagesQuaid-E-Awam University of Engg., Sci. & Tech., Nawabshah Department of Telecommunication Engineering Amplifiers & Oscillatorsakjan303No ratings yet
- Device Exp 2 Student ManualDocument4 pagesDevice Exp 2 Student Manualgg ezNo ratings yet
- Postlab Report #5Document11 pagesPostlab Report #5Poyraz EmelNo ratings yet
- Diode Clipper and Clamper CircuitsDocument12 pagesDiode Clipper and Clamper CircuitsBorse RajNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 ElectronicsDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 ElectronicsRhea Daluddung SanchezNo ratings yet
- Electronics 1Document42 pagesElectronics 1Shanti Emmanuelle EscabarteNo ratings yet
- (ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportDocument11 pages(ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportLawrence Abram AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- BJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseDocument29 pagesBJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseKrista JacksonNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier Circuit AnalysisDocument14 pagesDiode Rectifier Circuit Analysistungpham2014No ratings yet
- Midterm 2013 SolutionDocument5 pagesMidterm 2013 SolutionArunabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Lab ExperimentDocument8 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Lab ExperimentDevee AmbasNo ratings yet
- IIT Patna Voltage to Frequency ExperimentDocument2 pagesIIT Patna Voltage to Frequency ExperimentHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 ReportDocument9 pagesLab 2 Reportapi-302057574No ratings yet
- Question of EE ProjectDocument5 pagesQuestion of EE ProjectANJALI KUMARINo ratings yet
- Experiment-1 Title: Diode As Clipper & Clamper Circuit ObjectivesDocument11 pagesExperiment-1 Title: Diode As Clipper & Clamper Circuit ObjectivesGPA Innovation LabNo ratings yet
- FEC002-Lab-ManualDocument86 pagesFEC002-Lab-ManualjunalynnerosaNo ratings yet
- EE100 Gyrator GuideDocument7 pagesEE100 Gyrator GuideDennis Ojok OciiNo ratings yet
- Ex 305Document51 pagesEx 305DineshKumarCholkarNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument34 pagesBasic ElectronicsAdnan Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at RangsitDocument13 pagesSirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at RangsitMohd Helmy Hakimie RozlanNo ratings yet
- Expt 1Document5 pagesExpt 1Shang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- EEE111 - Lab ManualDocument28 pagesEEE111 - Lab ManualAnindita MishiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Network Lab Negative Impedance Converter & Gyrator Circuit ExperimentsDocument5 pagesElectrical Engineering Network Lab Negative Impedance Converter & Gyrator Circuit ExperimentsAkhilesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- DC & AC Operation of a Transformer Coupled Two-Stage AmplifierDocument9 pagesDC & AC Operation of a Transformer Coupled Two-Stage AmplifierdummyNo ratings yet
- Lab#02: Characteristics of Power Diode: Objective: To Become Familiar With The Operating Principles of Power DiodesDocument5 pagesLab#02: Characteristics of Power Diode: Objective: To Become Familiar With The Operating Principles of Power DiodesUsmanIbrahimNo ratings yet
- FDC Lab ManualDocument25 pagesFDC Lab ManualtovilasNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document6 pagesLab 2hkvaldez0019No ratings yet
- Doc03 Lab Manual ExperimentsDocument28 pagesDoc03 Lab Manual ExperimentstennisartanongNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 06 B: Title: DC-Power Supply: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimDocument14 pagesExperiment No. 06 B: Title: DC-Power Supply: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimStar LordNo ratings yet
- Aee221l Experiment #6Document4 pagesAee221l Experiment #6Vinje Joshua SumileNo ratings yet
