Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscular Tissue Study Outline
Uploaded by
Jet Toralba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThis document provides an outline for a lecture on muscular tissue. It discusses the three main types of muscular tissue - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, found in the bones, and moves the skeleton. Cardiac muscle is only found in the heart, striated and involuntary. Smooth muscle lines internal organs and structures, is non-striated and involuntary. The document also covers muscle fiber types, exercise effects on skeletal muscle, and development and aging of muscular tissue.
Original Description:
Muscular Tissue Outline
Original Title
MUSCULAR TISSUE STUDY OUTLINE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an outline for a lecture on muscular tissue. It discusses the three main types of muscular tissue - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, found in the bones, and moves the skeleton. Cardiac muscle is only found in the heart, striated and involuntary. Smooth muscle lines internal organs and structures, is non-striated and involuntary. The document also covers muscle fiber types, exercise effects on skeletal muscle, and development and aging of muscular tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesMuscular Tissue Study Outline
Uploaded by
Jet ToralbaThis document provides an outline for a lecture on muscular tissue. It discusses the three main types of muscular tissue - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, found in the bones, and moves the skeleton. Cardiac muscle is only found in the heart, striated and involuntary. Smooth muscle lines internal organs and structures, is non-striated and involuntary. The document also covers muscle fiber types, exercise effects on skeletal muscle, and development and aging of muscular tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY:
LECTURE ON THE MUSCULAR TISSUE
MUSCULAR TISSUE STUDY OUTLINE
10.1 Overview of Muscular - Slow Oxidative
Tissue - Fast Oxidative-Glycolytic
- Types of Muscular Tissue - Fast Glycolytic
- Functions of Muscular 10.4 Exercise and Skeletal
Tissue Muscle Tissue
- Properties - Effective Stretching
10.2 Skeletal Muscle Tissue - Strength Training
- Structure 10.5 Cardiac Muscle Tissue
- Connective Tissue 10.6 Smooth Muscle Tissue
Coverings 10.7 Development of
- Nerve and Blood Supply Muscles
- Microscopic Anatomy 10.8 Aging and Muscular
- Muscle Proteins Tissue
- Contraction and
Relaxation
- Muscle Tone Key Medical Terms
- Isotonic and Isometric Associated with Muscular
Contractions Tissue
10.3 Types of Skeletal
Muscle Fibers
10.1 OVERVIEW OF THE MUSCULAR TISSUE
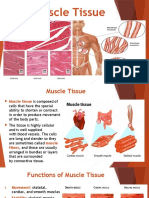
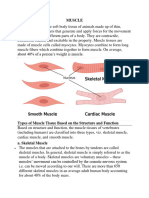
Types of Muscular Tissue:
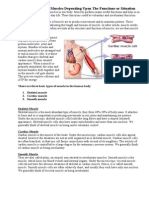
1. Skeletal Muscle Tissue
: move bones of the skeleton
: striated (visibility of alternating light and dark protein
bands called striations)
: voluntary actions (its activity can be controlled)
2. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
: only in the heart as it forms the heart wall
: striated and involuntary (its activities cannot be
consciously controlled)
: autorhythmicity – built-in intrinsic rhythm.
: several hormones and neurotransmitters adjust
heart rate by speeding up or slowing down the pacemaker of
the heart.
3. Smooth Muscle Tissue
: located in the walls of hollow internal structures and
hair follicles in the skin.
: nonstriated and involuntary
: also has autorhythmicity
* Cardiac and smooth muscles are regulated by neurons of the
autonomic division of the nervous system and by hormones
released by endocrine glands.
