100% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views4 pagesHistory of Accounting
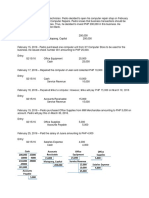
Historical accounting records date back to ancient civilizations in 2500 BC. Double-entry bookkeeping evolved in Italy between the 13th-15th centuries and was popularized by Luca Pacioli in 1494. Modern accounting standards developed over subsequent centuries with innovations including codified accounting principles and the establishment of professional accounting organizations.
Uploaded by
Faith ClaireCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views4 pagesHistory of Accounting
Historical accounting records date back to ancient civilizations in 2500 BC. Double-entry bookkeeping evolved in Italy between the 13th-15th centuries and was popularized by Luca Pacioli in 1494. Modern accounting standards developed over subsequent centuries with innovations including codified accounting principles and the establishment of professional accounting organizations.
Uploaded by
Faith ClaireCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd