Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earning Outcomes: LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)
Uploaded by
Jhay Mark Berioso AmparoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earning Outcomes: LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)
Uploaded by
Jhay Mark Berioso AmparoCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Laguna State Polytechnic University
Province of Laguna
LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
Learning Outcomes Level I Institutionally Accredited
Student Learning Strategies
Offline Activities
(e-Learning/Self- Lecture Guide
Paced) Introduction:
Ichthyology studies taxonomy, evolution, morphology, anatomy and
embryology of fish, species and age structure of populations and their
quantities, migration and geographical distribution of fish in waters of different
climatic zones, etiology and ecology of fish.
Module 1. Fish Basic Anatomy
Lesson 1. The External Anatomy of a Fish:
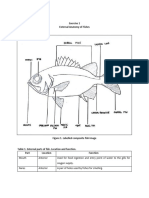
FISH EXTERNAL ANATOMY
Lesson 2. The Boundaries of Fish Body
The Head
Mouth - serves for taking in food; also for the
breathing current of water.
Eyes - Used for sight, fish can detect colors and see
short distance with their eyes. They use their vision
to escape predators and find food.
Nares (Nostril) - Similar to nostrils, except nares are
LSPU SELF-PACED LEARNING MODULE: TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING
Republic of the Philippines
Laguna State Polytechnic University
Province of Laguna
used for smelling only (nostrils are used for both
smelling and breathing).
Operculum - It covers the fish gills. It also serves as
the exit passage of the water on the mouth of the
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
fish.
Level I Institutionally Accredited Barbels - Also known as whiskers, located under the
mouth of a fish. These are tactile and taste organs
used for locating food in dark or muddy waters.. Not
all fish have barbells.
The Body
Vent - The vent removes waste and extra water. It is
also the outlet for eggs or milt (sperm) during
spawning.
Body Covering or Scales – Fish are covered with
scales, which protect the body from skin damages.
Lateral Line - is a series of fluid-filled ducts located
just under the scales. It picks up vibrations in the
water that enable fish to detect predators, find food,
and navigate more efficiently. It help the fish detect
water current and water pressure changes.
Peduncle – It is situated at the edge of the tail fin
that lies on the end or outside of the caudal fin.
The Fins - used for movement, stability, nest-
building, spawning, and as tactile organs. Fins can
be single or paired.
Offline Activities
(e-Learning/Self- Types of Fins:
Paced)
Anal Fin- A single fin located on the underside of the
body just forward of the caudal fin. Used to stabilize
the fish while it is swimming.
Pelvic or Ventral Fins - A paired fin located forward
of the anal fin and are used to provide further
stability in swimming.
Pectoral Fin- A paired fin located near the gill cover.
It is used for manoeuvring the fish.
LSPU SELF-PACED LEARNING MODULE: TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING
Republic of the Philippines
Laguna State Polytechnic University
Province of Laguna
Dorsal fin - A single fin, but some species may have a
second fin. It is located on the back of the fish. It
serves to help balance the fish while swimming.
Adipose fin - is a tiny fin found between the dorsal
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
and caudal fins on some fish a soft, fleshy fin.
Level I Institutionally Accredited
Finlets - small fins generally behind the dorsal and
anal fins. They are rayless and non-retractable.
Caudal Keel - May be single, paired, or double pairs.
The Tail
Tail fin - Also known as the caudal fin. Fish used tail
fin for propulsion.
Lesson 3. . Internal Parts of a Fish
Offline Activities
(e-Learning/Self-
Paced)
Spine - The primary structural framework, upon which the fish's body is
built, connects to the skull at the front of the fish and to the tail at the
rear.
LSPU SELF-PACED LEARNING MODULE: TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING
Republic of the Philippines
Laguna State Polytechnic University
Province of Laguna
Spinal cord - Connects the brain to the rest of the body and relays
sensory information from the body to the brain, as well as instructions
from the brain to the rest of the body.
Brain - This is the control center of the fish, where both automatic
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
functions, such as respiration, and higher behaviors occur. All sensory
Level I Institutionally Accredited
information is processed here.
Swim (or air) bladder - This hollow, gas-filled balance organ allows a
fish to conserve energy by maintaining neutral buoyancy (suspending)
in water.
Gills - Allow a fish to breathe underwater.
Kidney - This filters liquid waste materials from the blood, and these
wastes are then passed out of the body.
Stomach and intestines - These break down food and absorb nutrients.
Pyloric caeca - This organ with fingerlike projections is located near
the junction of the stomach and the intestines. It is known to secrete
enzymes that aid in digestion, may function to absorb digested food, or do
Offline Activities
both.
