Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urinary System
Uploaded by
AntonioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Urinary System
Uploaded by
AntonioCopyright:
Available Formats
Our Lady of Fatima University
College of Arts and Sciences
Natural Science Department
GZOO111 LABORATORY
EXERCISE NO. 15
THE URINARY STRUCTURES
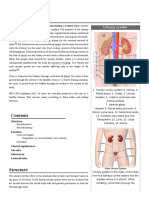
The urinary system is composed of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and associated
structures. The functions of the urinary system include maintaining extracellular fluid balance, excreting
wastes, and maintaining blood pH
I. Objective:
Identify the major organs of the urinary system and find them in model or charts
Describe the gross anatomical features of the kidney and identify them in figures,
models and specimens.
Describe the features of the nephron and locate them in figures and models
II. Materials:
Atlas of human anatomy
Anatomy and physiology book
Dissectible models of kidney
III. Procedure:
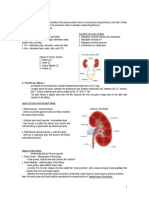
A. The Kidney model
Locate these features of the human kidney on a model or chart of a frontal section
1. Locate the hilum and renal capsule from this perspective
2. Identify these structures located just within the hilum:
Renal sinus – a fat filled cavity
Renal pelvis – a wide section of the urinary channel, distal to the ureters
Calyces – branches of the pelvis, they extend from the kidney tissue proper
3. The kidney tissue proper is divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla, as is the tissue
of many organs. Renal pyramids are cone shaped sections of tissue lying mostly within the
medulla. Each appears as a triangle in a frontal section. Each is composed of collecting ducts
that conduct urine toward the papilla, which is surrounded by the end of calyx.
B. The Nephron model
1. Locate the main features of the nephron and associated structures in a model or chart.
Renal corpuscle
Proximal convulated tubule
Loop of Henle
Distal convulated tubule
URINARY SYSTEM
1. Illustrate and Label all the organs of the urinary system
2. Illustrate and label all the parts of the Kidney (Frontal section)
3. Illustrate and Label all the parts of a nephron:
IV. A. Questions:
(Use another sheet of paper for your answer)
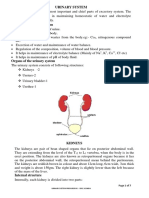
1. Name the structures that make up the urinary system. List the functions of the urinary system
Kidney - The kidneys' job is to filter your blood. They remove wastes, control the body's fluid
balance, and keep the right levels of electrolytes. All of the blood in your body passes through
them several times a day.
Ureter - duct that transmits urine from the kidney to the bladder
Urinary bladder - The urinary bladder is a hollow elastic organ that functions as the body’s urine
storage tank before passing into the urethra and exiting the body
Urethra - are pelvic urinary organs whose respective functions are to store and expel urine
outside of the body in the act of micturition (urination).
2. What structures that surround the kidney?
Fibrous capsule
Perirenal fat
Renal fascia with posterior and anterior layers
Pararenal fat
Renal capsule
3. What is the functional unit of the kidney? Name its parts
nephron
4. What are the functions of the ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra? Describe their structure.
Ureters – transmit urine from kidney to urinary bladder (Each ureter is a narrow tube that is
about 12 inches (30 cm) long. A ureter has thick contractile walls, and its diameter varies
considerably at different points along its length. The tube emerges from each kidney, descends
behind the abdominal cavity, and opens into the bladder )
Urinary bladder – is a storage tank of the urine and the bladder is about the size and shape of a
pear when it’s empty the bladder is lined by layers of muscle tissue that stretch to hold urine.
The normal capacity of the bladder is 400-600 mL.
Urethra - is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral orifice, which is the
opening of the urethra on the surface of the body. The urethra in males travels through
the penis, so it is much longer than the urethra in females. In males, the urethra averages
about8 inch long, whereas in females it averages only about 1.5 inch long. In males, the urethra
carries semen as well as urine, but in females, it carries only urine.