- Zero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorDocument7 pagesZero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorTimoth Dev50% (2)
- Diod RectifierDocument35 pagesDiod RectifierRizalNo ratings yet
- PART A: Power Factor CorrectionDocument5 pagesPART A: Power Factor CorrectionShajedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment 3Document15 pagesLaboratory Experiment 3JOHN LOUIE SUDENo ratings yet
- To Construct A Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit and To Check Its Output Waveform On Oscilloscope Theory Half-Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesTo Construct A Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit and To Check Its Output Waveform On Oscilloscope Theory Half-Wave RectifierartistryrivalNo ratings yet
- Expt. No. 2 - Basic Operational Amplifier Circuit PDFDocument2 pagesExpt. No. 2 - Basic Operational Amplifier Circuit PDFPradeep DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Automobiles PraticalDocument12 pagesAutomobiles PraticalBorse RajNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1. Diode Characteristics HalfDocument10 pagesLab Report 1. Diode Characteristics HalfayasumireNo ratings yet
- 6655 Lab Manual 2Document162 pages6655 Lab Manual 2Brett Hendricks100% (1)
- Parameters of Op-Amp: D A C - A - D - 2019Document4 pagesParameters of Op-Amp: D A C - A - D - 2019Rajesh KbNo ratings yet
- Mamaradlo ErikaMae 2B Expt2 FinalDocument10 pagesMamaradlo ErikaMae 2B Expt2 FinalErika Mae MamaradloNo ratings yet
- 6655 Lab Manual PDFDocument160 pages6655 Lab Manual PDFkL10111No ratings yet
- Solutions To Homework 1: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)Document8 pagesSolutions To Homework 1: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)joa91189100% (1)
- 4 - ELD255 - Lab 4 - Full Wave Rectifier - Sep-28-18Document3 pages4 - ELD255 - Lab 4 - Full Wave Rectifier - Sep-28-18killtime921No ratings yet
- 183 Eee202s Exp1Document13 pages183 Eee202s Exp1Shamsul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument8 pagesLab 1 - Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsMD NAZMUN HASAN NAFEESNo ratings yet
- The Diode ClamperDocument6 pagesThe Diode ClamperTitan MalokaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Experiment 4Document13 pagesElectronic Devices Experiment 4ArvinALNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Rr158-Chien Luoc Giam Nguy Co Viem DaDocument83 pagesRr158-Chien Luoc Giam Nguy Co Viem DaLong HàNo ratings yet
- Getting To Grips With Manual Handling PDFDocument12 pagesGetting To Grips With Manual Handling PDFraoultrifan7560No ratings yet
- Skin WashingDocument1 pageSkin WashingLong HàNo ratings yet
- Rr525-Su Dung Gang Tay Bao Ve Voi Hoa Chat in UVDocument66 pagesRr525-Su Dung Gang Tay Bao Ve Voi Hoa Chat in UVLong HàNo ratings yet
- Use of Lifting and Handling AidsDocument12 pagesUse of Lifting and Handling AidsHealthSafety100% (4)
- Reusable GlovesDocument1 pageReusable GlovesLong HàNo ratings yet
- HSE Guide to Skin Checks for Early Dermatitis SignsDocument1 pageHSE Guide to Skin Checks for Early Dermatitis SignsLong HàNo ratings yet
- Correct Removal of Gloves: Single Use Gloves (Splash Resistant)Document1 pageCorrect Removal of Gloves: Single Use Gloves (Splash Resistant)Long HàNo ratings yet
- Printing With Isocyanate-Based Inks: COSHH Essentials For PrintersDocument4 pagesPrinting With Isocyanate-Based Inks: COSHH Essentials For PrintersLong HàNo ratings yet
- ArtiosCAD Specification Sheet Under 40 CharactersDocument1 pageArtiosCAD Specification Sheet Under 40 CharactersLong HàNo ratings yet
- Skin WashingDocument1 pageSkin WashingLong HàNo ratings yet
- Printing With UV-curable Inks and Coatings: COSHH Essentials For PrintersDocument4 pagesPrinting With UV-curable Inks and Coatings: COSHH Essentials For PrintersLong HàNo ratings yet