(e-Learning/Self-
Paced) Vent - This is the site of waste elimination from the fish's body. It is also
the outlet for eggs or sperm during spawning.
Liver - This important organ has a number of functions. It assists in
digestion by secreting enzymes that break down fats, and it also serves
as a storage area for fats and carbohydrates as well as it works in the
destruction of old blood cells and in maintaining proper blood
chemistry, as well as playing a role in nitrogen (waste) excretion.
Heart - This circulates blood throughout the body.
Gonads (reproductive organs) - The male organs, which produce milt
for fertilizing the eggs, are much smaller and white but found in the
same general location.
Muscles - Provide movement and locomotion.
LSPU SELF-PACED LEARNING MODULE: TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING
Republic of the Philippines
Laguna State Polytechnic University
Province of Laguna
Performance Tasks
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
Level I Institutionally Accredited
PT 2 – Offline:
a. Individual activity:
Make a schematic drawing of external and internal fish anatomy and note all of the
body parts.
b. Quiz. Quiz will be posted in Google classroom and to be accomplish within the given
period/time.
All outputs are due to submit on or before the given due dates in google classroom.
Understanding Directed Assessment
1. Methods of assessment of students learning competencies will be thru
a. Multiple test questions at the end of the unit. (Online and Offline)
b. Post copy of task output Image Pad in google classroom.
c. Scoring by Rubrics for PT outputs.
2. Tools for assessment – Online tools generated, Rubric, Paper and pen
Learning Resources
- Fish Base 200
- Lagler, Karl – Ichthyology
- Fisheries Biology and Management
- Laboratory Manual in Zoology
LSPU SELF-PACED LEARNING MODULE: TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING
You might also like
- Anatomy of FishesDocument2 pagesAnatomy of FisheslararariingNo ratings yet
- Notes Anatomy of A FishDocument1 pageNotes Anatomy of A FishMarie Flor BongatoNo ratings yet
- External Anatomy of Vertebrates Class AgnathaDocument9 pagesExternal Anatomy of Vertebrates Class AgnathaJerico YoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 20: Vertebrates II: Marine BiologyDocument13 pagesLesson 20: Vertebrates II: Marine BiologysfdasdfasdfNo ratings yet
- Adaptations of Animals To Their Environment: PART I. Adaptive Skeletal Features. QuestionsDocument4 pagesAdaptations of Animals To Their Environment: PART I. Adaptive Skeletal Features. QuestionsFaustine De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Anatomy of A FishDocument1 pageActivity 1 - Anatomy of A FishMarie Flor BongatoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FishDocument2 pagesParts of A FishCynthia UnayNo ratings yet
- GZ Lab Finals RevDocument5 pagesGZ Lab Finals Revgerlyn duranNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument20 pagesUntitledJaime MaestreNo ratings yet
- Report Text ConceptDocument4 pagesReport Text ConcepttarraassyifarahmanNo ratings yet
- Aquatic MammalsDocument16 pagesAquatic MammalsparthaNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document6 pagesLab 7s11191100No ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document5 pagesLesson 3Meco ChicaNo ratings yet
- Basic Science Lesson Notes 8 PDFDocument46 pagesBasic Science Lesson Notes 8 PDFRavineel KumarNo ratings yet
- Adaption of AnimalsDocument7 pagesAdaption of AnimalsShambhavi GroverNo ratings yet
- Magno AFA 1 Module 3 EndtermDocument20 pagesMagno AFA 1 Module 3 EndtermRube Joy ShopNo ratings yet
- Eucoelomates Lab ReportDocument13 pagesEucoelomates Lab Reportsatvindar singhNo ratings yet
- Snout Are Called Nostrils, or Nares.:: Have No FearDocument22 pagesSnout Are Called Nostrils, or Nares.:: Have No FearKristine Joy Eyao BalayoNo ratings yet
- Part 1: CoastalDocument2 pagesPart 1: Coastalapi-654033969No ratings yet
- Fin Whale Seven Life ProcessesDocument1 pageFin Whale Seven Life ProcessesFannyNo ratings yet