5. Name and describe the three general processes that are involved in the production of urine.
B. Put in order:
Arrange the following structures in the order in which substances flow through urinary
system, beginning with the site of filtration:
A. ascending limb of the loop of henle
B. Bowman’s capsule
C. calyces
D. collecting duct
E. descending limb of the loop of henle
F. distal convoluted tubule
G. proximal convoluted tubule
H. renal pelvis
I. ureters
J. urethra
K. urinary bladder
altor
You might also like
- ASAM Application Guidance 8 2019Document22 pagesASAM Application Guidance 8 2019Victor Daniel Rivera Carrion100% (1)
- Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesUrinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Urinary SystemIan CruzNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary SystemElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Functional Nitric Oxide NutritionDocument131 pagesFunctional Nitric Oxide NutritionIuliu Ciupe-Vaida100% (3)
- Session #41 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document5 pagesSession #41 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary SystemDocument23 pagesGenitourinary SystemRisma ZulfianiNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 1 1aDocument88 pagesRenal Physiology 1 1afentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking AgentsnewDocument22 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking Agentsnewvinay0717100% (1)
- Introduction To Physical ExaminationDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Physical ExaminationMuhammad SyarmineNo ratings yet
- General Zoology 1 LaboratoryDocument4 pagesGeneral Zoology 1 LaboratoryKirsten AletheaNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy: Lesson 8: Urogenital SystemDocument19 pagesBasic Human Anatomy: Lesson 8: Urogenital SystemIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Excretory System Lecture 1 JUWDocument12 pagesExcretory System Lecture 1 JUWamjad.46987No ratings yet
- Urinary System TheoryDocument29 pagesUrinary System Theoryوجد عمرNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System: Gansheng-Wei Department of AnatomyDocument17 pagesThe Urinary System: Gansheng-Wei Department of Anatomyprasun_vNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document6 pagesLab 7InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument18 pagesRenal SystemS GNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Laboratory 1Document2 pagesGeneral Zoology Laboratory 1Luther Abaya MolinaNo ratings yet
- Human Urinary System NGDocument26 pagesHuman Urinary System NGDenisco NkemgneNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary SystemRoiland Atienza BaybayonNo ratings yet
- Excretory System 2021Document27 pagesExcretory System 2021fashion20trendsNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary SystemDocument26 pagesGenitourinary SystemKharismatul MaghvirohNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 10: Frog Circulatory and Excretory SystemDocument5 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 10: Frog Circulatory and Excretory SystemMaricris GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Lesson AssignmentDocument22 pagesLesson AssignmentFatima AzziffNo ratings yet
- 13EXCRETORYDocument3 pages13EXCRETORYDaniellaRuth Cajurao CanalesNo ratings yet
- Topik 2 2021Document26 pagesTopik 2 2021AnnisNo ratings yet
- Ran Ii-Urinary System - 123718Document16 pagesRan Ii-Urinary System - 123718joykibaki066No ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesThe Urinary SystemOji KangjiNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesThe Urinary SystemDaniel NevadoNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Kidney and ExcretionDocument57 pagesPhysiology of Kidney and ExcretionWenny KalamiNo ratings yet
- Kidney and NephronDocument41 pagesKidney and NephronMd Atikur AminNo ratings yet
- مشروع ابو زنيد1Document15 pagesمشروع ابو زنيد1Hareth mohammad mahmod NawajaNo ratings yet
- Zoo 1 Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument17 pagesZoo 1 Excretion and OsmoregulationMaheshkumar KalalNo ratings yet
- الجهاز البولىDocument6 pagesالجهاز البولىNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 13 Urinary System NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 13 Urinary System NotesVGH CREATIONS Lucky's.lyrical.statusNo ratings yet
- Definition of Excretory SystemDocument10 pagesDefinition of Excretory SystemTamkeen sheraniNo ratings yet
- PINK Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project PresentationDocument31 pagesPINK Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project Presentationereneovalerozo22No ratings yet
- Tugas Bhs. InggrisDocument1 pageTugas Bhs. Inggrisferly edianaNo ratings yet
- Biology Art Integrated ProjectDocument5 pagesBiology Art Integrated ProjectAdvika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Xcretory System: BY: Pramod KumarDocument50 pagesXcretory System: BY: Pramod KumarCay C. CordovaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory - Urinary Anatomy - 3Document8 pagesLaboratory - Urinary Anatomy - 3Roisatul MunawarohNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys Are A Pair of Purplish-Brown Organs Is Located Below The Ribs Toward The Middle ofDocument6 pagesThe Kidneys Are A Pair of Purplish-Brown Organs Is Located Below The Ribs Toward The Middle ofJoana Bless PereyNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Agnatha and ChondrichthyesDocument14 pagesLab 9 Agnatha and ChondrichthyesAndriyansyahNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy Practical of The Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesGross Anatomy Practical of The Urinary SystemChristopher CheweNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Part 1Document8 pagesUrinary System Part 1عبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاح100% (1)
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary SystemMohammed Keyarul IslamNo ratings yet