- 7.5A Dome Fuse: Voltage Drop Measurement / Switch #17 (Instructor Led)Document4 pages7.5A Dome Fuse: Voltage Drop Measurement / Switch #17 (Instructor Led)Long HàNo ratings yet
- HSE Guide to Proper Hand Washing & Moisturizing TechniqueDocument1 pageHSE Guide to Proper Hand Washing & Moisturizing TechniqueslawiNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety Executive manual film developmentDocument3 pagesHealth and Safety Executive manual film developmentLong HàNo ratings yet
- Advice For Managers: COSHH Essentials For PrintersDocument3 pagesAdvice For Managers: COSHH Essentials For PrintersLong HàNo ratings yet
- Reusable GlovesDocument1 pageReusable GlovesLong HàNo ratings yet
- Measuring Amperage: Section 1 - Series Type Ammeter - Parasitic LoadDocument4 pagesMeasuring Amperage: Section 1 - Series Type Ammeter - Parasitic LoadLong HàNo ratings yet
- Electrical Diagnostic Tools WorksheetDocument2 pagesElectrical Diagnostic Tools WorksheetLong HàNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS MEASURING DEVICESDocument4 pagesELECTRICAL DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS MEASURING DEVICESLong HàNo ratings yet
- L652 Iwks 5-1Document2 pagesL652 Iwks 5-1Long HàNo ratings yet
- Radiator Fan Circuit: 1998 ES 300. Using The EWD Fill in The Blanks in Your Workbook: 1. Verify The SymptomsDocument8 pagesRadiator Fan Circuit: 1998 ES 300. Using The EWD Fill in The Blanks in Your Workbook: 1. Verify The SymptomsLong HàNo ratings yet
- Radiator Fan Circuit: 1998 ES 300. Using The EWD Fill in The Blanks in Your Workbook: 1. Verify The SymptomsDocument8 pagesRadiator Fan Circuit: 1998 ES 300. Using The EWD Fill in The Blanks in Your Workbook: 1. Verify The SymptomsLong HàNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Flexographic Printing Technology For Multi Busbar Solar CellsDocument12 pagesEvaluation of Flexographic Printing Technology For Multi Busbar Solar CellsLong HàNo ratings yet
- Six-step troubleshooting plan for headlight issuesDocument4 pagesSix-step troubleshooting plan for headlight issuesLong HàNo ratings yet
- Electrical Diagnostic Tools WorksheetDocument2 pagesElectrical Diagnostic Tools WorksheetLong HàNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Printing Substrate Properties On Color Characterization in Flexography According To The Iso SpecificationsDocument5 pagesThe Influence of Printing Substrate Properties On Color Characterization in Flexography According To The Iso Specificationsleandro3113No ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS MEASURING CURRENTDocument4 pagesELECTRICAL DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS MEASURING CURRENTLong HàNo ratings yet
- L652 Swks 5-1Document2 pagesL652 Swks 5-1Long HàNo ratings yet
- Six-Step Troubleshooting PlanDocument6 pagesSix-Step Troubleshooting PlanLong HàNo ratings yet
- Biomechanical Considerations For The Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethDocument13 pagesBiomechanical Considerations For The Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethSoraya BouchammaNo ratings yet
- (9781783475537 - The Neuroscience of Organizational Behavior) IntroductionDocument4 pages(9781783475537 - The Neuroscience of Organizational Behavior) IntroductionMiguelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 2Document4 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 2Mohd Adam AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Selenia Dimensions V1.8 Rev 3Document418 pagesService Manual Selenia Dimensions V1.8 Rev 3IMEEDCO SRL100% (1)