- ZOOLOGY - CHAPTER 11 - Report Outline 10th EditionDocument6 pagesZOOLOGY - CHAPTER 11 - Report Outline 10th EditionmariaNo ratings yet
- Lab - Annelids Powerful and Capable WormsDocument14 pagesLab - Annelids Powerful and Capable WormsZaraí RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Structure and FishDocument1 pageStructure and FishAiedjhay DuyacNo ratings yet
- La4 ReviewerDocument7 pagesLa4 ReviewerRhea Mae TabayagNo ratings yet
- AkuaDocument19 pagesAkuaFarhan ShabriNo ratings yet
- Fishery Arts Fishery Arts: Mrs. Sally C. SaldeDocument28 pagesFishery Arts Fishery Arts: Mrs. Sally C. SaldeJered Morato100% (1)
- The Amazing Praya DubiaDocument11 pagesThe Amazing Praya DubiaArda •No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive SystemHaron BusranNo ratings yet
- Amphibians - NotesDocument2 pagesAmphibians - NotesTímea TóthováNo ratings yet
- Fish CharacteristicsDocument1 pageFish CharacteristicsMohamad Shamson M HamdanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanJudith CabisoNo ratings yet
- Zoology NomenclatureDocument49 pagesZoology NomenclatureVioletaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Jurnal FKH - Perubahan Bentuk Eritrosit - Journal - UnairDocument5 pages4 - Jurnal FKH - Perubahan Bentuk Eritrosit - Journal - UnairEvi SintaNo ratings yet
- 007 ReportsDocument11 pages007 Reportsramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Biology ResearchDocument3 pagesBiology ResearchShaddy ShaddyNo ratings yet
- BTM 111 22Document24 pagesBTM 111 22Toke SadockNo ratings yet
- FishDocument3 pagesFishLoje Casupas MontonNo ratings yet
- Amphibians: Presented By: 17371506-010 AREEJ TARIQ 17371506-016 KHADIJA KARIMDocument17 pagesAmphibians: Presented By: 17371506-010 AREEJ TARIQ 17371506-016 KHADIJA KARIMMuhammad Karim KhanNo ratings yet
- Form & FunctionDocument17 pagesForm & FunctionMaria AgwantaNo ratings yet
- Whales Activities For Grades 3 5Document6 pagesWhales Activities For Grades 3 5Sne PopaturNo ratings yet
- Animal Sensory Organ (Alyabat&Asyiqin)Document5 pagesAnimal Sensory Organ (Alyabat&Asyiqin)asy kimNo ratings yet
- IJOAC16000162 Indian Mottled EelDocument5 pagesIJOAC16000162 Indian Mottled EelNirvanajunctureNo ratings yet
- Animal Adaptations: How Do Animals Survive in The Wild?Document31 pagesAnimal Adaptations: How Do Animals Survive in The Wild?Glenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6JOSYHLL LYKA ROSE VILLENANo ratings yet
- Phylum Mollusca (Notes)Document1 pagePhylum Mollusca (Notes)Kristine Claire AlberioNo ratings yet
- Fish, Amphibians, and Reptiles: Can I Find One?Document34 pagesFish, Amphibians, and Reptiles: Can I Find One?Rehan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Week 3Document83 pagesScience 4 Week 3Mechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Adaptation of Marine OrganismsDocument14 pagesAdaptation of Marine OrganismslaaltooNo ratings yet
- Red Life Group Scripts For 2nd Grading PresentationsDocument9 pagesRed Life Group Scripts For 2nd Grading PresentationsAthena Lianne Relano V-SSESNo ratings yet
- AMPHIBIANS - Notes, Biology GCSE - DETAILED!!Document2 pagesAMPHIBIANS - Notes, Biology GCSE - DETAILED!!Elizabeth KálusováNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OceanDocument12 pagesAnatomy OceanLOKE SHIAU CHYI MoeNo ratings yet
- Science Reviwer Q2 G3Document5 pagesScience Reviwer Q2 G3Leyla AureNo ratings yet
- Outer Stratified EpidermisDocument8 pagesOuter Stratified EpidermisAsma AslamNo ratings yet
- Lower Chordata Lecture - 2023Document5 pagesLower Chordata Lecture - 2023BHEKUMUSA MASEKONo ratings yet
- Fish Biology F22Document35 pagesFish Biology F22Rennik McCaigNo ratings yet
- Structure: Pisces Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves Mammalia PoikilothermsDocument43 pagesStructure: Pisces Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves Mammalia PoikilothermsTapan Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- External Parts of Fish and UsesDocument1 pageExternal Parts of Fish and UsesBohna Francisco50% (2)