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY:
LECTURE ON THE MUSCULAR TISSUE
You might also like
- Teaching Notes - Muscle TissueDocument2 pagesTeaching Notes - Muscle TissueSusan FNo ratings yet
- العضلاتDocument8 pagesالعضلاتNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Physiology05 Muscle CellDocument37 pagesPhysiology05 Muscle CellsmpoojasubashNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Q&aDocument11 pagesMuscular System Q&aRashini FernandoNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Materi Jaringan Otot Dan Jaringan SarafDocument58 pagesMateri Jaringan Otot Dan Jaringan SarafMitha ArthameviaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Diseases: Presented by Group 5Document175 pagesMusculoskeletal Diseases: Presented by Group 5Niko Agustin BalilihanNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtDocument9 pagesActivity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtAMEER MUHMIEN JALMAANI. LERIOSNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 (Muscular System)Document7 pagesUNIT 3 (Muscular System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Lecture Note (Specialization)Document97 pagesExercise Physiology Lecture Note (Specialization)Shameem AliNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- 1.2 TheMuscularSystemDocument60 pages1.2 TheMuscularSystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- Muscle Macro Structures (Physiology)Document81 pagesMuscle Macro Structures (Physiology)YangNo ratings yet
- Muscular-System-Handouts - BiologyDocument7 pagesMuscular-System-Handouts - BiologyApril Joy T. GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesUnit - 6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument13 pagesMusclessoulpatch_85100% (1)
- Muscle and Nerve HistoPHysioDocument91 pagesMuscle and Nerve HistoPHysioashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Human Biology 11th Edition Starr Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Biology 11th Edition Starr Solutions Manualjillhenrysetcjnzrfp100% (28)
- Functions of MusclesDocument5 pagesFunctions of MusclesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Human Biology 11Th Edition Starr Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesHuman Biology 11Th Edition Starr Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFninhdermotc1u100% (9)
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Muscles WorksheetDocument4 pagesMuscles WorksheetAndreea BuicuNo ratings yet
- (Iin Tuhumury) Paper Anatomy of The Muscle System in HumansDocument11 pages(Iin Tuhumury) Paper Anatomy of The Muscle System in Humansyance djilarNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology W3 - EmmanuelaDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology W3 - EmmanuelaRamizNo ratings yet
- Purple Illustrative The Human Body PresentationDocument14 pagesPurple Illustrative The Human Body PresentationElaineNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument6 pagesMuscle Physiologytewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Muscular Tissue I Reading: Chapter 10Document34 pagesMuscular Tissue I Reading: Chapter 10Marc Andreo MalalaNo ratings yet
- YU - General - Muscles 1Document57 pagesYU - General - Muscles 1Mohammad BarakatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Muscle TissueDocument14 pagesLesson 3 Muscle TissueFaith SimbulanNo ratings yet
- A & P Lecrure Notes For TestDocument1 pageA & P Lecrure Notes For Testdesrivera30No ratings yet
- Body Mechanics and Movement Learning Objectives:: by The End of This Lecture, The Student Will Be Able ToDocument19 pagesBody Mechanics and Movement Learning Objectives:: by The End of This Lecture, The Student Will Be Able TomahdiNo ratings yet
- Ana 221 Muscle TissueDocument12 pagesAna 221 Muscle TissueAmadi CedarNo ratings yet
- Muscle: 14. Different Types of MusclesDocument79 pagesMuscle: 14. Different Types of MusclesDr Estari MamidalaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument20 pagesMuscular SystemAltaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System NotesDocument32 pagesThe Muscular System NotesVivien Talavera0% (1)
- Muscular System Final1Document33 pagesMuscular System Final1Karl Maurice ApogNo ratings yet
- Health Education ClassDocument8 pagesHealth Education ClassAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE B.Sc-IIDocument13 pagesMUSCLE B.Sc-IIAjinkya BansodeNo ratings yet
- SAKUNADocument19 pagesSAKUNAErika Lee ToretaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System-251606Document8 pagesThe Muscular System-251606sselt gayNo ratings yet
- Muscles EngDocument3 pagesMuscles Engkaneki.ghoul1710No ratings yet
- Pair Activity: B. Concept MasteryDocument3 pagesPair Activity: B. Concept MasteryNichole DequitoNo ratings yet
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pages3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- K00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesK00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular Systemroesil juniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Group 5 PRESENTATIONDocument21 pagesAnatomy Group 5 PRESENTATIONambaig661No ratings yet
- Classification of Muscles Depending Upon The Functions or SituationDocument1 pageClassification of Muscles Depending Upon The Functions or SituationSyed Bilal HussainNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Body System: Name: Akanksh Grade: 10KC Lesson: Skeletal System & Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Body System: Name: Akanksh Grade: 10KC Lesson: Skeletal System & Muscular SystemAkanksh SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Muscular, Skeletal, and Nervous SystemDocument53 pagesChapter 3. Muscular, Skeletal, and Nervous SystemFatiha AmiraNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument27 pagesMuscular SystemJOHN ANDREI ZARSADIASNo ratings yet
- Musc Nerv PDFDocument9 pagesMusc Nerv PDFJoshua RaninNo ratings yet
- Exercise #12: Muscular TissueDocument3 pagesExercise #12: Muscular TissueDaks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesAssignment For Muscular SystemIrene Grace Z. RagasNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4CLAUDIU---ALIN BOARTANo ratings yet
- Short Answer Essay Dec15Document4 pagesShort Answer Essay Dec159pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- 11J - Caybot - Jash Jovian - Task10Document11 pages11J - Caybot - Jash Jovian - Task10JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 The Muscular SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 6 The Muscular Systemrafaelarmildez02No ratings yet
- M. M. College of Nursing Mullana Ambala: Topic: Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesM. M. College of Nursing Mullana Ambala: Topic: Muscular SystemBhawna PandhuNo ratings yet