- Study of Human Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesStudy of Human Urinary SystemKʀɩsʜʌŋ ĸʀ ƦoƴNo ratings yet
- Virgenmilagrosa University Foundation Martin P. Posadas Ave., San Carlos City, Pangasinan Virgenmilagrosa Special Science High SchoolDocument5 pagesVirgenmilagrosa University Foundation Martin P. Posadas Ave., San Carlos City, Pangasinan Virgenmilagrosa Special Science High SchoolNaomi Aira Gole CruzNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument28 pagesUrinary Systemgabanule brandonNo ratings yet
- 13EXCRETORYDocument3 pages13EXCRETORYDaniellaRuth Cajurao CanalesNo ratings yet
- How To Dissect A SharkDocument14 pagesHow To Dissect A SharkgregNo ratings yet
- Ratification Page: Andi Citra Pratiwi, S.PD, M.Ed Muhammad Nur Arsyad, S.PDDocument18 pagesRatification Page: Andi Citra Pratiwi, S.PD, M.Ed Muhammad Nur Arsyad, S.PDFatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Q4 LAS 4 Module 14Document5 pagesGen Bio 2 Q4 LAS 4 Module 14KatsumiJ Aki100% (1)
- Excretion & OsmoregulationDocument35 pagesExcretion & OsmoregulationChetan KuteNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesUrinary SystemCurex QANo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersDocument16 pagesAssessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument8 pagesExcretory SystemShannen Christen NaraceNo ratings yet
- C-8 8. Excratory SystemDocument10 pagesC-8 8. Excratory SystemAbesh BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Mr. Diaz Medical English II: WWW - Usat.edu - PeDocument10 pagesMr. Diaz Medical English II: WWW - Usat.edu - PelakjdlkaNo ratings yet
- Excretory and Endocrine System: Spgbio 2 12-NewtonDocument9 pagesExcretory and Endocrine System: Spgbio 2 12-NewtonElian BiadoNo ratings yet
- Week 14 109Document2 pagesWeek 14 109Jin Andrei BatungbacalNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Heterogenious Class For Senior High School of Student of Mystical Rose School of Caloocan IncDocument7 pagesThe Effectiveness of Heterogenious Class For Senior High School of Student of Mystical Rose School of Caloocan IncAntonioNo ratings yet
- The Impact of The Continued Use of The Gadget On The Student, Indoors During This Pandemic''Document9 pagesThe Impact of The Continued Use of The Gadget On The Student, Indoors During This Pandemic''AntonioNo ratings yet
- Contreras, Luis Antonio P. Grade 12 ABM TopazDocument2 pagesContreras, Luis Antonio P. Grade 12 ABM TopazAntonioNo ratings yet
- Contreras, Luis Antonio P. Grade 12 ABM TopazDocument2 pagesContreras, Luis Antonio P. Grade 12 ABM TopazAntonioNo ratings yet
- The Sun and The Moon ContrerasDocument1 pageThe Sun and The Moon ContrerasAntonioNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Business ESSAYDocument2 pagesThe Nature of Business ESSAYAntonioNo ratings yet
- Periodic Health ExaminationDocument38 pagesPeriodic Health ExaminationHilma NadhifaNo ratings yet
- Common Illnesses and Classique ProductsDocument52 pagesCommon Illnesses and Classique Productsmj_jm255114100% (1)
- 21episcleritis & ScleritisDocument11 pages21episcleritis & ScleritisNana Mu'awanahNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis Bladder CADocument9 pagesPathogenesis Bladder CAHannah LeiNo ratings yet
- Alloderm - Breast ReconstructionDocument180 pagesAlloderm - Breast ReconstructionFlorina PopaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument32 pagesProjectNithya sudevNo ratings yet
- 43THYROID II 2021 ThyroiditisDocument29 pages43THYROID II 2021 ThyroiditisRaju ThapaNo ratings yet
- Trauma and Stressor Related DisordersDocument5 pagesTrauma and Stressor Related DisordersVillarino, Ian C.No ratings yet
- Ward ClassDocument36 pagesWard ClassPaul Michael BaguhinNo ratings yet
- Rad UMR0777491 4020126 1701Document4 pagesRad UMR0777491 4020126 1701sureshmaila9966No ratings yet
- NCM 104 - Medical Surgical Nursing: Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument7 pagesNCM 104 - Medical Surgical Nursing: Bachelor of Science in NursingMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJanie StubbertNo ratings yet
- Subject Plan B.SC Nursing 1 Year: MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesSubject Plan B.SC Nursing 1 Year: MicrobiologySandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Infections and Inflammations of The MouthDocument9 pagesInfections and Inflammations of The MouthSangeeta BSRNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing: Ritche D. Vidal, M.DDocument70 pagesPerioperative Nursing: Ritche D. Vidal, M.DAnel CapaNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Why Does This Sample Need Recollected? Beth Warning, MS, MLS University of Cincinnati MLS ProgramDocument8 pagesObjectives: Why Does This Sample Need Recollected? Beth Warning, MS, MLS University of Cincinnati MLS ProgramMarj MendezNo ratings yet
- SarkopeniaDocument8 pagesSarkopeniaRamadhanaNo ratings yet
- BDR Manual - Complete BookDocument58 pagesBDR Manual - Complete BookRownakulNo ratings yet
- FIRST AID Is The Immediate Care Given To A Person Who Have Been Injured or Suddenly Taken IllDocument4 pagesFIRST AID Is The Immediate Care Given To A Person Who Have Been Injured or Suddenly Taken IllNat CatalanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System and Glands of The Human BodyDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine System and Glands of The Human BodyFungo JasmineNo ratings yet
- 1 Nursing ProcessDocument30 pages1 Nursing ProcessCrystal Ann TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Acl PCL PresentationDocument17 pagesAcl PCL PresentationSafwan Idham RamlanNo ratings yet
- PijhjiiiiDocument14 pagesPijhjiiiiSofiNo ratings yet
- EPM MCQs Post Course Test 2017 v1Document2 pagesEPM MCQs Post Course Test 2017 v1Maisie RobertsNo ratings yet
- Hand and Wrist Swelling Management Jul18Document2 pagesHand and Wrist Swelling Management Jul18testNo ratings yet
- Atomidine 1930 Nascent Iodine UsesDocument13 pagesAtomidine 1930 Nascent Iodine Useselizabeth anne100% (2)