- Animal Adaptations: Self-Directed Tour Grades Three Through FiveDocument22 pagesAnimal Adaptations: Self-Directed Tour Grades Three Through FiveAvinash KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesDigestive SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Dolphins: The Ultimate Dolphin Book for Kids: Animal Books for Kids, #25From EverandDolphins: The Ultimate Dolphin Book for Kids: Animal Books for Kids, #25No ratings yet
- 1.6 Process Alarm Management: M. S. Mannan, H. H. WestDocument5 pages1.6 Process Alarm Management: M. S. Mannan, H. H. WestkangsungjinNo ratings yet
- 2020 Guidelines WebDocument249 pages2020 Guidelines WebDaryl Barrios LamedaNo ratings yet
- Effective MicroorganismsDocument8 pagesEffective MicroorganismswawahalimNo ratings yet
- How To Do Logic Checks During Plant Pre-CommissioningDocument2 pagesHow To Do Logic Checks During Plant Pre-CommissioningVraja KisoriNo ratings yet
- Industrial Charcoal Production With Power Generation at Mully Children'S Family Yatta, KenyaDocument87 pagesIndustrial Charcoal Production With Power Generation at Mully Children'S Family Yatta, KenyapramitasNo ratings yet
- UFFL Company Case StudyDocument6 pagesUFFL Company Case StudyDell CaasieNo ratings yet
- Stevia Rebaudiana: A Review On The Improvement of Stevia ( (Bertoni) )Document28 pagesStevia Rebaudiana: A Review On The Improvement of Stevia ( (Bertoni) )henry72No ratings yet
- Natural Gas Filters PDFDocument10 pagesNatural Gas Filters PDFKirthiga RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- The Anti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act (Ra 9262)Document39 pagesThe Anti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act (Ra 9262)Mimhy VallegaNo ratings yet
- 0568Document77 pages0568selvakrishna0% (1)
- Worksafe Bulletin: Carbon Monoxide Exposure During Film ShootsDocument3 pagesWorksafe Bulletin: Carbon Monoxide Exposure During Film ShootsBuddho BuddhaNo ratings yet
- DLL Mapeh-4 Q1 W3Document8 pagesDLL Mapeh-4 Q1 W3dianne grace incognitoNo ratings yet
- Pride 18-19 FinalDocument3 pagesPride 18-19 FinalSushant PatilNo ratings yet
- Final Research Paper - Cancer Is A Man-Made DiseaseDocument22 pagesFinal Research Paper - Cancer Is A Man-Made Diseaseapi-358498359No ratings yet
- Elvis Ngila ProjectDocument33 pagesElvis Ngila ProjectJP firmNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Essay HomeworkDocument8 pagesPersuasive Essay Homeworkafhbgohob100% (2)
- Video Essay Script Draft 2Document2 pagesVideo Essay Script Draft 2api-480313267No ratings yet
- Defects in Metal Additive Manufacturing ProcessesDocument11 pagesDefects in Metal Additive Manufacturing ProcessesNiraj 93No ratings yet
- 4100R Series - Thick Film Molded DIPsDocument3 pages4100R Series - Thick Film Molded DIPssiogNo ratings yet
- Concrete Limitting Values For Exposure Grade Pages From en 206Document1 pageConcrete Limitting Values For Exposure Grade Pages From en 206Ahmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNo ratings yet
- CIVE378 Exam1 ReviewDocument2 pagesCIVE378 Exam1 ReviewJoshtion ShahNo ratings yet
- D - 14k - 3 - Delta Checklist ISO 14001-2015 - 20150917 - Short - EnglDocument9 pagesD - 14k - 3 - Delta Checklist ISO 14001-2015 - 20150917 - Short - EnglPRASAD SHETTYNo ratings yet
- Quantum Dot - MapDocument1 pageQuantum Dot - MapRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet, Drawings & QAP For Pressure Relief Valve DN400 PN16-LBC - 180920 PDFDocument4 pagesDatasheet, Drawings & QAP For Pressure Relief Valve DN400 PN16-LBC - 180920 PDFYogesh GawadeNo ratings yet
- OK 67.70 ESAB 309moDocument1 pageOK 67.70 ESAB 309moSadashiva sahooNo ratings yet
- Emkarate Rl220h Msds v1.5Document11 pagesEmkarate Rl220h Msds v1.5luanacompany954No ratings yet
- 9 Rinku - Ji MantrijiDocument12 pages9 Rinku - Ji MantrijiCine Dada100% (1)
- Scope of Service For Units - EmergencyDocument2 pagesScope of Service For Units - EmergencyramannishuNo ratings yet
- Ashutosh SynopsisDocument24 pagesAshutosh SynopsisAshutosh Masih0% (1)
- Laporan Case Mix Gabungantgl 27-12-2023Document191 pagesLaporan Case Mix Gabungantgl 27-12-2023Adhita Septianty ningrumNo ratings yet