- Office Address: National Government Center EDSA, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines Telephone Nos.: (02) 929-6071 To 78 Website: WWW - Nia.gov - PH Telefax No. (632) 928-9343 TIN No. 000-916-415Document2 pagesOffice Address: National Government Center EDSA, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines Telephone Nos.: (02) 929-6071 To 78 Website: WWW - Nia.gov - PH Telefax No. (632) 928-9343 TIN No. 000-916-415IMEG MindanaoNo ratings yet
- JNTUK - Revised Syllabus For M. Tech Transportation EngineeringDocument20 pagesJNTUK - Revised Syllabus For M. Tech Transportation Engineeringvamsi_rsNo ratings yet
- The Role of Studying Abroad in Attitudes Towards Immigration A European Context Yakup Öz, Enes GökDocument21 pagesThe Role of Studying Abroad in Attitudes Towards Immigration A European Context Yakup Öz, Enes GökSTAR ScholarsNo ratings yet
- Final ResearchDocument56 pagesFinal ResearchJosiah ManyongoriNo ratings yet
- Galileo (Satellite Navigation)Document21 pagesGalileo (Satellite Navigation)irayoNo ratings yet
- TPL5010 Nano-Power System Timer With Watchdog Function: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument27 pagesTPL5010 Nano-Power System Timer With Watchdog Function: 1 Features 3 Descriptionelfak.2000No ratings yet
- Fish Bowl Strategy: Fishbowl Is A Strategy For Organizing Medium-To Large-Group Discussions. Students AreDocument2 pagesFish Bowl Strategy: Fishbowl Is A Strategy For Organizing Medium-To Large-Group Discussions. Students AreAllysa Marie BorladoNo ratings yet
- Plant Pathology Curriculum Revised for BSc, MSc and PhD DegreesDocument90 pagesPlant Pathology Curriculum Revised for BSc, MSc and PhD Degreesjahangir khanNo ratings yet
- Finals Quiz 1 ReviewerDocument20 pagesFinals Quiz 1 ReviewerAngelo DongonNo ratings yet
- Sample Narrative Report and Documentation 2024 InsetDocument3 pagesSample Narrative Report and Documentation 2024 InsetWILSON CASTRONo ratings yet
- RatioLog and ProportionDocument6 pagesRatioLog and ProportionshlokNo ratings yet
- Major Test 01 7th PDFDocument4 pagesMajor Test 01 7th PDFKids robotics TeamNo ratings yet
- 8.me331f20 Static Force Analysis ExamplesDocument7 pages8.me331f20 Static Force Analysis ExamplesTaylan KaraçelikNo ratings yet
- Catalogo General MAGPOWRDocument16 pagesCatalogo General MAGPOWRananda.slp.admonNo ratings yet
- List of Gravitationally Rounded Objects of The Solar SystemDocument12 pagesList of Gravitationally Rounded Objects of The Solar Systemsebastian431No ratings yet
- Vision IAS Notes List of BookletsDocument1 pageVision IAS Notes List of BookletsBhavya KohliNo ratings yet
- Managing Supply Chain Risks R1Document48 pagesManaging Supply Chain Risks R1DebashishDolonNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Global Perspectives Primary Lesson PackDocument16 pagesCambridge Global Perspectives Primary Lesson PackThin Thant ThantNo ratings yet
- WLP G10 Q1 W1 LithosphereFatalla PDFDocument4 pagesWLP G10 Q1 W1 LithosphereFatalla PDFJoanne TalingeNo ratings yet
- Gauss's LawDocument10 pagesGauss's LawAliceAlormenuNo ratings yet
- Kesimira Qonita (18930066)Document12 pagesKesimira Qonita (18930066)Kesimira QonitaNo ratings yet
- Closing Speech for Mental Health WeekDocument2 pagesClosing Speech for Mental Health WeekPARDS MOTOVLOGS100% (2)
- Aits Syllabus - 2018-19 Final ..-1Document4 pagesAits Syllabus - 2018-19 Final ..-1DrNaresh SahuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - PMP Authorized Exam Prep - V3 - Business EnvironmentDocument105 pagesLesson 1 - PMP Authorized Exam Prep - V3 - Business EnvironmentmaiyomarionneNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Waste, Environment, Makassar, TPA AntangDocument5 pagesKeywords: Waste, Environment, Makassar, TPA AntangWahidin Alamnuari RachmanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 09 Algebra 1 Honors Concepts (Revised)Document9 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 09 Algebra 1 Honors Concepts (Revised)Anni LaritaNo ratings yet